本文目录
英语定语从句语法讲解
英语定语从句语法解析 篇1
1.先行词为all, anything, something, nothing, everything, much, little, none等不定代词时,关系代词一般只用that,不用which。在大多数情况下that可以省略.
Please tell me everything you know about the matter.
Thats all we can do at the moment.
2.as引出的限制性定语从句
在such as的结构中as可作关系代词,引出限制性定语从句。有时和same连用,在从句中可作主语、宾语或表语等。
Such people as were recommended by him were reliable.
Ive never seen such a talented young man as he is.
I have the same trouble as you .
3.as引出的非限制性定语从句
as可作关系代词引出非限制性定语从句,代替整个主句,通常译为(正)如一样,(正)象一样等。as引导的从句一般用逗号与主句隔开,可以位于主句的前面、中间或后面.
I live a long way from work, as you know.
She did not, as her friend had feared, break down.
As is generally accepted, economic growth is determined by the smooth development of production.
4.分隔式定语从句
定语从句一般紧跟在先行词之后,但有时会被其他句子成分与先行词隔开,从而构成分隔式定语从句。
英语定语从句语法解析 篇2
1)介词后面的关系词不能省略。
2)that前不能有介词。
3)某些在从句中充当时间,地点或原因状语的介词+关系词结构可以同关系副词when 和where 互换。例如:
This is the house in which I lived two years ago. 这是我两年前住过的房子。
This is the house where I lived two years ago.
Do you remember the day on which you joined our club? 还记得你加入我们俱乐部的那一天吗?
Do you remember the day when you joined our club?
18.6 as, which 非限定性定语从句
由as, which 引导的非限定性定语从句,as和which可代整个主句,相当于and this或and that。As一般放在句首,which在句中。例如:
As we know, smoking is harmful to ones health. 如我们所知,吸烟有害健康。
The sun heats the earth, which is very important to us. 太阳使地球暖起来,这对我们人类很重要。
典型例题
1)Alice received an invitation from her boss, ___came as a surprise.
A. it B. that C. which D. he
答案C. 此为非限定性从句,不能用 that修饰,而用which.,it 和he 都使后句成为句子,两个独立的句子不能单以逗号连接。况且选he句意不通。
英语定语从句语法解析 篇3
1、限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句
定语从句就其与先行词的关系而言,可分为限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句。限定性定语从句和先行词之间没有逗号,表示对先行词起修饰限制作用;而非限定性定语从句和先行词之间有逗号分开,是对先行词进行补充说明,相当于并列句。
如:He is the man who has a strong personality. 他是个个性很强的人。(限定性定语从句)
My brother, who works abroad, is coming next week. 我哥哥在国外工作,他下周将回来。(非限定性定语从句)
注:
1) 非限定性定语从句不能用that来引导,一般用which,as或who(指人)。用which或as引导时,既可以修饰主句的部分内容,也可修饰主句的全部内容。如:
He spoke confidently, which impressed me most. (which指代整个主句,在从句中作主语)
2) as引导的非限定性定语从句既可以放在主句之前,也可以放在主句之后,但which或who引导的非限定性定语从句不能放在主句之前。如:As we all know, the moon is a satellite of the earth.The large area is covered with thick snow, which affects people‘s life greatly.
3) 在限定性定语从句中,关系代词作宾语时可以省略;但在 非限定性定语从句中,关系代词作宾语时不能省略。如:
The film (which) I saw last night is about a young teacher. (which可以省去)
She introduced me to her husband, whom I hadn’t met before. (whom不能省去)
2、只用关系代词that,不用 which,who或whom的几种情况
1)当先行词是all, everything, nothing, something, anything, little, much, none, few等时。如:All that you want are here.
2) 当先行词被all, no, some, any, every, a few, a little, much, only, very等修饰时。如:There is no person that doesn’t make mistakes.
3)当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。如:This is the best film that I have ever seen.
4)当出现两个或两个以上的先行词,并同时兼指人和物时。如: We are talking about the people and countries that we have
visited.
5) 当主句是以which 或 who 开头的特殊疑问句时。如: Who is the person that is standing over there?
6) 当定语从句为there be 句型时,关系代词只用that,
但经常可以省略。如: I know the difference (that) there is between you.
7)当关系代词在从句中作表语时,常用that。如:He does not seem to be the man that he was
他似乎和过去不一样了。
3、 as 与其他词连用引导的定语从句
as 引导定语从句时,可指人也可指物,通常与the same,such,so等连用,形式为:the same… as,such… as,as …as,so… as。As在定语从句中可作主语、宾语、表语等。如:
She knew he felt just the same as she did. 她知道他的感觉与她自己的一样。(as代替事,作宾语)
I lend you such books as will interest you. 我借给你使你感兴趣的书。(as代替物,作主语)
注:the same… as 和the same… that的用法不同。as引导的定语从句表示其内容与主句所讲的事物“相似”,指同类事物;that引导的定语从句表示其内容与主句所讲的事物是“同一个”,指同一事物。如:
This is the same pen as I lost yesterday. 这和我昨天丢的笔一样。(类似的笔)
This is the same pen that I lost yesterday. 这支笔就是我昨天丢的'那支。(同一支笔)
4、“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
在“介词+which/whom”结构中,介词的选择取决于3种情况:
1)定语从句中谓语动词或表语的搭配。如: This is the college in which I am studying. He is the man about whom we are talking.
2)先行词与介词的习惯搭配。如: The speed at which the machine operates is shown on the meter.
仪表上显示出这台机器运转的速度。
3)当定语从句为最高级时只能用of which; 否则用其他介词。如: I have five dictionaries of which Longman Dictionary is the best. I have five dictionaries among which Longman Dictionary is published in UK.
注:不可拆分的动词短语介词不能提前,如put up with;有的短语可能有不同的介词搭配,此时需要根据上下文来确定。如:be familiar with/to,compare with/to等。
有时为表意清楚,还可以在关系副词where/ when前加介词from, to等。如:
China is the birthplace of kites, from
where kite flying spreads to Japan, Korea, Thailand and India.
中国是风筝的故乡,从这里,放风筝的运动传到了日本、韩国、泰国和印度。
注 定语从句和同位语从句的区别
定语从句在复合句中的功能相当于形容词,它对先行词起修饰、描述或限制作用。而同位语从句则属于名词性从句,对与它有同位关系得名词作进一步解释,使其内容具体化。例如:
She felt very sad because of the news that her husband was killed in an aircraft crash. (同位语从句)
The fact that she told me made me very angry. (定语从句)
英语定语从句语法解析 篇4
关系代词as与which引导的非限制性定语从句,其先行词都可以是整个主句,指代主句的整个意 思。但as和which具有不同的词义、句法和用法。
1. as引导的从句表示说话人的看法、态度、解释或评论
引导定语从句时,as仍具有正如,像,由……可知等意思,翻译时 有时可不必译出。as定语从句常含有这些动词:see, know, hear, watch, remember, say, tell, show, expect, guess等,这类动词与as连用几乎成了一种固定搭配。as引导的此类从句可以置于句首、句中或 句尾。如:
The famous magician Liu Qian, as we all know, is from Taiwan. 众所周知,著名魔术师刘 谦是台湾人。
There is a net bar around here, as I remember. 我记得这儿附近有一家网吧。
As is often the case, girls like dolls while boys like guns. 女孩子喜欢玩具而男孩子 喜欢枪,这是常见的情况。
2. which引导的从句对主句所叙述的事情进行补充说明,表明事物的状态或结果
which此时指前面主句所提到的这件事,常译为这一点,这件事等。这时它所引 导的从句与主句之间常含有并列、因果关系。注意,它引导的从句不像as那样位置灵活,它只能位于主句 的后面。如:
He changed his mind again, which made us all angry. 他又改变了主意,这使我们大家都生 气了。
She tore up my photos, which (=and that) upset me.她撕碎了我的照片,这使我很不安。
3. 在从句中作定语或介词的宾语时,要用which,不用as
Jenny might come, in which case I‘ll ask her. 詹妮可能会来,要是那样的话我就去问 她。
She graduated from a local middle school, after which she went to Beijing University. 她毕业于当地的一所中学,之后她去了北京大学。
4. 当从句的谓语动词是否定形式或含着一个复合宾语时,一般用which而不用as
He pretended not to know me, which I didn’t understand. 他假装不认识我,这是我搞 不明白的。
He admires everyone in his class, which I find quite strange. 他羡慕班里的每个学生, 我认为太奇怪了。
【特别说明】
as引导非限制性定语从句的最大特点是位置灵活;其次,as有以下常见的,而which不具备的 固定表达:
as we all know 众所周知
as I can remember 正如我所记得的
as often happens 正如经常发生的那样
as we expect 正如我们预料的那样
as you see 这一点你明白
as was expected 正如预料的那样
as can be seen 看得出来
as may be imagined 正如可以想象的那样
as has been said above 如上所述
as we all can see 正如我们都能看到的那样
as is often the case 像常规那样
as everybody can do 正如人人都能做到的那样
英语定语从句语法解析 篇5
1. 分隔定语从句。
先行词与定语从句之间有时也会插入别的成分,构成先行词与定语从句的隔离,这种从句叫分隔定语从句。例如:
This is the article written by him that I spoke to you about.
He was the only person in this country that was invited.
①因定语从句过长,为使句子保持平衡,常将定语从句和其所修饰的名词或代词分开。
The film brought the hours back to me when I was taken good care of in that faraway village.
②在定语从句中使用“插入语”以增加语言的灵活性。
The pen I thought I had lost is on my desk,right under my nose.
2. as 和 which 引导的定语从句。
① as 有“正如,就像”之意,在非限制性定语从句中充当主语、宾语或表语,从句可位于主句的前面、中间或后面,一般用逗号与主句隔开。
As we had expected,her performance was wonderful.
A panda, as we know,is a lovely animal.
Tom is the tallest in our class,as you know.
但 which 引导的非限制性定语从句一般只能放在主句之后。例如:
The result of the experiment was very good,which we hadn’t expected.
②在主谓宾结构的非限制性定语从句中,which 和 as 作宾语时可互换使用。
He was an Englishman,which / as I knew from his accent.
作主语时通常用 which ,而不用 as .但在“主语 +be+done ”结构中,as 作主语。例如:
He passed the examination,as was known.
③ as 引导非限制性定语从句时,通常用在表示肯定意义的从句中,而不能用在表示否定意义的从句中; which 则不受此限制。例如:
Mummy treats me just as a baby,which (不用 as ) I can’t bear.
She married again,which (不用 as )was unexpected.
④在宾补结构的非限制性定语从句中,作主语或宾语时,宜用 which ,而不用 as .例如:
He believed in God,which (不用 as ) I find strange.
He changed his mind,which (不用 as ) made me very angry.
⑤定语从句中动词若为表示知觉的词,如 see ,expect ,say ,know 等时,用 as 而不用 which .
As we expected / know, Xiao Ming took the first place in the game.
⑥ as 引导的定语从句与 it 作形式主语的主语从句和以 what 引导的主语从句的区别。试比较:
As is known to everybody,the moon travels round the earth once every month.
It is known to everybody that the moon travels round the earth once every month.
What is known to everybody is that the moon travels round the earth once every month.
3. 定语从句与并列句的识别。
定语从句与主句之间要用“逗号”分隔,并且不能加入 and , but , so 等连接词。并列句一般由 and , but , so 等词连接,或中间用“分号”隔开。例如:
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows,most of which hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. (定语从句)
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows,and most of them hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. (并列句)
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows;most of them hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. (并列句)
Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase,the price of which was reasonable. (定语从句)
Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase;the price of it was reasonable. (并列句)
John’s parents kept telling him that he should work hard,but it didn’t help. (并列句)
4. that 引导的定语从句与结果状语从句的区别。
This is so interesting a book that all of us want to read it. ( so …… that 引导的结果状语从句)
This is so interesting a book as all of us want to read. ( as 引导的定语从句)
通过以上两个例句不难看出, so …… that 引导结果状语从句,而定语从句中先行词前有 so , such , the same 修饰时,常用“ as ”来引导定语从句。
5. 定语从句与同位语从句的区别。
同位语从句是位于名词 answer , belief , doubt , decision , explanation , fact , hope , idea , information , news , order , problem , promise , truth 等后的句子,并对这些句词进行补充说明或解释;从句一般是一个完整的句子,引导词 that 只起引导作用,不作句子成分,且 that 不可省略;同位语从句不可用 which 引导。而定语从句通常是一不完整的句子,缺少主语或宾语等。作宾语时, that 可省略。
The fact that she hasn’t known the result of the examination is clear. (同位语从句)
The fact (that / which) she told me yesterday is very important. (定语从句)
「巩固性练习」
1. _________ is mentioned above, the number of the students in senior high school is increasing.
A. As B. It C. That D. What
2. Now Children like to go to the fast food restaurant, _________ as the name says, eating doesn’t take much time.
A. which B. that C. what D. where
3. Sometimes the earthquake is so violent that it can destroy the whole city, _________ happened in Tang Shan in 1976.
A. as B. that C. where D. like
4. Recently my father bought a Chinese painting, _________ was very reasonable.
A. the price of it B. which price
C. the price of which D. its price
5. We will be shown around the city: schools, museums, and some other places, _________ other visitors seldom go.
A. what B. which C. where D. when
6. We were next-door neighbors for three years, during ________ time we met only twice.
A. which B. this C. in which D. same
7. Living in the central Australia desert has its problems, _________ getting water is not the least.
A. as B. for what C. of which D. for what
8. We should do more such exercises in the future, I think, ________ those we did yesterday.
A. as B. which C. that D. it
9. Gone are the days _________ we spent together in the village.
A. that B. when C. in which D. on which
10. He failed his exam, _________ proves that he wasn’t working hard enough.
A. as B. which C. that D. A and B
11. He must be from Africa, _________ can be seen from his skin.
A. that B. as C. who D. what
「参考答案」
1. A 2. D 3. A 4. C 5. C 6. A
7. C 8. A 9. A 10. D 11. B
高中英语语法归纳总结之定语从句
下面就是我给大家带来的高中英语语法知识 总结 :定语从句,希望能帮助到大家!
高中英语语法知识总结:定语从句
易错点1 关系代词与关系副词的混用
1.定语从句相当于一个形容词,起定词作用, 修饰名词或代词
2.定语从句的引导词的三种功用:( 1)引导定语从句(2)替代先行词(3)在定语从句中充当一定的成分。
3.解题要领:根据定语从句中所缺成分来确定是用关系代词还是关系副词,决不要因先行词是时间名词就用when,是地点名词就用where。
易错点2 关系代词who、whom、whose的误用
对于定语从句关系词的考查,首先要确定从句是什么类型的从句,然后再分析关系词在从句中的成分,最后选择正确的词。要求考生具有一定的 句子 分析能力,和理解能力。如果缺少主宾表,要用that或which,缺少状语用关系副词when,where,why,缺少定语用whose。
易错点3 关系代词that和which的误用
只用which,不能用that的情况
(1) 在介词提前到关系代词之前形成"介词+关系代词"结构来修饰表事物的先行词时, 关系代词必须用which.如:
☞The house in which we live is very large. 我们住的房子非常大。
这就是老师正在谈及的那本参考书。
注意:如果介词不放在修饰事物的限定性定语从句的句首, which就可换为that, 如:
☞This is the question which/that we’ve had so much discussion about. =This is the question about which we’ve had so much discussion. 这就是我们已经多次讨论过的问题。
(2) 先行词为"those+表事物的复数名词"时, 关系代词通常只用which而不用that。如:
☞Students should keep in mind those regulations which restrict their behavior.
学生应牢记那些规范自己的行为准则。
☞A bookshop should deal with a variety of those best sellers which are newly published.
书店应该经营新出版的各种畅销书。
(3)当先行词指物,关系词在句中作主语或宾语,引导非限制性定语从句的关系词只能用which,而不用that。
易错点4 介词后接关系代词的误用
●使用"介词+关系代词"要注意以下几点:
(一)选用介词的依据:
(1) 根据定语从句中谓语动词的搭配习惯(即固定 短语 )。
(2) 根据先行词的搭配习惯(约定俗成,不一定是短语)。
(3) 根据句子的意思来选择。
(4) 表示"所有"关系或"整体中的一部分"时,通常用介词of。
(二)在定语从句中,含介词的短语动词不可拆开使用(短语拆开后含义发生变化),如look after, look for等。
(三)"of which / whom"有时可以用"whose+名词"结构来改写。
(四)当先行词为way并且定语从句中缺少状语时,通常用in which或that引导定语从句(in which或that可省略);如果定语从句中不缺少状语,则用关系代词引导(that 或which 可省略)。
(五)in that不可以引导定语从句,但可以引导原因状语从句。
二、"介词+关系代词"与关系副词的转化
(1)当先行词表示地点,定语从句中缺少地点状语时,通常用关系副词where引导,此时也可选用表示地点的介词+which来代替关系副词where。
(2) 当先行词表示时间,定语从句中缺少时间状语时,通常用关系副词when引导,此时也可选用表示时间的介词+which来代替关系副词when。
(3) 当先行词为reason,定语从句中缺少表示原因状语时,通常用关系副词why引导,此时也可以用for which来代替关系副词why。
易错点5 定语从句与同位语从句的区别
定语从句与同位语从句的区别:
1. 被修饰的词不同:同位语从句的前面一般是数量有限的、表示抽象意义的名词;而定语从句的先行词是无数的指人或物名词。
2. 从句的作用不同:同位语从句表示同位名词的具体内容,而定语从句是对先行词的限制、描绘或说明。
3. 引导词不同:what, how, whether等不能用引导定语从句,但可用于引导同位从句。
4. 引导词的作用不同:引导同位语从句的that是连词,在从句中不充当任何成分;而引导定语从句的that为关系代词,在从句中充当一定的句子成分。
5. 判定定语从句和同位语从句的 方法 :由于同位语从句是用以说明被修饰名词的具体内容的,所它可以转换同位名词的表语;而定语从句则不能作这种转换。
易错点6 定语从句与强调句型的区别
定语从句对名词或代词的修饰和限制,关系词可能是that, which, as, who, but, 另一方面,句子中的It有所指;而强调句型是对某部分加强语气,强调语气的连接词只能是that, who,并且句子中的It 没有任何意义;一般比较明显,而有时就难以区别,还需要根据上下文的语境来判断。
它究竟是强调句型还是定语从句,就要从语境上来考查。如果它是用来回答What is this / that? 这样的问题,意思是:它是一本他想要的书。句子显然是定语从句。如果是用来回答What does he want? 这样的问题,那么意思是:他想要的是一本书。显然,句子是强调句型。
易错点7 关系代词as和which的区别
关系代词as和which引导定语从句的不同点
1. as可以放在主句前后,也可插入主句之中;而which引导的非限制性定语从句只能位于主句之后。
2. 在非限制性定语从句中,which后的be动词不可省;而as后的be动词可以省略。
3. which在非限制性定语从句中作主语时可用各类动词作谓语;而as作主语时,谓语常用系动词,如be,seem,become等,一般不用其他行为动词。
4. as常用"正如"含义,常用的结构有as we know(众所周知);as often happens(正如常发生的那样);as is often the case(情况常常如此);as we all can see(正如我们看到的);be announced / expected / known / imagined / mentioned / said / shown / reported等。这些结构常放句首,偶尔也可以放句中或句末。
5. 非限制性定语从句中,which可指代主句中的某一个单词,as不可以。
6. "介词+关系代词(介宾代物)"中关系代词只能用which。
7. 从句中的谓语动词是否定形式时,常用which。
一、关系代词和关系副词基本用法
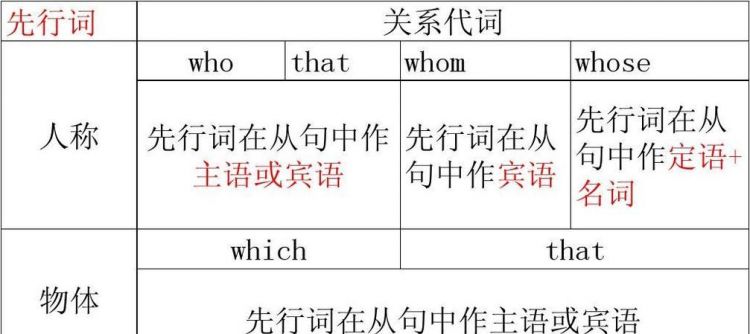
根据关系词在定语从句中的不同用法,可分为关系代词和关系副词。关系代词主要有who, whom, which, that, whose等,在定语从句中作主语、宾语、定语等;关系副词主要有when, where, why等,在定语从句中作状语。具体用法如下:
1.关系代词的用法
当先行词指人时,若它在从句中作主语,则用who;若它在从句作宾语,则用whom或who;若它在从句中作定语,则用whose。如:
☛The man who told me this refused to tell me his name. 告诉我这事的人不肯告诉我他的名字。
☛The woman whose umbrella you took is very angry about it. 你拿了那个女人的伞,她非常生气。
当先行词指物时,若在定语从句中作主语或宾语,则用which;若它在定语从句中作定语用,则用of which或whose。如:
☛I saw something in the paper which might interest you. 我在报上看到一样可能使你感兴趣的东西。
☛He’s written a book the name of which (whose name) I’ve forgotten. 他写了一本书,书名我给忘了。
2.关系副词的用法
关系副词主要有when, where, why等,在定语从句中作状语,分别表示时间、在点和原因。when主要放在time, day, years, season, age, occasion等时间的名词后;where主要放在place, city, town, village, house等地点名词后;why则通常只放在reason后。如(***):
☛Wednesday is the day when the shops are not open in the afternoon. 星期三下午商店不开门。
☛Give me one reason why we should help you. 给我举出一个我们应当帮助你的理由。
要特别注意,activity, case, point, even, situation, job, organization, position等抽象名词后接where引导定语从句的用法(这是近几年高考的一个新 热点 )。如:
☛I don’t want a job where I’m chained to a desk all day. 我不想找一份整天坐办公桌前的工作。
☛Today, we’ll discuss a number of cases where beginners of English fail to use the language properly. 今天,我们将讨论一些英语初学者对英语使用不当的问题。
☛The treatment will continue until the patient reaches the point where he can walk correctly and safely. 治疗将会持续到病人可以正常且安全地行走。
☛If you risk something important, you cause it to be in a dangerous situation where you might lose it. 你如果拿重要的东西去冒险,那你就是将它置于一种可能会失去它的危险境地。
二、使用非限制性定语从句的情况:
1. 关系代词指代整个主句时,使用非限制性定语从句。
☛You did a lot for me, for which I was grateful. 你为我做了许多,对此我很感激。
☛The Diaoyu Island belongs to China, as is known to us. 众所周知,钓鱼岛属于中国。
☛A middle-aged woman killed her husband, which frightened me very much. 一个中年女子杀害了自己的丈夫,这令我十分恐惧。
2. 当先行词指的是世界上独一无二的事物或人名地名等专有名词时,使用非限制性定语从句。
☛China, which is my motherland, is developing fast. 中国是我的祖国,正在快速发展。
☛Eason, who was a pop star, got married last year. 伊森去年结婚了,他是明星。
☛Last Sunday they reached Nanjing , where a conference was to be held. 他们上周日到达南京,有个会议要在那里举行。
3. 当先行词指的是某人只有一个亲属(son,daughter等)时,使用非限制性定语从句。
☛He has a daughter, who is studying in London. 他有个女儿,现在正在伦敦学习。(只有一个女儿)
☛This is my teacher, who has something to tell you. 这是我的老师,他有一些事情要告诉你。
三、限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别
1. 形式不同
限制性定语从句主句和从句之间不用逗号隔开,口语中使用时也不停顿;而非限制性定语从句与主句之间通常有逗号隔开,口语中使用时有停顿。
2. 功能不同
限制性定语从句用于对先行词的意义进行修饰、限制和识别,如果去掉,就会造成句意不完整或概念不清;而非限制性定语从句用于对先行词起补充说明作用,如果省略,句意仍然清楚、完整。
☛People who take physical exercise live longer. 进行体育锻炼的人活得长些。(若把从句去掉句子就失去意义)
☛His daughter, who is in Boston now, is coming home next week. 他女儿现在在波士顿,下星期回来。(若把从句去掉,句子意义仍然完整)
3. 翻译不同
在翻译定语从句时,一般把限制性定语从句翻译在它所修饰的先行词之前,而把非限制性定语从句与主句分开。
☛He is the man whose car was stolen. 他就是汽车被窃的那个人。
☛I’ve invited Jim, who lives in the next flat. 我邀请了吉姆,他就住在隔壁。
4. 含义不同
比较下面的两个句子:
☛I have a sister who is a doctor. 我有一个医生的姐姐。(姐姐不止一个)
☛I have a sister, who is a doctor. 我有一个姐姐,她是当医生的。(只有一个姐姐)
5. 先行词不同
限制性定语从句的先行词只能是名词或代词,而非限制性定语从句的先行词则可以是名词或代词,也可以是短语或句子;另外,当先行词为专有名词或其他具有独一无二性的普通名词时,通常要用非限制性定语从句,而不用限制性定语从句。
☛Peter drove too fast, which was dangerous. 彼得开车很快,这是很危险的。(which指drive too fast)
☛He changed his mind, which made me very angry. 他改变了主意,这使我很生气。(which指整个主句)
☛Mr. Smith, who is our boss, will leave for Japan next week. 我们的老板史密斯先生下周要去日本。(先行词为专有名词,要用非限制性定语从句修饰)
☛Her father, who has a lot of money, wishes her to study abroad. 她父亲很有钱,希望她 出国 学习。(先行词为表独一无二意义的普通名词,要用非限制性定语从句修饰)
6. 关系词不同
关系词that和why可用于限制性定语从句中,通常不用于非限制性定语从句;另外,在限制性定语从句中,关系词有时可以省略,而在非限制性定语从句中关系词一律不能省略。
四、"介词+关系代词"引导的定语从句:
●"介词+关系代词"的用法
当关系代词在定语从句中作介词宾语时,我们通常用"介词+关系代词"引导定语从句。如果指"人",用"介词+whom";如果指"物",用"介词+which"。
●"介词+关系代词"结构中介词的选用
1.一般来说,确定关系代词前的介词,可以从以下三方面入手:①先行词的意义;②从句中的动词或形容词与先行词的固定搭配;③句子的意思。
☞I’ll never forget the time during which I spent my childhood in the country.
我永远不会忘记孩童时代我在乡村度过的时光。
2.表示"整体和部分关系",介词常用of。在some,any,few,none,all,both,neither,most,each等代词或数词的前、后可以用of which/whom。
☞John invited about 40 people to his wedding,most of whom are family members.
约翰邀请了大约40人参加他的婚礼,他们当中绝大部分是家庭成员。
3.有时"介词+where"可以引导定语从句,此时要和"介词+which"引导的定语从句从意思上加以区别。
☞His head soon appeared out of the window,from where he saw nothing but trees.
他的头很快从窗口探了出来,从那里除了树木他什么也看不到。(from where相当于from out of the window,而不是from the window)
●在定语从句中,含介词的短语动词不可拆开使用(短语拆开后含义发生变化),如look after, look for等。
●"of which / whom"有时可以用"whose+名词"结构来改写。
●当先行词为way并且定语从句中缺少状语时,通常用in which或that引导定语从句(in which或that可省略);如果定语从句中不缺少状语,则用关系代词引导(that 或which 可省略)。
五、关系代词只用that而不用 which的情况
1.先行词是all,something,everything,anything,nothing,little,much,few等不定代词或先行词被all,any,every,no,little,much,some等词修饰。
☞All the people that come from the country work much harder.
所有来自农村的人工作都更努力得多。
2.先行词被序数词、 形容词最高级、 the only, the very, the last等修饰时, 关系代词通常只用that, 不用which.如:
☞The first English novel that I read was Cities.
我读的第一本英文小说是《城市》。
☞This is one of the most exciting football games that I have ever seen.
这是我见过的最激动人心的 足球 比赛之一。
☞This is the only thing that we can do now.
这是我们现在惟一能做的事情。
3.先行词既有人又有物时,关系代词只用that,不用which.如:
☞The scientist and his achievements that you told me about are admired by us all.
我们所有人都钦佩你告诉我的那位科学家和他所取得的成就。
☞The foreign visitors spoke highly of the pioneers and their performances that they saw at the Children’s Palace.
外国游客高度赞扬了他们在少年宫所看到的少先队员以及他们的表演。
4.关系代词在限定性定语从句中作表语并带有类比含义时,通常只用that,不用which.如:
☞He is no longer the star that he was.
他不再是过去的那位明星了。
☞Our school is no longer the school that it used to be.
我们的学校不再是以前的那所学校了。
5.句中其他位置已出现which,为避免重复,不用which而用that引导限定性定语从句。如:
☞Which is the car that has overtaken us?超过我们的是哪辆车?
定语从句高考题语法填空版
一.几个基本概念
1.定语从句的定义:用作定语的从句叫定语从句。
2.先行词:被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词。
3.定语从句的位置:紧跟先行词(名词或代词)之后。
4.引导词:引导定语从句的词(包括关系代词和关系副词)。
﹙1﹚关系代词:that/who/whom/which/as
﹙2﹚关系副词:when/where/why
5.引导词的位置:位于定语从句之前(先行词之后)。【as除外】
6.引导词的功能(作用):
﹙1﹚连接先行词和定语从句。
﹙2﹚在定语从句中充当一定的成分(关系代词充当主语或宾语,关系副词充当状语)。
7.定语从句的类型:
﹙1﹚限定性定语从句(主句和定语从句之间无逗号)。
① 直接由引导词引导定语从句
The man who you’re talking to is my friend.
② 由介词+关系代词(whom/which)引导
The man to whom you’re talking is my friend.
I need a pen with which I can write a letter.
=I need a piece of paper on which I can write a letter.
介词的选用可根据从句中的相关词组确定,该介词通常可以放在关系代词之前,也可放在从句之尾。例如:
The man (who/whom/that) I talked about at the meeting is from Beijing University.
=The man about whom I talked at the meeting is from Beijing University.
The palace (which/that) I often pay a visit to was built in the 17th century.
=The palace to which I often pay a visit was built in the 17th century.
﹙2﹚非限定性定语从句(主句和定语从句之间用逗号隔开)。
① 直接由引导词引导定语从句。
② 由介词+关系代词(whom/which)引导。
I live in a house far away from the city, in front of which is a big tree.
There is an apple tree standing at the gate, on which are many apples.
This is the man to whom I gave the book.
③ 由“代词/名词+of+whom/which”或“of which/ whom +名词/代词”(先行词指
人用whom,指物用which)引导。One, some, any, none, all, both, several, many, most, neither, either等词、数词、分数或百分比与of whom或of which连用。
He has five children, two of whom are abroad.
(比较:He has five children, and two of them are abroad.)
We have three books, none of which is/are interesting.
(比较:We have three books, but none of them is/are interesting.)
除why和that不能引导非限定性定语从句外,其余引导词都可以,用法同限定性定语从句一样。但要注意以下区别。
1.在形式上非限定性定语从句与主句有逗号隔开。
2.非限定性定语从句的作用:它只是补充说明先行词的情况,翻译时可译成两个句子。
The engineer, whose leg was badly hurt, was quickly sent to hospital.
(那位工程师被很快送往医院,其腿部受了重伤)
The engineer whose leg was badly hurt was quickly sent to hospital.
(那位腿部受了重伤的工程师被很快送往医院)
3.在非限定性定语从句中,任何引导词都不能省略(包括引导词在此定语从句中充当宾语在内)。指人做主语时只能用who, 做宾语时用whom;
指物做主语,宾语都用which; 关系副词用when或where,也不能省略。
The man, ______ is sitting on the chair, is my father.
The woman, _______ I met yesterday, is my English teacher.
The city, _______ is far away, is very beautiful.
He went to America, ______ his parents live.
He joined the Army yesterday, ______ I left, too.
4.whose引导非限定性定语从句:
The house, whose window faces south, is mine.
=The house, the window of which faces south, is mine.
=The house, of which the window faces south, is mine.
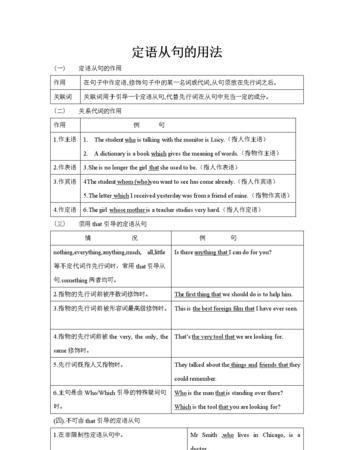
二。定语从句中关系代词和关系副词的基本用法。
1.who/that指人是主格在定语从句中代替先行词,又作定语从句的主语,不能省略。
Do you know the gentleman who/that is sitting there?
2.whom/who/that指人是宾格,在定语从句中代替先行词,又作定语从句的宾语(动宾或介宾)。
① 当作动宾(动词后接宾语)时,关系代词可省略。
Do you know the gentleman (whom/who/that) we met just now?
② 当作介宾(介词后接宾语)时:
介词不提前时,关系代词可省略;
介词提前时,关系代词不可省,即介词+whom(指人时介词后的关系代词只能用whom)。
The man (whom/who/that) I spoke with is my teacher.
The man with whom I spoke is my teacher.
※注:固定的动词短语(动词+介词)如look for, take care of等不能把动词与介词拆开,既介词不能提至引导词前。
She is the right girl (who/whom/that) we are looking for.
3.whose: 指人或物,是所有格“…的”形式。Whose+n.一起在定语从句中充当主语、宾语(动宾或介宾)即先行词的什么东西怎样了,whose不能省略。Whose+n. = the +n. + of which/whom= of which/ whom+ the =n.
I didn’t find the desk whose leg was broken. (主语)
He is the student whose pencil I broke yesterday. (动宾)
The boss in whose company I work is very kind. (介宾)
4.which/that 指物,指代先行词且在定语从句中作主语或宾语(动宾或介宾)。
① 当作动宾时,关系代词可省略。
② 当作介宾时:
介词不提前时,关系代词可省略;
介词提前时,关系代词不可省,即介词+which(指物时介词后的关系代词只能用which)。
The house which/that was destroyed in the earthquake is weak.
The pen (which/that) you found yesterday is mine.
The games (that/which) the young men competed in were difficult.
The games in which the young men competed were difficult.
※注:介词+关系代词即介词+whom/which(先行词指人用whom,指物用which)。
※5.as指人或物,在定语从句中可作主语,宾语,表语或状语,不能省略。主要用于 “the same …as…;such …as…;so …as…;as … as…;as follows”固定结构中,形式固定此时的引导限定性定语从句。要用as代替who(m), which, 或that引导定语从句:
Such people as knew Hill thought he was honest.
Such people as Hill knew thought he was honest.
My hometown is no longer the same as it was.
Here is so big a stone as no one can lift.
The child knows as much as grow-ups (know).
I’d like to have the same books as are used in your school.
He is not such a person as I expected.
He will marry as pretty a girl as he can find.
※注:which和as可引导非限定性定语从句:可以指代主句中的一部分或整个句子的内容,which和as都可以指代主句中的一部分或整个句子的内容,有时可以互换。因此,当as/which指代前面的整个句子,或前句中的部分内容作定语从句的主语时,谓语用单数。
Our team lost the game, as/which was reported in the newspaper.
She was terrified, as/which I could see from her eyes.
He married her, as/which was natural.
区别:
①as引导的非限制性定语从句可以放在主句前面、插在主句中间或放在主句末尾;而which引导的非限制性定语从句只能放在主句后面。
He married her, as/which was natural.
=As was natural, he married her.
Mark Twin is a great writer, which/as is known to all.
=As is known to all, Mark Twin is a great writer.
②as引导的从句有“正如”、“正像”之意,而which则无此意。常用句型有:
as we all know, as is known to all, as everybody can see, as is expected, As is known/ said/ reported/ told/ we all know等。如:
As we all know, paper was first made in China.
To shut your eyes to facts, as many of you do, is foolish.
③主句和从句有因果关系时,用which.
Our class has won the football match, which made us very happy.
Bamboos are hollow, which makes them very light.
④从句含否定意义时常用which.
She didn’t pass the exam, which we couldn’t expect.
She didn’t pass the exam, as we expected.
6.when关系副词:指时间。在定语从句中作时间状语,不能省略。此时的when还可用介词+which替换(此时先行词一定是表时间的名词)。
I still remember the time when I joined the League.
=I still remember the time on which I joined the League.
=I still remember the time (which/that) I joined the League on.
7.where关系副词:指地点。在定语从句中作地点状语,不能省略。此时的when还可用介词+which替换(此时先行词一定是表地点的名词)。
I still remember the school where I joined the League.
=I still remember the school in which I joined the League.
=I still remember the school (which/that) I joined the League in.
※注:对关系副词when, where的认识。
①. 先行词是时间的名词,并非都用关系副词when引导定语从句。
I’ll never forget the time (which/that) I spent in Beijing.
②. 先行词是地点的名词,并非都用关系副词where引导定语从句。
This is the factory (which/that) he visited yesterday.
③. 当句型为It/This/That is(was) the first(second…last) time引起的句子时用that连接其后的句子。此时的time是次数,不是时间。
It/This is the first time that we travel.
It/This is the last time that I shall give you a lesson.
8. why指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语,先行词通常为reason,不能省略。且why引导的定语从句只能是限定性定语从句。Why= for which
I don’t know the reason why he was late yesterday.
The reason why(for which) he was late is that he missed the bus.
※注:当先行词为reason时,关系副词并非都用why.
This is the reason (that/ which) he gave/ explained to us.
【判断用关系代词还是关系副词】
从句缺少的是主语、宾语还是状语是确定用关系代词还是关系副词的关键。试比较:
I will never forget the day (which/that) I spent in Hongkong.
( spent是及物动词,后缺宾语,因此用关系代词或省略 )
I will never forget the day when/on which Hongkong returned to its motherland.
( 从句主谓宾结构完整,缺状语,因此用关系副词或介词加关系代词 )
The reason (that/which)he gave for not coming to school yesterday isn’t believable.
( gave是及物动词,后缺宾语,因此用关系代词或省略 )
The reason why he didn’t come to school yesterday isn’t believable.
( 从句主谓宾结构完整,缺状语,因此用关系副词或介词加关系代词 )
三。 值得注意的几个问题:
第一。 当先行词是物时,关系代词(that/which)只用that的情况。
1.当先行词被序数词或形容词的最高级修饰时。
This is the best film that has been shown this year.
This is the first book (that) I borrow from the library.
※He is the first student that/who came to school today.
2.当先行词为两个或两个以上分别指人和物的名词时。
He talked about the teachers and the school (that) he had visited.
3.当先行词本身是all的,用that.(all that=what)
All that (what) I want to say to you is “Thank you”.
=All (what) I want to say to you is “Thank you”.
Go over all that (what) we learned.
=Go over all (what) we learned.(that在定语从句中充当宾语可以省略)
4.先行词为something, anything, nothing, everything, thing时,用that.
I’ll tell you anything (that) I know.
5.当先行词前有all, much, little, many, (a) few, every, some, any, no, only, the very, one of, the only, the last, the next等修饰语时。
This is one of the books (that) I’m very interesting in.
※ This is one of the books in which I’m very interesting.
This is the only book (that) I read.
He is the only one of the boys that likes playing the piano.
All the glasses that were on the table fell off onto the floor.
6.(人,物),当先行词在以who或which开头的特殊疑问句中时,用that引导以避免混淆。
Who is the man that is talking with the lady?
Which of you that know the answer can come to the front?
7.当先行词是在定语从句中作表语时,用that.
He likes the girl that she used to be.
第二。 当先行词是物时,关系代词(that/which)只用which的情况。
1.作介宾且介词置于引导词之前时。
The room in which he lives is very large.
2.引导非限定性定语从句时(主,宾都用which,都不能省略).
Football, which is a very interesting game, is played all over the world.
The house, which I visited yesterday, is very large.
3.which指整个句子的内容或部分内容,引导非限定性定语从句。
He always makes fun of me, which upsets me.
第三。其他特殊情况。
1.先行词是these, those指人时,关系代词只用who.
Those who are playing over there are my students.
2.先行词是人称代词(he, she…)时,关系代词只用who.
He who doesn’t reach the Great Wall is not a true man.
3.不定代词someone, anyone, everyone, no one, somebody, anybody, everybody作先行词时,关系代词用who.
Anybody who breaks the rules would be punished.
4.①先行词是the only one of +可数名词复数,在定语从句中作主语时,定语从句中的谓语用单数形式(因为此时的先行词是the only one,而不是of 后的可数名词复数).
He is the only one of the boys that likes playing the piano.
This is the only one of the books that is borrowed.
②先行词是one of +可数名词复数,在定语从句中作主语时,定语从句中的谓语用复数形式(因为此时的先行词是of 后的可数名词复数,而不是one).
This is one of the students who are late.
5.当主句缺先行词时,用the one 代替,但须注意:the one只能代替可数名词单数。如为不可数名词时,指什么用什么。
Is this school the one I visited yesterday?
Is pop music the music he likes best?
6. 当先行词是the way,在定语从句中充当方式状语时(the way表“以…方式/方法”),引导词通常用that或省略,也可用in which.
I don’t like the way (that) you speak.
=I don’t like the way in which you speak.
=I don’t like the way (which/that) you speak in.
【“介词+关系代词”十种情况】
在定语从句中,介词+关系代词结构是一种较为复杂的问题。现就几种常见的介词+关系代词的结构浅析如下:
1.介词+which在定语从句中分别作时间、地点和原因状语,代替相应的关系副词when, where和why.如:I still remember the day on which (when) I first came to school.我仍然记得初来学校的那一天。
The factory in which (=where) I work is a large one.我工作的工厂是一个大工厂。
This is the reason for which (=why) he was late.这就是他为什么迟到的原因。
2.介词+which(指物)/ whom(指人)在定语从句中作地点状语,表示存在关系,定语从句主谓一般要倒置。
They arrived at a farmhouse, in front of which sat a small boy.他来到一处农舍,前边坐着一个小男孩。
I saw a man, on the head of whom stood a bird.我看见一个人,他的头上站着一只鸟。
3.介词+ which(指物)/ whom(指人)在定语从句中作目的、方式或地点状语。这种结构中的介词一般受动词或介词后的名词所制约。如:
Could you tell me for whom you’ve bought this coat?你能告诉我这件衣服是给谁买的吗?
The man, from whom I learned the news, is an engineer.这人是一位工程师,我是从他那里得到这消息的。
4.介词+which/whom,用于被动结构的定语从句中,作状语,说明动作的出发者。如:
The wolf by which the sheep was killed was shot.伤害羊的.那只狼被打了。
The man by whom the wolf was shot was a good hunter.打死狼的那人是个好猎手。
5.不定代词+of+which/whom,在定语从句中作主语,说明整体中的部分,常用的不定代词有:both, all, any, some, each, none, most等。如:
There are a lot of books here, none of which belongs to me.这儿有许多书,可一本也不属于我。
Yesterday Mary bought a few clothes, all of which were expensive.昨天玛丽买了一些衣服,他们都很贵。
6.数词+of+which/whom,在定语从句中作主语,说明整体与部分的关系。数词可以是基数词、序数词、分数或百分数。如:
In our class there are fifty-four students, twenty-five of whom are girls.我们班有54名学生,25人是女生。
Two watches were stolen, one of which was mine.两只手表被偷了,其中一只是我的。
7.名词+of+which代替whose+名词,在定语从句中作定语。如:
I saw some trees, the leaves of which (=whose leaves) were black with disease.我看见一些树,他们的叶子因害病而发黑。
I live in a house, the windows of which are all broken.我住在一所房子里,其窗都破了。
8.介词+ which(指物)/ whose(指人)修饰后边的名词。如:
It rained all night and all day, during which time the ship was broken into pieces.雨下了一天一夜,就在这期间轮船撞碎了。
The driver was the man from whose room she had stolen the maps.司机就是那个人,她从他的房间偷走地图。
9.形容词最高级+of+which/whom结构,在定语从句中,作定语,表部分关系。如:
China has thousands of islands, the largest of which is Taiwan.中国有成千上万个岛屿,其中最大的是台湾岛。
In our class there are twenty girls, the cleverest of whom is Li Hua.我们班有20名女生,最聪明的是李华。
10.介词+which+不定式。此种用法多见于正式文体中,相当于一个定语从句。如:
At last he had something about which to write home.他终于有了给家里写信的内容了。
He had no key with which to open the door.他没有开门的钥匙。
He has a small room in which to live.
【运用定语从句时应注意的几个问题】
1. 关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,定语从句的谓语动词应和先行词的人称和数保持一致。
This is one of the books which were written by Mark Twain.这是马克吐温所写的书中的一本。(先行词是books,因此动词应用were.)
2. 关系代词或关系副词在从句中充当一个句子成分,因此要注意避免从句中句子成分的重复出现。
This is the most beautiful place that I have visited it.
This is the most beautiful place that I have visited. 这是我参观过的最美的地方。(去掉it,因that代替先行词the most beautiful place在定语从句中作visit的宾语,再加it就多余了。)
The school where I worked there is a big one.
The school where I worked is a big one.我所工作过的学校是一所大学校。(去掉there,因where既引导定语从句,又在从句中代替in the school作状语。)
3. 关系代词在定语从句中作主语时不可省略。
The books were on the table were given to you.
The books that were on the table were given to you.桌上的那些书是给你的。(关系代词that作主语不能省)
4. “one of the +复数名词”后的定语从句中谓语动词的单复数情况。
“one of the +复数名词”时,复数名词是先行词,所以谓语动词常用复数形式。如果“one of the +复数名词”前面有the very /only等修饰语,则谓语动词用单数形式,因为先行词是,而不是复数名词。如:
He is the only one of the students who speaks Japanese in our class.他是我们班唯一说日语的学生。(the only one是先行词)
He is one of the students who speaks Japanese in our class.他是我们班里说日语的学生之一。(students是先行词)
5. 定语从句中who和whom的选用。
关系代词who/whom引导定语从句时,作主语用主格who,作宾语用宾格whom.在其引导的定语从句带有插入语,而又不用逗号分开时,要用who.
Mary is a girl who I think is clever.
在定语从句who I think is clever中, I think是插入语,去掉后Mary is a girl who is clever是一个完整的句子,who是定语从句的主语,不能用whom替换。但下面的句子,情况就不同了:
Mary is a girl whom I think to be clever.在定语从句whom I think to be clever中,如把I think看作插入语而去掉,则剩下的部分Mary is a girl whom to be clever很明显不是一个完整的句子结构,所以I think不能被看作是插入语,而是定语从句在的主谓结构,whom作think的宾语,to be clever是whom的宾补。
6. 定语从句中关系代词或关系副词的选择取决于它们在从句中所充当的句子成分。如作主语和宾语用关系代词;作状语,用关系副词。
I’ll never forget the day when I went abroad myself.(when在从句中代替时间状语on the day,此句可分解为I’ll never forget the day. I went abroad myself on the day.)
I’ll never forget the days that we spent together.(that代替the days,在从句中作spent的宾语,该句可分解为I’ll never forget the days. We spent the days together.)

定语从句的用法归纳总结视频讲解
定语从句是高中英语的重要语法项目之一,它的结构和用法比较复杂。我们应从哪些方面有效地复习定语从句呢?下面就是我给大家带来的定语从句的用法讲解,希望大家喜欢!
[定语从句的种类]
定语从句分为限制性和非限制性两种。限制性定语从句是 句子 不可缺少的部分,如去掉主句意思就不完整或失去意义;非限制性定语从句是先行词的附加说明,去掉也不会影响主句的意思。它与主句之间通常用逗号分开,一般不用that引导,关系词不可省略。如:
This is the book that I want to read. (限制性)
Tom’s father, who arrived just now, is a famous scientist. (非限制性)
非限制性定语从句的先行词成分可以是整个主句,非限制性定语从句常用which引导,修饰整个句子。定语从句的谓语动词要用第三人称单数。例如:
The weather turned out to be very good, which was more than we could expect.
关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词所指代的先行词是表示人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。
在定语从句中,who和that既可作主语又可作宾语,whom只可作宾语(作宾语时可以省略)。如:
Is he the man who/that wants to see you? (who/that在从句中作主语)
The man (whom/who/that) you spoke to just now is our English teacher. (whom/who/that在从句中作宾语,可省略)
[whose]
在定语从句中作定语,可用来指人或物,表示物时相当于“the+名词+of+which”或“of+which+the+名词”。如:John, whose wife is ill, can’t come to the party.
[which & that]
which和that指代的先行词是表示事物的名词或代词,在定语从句中可作主语、宾语等。如:
Please show me the radio that/which you have just bought. (that/which在从句中作宾语,可省略)
This is the film that/which created a great sensation. (that/which在从句中作主语)
只能用that而不能用which的情况:
1. 先行词是最高级或被最高级修饰时。如:This is the best dictionary that I’ve ever used.
2. 先行词是序数词或被序数词修饰时。如:The first thing that we should do is to get some food.
3. 当先行词是anything, everything, nothing, something, few, all, none, little, some等不定代词时,或是由every, any, all, some, no, little, few, much等词修饰时。如:Tom told his father all that had happened.
There is little that I can do for you.
4. 先行词既有人又有物时。如:They talked about the teachers and the schools that they knew.
5. 先行词被the only,the very,the right等修饰时。如:This is the very book that I want to have.
6. 在which,who,whom引起的问句中,为避免重复。如:Who is the girl that talked to you yesterday?
7. 关系代词在定语从句中作表语时。如:China is not the country that it was.
只能用which,不能用that的情况:
1. 在非限制性定语从句中。如:Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a very long histroy.
2. 在介词后面,即“介词+which(指物)”。如:This is the house in which we lived three years ago.
[as]
关系代词as代替的先行词是人或物的名词, 在从句中作主语、宾语和表语。
as引导限制性定语从句时,常和such, the same, as(so)连用, 构成such ... as, the same ... as, as/so ... as等结构,在从句中可作主语、宾语和表语。如:
Don’t trust such men as praise you to your face. (在定语从句中作主语)
I have the same trouble as you have. (在定语从句作宾语)
It’s as pleasant a film as I have ever seen. (在定语从句作宾语)
但是当先行词被the same修饰时,that也可以引导定语从句,但意义有所不同。the same ... as(指同样或同类的), the same ... that(指同一个)。例如:
This is the same watch as I lost.
This is the same watch that I lost.
as也可单独使用,引导非限制性定语从句,修饰整个主句或主句中的一部分,放在句首、句中或句末。如:
As is known to us all, smoking is harmful to one’s health. (指代整个主句,在从句中做主语)
He is late, as is often the case. (指代整个主句,在从句中做主语)
Light, as everybody knows, travels much faster than sound. (指代整个主句,在从句中做宾语)
as和which作关系代词的用法比较:
which引导的非限定性定语从句只能放在主句之后,which指代前面的一个句子或主句中的某一成分;as引导的非限定性定语从句能放在主句之前、中、后,既可指前面已经提到的情况,也可指后面提到的情况。
as引导从句时,有“为人所熟知”的含义,which则没有这层意思。as引导的从句往往表示的是一种附加说明,which引导的从句一般是较为重要的陈述。如:
His mother is ill, which makes him very sad.
As is expected, the England team won the football match.
[关系副词引导的定语从句]
关系副词when, where, why可代替的先行词是时间、地点或理由的名词,在从句中作状语, 相当于“介词+which”结构。例如:
I’ll never forget the time when/during which we worked in the factory.
This is the village where /in which he was born.
I don’t know the reason why/for which she looks unhappy today.
[判定用关系代词还是用关系副词]
关系代词与关系副词的选用,应看先行词在定语从句中充当什么成分:若作主语、宾语或定语,则用关系代词who,whom,that,which,whose,as等;若作状语, 就用where, when, why等关系副词。如:
The reason why I’m writing is to tell you about a party on Sunday. (状语)
The reason that/which he gave us sounded reasonable. (宾语)
Pisa is a city, which has a leaning tower. (主语)
Pisa is a city, where there is a leaning tower. (状语)
[介词+关系代词]
当关系代词作介词宾语时,就出现了“介词+关系代词”的结构引导定语从句的现象。当先行词指物时用“介词+which”,指人时用“介词+whom”,且关系代词不能省略。而这种结构中较难解决的问题是介词的选择问题:
1. 介词的确定可以根据整个句意来确定。
Oxygen is a kind of gas, without which we couldn’t live.
2. 介词可以根据与先行词的搭配来确定。
He gave me the book for which he paid a lot of money. (动词与介词搭配)
1949 was the year in which the P.R.C. was founded. (名词与介词搭配)
The snake, of which she used to be afraid, is her favorite animal now. (形容词与介词搭配)
定语从句的用法讲解相关 文章 :
1. 英语中as引导的定语从句的相关讲解
2. 定语从句中关系词的用法讲解
3. 英语定语从句的用法
4. 英语数词的分类和用法
5. 高中英语语法知识总结:定语从句
6. 考点初中英语定语从句的用法
7. 非限制性定语从句的用法讲解
8. 英语语法:定语从句
9. 定语从句语法知识点汇总
以上就是关于定语从句语法总结 ,英语定语从句语法讲解的全部内容,以及定语从句语法总结 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

