本文目录
请大家给我讲下虚拟语气常用的几种形式英语
虚拟语气是一种动词形式,表示说话人的一种愿望,假设,怀疑,猜测, 建议等含义,虚拟语气所表示的含义不是客观存在的事实.它的用法在表情达意的过程中发挥着重要的作用.近几年高考在单项选择这一题型中出现不多,但在完形填空和短文改错中仍然大量出现.例如,2003年高考完形填空第38题考察的就是在篇章语境中的虚拟语气在宾语从句中的用法.虚拟语气的实际用法主要包括以下几种:
1、 虚拟语气用在简单句中,表示“强烈的祝愿或命令的语气”. 常用“May+主语+动词原形”或“主语+动词原形”.例如:May the friendship between us last long. 祝愿我们的友情天长地久. You go out! 你出去!
2、 虚拟语气在宾语从句中的用法.由wish引导的宾语从句常表示说话人的一种强烈的却暂时无法实现的愿望.
How I wish she would be on my side!(But in fact it’s quite impossible.我多么希望她能站在我一边啊!
How I wish I could help him! 我多么希望我能帮助他啊! How I wish I had watched the close NBA game last night.
另外,在表示“命令”、“坚持”、“要求”或“建议”等意义的及物动词(order, command, demand, require, insist, suggest, propose, advise)之后的宾语从句中的谓语动词同样常使用虚拟语气,表示说话人的要求,其结构为:主语+should+动词原形,其中的should常可省略.例如:The head teacher demanded that we (should ) finish the task in time today.
但是,当insist表示“坚持认为”的意思时,或suggest表示“暗示”或“表明”之意时,宾语从句仍用陈述语气.试比较:My parents insisted that I ( should) enter a key university. /My parents insisted that they were right.
The soldier’s pale face suggested that he was happy to have given his life to his motherland.
The monitor suggested that we (should ) hold a class meeting tomorrow afternoon to discuss the problem.
3、 虚拟语气用在主语从句中.
在句型 "It is important (necessary, strange, natural, a pity, suggested, advised, demanded, commanded, ordered ) that . " 中,that 后面的从句中的谓语动词常用:“ should + 动词原形 ”.例如:
It's necessary that we should have a walk now. 我们有必要出去散散步.
It's natural that she should do so. 她这样做是很自然的.
It's suggested that we should take good care of the patient.
同理,在表示“命令”、“坚持”、“要求”或“建议”等意义的名词前后的主语从句、表语从句和同位语从句中的谓语动词同样用虚拟语气,既:“主语+(should)+ 动词原形”的句型.例如:
His suggestion /advice is that we should start early tomorrow morning.
3、虚拟语气用在状语从句中.
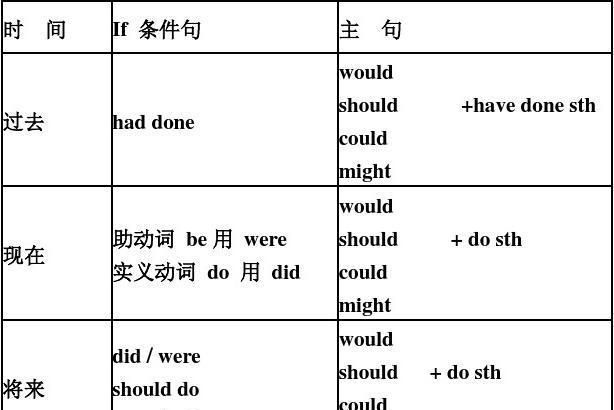
虚拟语气最多地用在表示条件的状语从句和表示结果的主句中.在表示与事实相反的虚拟语气时,动词有三种虚拟形式,即虚拟条件现在式,过去式和将来式.
1) 虚拟条件现在式:表示与现在事实相反的假设及根本不可能的假设或结果:
条件状语从句
结果主句
If 主语+ 动词过去式(be 用were)
主语+ would/could/should/might + 动词原形
2)虚拟条件过去式:表示与过去事实相反的假设或结果:
条件状语从句
结果主句
If+主语+ had + 过去分词
主语+should/ would/could/might+ have+ 过去分词.
3)虚拟条件将来式:表示与将来事实相反的假设或结果:
条件状语从句
结果主句
If+ should /were to +动词原形
主语+ should/ would/could/might+动词原形
If I were you, I should get it. 如果我是你,我就买了它.
If I had time now, I would study French. 如果我现在有时间,我会学习法语的.
If you had got up earlier, you could have caught the train. 如果你早一点起床,就会赶上火车的.
If it were to be fine tomorrow, I would go shopping with my friends.
如果明天天气好,我将和朋友们一起去买东西.
虚拟语气有哪几种句型结构
(1)
对现在情况的虚拟
对现在情况的虚拟,条件句中谓语动词用一般过去时,主句用“would/should/might/could+动词原形”。
(2)
对过去情况的虚拟
对过去情况的虚拟,条件句中谓语动词用过去完成时,主句用“would/should/might/could+have+过去分词”。
(3)
对将来情况的虚拟
对将来情况的虚拟,条件句中谓语动词可用should
do,
were
to
do或动词的过去式三种形式表示,但意义略有不同。should表示的可能性最大,动词过去式的可能性次之,were
to
do的可能性最小。主句谓语动词用“would/should/might/could+动词原形”。
(4)
错综时间条件句
有时条件从句谓语动词表示的动作和主句谓语表示的动作发生的时间不一致,这类句子称为错综时间条件句。此时主从句动词的形式应根据各自所表示的时间进行调整。
If
you
had
taken
my
advice
then,
you
wouldn't
be
in
trouble
now.
如果当时听我劝,你现在就不会有麻烦了。(if条件句是对过去的虚拟,故用过去完成时,而主句是对现在的虚拟,故用“would+动词原形”形式。)
(5)
表示“建议、命令、要求、坚决做”等动词后的宾语从句常用“(should+)动词原形
(6)
wish后的宾语从句
wish后的宾语从句用一般过去时表示现在的情况,用过去完成时表示过去的情况,用would/could
do表示将来的情况。
(7)
would
rather
后的宾语从句
would
rather后的从句常用一般过去时形式,表示现在或将来的情况;用过去完成时,表示过去的情况
(8)It
is/was
important
(necessary,
appropriate,
proper,
right,
essential,
vital,
etc.)
that

虚拟语气的结构和用法
(一)、 (完全结构) 主句与从句都是相反的表意: if / even if (even though):如果/即使
1、与过去虚拟:
【"从句If + had done, 主句+ could/should/would/might' ve done"】能/该/会/可以
If I hadn't got up so late, I could've got there earlier.
If I had got up earlier, I could've caught the train.
If I hadn't fixed my car, I should've taken part in the conference call.
If you had passed the exam, I would've bought a car for you.
If I had got there earlier, that kid might've been rescued/saved.
If I had known he was this kind of person, I wouldn't have helped him.
If you had told me earlier, I wouldn't have been so angry with him.
2、与现在虚拟:
【从句If + did/were , 主句 could/shoud/would/might do 】
If I had money, I might buy a car.
If I had a brother or sister, I could ask him/her for help.
If I were you, I wouldn't do that.
Even if i knew, i wouldn't tell you.
3、与将来虚拟:
【从句If + did/were to/should do , 主句 could/should/would/might do】
If it rained tomorrow, we would call off the class.
If it were to rain tomorrow, we would call off the class.
If it should rain tomorrow, we would call off the class.
Even if i should go/ i went/ i were to go, i wouldn't take you with me.
(二)、 (简化版) 只有主句表意相反=与 结果 相反
【从句正常陈述, 主句虚拟(同上),用otherwise/or/but for/without连接 】
1、与过去结果相反:
I got up so late, otherwise/or, I could've got there earlier.
I got up so late, otherwise/or, I could've caught the train.
The traffic was heavy, otherwise, I could've taken part in the conference call.
I didn't know he was this kind of person, otherwise, I wouldn't have helped him.
Without/but for your support, I couldn't have finished my homework.
Without/but for your support and help, this book couldn't have been possible.
2、与现在结果相反
I don't have money, otherwise, I might buy a car.
I am not you, otherwise I wouldn't do that.
I don't have a brother, or, I could ask him for help.
Without/but for sunlight, there would be no life on the planet.
Without water, we couldn't live.
3、与将来结果相反
It might not rain tomorrow, or, we would call off the class.
(三)、 (简化版) 与从句相反=与 事实 相反
【 从句虚拟 , 将来时 稍有变化】
1、 wish / How I wish : 我多希望……
(与现在事实相反)
How I wish you came.
I wish I had a lot of money.
I wish I could have more time to be with them. ----can的过去式
I wish i didn't need to study so hard everyday.
How I wish it were not raining.
How I wish i were as strong as you.
How I wish I were you.
I wish everyday were my birthday.
(与过去事实相反)
I wish I hadn't eaten so much watermelon.
I wish I hadn't seen him.
I wish I hadn't heard this news.
I wish I hadn't been so angry with him.
(将来事实相反)
I wish it could/would rain tomorrow.
I wish i could grow up faster.
2、I f only ……:要是……就好了--------------------->>意思、用法=I wish
(与现在相反)
If only i knew he was this kind of person.
If only i had a lot of money.
If only it were not raining.
If only i were you.
If only i were as strong as you.
(过去相反)
If only you had come yesterday.
If only i had taken your advice.
If only i had studied english hard.
(将来相反)
If only he could come tomorrow.
3、 as if (as though) : 好像(此处是虚拟用法,不虚拟就正常时态)
(现在相反)
She likes the baby as if the baby were hers.
He looks as if he were drunk.
(过去相反)
They talked as if they had been friends for years.
He speaks english so fluently as if he had been to the US.
(将来相反)
He studies english so hard as if he would go to the US.
4、 would rather : 宁愿……
(现在相反)
I'd rather you gave me money now.
I'd rather you were not my friend.
(过去相反)
I'd rather you had left.
I'd rather you hadn't told me this thing.
(将来相反)=【现在相反用法: did/were】
I'd rather you didn't come tomorrow.
I'd rather it didn't rain tomorrow.
I'd rather you came tomorrow.
虚拟语气有几种形式
虚拟语气的用法及形式:
一、表示与现在事实相反的情况:
从句:If 主语+过去时(Be动词用were)
主句:主语+should/would/could/might+do
二、表示与过去事实相反的情况:
从句:If 主语+had+done
主句:主语+should/would/could/might+have done
三、表示对将来情况的主观推测:
主句:主语+should+do
从句:①if+主语+were to do
②if+主语+should/would/could/might+do
③if+主语+did(动词过去式)/were
四、 有时,虚拟条件句中,结果主句和条件从句的谓语动作若不是同时发生时,虚拟语气的形式应作相应的调整。这种条件句叫错综条件句。
①从句的动作与过去事实相反,而主句的动作与现在或现在正在发生的事实不符。
②从句的动作与现在事实相反,而主句的动作与过去事实不符。
五、 当虚拟条件句的谓语动词含有were,should,had时,if可以省略,这时条件从句要用倒装语序,即把were,should,had等词置于句首,这种多用于书面语。
六、非真实条件句中的条件从句有时不表达出来,只暗含在副词、介词短语、上下文或其他方式表示出来,这种句子叫做含蓄条件句,在多数情况下,条件会暗含在短语中,如without…,but for…等。
七、 有时,虚拟条件句中,主、从句可以省略其中的一个,来表示说话人的一种强烈的感情。

扩展资料
虚拟语气种类:
1、陈述语气:表示动作或状态是客观存在的、确定的或符合事实的,用于陈述句、疑问句和某些感叹句中。
2、祈使语:表示说话人对对方的请求、警告,建议或命令。
3、虚拟语气:虚拟语气表示说话人的主观愿望、猜疑、建议或与事实不符的假设等,而不表示客观存在的事实。虚拟语气是由句中的谓语动词的特殊形式表示出来的。
参考资料:百度百科-虚拟语气
以上就是关于虚拟语气常用的七种基本结构,请大家给我讲下虚拟语气常用的几种形式英语的全部内容,以及虚拟语气常用的七种基本结构 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
