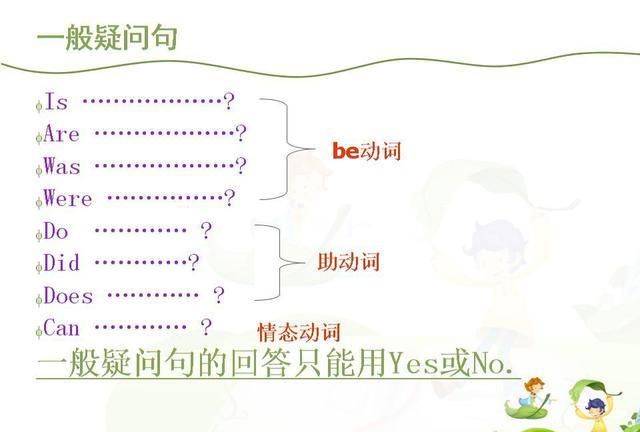
本文目录
简单的英语语法句子
1.* I am like my parent.
i like my parent.
2.* He is loves his teacher.
he loves his teacher.
3.* He keeps swim every day.
he keeps swimming everyday.
keep的固定用法:keep + doing something.
4.* He wants drink a glass of water.
he wants to drink a glass of water.
5.* He likes play violin.
he likes playing violin.
6.* Jack do not love mathematics.
jack does not love mathematics.
7.* Mary hate singing.
mary hates singing.
8.* My mother cook very good food.
my mother cooks very good.
9.* He want me to see him tomorrow.
he wants me to see him tomorrow.
10.* He not knows my name.
he does not know my name.
11.* I not like you.
i do not like you.
12.* He not like swimming.
he does not like swimming.
13.* You not went home.
you did not go home.
14.* I not like swimming.
i do not like swimming.
15.* I wanted to went to my mother’s home.
i wanted to go my mother's home.
16.* I do not like to swimming.
i do not like swimming. / i do not like to swim.
更好点的答案是 i do not like swimming。这里把swim当成一种习惯或个人喜好。i do not like to swim 更多的是不想去游泳的意思。
17.* I did not ate dinner.
i did not eat dinner.
18.* I will not went home.
i will not go home.
19.* He did not went home.
he did not go home.
20.* You may leaving now.
you may leave now.
21.* He can swimming.
he can swim。
22.* He does not goes to work.
he does not go to work./he did not go to work.
这些句子的错误大体可划分为:
- 动词在助动词和情态动词后面应该为原型 如17,18,21,22
- 陈述句的否定形式需要用助动词(do did does..)如14
- to 的后面要用动词原形 如15
简单的英语语法句子
如果有没后面的in hunan要用any other cities. 但是guangzhou不属于hunan。所以只用any city就可以。
英语单词中的多音节词的比较级用more
例如:more important,more expensive,more beautiful
而much是在比较级单词用表示程度更进一步的。
例如:much cheaper, much lighter, much more important.tall不属于多音节,所以肯定不能用more. 同理:tall, fat ,thin.只能用much或者不用。
个人觉得都不是很好。不用将来时态,用现在时态。
they have a lot of time to pursue their hobbies. (你觉得呢??)
after you disuss it with your deskmate, you may know how to say about it.
discuss sth with sb 和某人讨论某事.
宾语从句后面可以用特殊疑问词直接加不定式提问。
希望帮到你。
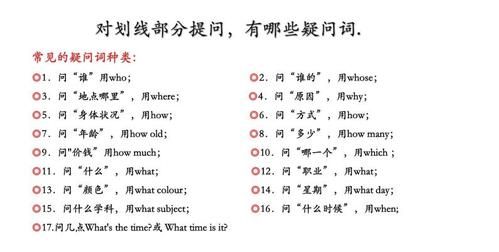
英语中有趣的语法问题
很简单,选择B
for后面跟了一段时间,也就是说我使他振奋用了20分钟,这段时间内我一直持续这个动作,所以用过去完成进行时。即B
区别:
现在完成时
(一)构成:have/has + 过去分词
(二)用法:
1. 在未指明具体时间的情况下,现在完成时动词通常可以表示在说话之前已经完成,而后果或影响至今仍存在的动作。现在完成时把过去的动作和现在的结果联系起来。
It has taken effect since the first day of your employment. 在你上班的第一天就开始实施。
2.现在完成时动词可以表示开始于过去持续到现在(也许还会继续进行下去)的动作或状态。例如:
I have studied English since 1975. 我从一九七五年起就学习英语。
Come, go, leave, arrive, join, die, bury和marry等动词所表示的动作是一时的,不能延续的,故不能与for, since…等开头的表示一段时间的状语连用。如不能说"He has come to Beijing for seven years."。可以说:He has been in Beijing for seven years.
现在完成时不能和明确指出的表示过去的时间的状语(如:yesterday, last year, in 1976, two days ago, just now, when I came in等)连用,但可以和不明确指出时间的状语
(如:already, yet, sometimes, always, often, before, lately, recently, once, twice, ever, never等)连用;也可以和表示包括现在在内的时间状语(如:this morning, today, this week, this year等)连用。
现在进行时
(一)构成:is (am, are +现在分词(动词 + ing)
现在分词的构成规则如下:一般情况-ing;以不发音的-e结尾,去-e再加-ing;以重读闭音节结尾,末尾为一个辅音字母,它的前面是单个元音字母,将词尾的辅音字母双写,再加-ing。
以-ie结尾的动词构成现在分词时,要变-ie为-y,再加-ing。例如:die-dying, lie-lying,tie-tying。
(二)用法:
1. 现在进行时动词表示说话时正在发生或进行着的动作。例如:
She is majoring in economics. 她正在主修经济学。
有时表示现阶段正在进行而说话时不一定正在进行的动作。例如:
Are you working hard this term? 你这学期学习努力吗?
2. 现在进行时动词表示即将发生的动作(如在最近按计划安排好要进行的动作)。Come , go, leave, start, arrive等动词与表示将来时间的状语连用表示这种意义。例如:
They are going to Shanghai on Friday. 他们这星期五去上海。
John is coming here next week and will stay here until May. 约翰下星期来,将在此待到五月。
3. 现在进行时动词常与always, continually, constantly等副词连用,表示反复出现的或习惯性的动作。例如:
He is always asking questions. 他老爱提问题。

英语语法知识问答大全
直接引述别人的原话,叫直接引语。用自己的话转述别人的话,叫间接引语。间接引语在多数情况下构成宾语从句。直接引语一般前后要加引号,间接引语不用引号。
例如:Mr Black said, “I'm busy” 布莱克先生说:“我很忙”(直接引语)
Mr Black said that he was busy. 布莱克先生说他很忙。(间接引语)
1 陈述句 直接引语如果是陈述句,变为间接引语时,用连词that引导(that在口语中常省略),从句中的人称、时态、指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等要作相应变化。在这一方面,汉语和英语有许多相似之处,因此,在做直接引语和间接引语转换练习时,要特别注意句子的意义。
1)人称的变化
a) He said, “I like it very much.”他说:“我非常喜欢它。”
He said that he liked it very much.他说他非常喜欢它。
b) He saidto me, “I've left my book in your room.” 他对我说:“我把书放在你的房间里了。”
He told me that he had left his book in my room.他告诉我他把书放在我的房间里了。
2)时态的变化 如主句的谓语动词是一般过去时,直接引语变间接引语时,从句的谓语动词在时态方面要作相应的变化。如主句的谓语动词是现在时,从句的时态则无需变化。
时态的变化
例句 直接引语
间接引语
一般现在时
→一般过去时
He said, “I'm afraid I can't finish this work.”
He said that he was afraid he couldn't finish that work.
现在进行时
→过去进行时
He said, “I'm using theknife.”
He said that he was using the knife.
现在完成时
→过去完成时
She said, “I have not heard from him since May.”
She said that she had not heard from him since May.
一般过去时
→过去完成
He said, “I came to help you.”
He said that he had come to help me.
过去完成时不变
He said, “I had finished my homework before supper.”
He said that he had finished his homework before supper.
3)指示代词、时间状语、地点状语和动词的变化:
变化
例句直接引语
间接引语
this-that
这个-那个
She said, “Iwill come this morning."
She said that she would go that morning.
these-those
这些=那些
He said, "These books are mine."
He said that those books were his.
now-then
现在-那时
He said, "It is nine 0'clock now."
He said that it was nine 0'clock then.
today-that day
今天-那天
He said, "I haven't seen her today."
He said that he hadn't seen her that day.
yesterday-
the day before
昨天-前一天
she said, "I went there yesterday."
She said that she had gone there the day before.
tomorrow-
the next
(following) day
明天-第二天
she said, "I'll go there tomorrow."
She said that she would go there the next (following) day.
here-there
这里-那里
come-go
来-去
注:(1)直接引语如果是客观真理,变为间接引语时,时态不变。如:
He said, "Light travels much faster than sound."
He said that light travels much faster than sound.
(2)如果在当地转述,here 不必改为there,动词come 不必改为go. 如果在当天转述yesterday, tomorrow 等时间状语也不必改变。
如何把直接引语变间接引语
“一随主”是指在直接引语变间接引语时,如果从句中的主语是第一人称或被第一人称所修饰。从句中的人称要按照主句中主语的人称变化如:
She said. "My brother wants to go with me. "→She said her brother wanted to go with her.
“二随宾”是指直接引语变间接引语时,若从句中的主语及宾语是第二人称。或被第二人你所修饰。从句中的人称要跟引号外的主句的宾语一致。如果引号外的主句没有宾语。也可以用第一人称,如:
He said to Kate. "How is your sister now?"→He asked Kate how her sister was then。
“第三人称不更新”是指直接引语变间接引语时。如果从句中的主语及宾语是第三人称或被第三人称所修饰从句中的人称一般不需要变化如:
Mr Smith said。 "Jack is a good worker。"→Mr Smith said Jack was a good worker。
变时态:
直接引语在改为间接引语时、时态需要做相应的调整。
现在时它需改为过去时态;过去时态改为完成时;过去完成时则保留原来的时态。如:
1)She said. "I have lost a pen."→She said she had lost a pen
2)She said. "We hope so."→She said they hoped so.
3) She said. "He will go to see his friend。"→She said he would go to see his friend。
但要注意在以下几种情况下。在直接引语变为间接引语时,时态一般不变化。
①直接引语是客观真理。
"The earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth, the teacher told me. → The teacher told me the earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth。
②直接引语是过去进行时,时态不变。如:
Jack said. "John, where were you going when I met you in the street?"→Jack asked John where he was going when he met him in the street。
③直接引语中有具体的过去某年、某月、某日作状语,变为间接引语时,时态不变。如:
Xiao Wang said. "I was born on April 2l, 1980。" →Xiao Wang said he was born on April 20, 1980。
④直接引语如果是一般现在时。表示一种反复出现或习惯性的动作,变间接引语,时态不变。如:
He said, "I get up at six every morning。" →He said he gets up at six every morning。
⑤如果直接引语中的情态动词没有过去时的形式(例:ought to, had better, used to)和已经是过去时的形式时,(例:could, should, would, might)不再变。如:
Peter said. "You had better come have today。" →Peter said I had better go there that day。
三、如何变状语:
直接引语变间接引语,状语变化有其内在规津,时间状语由“现在”改为“原来”(例:now变为then, yesterday。变为 the day before)地点状语,尤其表示方向性的,或用指示代词修饰的状语,由“此”改为“彼”(例:this 改为that),如:
He said, "These books are mine." →He said those books were his.
四、如何变句型:
①直接引语如果是陈述句,间接引语应改为由that引导的宾语从句。如:She said, "Our bus will arrive in five minutes."→She said that their bus would arrive in five minutes.
②直接引语如果是反意疑问句,选择疑问句或一般疑问句,间接引语应改为由whether或if引导的宾语从句.如:He said, "Can you swim, John?" →He asked John if he could swim.
"You have finished the homework, haven‘t you?" my mother asked. →My mother asked me whether I had finished the homework.
"Do you go to school by bus or by bike?" →He asked me if I went to school by bus or by bike.
③直接引语如果是特殊问句,间接引语应该改为由疑问代词或疑问副词引导的宾语从句(宾语从句必须用陈述句语序)。
She asked me, "When do they have their dinner?"→ She asked me when they had their dinner.
④直接引语如果是祈使句,间接引语应改为"tell(ask, order, beg等) sb (not) to do sth."句型。如:
"Don’t make any noise," she said to the children. →She told (ordered) the children not to make any noise. "Bring me a cup of tea, please," said she.→She asked him to bring her a cup of tea.
⑤直接引语如果是以“Let‘s”开头的祈使句,变为间接引语时,通常用“suggest +动句词(或从句)。”如:
He said, "Let’s go to the film." →He suggested going to the film.或He suggested that they should go to see the film.
引述别人的话有两种方式:一是使用引号引出人家的原话,这叫做直接引语;一是用自己的话把人家的话转述出来,这叫做间接引语。例如:
John said, "I’m going to London with my father."
约翰说:"我要和父亲到伦敦去。"(引号内是直接引语)
John said that he was going to London with his father.
约翰说,他要和他父亲去伦敦。(宾语从句是间接引语

以上就是关于英语语法问题提问20个,简单的英语语法句子的全部内容,以及英语语法问题提问20个 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
