本文目录
状语从句的语法总结
状语从句英语专四语法辅导总结
复 合句——副词性(状语)从句

副词在句中起状语作用,故如果起状语作用的部分为一个句子,那么该句便是副词性从句,也称状语从句。状语从句可细分为:时间、地点、条件、原因、让步、目的、结果、比较、方式等。
状语从句的测试重点为:考查考生对主从句之间逻辑意义关系的把握,看其是否能选择正确的从属连词。
1.条件状语从句的常考知识点
(1)if与unless的用法。 if和unless都是引导条件状语从句的连词,考生应尤其注意unless的用法,因为它表示反面条件,相当于if not“如果不”、“除非”。如:In debating, one must correct the opponent’s facts, deny the relevance of his proof, or deny that what he presents as proof, if relevant, is sufficient.
(2)复合连词as long as,so long as,as far as,on condition that,in the event that;动词及分词provided(that),providing(that),given that, suppose/supposing(that),assuming,say等引导条件状语从句。如:
You can arrive in Beijing earlier for the meeting provided you don’t mind taking the night train.
Assuming he is diligent in his studies at ordinary times, he is sure to pass the test.
In the event that she has not been informed, I will tell her. (如果……)
You can go swimming on condition that you don’t go too far from the river bank. (如果……)
Suppose it rained, we would still go. (假如……)?Say it were true, what would you do about it??(假如……)
(3)祈使句表示条件。如:Dress warmly, or else you’ll catch cold.
Talk to anyone in the drug industry, and you’ll soon discover that the science of genetics is the biggest thing to hit drug research since penicillin was discovered.
2.让步状语从句的常考知识点
(1)as 引导让步从句,要求用倒装结构,把强调的`部分置于句首。如: Much as he likes her, he does get irritated with her sometimes.
Humble as it may be, there is no place like home.
(2)while引导让步从句。如:
Everybody cheats a little, some psychologists say, while others insist that most people are basically honest and some wouldn’t cheat under any circumstances.
(3)复合连接词for all that和分词granting/granted(that)引导让步从句。如:
Granted you have made much progress, you should not be conceited.
For all that computers can provide us with great help, they shouldn’t be seen as substitutes for fundamental thinking and reasoning skills.
3.时间状语从句的常考知识点
(1)before表示汉语的 “只有/必须……才能”。如:?New ideas sometimes have to wait for years before they are fully accepted.
(2)when引导时间从句时,如果出现在后半句,则表示“这/那时突然”。如:
I have just started back for the house to change my clothes when I heard the voices.
(3)when it comes to 是习惯用法,意为“当谈到……时”。如:
Doing your homework is a sure way to improve your test scores, and this is especially true when it comes to classroom tests.
(4)名词短语、介词短语each /every time, the moment/second/minute, in the time, by the time起连词作用。如:
I hope her health will have improved greatly by the time we come back next year.
My pain must have been apparent the moment I walked into the room, for the first man I met asked sympathetically: “Are you feeling all right?”
Mercury’s velocity is so much greater than the Earth’s that it completes more than four revolutions around the Sun in the time it takes the Earth to complete one.
(5)副词directly, immediately, instantly, now引导时间从句, 相当于as soon as。如:
The policemen went into action directly they heard the alarm.
4.原因状语从句的常考知识点
(1)in that引导原因从句时,有时翻译成“是因为”、“就在于”。如:
Advertising is distinguished from other forms of communication in that the advertiser pays for the message to be delivered.
Criticism and self-criticism is necessary in that it helps us to find and correct our mistakes.
(2)now that表示 “既然” ; seeing that, considering表示“鉴于”、“考虑到”。如:
Now that we have all the material ready, we should begin the new task at once.
He did poorly in the examinations, considering how hard he had tried for them.
Seeing that she is lawfully old enough to get married, I don’t think you can stop her.
其他引导原因状语从句的连接词语还有: for the (simple) reason that, by reason that, on the grounds that, in as much as, in so far as等。
5.while, whereas 引导对比从句
如: While the teenage population in the United States has declined over the past decade, violent crimes committed by juveniles have sharply increased.
A baby might show fear of an unfamiliar adult, whereas he is likely to smile and reach out to another infant.
6.so…that…, with the result that, so much so that 引导结果状语从句
如: Over the years, a large number of overseas students have studied at that university with the result that it has acquired substantial experience in dealing with them.
He himself believed in freedom, so much so that he would rather die than live without it.
7.in order that, in case, for fear that, lest (用虚拟语气) 引导目的状语从句
如: Give me your telephone number, in case I need your help.
Helen listened carefully in order that she might discover exactly what John wanted.
8.where作为连接副词的一种用法, 翻译为“在……地方”
如: In Japan, a person’s capabilities are not forced into an inflexible specialty. Where there is willingness and intelligence, there is a place within the company to try and to succeed.
;初中英语宾语从句知识点总结
状语从句
状语从句在复合句中作状语,修饰动词、形容词或副词等。状语从句可以表示时间、条件、原因、地点、目的、结果、让步、方式、比较等意义。
各类状语从句连接词(短语)
时间 when, while, as, as soon as, since, until, after, before
条件 If, unless
原因 As, because, since
地点 Where
目的. So that, in order that
结果 So that, so…that, such…that
让步 though, although, even if, however
方式 As
比较 than, (not)as…as
时间状语从句:
Whenever he comes, he brings a friend. 他每次来都带个朋友。
条件状语从句:
As long as I am alive, I will go on studying. 只要我活着, 我就要学习。
原因状语从句:
Since we live near the sea, we enjoy nice weather.由于我们住在海边,能享受到好的天气。
地点状语从句:
Put it where we can all see it.把它放在我们都能看到的位置。
目的状语从句:
Finish this so that you can start another.把这个做完,你可以开始另一个。
结果状语从句:
He was so angry that he couldn’t say a word. 他气得说不出话了。
让步状语从句:
Though he is in poor health, he works hard.虽然他身体不好,但是他工作很努力。
方式状语从句:
Students do as the teachers say.学生们按照老师说的去做。
比较状语从句:
The work isn’t as easy as I thought.这项工作比我想象得难。

专升本英语语法知识点汇总
状语从句 (Adverbial Clause) 是指 句子 用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。状语从句中的从句可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语或整个句子。下面就是我给大家带来的状语从句英语语法知识点汇总,希望大家喜欢!
1 地点状语从句
地点状语从句通常由where, wherever 引导。
Where I live there are plenty of trees.
我住的地方树很多。
Wherever I am I will be thinking of you.
不管我在哪里我都会想到你。
2 方式状语从句
方式状语从句通常由as, (just) as…so…, as if, as though引导。
1) as, (just) as…so…引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在(just) as…so…结构中位于句首,这时as从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体,例如:
Always do to the others as you would be done by.
你希望人家怎样待你,你就要怎样待人。
As water is to fish, so air is to man.
我们离不开空气,犹如鱼儿离不开水。
Just as we sweep our rooms, so we should sweep backward ideas from our minds.
正如打扫房屋一样,我们也要扫除我们头脑中落后的东西。
2) as if, as though
两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大。汉译常作"仿佛……似的","好像……似的",例如:
They completely ignore these facts as if (as though) they never existed.
他们完全忽略了这些事实,就仿佛它不存在似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
He looks as if (as though) he had been hit by lighting.
他那样子就像被雷击了似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
It looks as if the weather may pick up very soon.
看来天气很快就会好起来。(实现的可能性较大,谓语用陈述语气。)
说明:as if / as though也可以引导一个分词 短语 、不定式短语或无动词短语,例如:
He stared at me as if seeing me for first time.
他目不转睛地看着我,就像第一次看见我似的。
He cleared his throat as if to say something.
他清了清嗓子,像要说什么似的。
The waves dashed on the rocks as if in anger.
波涛冲击着岩石,好像很愤怒。
3 原因状语从句
比较:because, since, as和for
1) because语势最强,用来说明人所不知的原因,回答why提出的问题。当原因是显而易见的或已为人们所知,就用as或 since。
I didn't go, because I was afraid.
Since /As the weather is so bad, we have to delay our journey.
2) 由because引导的从句如果放在句末,且前面有逗 号,则可以用for来代替。但如果不是说明直接原因,而是多种情况加以推断,就只能用for。
He is absent today, because / for he is ill.
He must be ill, for he is absent today.
4 目的状语从句
表示目的状语的从句可以由that, so that, in order that, lest, for fear that, in case等词引导,例如:
You must speak louder so that /in order that you can be heard by all.
He wrote the name down for fear that(lest) he should forget it.
Better take more clothes in case the weather is cold.
5 结果状语从句
结果状语从句常由so… that 或 such…that引导,掌握这两个句型,首先要了解so 和 such与其后的词的搭配规律。
比较:so和 such
其规律由so与such的不同词性决定。such 是形容词,修饰名词或名词词组,so 是副词,只能修饰形容词或副词。 so 还可与表示数量的形容词many, few, much, little连用,形成固定搭配。
so foolish such a fool
so nice a flower such a nice flower
so many / few flowers such nice flowers
so much / little money. such rapid progress
so many people such a lot of people
( so many 已成固定搭配,a lot of 虽相当于 many,但 a lot of 为名词性的,只能用such搭配。)
so…that与such…that之间的转换既为 so与such之间的转换。
The boy is so young that he can't go to school.
He is such a young boy that he can't go to school
6 条件状语从句
连接词主要有 if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that 等。.
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。非真实条件句已在虚拟语气中阐述。
unless = if not.
Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired.
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.
典型例题
You will be late ___ you leave immediately.
A. unless B. until C. if D. or
答案A。 句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。可转化为 If you dong leave immediately, you will be late. B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为 You leave immediately or you will be late.
7 让步状语从句
though, although
注意: 当有though, although时,后面的从句不能有but,但是 though 和yet可连用
Although it's raining, they are still working in the field.
虽然在下雨,但他们仍在地里干活。
He is very old, but he still works very hard.
虽然他很老,但仍然努力地工作。
Though the sore be healed, yet a scar may remain.
伤口虽愈合,但伤疤留下了。 ( 谚语 )
典型例题
1) ___she is young, she knows quite a lot.
A. When B. However C. Although D. Unless
答案:C。意为虽然她很年轻,却知道许多。
2) as, though 引导的倒装句
as / though引导的让步从句必须表语或状语提前(形容词、副词、分词、实义动词提前)。
Child as /though he was, he knew what was the right thing to do.
= Though he was a small child, he knew what was the right thing to do.
注意: a. 句首名词不能带任何冠词。
b. 句首是实义动词,其他助动词放在主语后。如果实义动词有宾语和状语,随实义动词一起放在主语之前。
Try hard as he will, he never seems able to do the work satisfactorily.
= Though he tries hard, he never seems…
虽然他尽了努力,但他的工作总做的不尽人意。
3) ever if, even though. 即使
We'll make a trip even though the weather is bad.
4) whether…or- 不管……都
Whether you believe it or not, it is true.
5) "no matter +疑问词" 或"疑问词+后缀ever"
No matter what happened, he would not mind.
Whatever happened, he would not mind.
替换:no matter what = whatever
no matter who = whoever
no matter when = whenever
no matter where = wherever
no matter which = whichever
no matter how = however
注意:no matter 不能引导主语从句和宾语从句。
(错)No matter what you say is of no use now.
(对)Whatever you say is of no use now.
你现在说什么也没用了。(Whatever you say是主语从句)
(错)Prisoners have to eat no matter what they're given,
(对)Prisoners have to eat whatever they're given. 囚犯们只能给什么吃什么。
8 比较while, when, as
1)as, when 引导短暂性动作的动词。
Just as / Just when / When I stopped my car, a man came up to me.
2)当从句的动作发生于主句动作之前,只能用when 引导这个从句,不可用as 或 while。
When you have finished your work, you may have a rest.
3)从句表示"随时间推移"连词能用as,不用when 或while。
As the day went on, the weather got worse.
日子一天天过去,天气越变越坏。
9 比较until和till
此两个连词意义相同。肯定形式表示的意思是"做某事直至某时",动词必须是延续性的。否定形式表达的意思是"直至某时才做某事"。动词为延续性或非延续性都可 以。 正确使用这两个连词的关键之一就在于判断句中的动词该用肯定式还是否定式。
肯定句:
I slept until midnight. 我一直睡到半夜时醒了。
Wait till I call you. 等着我叫你。
(在肯定句中可用before代替 Let's get in the wheat before the sun sets.)
否定句:
She didn't arrive until 6 o'clock.
她直到6点才到。
Don't get off the bus until it has stopped.
公共汽车停稳后再下车。
I didn't manage to do it until you had explained how. 直到你教我后,我才会做。
1)Until可用于句首,而till通常不用于句首。
Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened.
直到你告诉我以前,出了什么事我一点也不知道。
2)Until when 疑问句中,until要放在句首。
---Until when are you staying? 你呆到什么时候?
--- Until next Monday. 呆到下周一。
注意:否定句可用另外两种句式表示。
(1)Not until …在句首,主句用倒装。
Not until the early years of the 19th century did man know what heat is.
直到19 世纪初,人类才知道热能是什么。
Not until I began to work did I realize how much time I had wasted.
直到我开始工作,我才认识到了我已蹉跎了几多岁月。
(2) It is not until… that…
10 表示"一…就…"的结构
hardly/scarcely…when/before, no sooner…than 和as soon as都可以表示"一…就…"的意思,例:
I had hardly / scarcely got home when it began to rain.
I had no sooner got home than it began to rain.
As soon as I got home, it began to rain.
注意:如果hardly, scarcely 或no sooner置于句首,句子必须用倒装结构:
Hardly / Scarcely had I got home when it began to rain.
No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
状语从句英语语法知识点汇总相关 文章 :
1. 最新九年级英语语法知识点总结大全
2. 初二英语语法知识点汇总
3. 高中英语语法知识点整理总结
4. 初一英语学习方法指导与学习方法总结
5. 复习中考英语知识点归纳
6. 英语语法大全总结
7. 初中英语语法知识点总结
8. 英语高一必修一语法知识点汇总
9. 英语语法总结大全
10. 初中英语语法 状语从句
初中英语状语从句归纳总结
列举英语语法状语从句的归纳总结
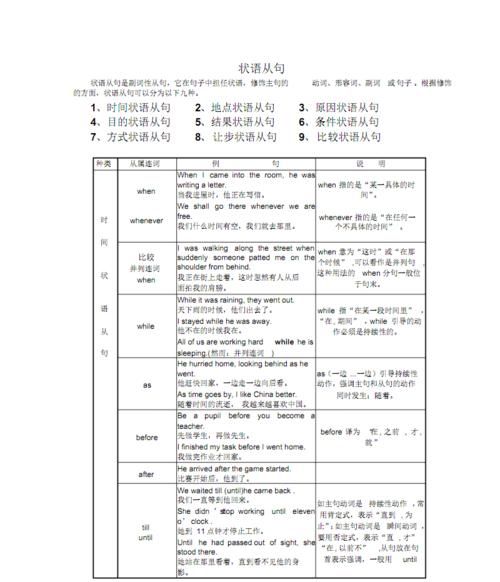
在复合句中修饰主句或主句中的某一成分的从句叫状语从句。状语从句通常由从属连词或起连词作用的词组引导,有时甚至不需要连词直接和主句连接起来。状语从句根据它表达的意思不同,可分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等九类。

一、 时间状语从句
时间状语从句是表示时间关系的从句。可以引导时间状语从句的.连词很多,根据意义和主从句之间的时间关系,通常可分为以下几种情况:
A. when, while, as, whenever
when, while, as表示主句谓语作和从句的谓语动作同时发生或几乎同时发生。
1.when
①when表示点时间时,从句中用短暂性动词;表示段时间时,用持续性动词。 When I got home, my family were already having dinner.
我到家的时候,全家已在吃晚饭。
(when表示点时间)
When they were still talking and laughing, the teacher came in.
当他们还在说笑的时候,老师进来了。(when表示段时间)
He waved ahello when he saw her.
当他看见她的时候,就挥手打了个招呼。(when表示点时间)
When you think you know nothing, you begin to know something.
当你认为自己一无所知的时候,就开始知道一些事情了。(when表示段时间)
注意:
当when意思是正当……时候(and at that moment)时,when只能跟在前一分句之后。 He was about to go to bed when the doorbel rang.
他正要上床,忽然门铃响了。
They were watching the World Cup when suddenly the lights went out.
他们正看着世界杯比赛,突然灯灭了。
They had just arrived home when it began to rain.
他们刚到家,天就开始下雨了。
②有时when表示虽然,尽管的含义,相当于although或since。
He walks when he might take a taxi.
尽管可以打的,但他还是步行。
How can you hope for mercy yourself when you show none
既然你不宽恕别人,你自己又怎能希望得到别人的宽恕呢?
2.while
①while通常表示一段时间,从句中宜用持续性动词作谓语。
Strike while the iron is hot.
趁热打铁。
She fell asleep while she was reading the newspaper.
她在看报的时候睡着了。
②while有时可以作并列连词,表示对比,可译成……而……。
I am fond of English while he likes maths.
我喜欢英语而他却喜欢数学。
We slept while the captain kept watch.
我们睡觉而上尉担任警戒。
③while有时可引导让步状语从句,意思是虽然。
While they love te children, they are strict with them.
虽然他们都爱他们的孩子,但却对他们要求严格。
提示:
虽然during 与 while 意思很相近,但是during是介词,不能引导从句。
3.as
①as表示点时间时,从句中用短暂性动词;表示段时间时,用持续性动词。as和when两者经常可以通用。
The thief was caught as when he was stealing in the supermarket.
小偷在超市行窃时被逮住了。
I saw Jim as when he left the meeting room.
吉姆离开会议室时候我看到了他。
②as表示 一边……一边……,强调从句和主句中两个动作交替进行或同步进行。 They talked as they walked.
他们边走边聊。
He looked behind from time to time as he went.
他一边走,一边不时地往后看。
③as表示随着
As time goes on, it's getting warmer and warmer.
随着时间的推移,天气变得越来越暖了。
As spring warms the earth, al flowers begin to bloom.
随着春回大地,百花开始绽放。
4.when, while, as的用法区别
①只有当从句表示的是段时间,即其谓语动词有持续性特征时,这三者可以通用互换。 I got the news on the radio when while as I was having breakfast.
我在吃早饭的时候从收音机里获悉这一消息。
②在下列情况下,三者彼此之间不能替换使用:
a.as更强调同一时间或紧接的一前一后或伴随着的变化。
We listened to the singer sing as he played the guitar.
我们听着歌星边弹吉它边演唱。
I thought of it just as you opened your mouth.
你一张嘴我就知道你要说什幺
As he grew older, he became less and less active.
随着他年龄的增长,他变得越来越不活泼了。
提示:
状语从句可放在主句之前或之后,放在主句之前时一般用逗号与主句分开。有时可置于主句中间,前后用逗号。
b.when更强调特定时间,还可表示从句中的动作先于或后于主句的动作。
When I had given Mary the spare ticket, I found my own already gone.
当我把多余的票给了玛丽时,我才发现我自己的票已不知去向。(从句动作发生在主句之前,注意主从句的时态)
When I finally got there, he meeting had been on for ten minutes.
当我最终赶到那里时,会议已开始十分钟了。(从句动作发生在主句之后,注意时态) c.while从句只能表示延续的动作或状态或主从句中动作的对比。
She thought I was talking about her daughter, while in fact, I was talking
about my daughter.
她以为我在谈论她女儿,而事实上,我在谈论我的女儿。
d.若表示两个短促动作几乎同时发生时,用as场合多于when。
As he finished his speech, the audience burst into applause.
他结束讲话时,观众爆发出雷鸣般的掌声。
5.whenever
whenever是when的强势语,它描述的不是一次性动作,而是经常发生的习惯性动作。 You are always welcome whenever you come.
无论你何时来都欢迎。
Whenever we met with diffiulties, they came to help us.
每当我们遇上困难的时候,他们就来帮我们。
B. before, after
1.before
before表示在一段时间之前。
I must finish all the work before go home.
回家之前我必须干完所有的活。
You must first learn to walk before you try to run.
在想要跑以前,你得先学会走。
He had learned English for three years before he went to London.
他去伦敦之前已学了三年英语。
提示:
before 从句往往带有否定的含义。
He ran off before I could stop him.
我还没来得及阻止他,他就跑掉了。
Thke it down berore you forget it.
趁着还没忘记的时候就记录下来。
必背:
before 常用句型 It is was will be
;以上就是关于英语原因状语从句归纳总结,状语从句的语法总结的全部内容,以及英语原因状语从句归纳总结 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
