本文目录
时间状语从句的用法和讲解
状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。其实状语从句也是有一定的使用 方法 的。下面我就给大家介绍状语从句的用法讲解。
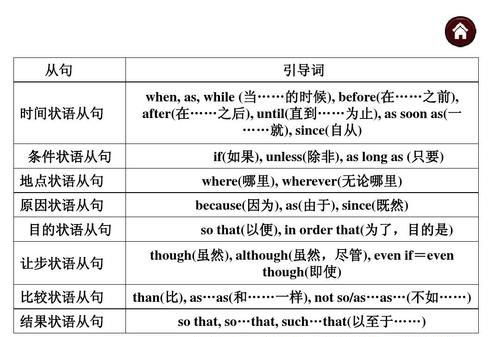
状语从句的概说状语从句即指在主从复合句用作状语的从句。按照其意义,状语从句可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句等。状语从句是 英语学习 中的一个语法重点,也是历年重点考查的内容之一。学习状语从句主要应注意引导状语从句的从属连词的用法与区别,以及从属连词在一定的语言环境中的意义与用法。
时间状语从句的介绍1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词很多,常见的有before, after, when, while, as, since, till, until, as soon as 等。
2. 表示“当…时候”的 while, when, as 的用法区别是:while从句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词;表示带有规律性的“每当”或当主、从句谓语动词的动作发生有先后时,只能用when;当表示“一边…一边…”或“随着”时,只能用as。另外,用于此义的 as 所引导的时间状语从句谓语只能是动作动词,不能是状态动词。如下面一道高考题的答案是B 而不能是A:
“I’m going to the post office.” “_____ you’re there, can you get me some stamps?”
A. As B. While C. Because D. If
3. until 在肯定句中通常只连用延续性动词,表示相应动作结束的时间;在否定句中通常连用非延续性动词,表示相应动作开始的时间,意为“直到…才”。如:
He waited until she was about to leave. 他等着一直到她准备离开。
I did not begin to work till he had gone. 他走了后我才开始工作。
4. 表示“一…就”除用as soon as 外,还可用 the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, no sooner…than, hardly…when 等。如:
I came immediately you called. 你一来电话我就来了。
Hardly had she arrived when it began to snow. 她刚到就下起雪来了。
The moment I have finished I'll give you a call. 我一干完就给你打电话。
5. every time, each time, (the) next time, (the) last time, by the time, the first time, any time 等以time 结尾的词语也可用作连词,引导时间状语从句。如:
Next time you come in, please close the door. 下次你进来,请关门。
He didn’t tell me anything the last time I saw him. 上次我见到他时他什么也没告诉我。
By the time I got home, she had already gone to bed. 我到家时她已睡觉了。
条件状语从句的介绍1. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词主要有 if, unless, as [so] long as等。如:
Don’t come unless I telephone. 除非我打电话,否则你别来。
If you watch carefully you will see how to do it. 如果你仔细瞧你会看出该怎样做。
As long as you do your best, we’ll be happy. 只要你尽力,我们就满意了。
2. in case 也可引导条件状语从句,其意为“如果”、“万一”。如:
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 如果我忘了,请提醒我。
让步状语从句的介绍1. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词主要有 although, though, however (=no matter how), even if (即使), whether…or (不论…还是)等连词。如:
The speech is good, though it could be better. 这次演讲不错,虽然还可以再好一点。
He went out even though it was raining. 尽管下雨,他还是出去了。
2. as 也可引导让步状语从句,但要将名词、形容词或副词等提到as 前,若提前的是单数可数名词,要省略a / an。如:
Teacher as he is, he can’t know everything. 虽然是老师,他也不可能什么都懂。
3. 连词while 有时也可表示“尽管”、“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。如:
While we don’t agree we continue to be friends. 尽管我们意见不同,我们还是朋友。
4. whatever, whoever, however, whenever, wherever 等引导让步状语从句。如:
Don’t lose heart whatever you do. 不管你做什么,都不要灰心。
Whoever you are, you can’t pass this way. 不管你是谁,你都不能从这里通过。
注:表示“虽然”的 though, although 不可与 but 连用,但可与 yet, still 连用。
点击下页还有更多 >>>原因状语从句的介绍
状语从句讲解视频
一 状语从句的种类
§ 1状语从句的种类
用来修饰谓语动词、其它动词、定语、状语或整个句子的从句叫做状语从句。状语从句可分为:
1.时间状语从句;(adverbial clause of time)
2.地点状语从句;(adverbial clause of place)
3.原因状语从句;(adverbial clause of cause)
4.条件状语从句;(adverbial clause of condition)
5.目的状语从句;(adverbial clause of purpose)
6.让步状语从句;(adverbial clause of concession)
7.比较状语从句;(adverbial clause of comparison)
8.程度状语从句;(adverbial clause of degree)
9.方式状语从句;(adverbial clause of manner)
10.结果状语从句。(adverbial clause of result)
§2状语从句的时态特点
一般情况下,时间和条件状语从句的谓语动词一般用“一般现在时”表示“一般将来时”,用“现在完成时”表示“将来完成时”。例如:
I will call you as soon as I arrive in Beijing. 我一到北京就给你打电话。(这是由as soon as引导的时间状语从句,从句中的谓语动词arrive是一般现在时,表示一般将来时,决不可用will arrive)
As soon as I have finished this work, I will go home. 我一完成此工作,就回家。(从句中的谓语动词用现在完成时have finished,表示将来完成时,决不可用will have finished)
If he comes back, please let me know.如果他回来了,请通知我。(从句中的谓语动词用comes back,表示一般将来时,决不可用will come back)
二 时间状语从句
§3时间状语从句(adverbial clause of time)
1.由when, while, as引导的时间状语从句。例如:
When you think you know nothing, then you begin to know something.当你以为自己一无所知的时候,你就是在开始知道一些事物了。
When truth is buried under the ground it grows, it chokes, it gathers such an explosive force that on the day it bursts out , it blows up everything with it.当真理被埋在地下的时候,它在生长,它感到压抑,它蓄存着这么一种爆炸性力量,一旦冒出,它就会炸破一切!
Strike while the iron is hot. 趁热打铁。
Will you watch my clothes while I have a swim. 我游泳的时候,请你照看一下我的衣服。
You can feel the air moving as your hand pushes through it. 当你的手在空气中挥动的时候,你就能感觉到空气在流动。
Our headmaster laughed as she spoke.我们的校长边谈边笑。
【区别】when, while和as的区别:when引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。并且when有时表示“就在那时”。例如:
When she came in, I stopped eating.她进来时,我在吃饭。(瞬时动词)
When I lived in the countryside, I used to carry some water for him.当的住在农村时,我常常为他担水。(延续性的动词)
We were about to leave when he came in.我们就要离开,就在那时他进来了。
While引导的从句的谓语动作必须是延续性的,并强调主句和从句的动作同时发生(或者相对应)。并且while有时还可以表示对比。例如:
While my wife was reading the newspaper, I was watching TV. (was reading是延续性的动词,was reading和was watching同时发生)
I like playing football while you like playing basketball.我喜欢踢足球,而你喜欢打篮球。(对比)
As表示“一边……一边”,as引导的动作是延续性的动作,一般用于主句和从句动作同时发生;as也可以强调“一先一后。例如:
We always sing as we walk.我们总是边走边唱。(as表示“一边……一边”)
As we was going out, it began to snow.当我们出门时,开始下雪了。(as强调句中两个动作紧接着先后发生,而不强调开始下雪的特定时间)
2.由before和after引导的时间状语从句。注意before引导的从句不再用否定式的谓语,并且当before引导的从句位于主句之后,有时译成“就,才”。还要注意主句和从句之间的时间关系。当主句用将来时,从句总是用现在时;如果before引导的从句谓语用的是过去时,则主句动词多用过去完成时,这样以便体现动作发生的先后。After表示主句动作发生在从句动作之后。主句和从句的动作的时间关系正好与before引导的从句相反。例如:
It will be four days before they come back. 他们要过四天才能回来。
Einstein almost knocked me down before he saw me.爱因斯坦几乎把我撞倒才看到我。
My father had left for Canada just before the letter arrived.我父亲恰好在信到之前去加拿大了。
They had not been married four months before they were divorced. 他们结婚还不到四个月就离婚了。
After you think it over, please let me know what you decide.你仔细考虑过以后,告诉我你是怎样决定的。
After we had finished the work, we went home.完成工作之后,我们回家了。(从句用过去完成时,主句用一般过去时)
3.由till或until引导的时间状语从句。till和until一般情况下两者可以互换,但是在强调句型中多用until。并且要注意的是:如果主句中的谓语动词是瞬时动词时,必须用否定形式;如果主句中的谓语动词是延续性动词时,用肯定或否定形式都可以,但表达的意思不同。例如:
I didn't go to bed until(till) my father came back.直到我父亲回来我才上床睡觉。
It was not until the meeting was over that he began to teach me English.直到散会之后他才开始教我英语。
I worked until he came back.我工作到他回来为止。
I didn't work until he came back.他回来我这才开始工作。
Please wait until I arrived.在我到达之前请等我。
4.由since引导的时间状语从句。 since引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。一般情况下,从句谓语动词用一般过去时,而主句的谓语动词用现在完成时。但在It is +时间+since从句的句型中,主句多用一般现在时。例如:
I have been in Beijing since you left. 自从你离开以来,我一直在北京了。
Where have you been since I last saw you? 自上次我和你见面以后,你到哪里去了?
It is four years since my sister lived in Beijing. 我妹妹不在北京住有四年了。
It is five months since our boss was in Beijing.我们老板离开北京有五个月了。
5.由as soon as, immediately, directly, instantly, the moment, the instant, the minute, 等引导的时间状语从句。这些连词都表示“一……就”。例如:
I will go there directly I have finished my breakfast. 吃完早饭,我立即到那里去。
The moment I heard the news, I hastened to the spot.我一听到消息,马上赶到了出事地点。
As soon as I reach Canada, I will ring you up. 我一到加拿大,就给你来电话。
【注意】hardly(scarcely, rarely)…when / before, no sooner…than相当于as soon as之意。主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。当hardly, scarcely, rarely和no sooner位于句首时,主句应用倒装语序。例如:
He had no sooner arrived home than he was asked to start on another journey. 他刚到家,就被邀请开始另一旅程。
No sooner had the sun shown itself above the horizon than he got out of bed to commence work.太阳刚从地平线上升起,他就起床劳动去了。
Hardly had I sat down when he stepped in.我刚坐下,他就进来了。
He had hardly fallen asleep when he felt a soft touch on his shoulder.这个阿拉伯人刚要入睡就感到肩膀上被轻轻一触。
6.由by the time引导的时间状语从句。注意时态的变化:在一般情况下,如果从句的谓语动词用一般过去时,主句的谓语动词用过去完成时;如果主句的谓语动词用一般现在时,主句的谓语动词用将来完成时。例如:
By the time you came back, I had finished this book.到你回来时,我已经写完这本书了。
By the time you come here tomorrow, I will have finished this work. 你明天来这儿的时候,我将已经完成此工作了。
7.由each time, every time和whenever引导的时间状语从句。例如:
Each time he came to Harbin, he would call on me. 他每次来哈尔滨,总是来看我。
Whenever that man says“To tell the truth”, I suspect that he's about to tell a lie.每当那个人说“说实在话”的时候,我猜想他就要说谎了。
You grow younger every time I see you. 每次遇到你,见你更年轻了。
8.由as long as和so long as引导的时间状语从句。这两个连词表示“有多久……就多久”。例如:
You can go where you like as long as you get back before dark. 你可以随意到哪里去,只要在天黑以前回来就行。
I will fight against these conditions as long as there is a breath in my body! 只要我一息尚存,我就要反对这种境况。
三 地点状语从句
§4地点状语从句 (adverbial clause of place)
地点状语从句一般由连接副词where, wherever等引导,已经形成了固定的句型,例如:
句型1:Where+地点从句,(there)+主句。
【注意】此句型通常译成“哪里……哪里就……”;主句在从句后面时,there可用可不用;如果主句在从句的前面时,一般都不用there。例如:
Where there is no rain, farming is difficult or impossible.在没有雨水的地方,耕作是困难的,或根本不可能的。
They were good persons. Where they went, there they were warmly welcomed. 他们都是好人。因此他们走到哪里都受到热烈欢迎。
You should have put the book where you found it. 你本来应该把书放回原来的地方。
Where the Communist Party of China goes, there the people are liberated.哪里有了中国共产党,哪里人民得解放。
句型2:Anywhere/ wherever+地点从句,+主句。
【注意】anywhere本身是个副词,但是,常可以引导从句,相当于连词,意思相似于wherever, anywhere引导的从句可位于主句之前,也可以位于主句之后。 而wherever本身就是个连词,表示“在何处,无论何处”。例如:
Wherever the sea is , you will find seamen.有海就有海员。

状语从句讲解ppt经典
一 状语从句的种类
§ 1状语从句的种类
用来修饰谓语动词、其它动词、定语、状语或整个句子的从句叫做状语从句。状语从句可分为:
1.时间状语从句2.地点状语从句;3.原因状语从句;4.条件状语从句;5.目的状语从句;6.让步状语从句;7.比较状语从句;8.程度状语从句;9.方式状语从句;10.结果状语从句。
§2状语从句的时态特点
一般情况下,时间和条件状语从句的谓语动词一般用“一般现在时”表示“一般将来时”,用“现在完成时”表示“将来完成时”。
二 时间状语从句
§3时间状语从句(adverbial clause of time)
1.由when, while, as引导的时间状语从句。
【区别】when, while和as的区别:when引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。并且when有时表示“就在那时”。
While引导的从句的谓语动作必须是延续性的,并强调主句和从句的动作同时发生(或者相对应)。并且while有时还可以表示对比。例如:
While my wife was reading the newspaper, I was watching TV. (was reading是延续性的动词,was reading和was watching同时发生)
As表示“一边……一边”,as引导的动作是延续性的动作,一般用于主句和从句动作同时发生;as也可以强调“一先一后。
As we was going out, it began to snow.当我们出门时,开始下雪了。(as强调句中两个动作紧接着先后发生,而不强调开始下雪的特定时间)
2.由before和after引导的时间状语从句。注意before引导的从句不再用否定式的谓语,并且当before引导的从句位于主句之后,有时译成“就,才”。还要注意主句和从句之间的时间关系。当主句用将来时,从句总是用现在时;如果before引导的从句谓语用的是过去时,则主句动词多用过去完成时,这样以便体现动作发生的先后。After表示主句动作发生在从句动作之后。主句和从句的动作的时间关系正好与before引导的从句相反。
3.由till或until引导的时间状语从句。till和until一般情况下两者可以互换,但是在强调句型中多用until。并且要注意的是:如果主句中的谓语动词是瞬时动词时,必须用否定形式;如果主句中的谓语动词是延续性动词时,用肯定或否定形式都可以,但表达的意思不同。例如:
4.由since引导的时间状语从句。 since引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。一般情况下,从句谓语动词用一般过去时,而主句的谓语动词用现在完成时。但在It is +时间+since从句的句型中,主句多用一般现在时。例如:
5.由as soon as, immediately, directly, instantly, the moment, the instant, the minute, 等引导的时间状语从句。这些连词都表示“一……就”。
【注意】hardly(scarcely, rarely)…when / before, no sooner…than相当于as soon as之意。主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。当hardly, scarcely, rarely和no sooner位于句首时,主句应用倒装语序。
6.由by the time引导的时间状语从句。注意时态的变化:在一般情况下,如果从句的谓语动词用一般过去时,主句的谓语动词用过去完成时;如果主句的谓语动词用一般现在时,主句的谓语动词用将来完成时。
7.由each time, every time和whenever引导的时间状语从句。
8.由as long as和so long as引导的时间状语从句。这两个连词表示“有多久……就多久”。
三 地点状语从句
§4地点状语从句 (adverbial clause of place)
地点状语从句一般由连接副词where, wherever等引导,已经形成了固定的句型,例如:
句型1:Where+地点从句,(there)+主句。
【注意】此句型通常译成“哪里……哪里就……”;主句在从句后面时,there可用可不用;如果主句在从句的前面时,一般都不用there。
句型2:Anywhere/ wherever+地点从句,+主句。
状语从句是句子的状语由一个从句充当,来修饰主句中的动词,形容词或副词等。状语从句都由从属连词引导,与主句连接,放在句末时,一般不在前面加逗号。
状语从句根据它表示的意思可分为时间,原因,条件,比较,结果,目的等类。
时间状语从句:是由when, as, while, after, before, since, until, as soon as 等从属连词引导的状语从句。
时间状语从句中的谓语动词不能用一般将来时,只能用一般现在时表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态。
原因状语从句: because, since, as和for都表示原因。because语势最强,回答why提出的问题,用来说明人所不知的原因。当能够很明显的看出原因或人们已知原因,就用as或since。
由because引导的从句如果放在句末,且前面有逗号,则可以用for来代替。但如果不是说明直接原因,而是多种情况加以推断,就只能用for。
目的状语从句:表示目的状语的从句可以由in order that, so that,等词引导。
结果状语从句:结果状语从句常由so...that 或 such...that引导,要掌握和区分这两个句型,
首先要了解so和such后面分别跟什么词。such是形容词,修饰名词或名词词组,so是副词,只能修
饰形容词或副词。so 还可与表示数量的形容词many, few, much, little连用,形成固定搭配。
如:The box is so heavy that I can't carry it.
让步状语从句:是由though, although 引导的状语从句。

英语状语从句的讲解和例子
你可以依据这些内容做一个PPT文件,自己用更方便
内容提示: 状语从句状语从句时间状语从句地点状语从句原因状语从句的状目的状语从句结果状语从句条件状语从句方式状语从句让步状语从句比较状语从句从句 1 .时间状语从句1)由连词when, while, as, as soon as, before, after, since, till/ until等引导。�6�1 主句用将来时, 从句常用一般现在时表将来I will tell him when he comes back. 2)while, when, as辨析While引导的时间状语从句只指一段时间,强调某一段时间内, 主从句动作同时发生。 从句动词常是延续性的When既可以指一个时间点,也可以是一段既可以指个时间点,也可以是时间, 可表示主从句的动作同时或先后...
状语从句状语从句时间状语从句地点状语从句原因状语从句的状目的状语从句结果状语从句条件状语从句方式状语从句让步状语从句比较状语从句从句 1 .时间状语从句1)由连词when, while, as, as soon as, before, after, since, till/ until等引导。• 主句用将来时, 从句常用一般现在时表将来I will tell him when he comes back. 2)while, when, as辨析While引导的时间状语从句只指一段时间,强调某一段时间内, 主从句动作同时发生。 从句动词常是延续性的When既可以指一个时间点,也可以是一段既可以指个时间点,也可以是时间, 可表示主从句的动作同时或先后发生。 从句动词可以是延续性的, 也可以是非延续性的。As强调主句、 从句动作相并发生,译为” 一边…一边…”段 When he returned , his wife was cooking.While he was reading, his wife was cooking.He hurried home, looking behind as he went . 对比训练 1____ he heard this, he got very angry. 2. I met Lucy____ I was walking along the river.3. ____ a child, he lived in the countrysidecountryside.A. when B. while C. as 另外, when/while还作并列连词,连接并列分句,while表示 “而,可是” 如:I like reading while my wife enjoys watching TV.when表示 “就在这时” 在下列结构中, 表示某件事正在发生或刚刚发生, 另一动作同时发生。1.be about to do… when…2.be doing… when…3.had done… when…e.g. We were about to start when it began to rain.I was playing computer games when mom came in. while的用法小结 :①While I was walking down the street, Icame across an old friend. ( while=_______)②He likes pop music, while I am fond offolk music. ( whilefolk music. ( while③While I really don’t like art, I find hiswork impressive. (while=___________)whenwhenbutbutalthoughalthough We were about to leave____ it began to rain.2. She thought I was talking about her son, ____, in fact, I was talking about my son.3. Hardly had I finished my composition ____ the bell rang.A. when B. while C. as D. during 3)until/till(不用于句首)“延续的动词(肯定式) +until ”表示“直到…为止”I waited for him until he came back.“非延续性动词(否定式) +until ”表示“直到才”“直到┅才”He didn’t go to bed until he finished his work.注意: not until 在句首时要倒装Not until he saw it himself did he believe it. 4)表示“一…就…”的句型(1)as soon as, once, the moment/ minute/ second, immediately/ directly/ instantlyAs soon as he comes, I’ll tell him.The moment I saw him, I recognized him.I l ft idi t l thI left immediately the clock struck 5.(2)on / upon doing / on (upon) one’s +nOn arriving at the station, the thief was arrested.On his arrival in Paris, he was recognized as a famous person.lk tk 5 (3)no sooner… than/ hardly… when / scarcely… whenNo sooner had they reached home than it started to rain.Hardly had I entered the room when the telephone rangtelephone rang. 5)Every time, each time等也可以引导时间状语从句Every time I caught a cold , I had pain in my head. 连接词before的小结:1. We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land.2. We hadn’t run a mile before he felt tired.4. Before I could get in a word, he had measured me.“……“……才”才”“ “不到不到…………就”就”“ “还没来得及”还没来得及”It will be a long time It will be a long time beforeIt won’t be long It won’t be long beforeIt is / has been two years It is / has been two years sincesthsth. .before………before…since sbsb did did 1 1) 句型) 句型It will be/wasIt will be/was+段时间+“ “还要过多久才还要过多久才……” 如:如: It will be two years It will be two years before the country.the country.2 2) 句型) 句型It will be/was notIt will be/was not+一段时间+“ “不多久就不多久就……”……”如:如:It wasn’t two years It wasn’t two years beforecountry.country.+段时间+before………” before he leaves before…he leaves +一段时间+before…before…before he left the he left the y y 一、 若since引导的状语从句的谓语动词是终止性的过去时, 则从句表示的时间是“从动作开始的那一时刻起” 。 如:He has studied very hard since he came to our school.自从他来到我们学校自从他来到我们学校, 他学习就非常努力。We have been missing them since they left here自从他们离开这里, 我们就一直很想念他们。他学习就非常 二、 若since引导的状语从句的谓语动词是持续性动词或表示状态的动词的过去时时, 则从句表示的时间是“从那持续动作或状态结束时算起” 。 如:I haven’t heard any noise since I slept. Sleep 为持续性动词, sleep的动作结束时,即“醒来” 时, 这句应译为“我醒后还未听到任何声音” 。John is now with his parents in New York, it is already three years since he was a teacher约翰现在和父母一起住在纽约, 他不当教师已经三年了。 How long is it since you lived in Shanghai?你离开(没住在) 上海多久了 延续性; 不… 多长时间了It is half a month since he was a League member.他退团(不当团员) 半个月了。It’s been quite some time since I was last in London我离开伦敦已很长时间了。比较比较: He has written to me frequently since I was ill.自从我病愈以来, 他屡次给我写信。(从句谓语为状态动词)He has written to me frequently since I fell ill.自从我生病以来, 他就屡次给我写信。(从句谓语为终止性动词) ’ll let you know ____ he comes back.A. before B. becauseC. as soon asD. althoughIt is about ten years _____ I met you last.A.since B. forB.C. whenD. asB.C. when D. as____ we got to the station, the train had left already.A.If B. UnlessC. Since D. When We didn’t go home _____ we finished the work.A. since B. until C. because D. thoughIt was not ______ she took off her dark glasses ______ I realized she was a ffiltAfamous film star. A. when; that B. until; that C. until; when D. when; thenhth tB. He was about halfway through his meal ______ a familiar voice came to his ears. A. why B. where C. when D. while Scientists say it may be five or six years ______ it is possible to test this medicine on human patients. A. since B. after C. before D. whe Why didn’t you tell him about the meeting? He rushed out of the room____I could say a word. A. before B. until C. when D. after _____ I accept that he is not perfect, I do actually like the person. A. While B. Since C. Before D. Unless Did you remember to give Mary the money you owed her?money you owed her? Yes. I gave it to her ______ I saw her. A. while B. the moment C. suddenly D. once 2. 让步状语从句引导词有:although, though, even if/though, as , while(尽管) whether…or…( 无论…还是… ),whoever= no matter whowhoever= no matter who whenever= no matter whenwhatever= no matter whatwherever= no matter wherehowever= no matter how 1)as 引导的让步从句要倒装, 句型为:形容词/ 副词/ 名词(不带冠词) / 动词(原形) +主语+谓语Young as he is, he knows a lot.Much as I like it, I can’t afford it.Farmer as he is he is well-educatedFarmer as he is, he is well-educated.Try as I might, I couldn’t lift the stone.2) although不倒装,不倒装, as 必须倒装though可倒装也可Although/Though he was ill he didn’t stop working. 3) no matter +疑问句引导让步状语从句No matter what happened, he shouldn’t mind.=Whatever happened, he shouldn’t mind.No matter who you are, you should obey the social rules.=Whoever you are, you should …oe e you a e, you s ou d4) whether …orWhether you believe it or not, it is true.whether… or…不管…还是…a. Whether the weather is good or bad, they will set off as they planned. B.Whether he drives or takes the train, he will be here on time. 1 、difficult it was. A. however B. no matter C. whatever D although 2、 The old tower must be saved, ______the cost. A. however B. whatever C. whichever D. wherever 对比训练 3 1 . Child ____ she is, she know a lot.2. He did the experiment ____ he was told.3. The pianos in the other shop will be cheaper, but not ____ good.A. during B. as C. so D. thoughE. both B and CHe tried his best to solve the problem, ___ 3. 地点状语从句引导词有: where, whereverI’ll follow you wherever you go.Where there is a will , there is a way.注意: 不要混同于where 引导的定语从句注意: 不要混同于where 引导的定语从句(有志者, 事竟成)与定语从句的区别: where引导定语从句,从句前有一个表示地点的名词。Go back where you came from.Go back to the village where you came from. When you read the book ,you 'd better make a mark ___ you have any question. A at which B at where C the place where D whereWhen you read the book ,you 'd better ymake a mark at the place _____ you have any question.A which B at whereC the place where D wherey 4. 原因状语从句由because, since, now that, as引导。(1). because 语气最强, 用来回答why提问,可用在强调句型中,引导的从句表示直接的、根本的原yin It was because he was ill that he didn’t go with us.(2).Since语气比because弱, 表示关系上的自然结果, 一般译成“既然, 鉴于” (往往放于主句之前) 表示显然的或已知的原表示显然的或已知的原因因..Since no one is against it ,let’s carry out the plan.(既然没人反对, …) (3).as语气最弱, 只说明一般的因果关系(可放于主句之前, 也可放于主句之后)Wear strong shoes as we shall do a lot of walking today.与与sincesince没多大区别(4).for也可以表示原因, 不是说明直接原因, 而是对某种情况加以推倒, 用于表示补充说明理由补充说明理由。He must be ill, for he is absent today.(5).now that用来说明一种新情况, 然后加以推理, now that放于句首时, that可省略。Now ( that) everybody is here, let’s begin.没多大区别 ______ the day went on, the weather got worse.A With B Since C While D AsA. With B. Since C. While D. AsHe took off his coat _______ he felt hot.A. because B. as C. if D. since 5. 目的状语从句引导词: in order that, so that(为了 ) ,for fear that , in case,谓语动词常含有can, could, may, might, will, would等情态动词。I’ll speak slowly so that everybody can understand me.He wrote the name down for fear that( in case) he would forget. in casein case与与for fear thatfor fear thatI will have to stay at home this evening I will have to stay at home this evening ______________ my teacher comes.______________ my teacher comes.in casein casebecause of the possibility of because of the possibility of sthsth happeninghappeningStudents of Class 13 are working hard Students of Class 13 are working hard theses days _________________ they theses days _________________ they might fail the exam.might fail the exam.for fear thatfor fear thatto avoid the danger of to avoid the danger of sthsth happeninghappening Ann listened carefully _____ she could discover what she needed.A. such thatB. in order thatC. becauseD. even though11 . I hurried ____ I wouldn’t be late for class.AiBA. sinceB. so thatC. as ifD. unlessth t 6. 结果状语从句:引导词有: so…that, such…that, so that常用句型:1)so+ adj. (adv.) + that2)so+ adj + a (an) + n +that2)so+ adj. + a (an) + n. +that3)Such +a (an) +adj. + n. + that4)Such +adj. + n (s) +thatHe spoke so fast that I couldn’t follow him.It was such a good day that we all went swimming. He left in ___a hurry ___he forgot to lock the door.A. such, that B. so, that B.C. such, as D. so, when.Farmers rotate (轮作) their crops _____ the soil will remain fertile.A. so that B. because of C. in order to D. rather thanIt was ____ a hundred people looked lost in it.A. so large a room that B. so large roomC. a such large room D. such large a roomHe has ____ little education that he can’t teach ____ little children. A. so; such B. too; such C. a; so D. very; so 7. 条件状语从句1. 由if, unless(= if not), so/ as long as(只要), suppose/supposing(假设,如果), in case(以防), on condition that, only if , if only引导。e g You may use the room as long as youe.g. You may use the room as long as you clean it up afterwards.2.“祈使句+and/ or/ or else/otherwise”引导的结果句, 祈使句在实际意义上相当于条件状语从句。Use you head, and you will find a way.Get up now, or you will be late. 1 、 The WTO cannot live up to its name ____ it does not include a country that is home to one fifth of mankind. A. as long as B. while2、It is known to all that _____ you exercise regularly, you won’t keep good health. A. unless B. whenever C. although D. if unless 相当于 if not, 意思是“除非…”“如果不…就…”。 这也是高考的热点之一。 复习时也应给予高度重视。1 、 _____ I can see, there is only one possible way to keep away from the danger. A. As long as B. As far as C. Just as D. Even if 2、 I always take something to read when I go to the doctor’s ________ I have to wait. A. in caseB. so that C. in order D. as if C. if D. even though 8. 方式状语从句引导词有: as(如同 ), as if/though (好像)They are talking as if (as though) they were old friends.注意:注意:as, like 都表示“像” ,as 是连词 , 后加句子like 是介词, 后加名词、 代词、 名词短语I work as others do .I work like others. 9.比较状语从句由as… as, not as/ so…as, than, the more… the moreHe ran as far as he could.The harder you try, the better you will understand. 四. 状语从句的时态问题问题1:1、 The house could fall down soon if no one______ some quick repair work. A has doneB is doingdone 2、 It is almost five years _______ we saw each other last time. A. before B. since C. after D. when 在条件, 时间和让步从句中, 用一般现在时表示一般将来时, 用现在完成时表将来完成时, 用一般过去时表过去将来时。 在 since 引导的时间状语从句中, 动词一般都用一般过去时, 而主句常用现在完成时。C doesD had 五、 状语从句的倒装问题问题1:1、 So difficult _____ it to live in an English-speaking country that I determined to learn English. A. I have felt B. have I felt C. I did feel D. did I feel2、 Not until all the fish died in the river _____ how serious the pollution was. A. did the villagers realize B. the villagers realizedC. the villagers did realize D. didn’t the villagers realize 状语从句的倒装一般有下面几种情况: ① 否定词开头; ② so 加 adj. 开头; ③ as / though引导的让步状语从句。Hardly had he got to the station when the train left.No sooner had he got to the station than the train left.Child as he is, he can speak seven foreign languages.

以上就是关于高中状语从句讲解ppt ,时间状语从句的用法和讲解的全部内容,以及高中状语从句讲解ppt 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

