提起初中英语情态动词用法归纳 想必大家都想知道。今天就给家解读一下。初中范围情态动词用法和常见的几种情态动词的用法初中英语情态动词用法归纳 的内容,让大家更深入了解初中情态动词的用法,一起来看看吧。
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 :初中英语中常见的情态动词
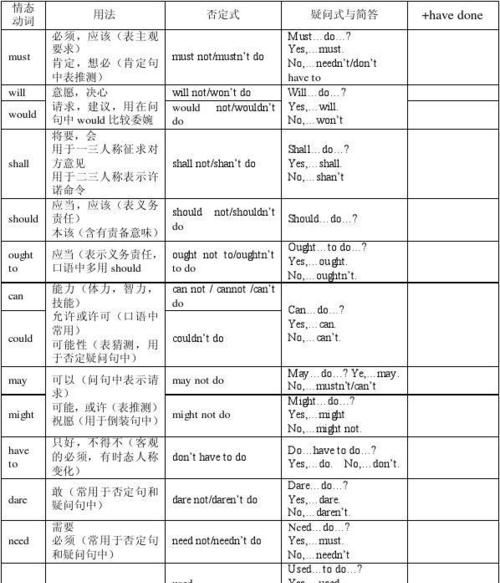
一、情态动词 can 的用法 1. 表示能力,意为“能、会”。如: —— Can you swim? 你会游泳吗? —— Yes,I can. 是的,我会。 —— Can you play the guitar? 你会弹吉它吗? —— No,I can’t. 不,我不会。 2. 表示请求或允许,多用于口语中,意为“可以、能”等。 如: Can I help you? 我可以帮忙吗? You can go home now. 现在你可以回家了。 3. 用于否定句、疑问句中,表示猜测、怀疑或不肯定。 如: —— Where can it be? 它可能会在哪儿? —— It may be in your pencil-box. 也许在你的文具盒里。 二、情态动词 may 的用法 1. 表示“许可、准许、请求许可”,此时与 can 同义,可以互换使用。 如: You may / can go to the cinema this evening. 你今晚可以去看电影。 注意: 许可对方时,其答语可以用 Yes,you may. 但由于用 may 作肯定回答,语气显得生硬、严肃,因而一般常用 Yes, please. / Certainly. / Of course. 等。这些肯定答语显得热情、客气。如: —— May I use your ruler? 我可以用一下你的尺子吗? —— Certainly. Here you are. 当然可以。给你。 拒绝对方时,其答语可以用 No,you mustn’t. / No,you can’t. 或 Sorry,you can’t. / No,please don’t. 等说法。如: —— May I watch TV now? 现在我可以看电视吗? —— No,you mustn’t. 不,不可以。 2. 表示可能性,意思为“可能、也许”,常用在肯定句中。 如: He may know you. 他可能认识你。 The may go to the Great Wall next week. 他们可能下周去长城。 注意: 在否定句中一般不用 may not ,常用 can’t 表示“不可能”。例如: He can’t be at home tonight. 今晚他不可能在家。 3. 用于特殊疑问句中,表示不确定,常可译为“会”。如: Who may call me at night? 谁会在晚上给我打电话呢? 4. 表示希望、祈求、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿”。如: May you have a good time. 祝你过得愉快。 May you be happy! 祝你幸福!
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 :初中英语:情态动词到底怎么样用呢
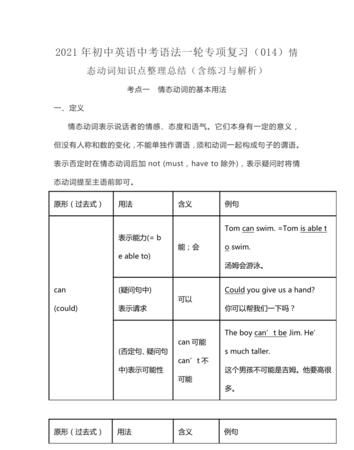
一、情态动词的基本用法
1.can
(1)(表示能力)能……;会……
She can drive,but she can’t ride a bicycle.
【注】 could表示“原来具备某种能力,现在没有这种能力了”,
但was/were able to则表示过去成功地做成了某事。
I could swim all the way across the lake,but I can’t now.
我原来能游过这个湖,但现在不能了。
The fire spread through the hotel very quickly but everyone was able
to get out.
大火很快蔓延了整个旅馆,但全体人员都脱离了危险。
(2)(表示可能、许可)能够……;可以……
“Can I use your telephone?”“Yes,of course you can.”
You can’t park your car in this street.
【注】 can可作“有时候会……”解,意思是平时或大部分时间不
是这样子,只是偶尔发生的事情。如:
Jogging can be harmful to the health.
慢跑有时候会对身体健康有害。
(3)(表温和的命令)请做……,得……
I’ll do the cooking,and you can do the washing.
我来做饭,请你去洗衣服。
(4)(用于疑问句中,表请求、提议)能不能……;要不要……
Can you give me a lift to the station?
Can’t you lend me ten dollars?
请你借给我10美元吧?
(5)(用于疑问句中,表惊讶、怀疑等)“(到底)可能有这样的事吗?”
Can it be that it was I,not he,who was mistaken?
难道错的会是我,而不是他吗?
(6)构成下列特殊句式:
①can not/can never...too...或cannot...enough “无论怎么……也不过分;
越……越好;非常……”。
One cannot be too careful. 越认真越好。
I cannot thank you enough.我对你感激不尽。
②cannot help doing.../cannot help but do.../cannnot but do...“禁不住;不
由得;不得不”。
I cannot help admiring the picture whenever I look at it.
When a close friend dies,you cannot but feel sad.
2.may
(1)(表准许、请求)可以……
You may go home now,Susan.苏珊,你现在可以回家了。
May I have a word with you,please?我可以跟你说句话吗?
(2)(表愿望、祝福)但愿;祝……。此时,句子要用倒装语序。
May you succeed!祝你成功!
(3)(用于目的状语从句中)为了;为了能够
He works hard so that he may get good grades.
(4)(用于让步状语从句中)即使;无论
Whatever he may say,I don’t believe him.
(5)构成句型:may/might as well do sth. “还是做某事的好;不妨去做
某事”
Since we’ve got nothing better to do,we might as well go for a walk.
既然我们没什么更好的事情可做,我们不妨去散散步。
3.must
(1)(表义务、必要性、命令)必须,得,要
“Must I wash the dishes at once?”“No,you needn’t.”“我得立
刻洗这些盘子吗?”“不,不必。”
Animals must eat to live.为了活下去,动物必须吃东西。
【注】 mustn’t表“禁止、不准”。
You mustn’t play with the knife;you may hurt yourself.
你不可玩刀子,你会把自己割伤的。
(2)(表必然性)必定
Everyone must die.每个人都必定会死。
(3)(表固执、不满等)偏偏;硬要;偏要
If you must know,I’m going to help him look for an apartment.
如果你偏要知道,那我告诉你,我要去帮助他找一套公寓。
4.shall
(1)用于疑问句中,与第一、三人称连用,表示征求对方的意见
Shall she go to the concert with us this evening?
Shall we go out for a walk?
【注】 may用于征求对方的许可,shall用于征求对方的意见或指示。
May I have a look?我能看一下吗?
Shall I have a look?要我看一下吗?
(2)用于第二、三人称,表示说话人的命令、警告、强制、允诺、威
胁或决心等
Don’t worry.You shall get the answer this very afternoon.
不要焦急,今天下午你就会得到答复。(允诺)
He shall be sorry one day.I tell you.
我告诉你,他早晚有一天会后悔的。(警告)
(3)(用于法律、规则等条文中)应……,须……,得……
The fine shall be given in cash.罚款应以现金缴纳。
5.should
(1)(表义务、责任)应该
We should attend the meeting.
我们应该参加这次会议。
(2)(表预期)应该会,想必会,一定会……吧
The concert should be great fun.音乐会一定会很有意思。
(3)(表惊讶、遗憾)竟然;居然
I’m glad that your story should have won the first prize.
我很高兴你的小说居然赢得头奖。
(4)(与疑问词连用,表示意外、纳闷、惊讶等)究竟是;到底
Who should come in but my old friend Betty!
我当是谁进来了呢,原来是我的老朋友贝蒂呀!
(5)(用于条件状语从句中)一旦;万一
If she should know the truth,she would be greatly depressed.
万一她知道了实情,她将会非常失望。
Should you change your mind,let us know.
你一旦改变主意,就通知我们。
(6)(用于表示命令、建议、请求的动词后面的that从句中,且should
可省略)应该;必须
She demanded that they (should) leave at once.
她要求他们立即离开。
(7)(用于以lest,for fear that,in case引导的状语从句中)以免;唯恐
She gave me a list just in case I should forget what to buy.
她给了我一张清单,以免我忘记买些什么。
6.would
(1)(表过去的习惯性动作)(从前)常常;经常
We would stay up all night talking about our future.
那时候,我们常常彻夜谈论我们的将来。
(2)(表示说话者的厌烦、焦躁)老是;偏要
That’s exactly like Susie.She would come to me just when I was busy.
苏西就是那个样子,她老是在我忙碌的时候来找我。
(3)(用于否定句中,主语一般是事物,表示某事物暂时的特性)就是
(不能)
That window wouldn’t open.那扇窗户打不开。
(4)表示请求或个人的想法、看法,使语气婉转
Would you mind if I opened the window?
我打开窗户你不介意吧?
二、情态动词表推测
情态动词must,can/could,may/might可以用来对事情进行推测。must
表推测时只能用于肯定句,是对现在或过去的事情进行的推测,不能
表对将来事情的推测,语气非常肯定,译为“一定……”。can/could
表推测时一般用于否定句或疑问句,也是对现在或过去的事情进行推
测,但could偶尔可用于肯定推测。may/might表推测时一般用于肯定句
或否定句,可对现在、过去或将来的事情进行推测,语气不很肯定,
译为“可能……”。
此时,一般有两种结构:“情态动词+be”和“情态动词+have
done”。
1.“情态动词+be”结构通常用来对现在或将来的状况进行推测。
The light is still on.He must be working in the office now.
灯还亮着,他现在一定还在办公室工作着。
Michael can’t be a policeman,for he’s much too short.
麦克不可能是警察,因为他太矮了。
He may be in the classroom.I’ll go and make sure.
他或许在教室里,我去弄弄清楚。
2.“情态动词+have done”结构用于对过去事情的推测。
I didn’t hear the phone.I must have been asleep.
我当时没有听到电话响,我一定是睡着了。
Tom hasn’t come back yet.He may have missed the bus again.
汤姆还没有回来,他可能又没赶上班车。
Jack can’t have arrived yet;otherwise he would have telephoned me.
杰克不可能来到,否则,他会给我来电话的。
【注】 might have done和could have done除了表对过去事情的推测
外,还可表示一种责备语气,意为“(过去)本来可以(能够)做某事,
但实际上没有做到”,此时不能用may或can。
He might have given you more help,even though he was very busy.即使再忙,他也可能再多给你一些帮助的。
三、情态动词表责备语气
情态动词should,ought to,could,might,need等常用来表示说话人
对过去事情的不满或遗憾,带有较强烈的责备语气。
1.should (ought to) have done “本应该……”,表示过去应该做而
(实际)没有做的事情,含有责备或遗憾的语气,其否定形式为
“should not/ought not to have done”。
I told Sally how to get there,but perhaps I should have written it out for her.当时我告诉了莎丽如何去那儿,但或许我还是该给她写出来为好。
【注】 should have done还可以表示惊讶、赞叹等情绪。
It’s wonderful that you should have achieved so much in these years.
太神奇了,这几年你竟然取得了这么大的成就。
2.could/might have done “本来能够(会)……”,表示过去
本来可以(能够)做某事,但实际上没有做到。
—I didn’t go to class last night because my car broke down.
—You could have borrowed mine.I wasn’t using it.
“我昨晚没去上课,我的车坏了。”
“那你该借我的呀,我那时没用它。”
3.needn’t have done“本来不需要……”,表示过去本来
没有必要做某事,但事实上却做了。
There was plenty of time.She needn’t have hurried.
当时时间很充足,她本没有必要那么匆忙的。
望采纳,谢谢。
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 :初中英语情态动词的用法
非常全,自己总结的哦!!!
Grammar—Modal-verb
Ⅰ.情态动词
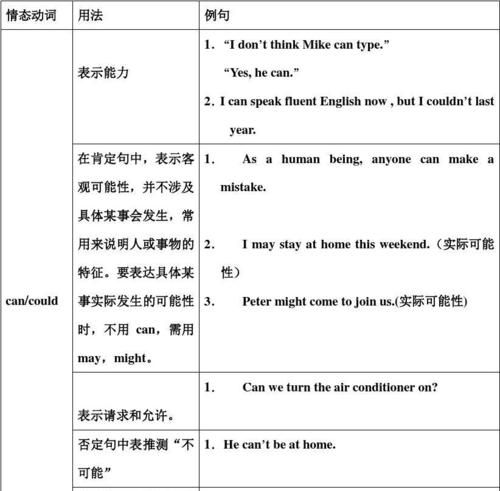
一、can/could
1.表示能力时
was/were able to 具体做成某件事(=managed to do )
could 只表示能够
2.can+感官动词
can taste/ see/ hear/ smell/ feel/ believe/ decide/ understand
3.can表示惊讶、不敢相信
Eg: How can you do like this?
4.cannot but do
cannot choose but do
cannot help but do
Eg: I cannot but feel sorry for her.
I cannot choose but follow her advice.
5.cannot… over/ enough/ too …都不过分;越…越好
Eg: You cannot over praise him.
6.理论上的可能性:
Eg: Accidents can happen on such rainy days.
Anyone can make mistakes.
The temperature can fall to -40℃.
7.can’t 表示否定推测:
Eg: It can’t be him, for he has gone to Paris yesterday.不能用mustn’t
8.can/could 表示允许、请求
Can/May I help you?
I wonder if I can/could do sth.(此处could不表示时态)
-Can/Could/May I use…?
-Yes, you can/may.
-No, you can’t/ may not/ mustn’t.(题目选项中如果表否定允许有mustn’t就选mustn’t)
You’d better not.(may问一般不用may回答)
I’d rather you didn’t.
9.can/could (not) have done
(1)本能做、没能够
(2)过去可能会做、过去不可能做
Eg: He could have killed Harry Potter, but he didn’t.(过去本能够)
He couldn’t have killed him 17 years ago, and he cannot do it now, either.(过去没能够)
Can he have gone to his aunt’s ?(过去可能会做)
He cannot have forgotten it. (过去不可能)
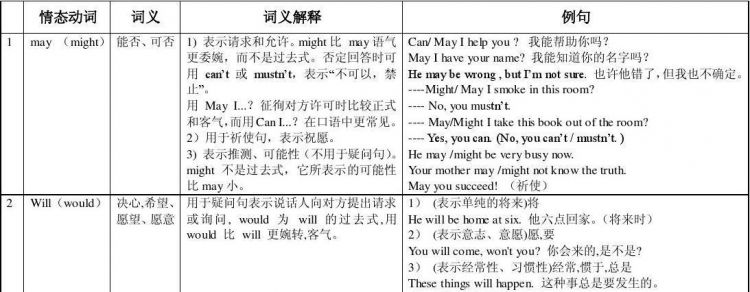
二、may/might
1.may /might 推测性用法 可能
He may be right.
He may not come today (可能不)
He may /might come tomorrow.
注意:只用于肯定和否定句中,不用于疑问句中
2.may not 可能不 can not不可能
He may not come He can’t come
3.may as well最好 may well理应,有足够的理由
You may(might)as well stay where you are.
-Shall we walk?
-We may as well.
4.表祝愿 May you be happy!
5.may (might) + have +done 表示对过去发生行为的推测,也许或许已经做
It may have been true.
He might not have settled the question.
He may not have finished the work.
I think he may have gone to bed.
6.may表示目的
Eg: You must go to bed early so that you can/may catch the train.
7.表示让步
Eg: However hard he may try, he cannot get the first place.
三、must
1. 表示义务意为“必须”(主观意志)
Eg: We must do everything step by step.
You mustn’t talk to her like that.
-Must we hand in our exercise—books now?
-No, you needn’t. / No, you don’t have to.
2.肯定推测(绝对不能用于否定推测!!!!否定推测用can’t/couldn’t)
Eg: He must be ill. He looks so pale.
She’s wearing a diamond necklace. She must have a lot of money.
3.偏要做,偏偏
Eg: Why must rain on Friday?
Must you speak so loudly?
If you must smoke, please go out!
4.must have done想必准时一定做了某事,否定是can’t/couldn’t have done
5. didn’t need to have done 过去没有必要做,具体是否做不强调
needn’t have done 本不必却做了
四、shall
1.在肯定句、否定句中表示命令、警告、威胁、许诺以及法律、规定、规章制度
Eg: You shall leave the room at once, and he shall, too.
It has been announced that candidates shall remain in their seat until all the papers have been collected.
-when can I get my computer back?
-Well, you shall have it on Saturday.
He shall be punished if he breaks the rule.
You should return the book to the library tomorrow.
You shall do as I say. 按我说的做。(命令)
You shall have my answer tomorrow. 你明天可以得到我的答复。(允诺)
He shall be sorry for it one day, I tell you. 有一天他会后悔的,我告诉你。(警告)
Nothing shall stop us from carrying out the plan. 什么也不能阻止我们执行这项计划。(决心)
2.表示请求、允许 Shall he/ she/ they/ I/ we……?
Eg: Shall I open the window?
Shall the driver wait outside?
五、should
1.用于第一人称疑问句中询问对方的意愿,但语气较委婉温和
What should we do now?
2.表示应该、必须,常与must 换用。(不常见)
We should (must) master a foreign language at least.
3.“should+be+表语”的结构,表示推测或惊奇。
They should be back by now.
I am sorry that she should be so careless.
4.“should+have+过去分词”的结构,表示过去该做而实际上尚未做的动作或行为;其否定则表示发生了不应该发生的行为。其同义结构“ought to have +过去分词”,表示过去“早应该”、“本当”之意,语气较强。
I should have thought of that. 这一点我是应当想到的。(但没想到)
They should not have left so soon.他们不应当走得这么早。(但已走了)
5. 在“It is natural (strange, natural, necessary, surprised, impossible, important ) that……”句型中,主语从句中的谓语动词要用“should +do”表示理所当然”、“奇怪”、“必要”、“惊异”等的意思。在lest(以免)、for fear (that) (以防)、in case(以备万一)等之后也要用should do;在advise, suggest, order, demand, request 等的从句中同样should do
It is necessary that he(should) be sent there at once.
It is strange that he should say so.
Let us go at once lest we should be late for the train.
6. Why/How should 结构表示说话人对某事不能理解,感到意外惊异等意思,意为“竟会”
Eg: Why should you be so late today?
How should I know? 我怎么会知道?(意为:我不知道)
六、will/would
1.表示意志,决心或愿望。
Surely we will support all the people in the world in their struggle for peace.
我们一定要支持全世界人民争取和平的斗争。
He would not let me try it . 他不肯让我去试。
I will do anything for you. 我愿为你做任何事。
None is so blind as those who won’t see. 不愿看的人眼最瞎。
If you will read the book, I’ll lend it to you. 如果你愿意读这本书,我会把它借给你
2.will表示经常性、习惯性、倾向性,would表示过去的习惯行为。
He would come to see me when he was in Beijing.他在北京时,常来看望我。
Every time she was in trouble, she would go to him for help.
Fish will die out of water. 鱼离开水就不能活。
3.用于第二人称作主语的疑问句中,表示对对方的请求,would的语气比will委碗
Would/will you kindly tell me the way to the station? 请问到火车站怎么走?Would you like another glass of beer? 再来杯啤酒好吗?
Would you mind cleaning the window? 请把窗户擦一下好吗?
Will you close the window? It’s a bit cold. 请你把窗户关上好吗?有点冷。
Won’t you drink some more coffee? 再来一点咖啡好吗?
4.表可能性
This will be the book you are looking for.这可能就是你要找的书。
She would be about 60 when she died.他死时大概60岁。
5.won’t拟人化
Eg: The door won’t open.
The car won’t start.
七、need
情态动词need 实意动词need
现
在
时 You need (not) do
He need (not) do You (don’t) need to do
He needs (doesn’t need) to do
过
去
时
You needed (didn’t need) to do
He needed (didn’t need) to do
将
来
时 You need (not) do
He need (not) do You will (not) need to do
He will (not) need to do
八、dare
句型
时态
情态动词dare
实义动词 dare
肯
定
句 现在时
dare to
dare/dares to do
过去时 dare to
dared to do
否
定
句 现在时
daren’t/dare not do
do/does not dare (to) do
过去时 dared not do
did not dare (to) do
疑
问
句 现在时
Dare he do?
Do you/Does he dear (to) do?
过去时 Dared he do? Did he dare (to) do
九、宁愿做某事
would rather do
would rather do than do
would do rather than do
would rather sb. did
prefer to do
prefer to do rather than do
prefer doing to doing
Ⅱ.情态动词表推测
一、情态动词表推测的三种句式
1.在肯定句中一般用must (一定),may(可能),might / could(也许,或许)。
(1)He must/may/might know the answer to this question?
他一定/可能/也许知道这个问题的答案。
(2)It is cold in the room. They must have turned off the heating.
屋里很冷,他们肯定把暖气关了。
2.否定句中用can’t / couldn’t(不可能), may not/might not(可能不)。
(1)It can’t/couldn’t be the headmaster. He has gone to America.
这不可能是校长,他去美国了。
(2)He may not/might not know the scientist. 他也许不认识那位科学家。
3.疑问句中用can/could (能……?)。
(1)Could he have finished the task? 他可能把任务完成了吗?
(2)Can he be at home now? 他现在能在家吗?
注:以上三种句式中情态动词的语气按程度都是依次递减的。Might, could并非may, can的过去式,而表示语气较为委婉或可能性较小。
二、情态动词表推测的三种时态
1.对将来情况的推测,用“情态动词 + 动词原形”。
(1)She must / may / might / could arrive before 5. 5:00前她一定/可能/也许到。
(2)She must/may/might/could walk miles and miles among the hills without meeting anyone.
她一定/可能/也许会在山里一连走好几英里而遇不到一个人。
2.对现在或一般情况的推测,用“情态动词 + be”,“情态动词 +be doing”或“情态动词 + 动词原形”。
(1)He must / may / might / could be listening to the radio now.
他一定/可能/也许正在听收音机。
(2)He can’t ( couldn’t ) / may ( might ) not be at home at this time.
这个时候他不可能/可能不在家。
(3)Mr. Bush is on time for everything .How can ( could ) he be late for the opening ceremony ?
布什先生一向准时,这次开幕式他怎么可能迟到呢?
3.对过去情况的推测,用“情态动词 + have +过去分词”。
(1)It must / may / might / could have rained last night .The ground is wet.
地湿了,昨晚肯定/可能/也许下雨了。
(2)The door was locked. He can ( could ) not / may ( might ) not have been at home .
门锁着,他不可能/可能不在家。
(3)Can / Could he have gotten the book?
难道他找到书了吗?
注:情态动词 should /ought to表推测时,意为“想必会,理应……”但与“have +过去分词”连用时,则又可构成虚拟语气意为“本应该做某事却没做”。例如:
(4)It’s seven o’clock. Jack should/ought to be here at any moment.
现在七点钟了,杰克理应随时到达。(推测)
(5)She should / ought to have attended your birthday party, but she had to look after her mother in hospital. (虚拟) 她本该出席你的生日晚会的,可是她得在医院照顾她妈妈。
(6)Tom should not /ought not to have told me your secret, but he meant no harm. (虚拟)
汤姆本不该告诉我你的秘密,可是他并无恶意。
Ⅲ.must反意疑问句
—应该 mustn’t
—必须 needn’t
—推测 还原成不含推测的句子一致
Eg: You must be tired, aren’t you?
You must have heard of it, haven’t you?
He can’t have gone out yesterday, didn’t he?
He can’t have gone out yet, has he?
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 :初中英语情态动词用法归纳课件
以上就是关于初中英语情态动词用法归纳 ,初中情态动词的用法的全部内容,以及初中英语情态动词用法归纳 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

