本文目录
名词性从句知识点总结
英语语法名词性从句知识:概念和用法介绍
2 英语语法名词性从句知识点:whether 和if引导名词性从句
3 英语语法名词性从句知识点:that, why 与 because 引导表语从句
4 英语语法名词性从句知识点:八种宾语从句不省略that
5 英语语法名词性从句知识点:that与whether引导名词性从句
6 英语语法名词性从句知识点:the fact that引导主语从句
7 英语语法名词性从句知识点:名词性从句的关键点
8 英语语法名词性从句知识点:except宾语的6种不同从句
9 英语语法名词性从句知识点:理解引导名词性从句的what
10 英语语法名词性从句知识点:what与that引导名词性从句区别
11 英语语法名词性从句知识点:whoever与no matter who的区别
12 英语语法名词性从句知识点:that if是什么意思
13 英语语法名词性从句知识点:形容词可用作状语吗
14 英语语法名词性从句知识点:宾语从句的时态呼应
15 英语语法名词性从句知识点:关系代词怎样省略
16 英语语法名词性从句知识点:引导的主语从句的what
17 英语语法名词性从句知识点:whatever引导主语从句的用法
18 英语语法名词性从句知识点:四类名词性从句详解
19 英语语法名词性从句知识点:这个答句是什么从句
20 英语语法名词性从句知识点:whichever引导主语从句的用法
21 英语语法名词性从句知识点:whoever引导主语从句的用法
22 英语语法名词性从句知识点:同位语从句的引导词问题
23 英语语法名词性从句知识点:同位语从句与定语从句的区别
24 英语语法名词性从句知识点:怎样学好名词性从句?
25 英语语法名词性从句知识:名词性从句基础
26 英语语法名词性从句知识:八种宾语从句不省略that
27 英语语法名词性从句知识:宾语从句学习指要
28 英语语法名词性从句知识:同位语从句学习指要
29 英语语法名词性从句知识:表语从句学习指要
30 英语语法名词性从句知识:主语从句学习指要
31 英语语法名词性从句知识:名词性从句用法详解
32 英语语法名词性从句知识:同位语边缘知识归纳
33 英语语法名词性从句知识:关系型 what引导名词性从句
34 英语语法名词性从句知识:四组名词性从句
35 英语语法名词性从句知识:应注意的两个问题
36 英语语法名词性从句知识:同位语从句用法详解
37 英语语法名词性从句知识:表语从句用法详解
38 英语语法名词性从句知识:宾语从句用法详解
39 英语语法名词性从句知识:主语从句用法详解
大概就这些,你可以自己再总结一下哈
名词性从句的种类及用法
1 that
2 that
3 what
4 What
5 when
6 what
7 What
8 when
9 that
10 What
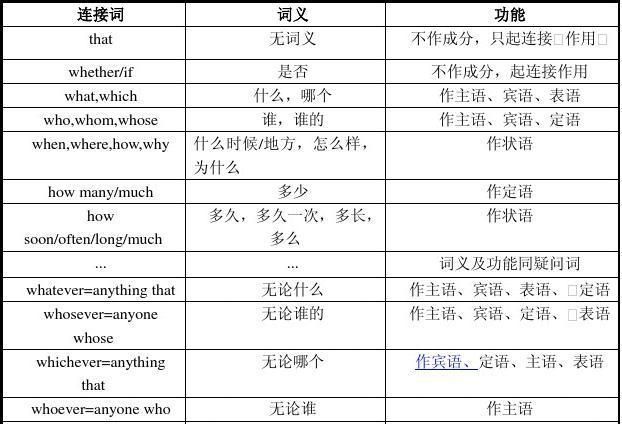
所谓名词性从句就是由特殊疑问词what, when, where, how, which, who或者that等引导的名词性从句。

名词性从句的分类
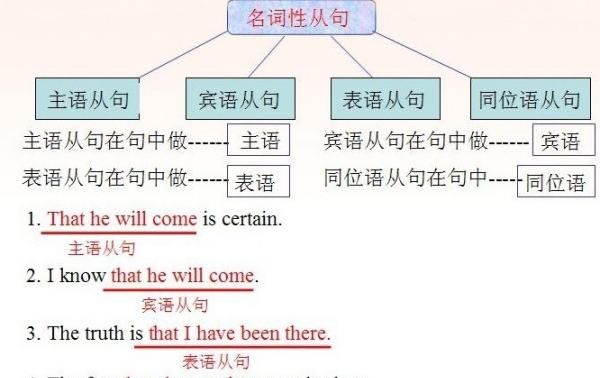
主语从句
主语从句通常由下列词引导:
1)从属连词that,whether,if等;
2)连接代词what,who,which,whatever,whoever,whom 等;
3) 连接副词how,when,where,why 等。
that在句中无词义,只起连接作用;连接代词和连接副词都在句中既保留自己的疑问含义、又起连接作用,在从句中充当主语的成分。注:whom、who指人,what指物,whatever,whoever表示泛指意义。例如:
What he wants to tell us is not clear. 他要跟我们说什么,还不清楚。
Who will win the match is still unknown. 谁能赢得这场比赛还不得而知。
It is known to us how he became a writer. 我们都知道他是如何成为一名作家的。
Where the English evening will be held has not yet been announced. 英语晚会将在哪里举行,还没有宣布。
有时为避免句子头重脚轻,常用形式主语it代替主语从句作形式主语放于句首,而把主语从句置于句末。主语从句后的谓语动词一般用单数形式。常用句型如下:
(1)It be+ 名词 + that从句
It's a great pity that they didn't get married.
他们没能结婚,真是令人惋惜。
It 's a good thing that you were insured.
你保了险,这可是件好事。
(2)It be + 形容词 + that从句
It's splendid that you passed your exam.
你通过考试了,真棒。
It's strange that there are no lights on.
真奇怪,没有一盏灯是开着的。
(3)It be + 动词的过去分词+ 主语从句
It's said that he has been there many times.
据说他去过那儿很多次。
(4)It + 不及物动词 + that 从句
另注意在主语从句中用来表示惊奇、不相信、惋惜、理应如此等语气时,谓语动词要用虚拟语气“(should) +do”,常用的句型有:
It is necessary (important, natural, strange, etc.) that …
It is suggested (requested, proposed, desired, etc.) that…
(5) it seems/happens+that 从句
众所周知的几种表达方式
(1)It is known to us that.
(2)As is known to us.
(3)what is known to us is that.
it引导的强调句结构:It is/was+被强调部分+that/who+句子其它部分。
eg:My father did the experiment in the lab yesterday evening.
强调主语:It was my father who did the experiment in the lab yesterday evening.
强调宾语:It was the experiment that my father did in the lab yesterday evening.
强调时间:It was yesterday evening that my father did the experiment in the lab.(注意不用when)
强调地点:It was in the lab that my father did the experiment yesterday evening.
宾语从句
名词从句用作宾语的从句叫宾语从句。引导宾语从句的关联词与引导主语从句表语从句的关联词大致一样,在句中可以作谓语动词或介词及非谓语动词的宾语。
1. 由连接词that引导的宾语从句。
由连接词that引导宾语从句时,that在句中不担任任何成分,在口语或非正式的文体中常被省去,但如果从句是并列句时,第二个分句前的that不可省。
He has told me that he will go to Shanghai tomorrow. 他已经告诉我他明天要去上海。
We must never think (that) we are good in everything while others are good in nothing. 我们决不能认为自己什么都好,别人什么都不好。
注意:在demand、order、suggest、decide、insist, desire, request, command, doubt等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,宾语从句常用“(should)+ 动词原形”。
I insist that she (should) do her work alone. 我坚持要她自己工作。
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once. 司令员命令部队马上出发。
2. 用who,whom, which, whose, what, when, where, why, how, whoever, whatever, whichever等关联词引导的宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,应注意句子语序要用陈述语序。
I want to know what he has told you. 我想知道他告诉了你什么。
She always thinks of how she can work well. 她总是在想怎样能把工作做好。
She will give whoever needs help a warm support. 凡需要帮助的人,她都会给予热情的支持。
3.可运用it做形式宾语。
①.动词make, find ,think,feel,consider,believe等后面有宾语补足语的时候,则需要用it做形式宾语,而将that宾语从句后置,结构:S.+vt+it+adj./n.+oc(宾语补足语)。
I think it necessary that we take plenty of hot water every day.我认为每天多喝开水是有必要的。
I feel it a pity that I haven't been to the get-together.我没去聚餐,感觉非常遗憾。
②.有些动词带宾语从句时需要在宾语与从句前加it,这类动词主要是:hate,take,owe,have,see to
I hate it when they with their mouths full of food.我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话。
We take it that you will agree with us.我们认为你会同意我们的。
He will have it that our plan is really pratical.他认为我们的计划确实可行。
4.用whether或if引导的宾语从句,其主语和谓语的顺序也不能颠倒,仍保持陈述句语序。此外,whether与if 在作“是否”的意思讲时在下列情况下一般只能用whether,不用if:
①whether引导主语从句在句首时;
Whether there is life on the moon is an interesting question. 月球上有没有生命是个有趣的问题。
Whether he can come to the party on time depends on the traffic.他能否准时参加派对得看交通情况。
②宾语从句放在句首表示强调时,只能用whether;
Whether this is true or not, I really don't know.这是否真实,我也不知道。
③引导表语从句,只能用whether;
The question is whether we can get in touch with her.问题是我们是否能联系上她。
④引导介词宾语时,只能用whether;
His father is worried about whether he lose his work.他的父亲担心他是否会失去工作。
I'm thinking about whether I should quit my present job.我正在考虑我是否应该辞去现 在的工作。
Everything depends on whether we have enough money.一切要看我们是否有足够的钱。
⑤if与whether都可以与or not连用,但后面紧跟着or not时只能用whether;
We didn't know whether or not she was ready.(此时只能用whether)
I wonder whether/if the news is true or not.(此时则二者都可以用)
⑥后接动词不定式时,用whether;
Can you tell me whether to go or to stay? 你能否告诉我是去还是留?
I can't decide whether to stay.我不能决定是否留下。
⑦用if会引起歧义时,只用whether;
Could you tell me if you know the answer ?
这句话有两种意思:“你能告诉我是否知道答案吗?”或“如果你知道答案,请告诉我,好吗?”。如用whether可避免歧义.
⑧whether可引导同位语从句,if不能引导同位语从句。
The question whether we should call in a specialist was answered by the family doctor.我们是否请专家由家庭医生来定。
5. 注意宾语从句中的时态呼应,当主句动词是现 在时,从句根据自身的句子情况,而使用不同时态。
I know (that) he studies English every day. (从句用一般现在时)
I know (that) he studied English last term. (从句用一般过去时)
I know (that) he will study English next year. (从句用一般将来时)
I know (that) he has studied English since 1998. (从句用现在完成时)
当主句动词是过去时态(could, would除外),从句则要用相应的过去时态,如一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时等;当从句表示的是客观真理,科学原理,自然现象,则从句仍用现 在时态。
The teacher told us that Tom had left us for America.
All of us know that the moon moves round the earth.
6. think, believe, imagine, suppose等等动词引起的否定性宾语从句中,要把上述主句中的动词变为否定式。即将从句中的否定形式移到主句中。
We don’t think you are here. 我们认为你不在这。
I don’t believe he will do so. 我相信他不会这样做。
表语从句
在复合句中,位于系动词之后作表语的从句叫表语从句。引导表语从句的关联词与引导主语从句的关联词大致一样,表语从句位于系动词后,有时用as if引导。
其基本结构为:主语+ 联系动词+ that从句
1.that 引导表语从句,无词义,只起连接作用,不可省。
2.联系动词可为be,look,seem,sound,appear等。
3.主语可为名词fact,truth,cause,question,explanation,trouble,assumption,belief等,代词this,that,these,it等。
The fact is that we have lost the game. 事实是我们已经输了这场比赛。
That’s just what I want. 这正是我想要的。
This is where our problem lies. 这就是我们的问题所在。
That is why he didn’t come to the meeting. 那就是他为什么不到会的原因。
It looks as if it is going to rain. 看上去天要下雨了。
Raw material is what we are badly in need of.原材料是我们所急需的。
China is not what it used to be.中国已不是过去的中国了。
【注意】
1.当主语是reason时,表语从句要用that引导而不是because。
The reason why he was late was that he missed the train by one minute this morning.
2.whether可引导表语从句,但与之同义的if却通常不用于引导表语从句。
3.That is why…译为“这就是……的原因/因此”。
其中why引导的名词性从句在句中做表语,该句型通常用于针对前面已经说过的原因进行总结。
That is why you see this woman before you know.这就是现在这位女士出现在你面前的原因。
That is why I came.这就是我来的原因。
区别:①That is why ……与That is the reason why …同义,只不过从语法结构上讲,前者中的why引导表语从句,后者中的why引导定语从句。
That is (the reason ) why I cannot agree.这就是我不能同意的理由。
②That is because …句型中从属连词because引导的名词性从句在此做表语,意为“这就是为什么……/因为……”。
That is because …指原因或理由。
That is why … 指由于各种原因所造成的后果。
He didn not see the film last night. That is because he had to help his little sister with her homework.昨晚他没有去看电影,那是因为他得帮助他的妹妹做作业。(第一句话说明结果,第二句话说明原因)
He had seen the film before. That is why he did not see it last night.他以前曾看过那部电影,因此他昨晚没有去看。(第一句话说明原因,第二句话说明结果)
同位语从句
同位语从句说明其前面的名词的具体内容。同位语从句通常由that引导,可用于同位语从句的名词有advice、demand、doubt、fact、hope、idea、information、message、news、order、problem、promise、question、request、suggestion、truth、wish、word等。例如:
The news that we won the game is exciting. 我们赢得这场比赛的消息令人激动。
I have no idea when he will come back home. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
The thought came to him that Mary had probably fallen ill. 他想到可能玛丽生病了。
同位语从句和定语从句的区别:
that作为关系代词,可以引导定语从句,充当句子成分,在从句中作宾语时可以省略; that引导同位语从句时,起连词的作用,没有实际意义,不充当句子成分,一般不能省略。
试比较下面两个例句:
I had no idea that you were here.(that引导同位语从句,不能省略)
Have you got the idea(that)this book gives you of life in ancient Greece?(that引导定语从句,作宾语,可以省略)
名词性that从句
(1)由从属连词that引导的从句叫做名词性that-从句。That只起连接主句和从句的作用,在从句中不担任任何成分,本身也没有词义。名词性that-从句在句中能充当主 语、宾语、表语、同位语和形容词宾语,例如:
主语:That she is still alive is her luck. 她还活着全靠运气。
宾语:John said that he was leaving for London on Wednesday. 约翰说他星期三要到伦敦去。
表语:The fact is that he has not been seen recently. 事实是近 来谁也没有见过他。
同位语:The fact that he has not been seen recently disturbs everyone in his office.
近 来谁也没有见过他,这一事实令办公室所有的人不安。
形容词宾语:I am glad that you are satisfied with your job.
你对工作满意我感到很高兴。
2)That-从句作主语通常用it作先行词,而将that-从句置于句末,例如:
It is quite clear that the whole project is doomed to failure. 很清楚,整个计划注定要失败。
It's a pity that you should have to leave. 你非走不可真是件憾事。
用it作形式主语的that-从句有以下四种不同的搭配关系:
a. It + be +形容词+ that-从句
It is necessary that… 有必要……
It is important that… 重要的是……
It is obvious that… 很明显……
b. It + be + -ed分词+ that-从句
It is believed that… 人们相信……
It is known to all that… 众所周知……
It has been decided that… 已决定……
c. It + be +名词+ that-从句
It is common knowledge that… ……是常识
It is a surprise that… 令人惊奇的是……
It is a fact that… 事实是……
d. It +不及物动词+ that-从句
It appears that… 似乎……
It happens that… 碰巧……
It occurred to me that… 我突然想起……
名词性wh-从句
1)由wh-词引导的名词从句叫做名词性wh-从句。Wh-词包括who, whom,. whose, whoever, what, whatever, which, whichever等连接代词和where, when, how, why等连接副词。Wh-从句的语法功能除了和that-从句一样外,还可充当介词宾语、宾语补语和间接宾语等,例如:
主语: How the book will sell depends on its author. 书销售如何取决于作者本人。
直接宾语:In one's own home one can do what one likes. 在自己家里可以随心所欲。
间接宾语:The club will give whoever wins a prize.
俱乐部将给得胜者设奖。
表语: My question is who will take over president of the Foundation. 我的问题是谁将接任该基金会主席职位。
宾语补足语:She will name him whatever she wants to. 她高兴给他起什么名字就取什么名字。
同位语: I have no idea when he will return.
我不知道他什么时候回来。
形容词宾语:I'm not sure why she refused their invitation. 我尚不能肯定她为什么拒绝他们的邀请。
介词宾语: That depends on where we shall go.
那取决于我们去哪儿。
2)Wh-从句作主语也常用先行词it做形式主语,而将wh-从句置于句末,例如:
It is not yet decided who will do that job.
还没决定谁做这项工作。
It remains unknown when they are going to get married. 他们何时结婚依然不明。
if, whether引导的名词从句
1)yes-no型疑问从句
从属连词if, whether引导的名词从句是由一般疑问句或选择疑问转化而来的,因此也分别被称为yes-no型疑问句从句和选择型疑问从句,其功能和wh-从句的功能相同, 例如:
主语:Whether the plan is feasible remains to be proved. 这一计划是否可行还有待证实。
宾语:Let us know whether / if you can finish the article before Friday. 请让我们知道你是否能在星期五以前把文章写完。
表语:The point is whether we should lend him the money. 问题在于我们是否应该借钱给他。
同位语:They are investigating the question whether the man is trustworthy. 他们调查他是否值得信赖。
形容词宾语: She's doubtful whether we shall be able to come. 她怀疑我们是否能够前来。
介词宾语: I worry about whether he can pass through the crisis of his illness. 我担心他是否能度过疾病的危险期。
2)选择性疑问从句
选择性疑问从句由关联词if/whether…or或whether…or not构成,例如:
Please tell me whether / if they are Swedish or Danish. 请告诉我他们是瑞典人还是丹麦人。
I don't care whether you like the plan or not.我不在乎你是否喜欢该计划。
if和whether的区别:
1、 在动词不定式之前只能用whether 。如:
例8 I can’t decide whether to stay. 我不能决定是否留下。
2、 在whether …… or not 的固定搭配中。如:
例9 I want to know whether it’s good news or not . 我想知道是否是好消息。
3 、在介词后,只能用whether。如:
例10 His father is worried about whether he lose his work . 他的父亲担心是否会失去工作。
4、宾语从句放在句首表示强调时,只能用whether 。如:
Whether this is true or not, I really don’t know. 这是否真的,我真的不知道。
(例11 Whether they can finish the work on time is still a problem . 他们是否能准时完成这项工作还是个问题。--此例为主语从句,有误,感谢指出)
5、用if会引起歧义时,只用whether。如:
例12 Could you tell me if you know the answer ?
这句话有两种意思:“你能告诉 我是否知道答案吗?”或“如果你知 道答案,请告 诉我,好吗?”。如用whether可避免 歧义。
否定转移
1) 将think, believe, suppose, expect, fancy, imagine等动词后面宾语从句的否定词转移到主句中,即主句的谓语动词用否定式,而从句的谓语动词用肯定式。
I don't think I know you. 我想我并不认识你。
I don' t believe he will come. 我相信他不回来。
注意:若谓语动词为hope,宾语从句中的否定词不能转移。
I hope you weren't ill. 我想你没有生病吧。
2) 将seem, appear 等后的从句的否定转移到前面。
It doesn't seem that they know where to go.
看来他们不知道往哪去。
It doesn't appear that we'll have a sunny day tomorrow.
看来我们明天不会碰上好天气。
3) 有时将动名词,介词短语或整个从句的否定转变为对谓语动词的否定。
I don't remember having ever seen such a man.
我记得从未见过这样一个人。 (not否定动名词短语 having…)
It's not a place where anyone would expect to see strange characters on the street.
在这里,人们不会想到在街上会碰上陌生的人。
(anyone 作主语,从句中的谓语动词不能用否定形式。)
4) 有时状语或状语从句中否定可以转移到谓语动词前。
The ant is not gathering this for itself alone. (否定状语) 蚂蚁不只是为自己采食。
He was not ready to believe something just because Aristotle said so. (否定because状语) 他并不因亚里斯多德说过如何如何,就轻信此事。
She had not been married many weeks when that man's younger brother saw her and was struck by her beauty. (否定状语many weeks) 她结婚还不到几个星期,这个人的弟弟就看见她了,并对她的美貌着了迷。
名词性从句指人用什么
在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词性从句 (Noun Clauses)。 名词性从句的功能相当于名词词组, 它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词性从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连词(5个):that (宾语从句或表语从句中"that"有时可以省略)
whether,if (均表示“是否”表明从句内容的不确定性)
as if ,as though (均表示“好像”,“似乎”)
以上在从句中均不充当任何成分
连接代词(10个):what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, whose,whoseever, which, whichever
连接副词(7个):when, where, how, why, whenever, wherever, however
不可省略的连词:
1. 介词后的连词。
2. 引导主语从句和同位语从句的连词不可省略。
That she was chosen made us very happy.
We heard the news that our team had won.
3. 在从句中做成分的连词.
比较

以上就是关于0个名词性从句 ,名词性从句知识点总结的全部内容,以及10个名词性从句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

