本文目录
高中英语时态8种基本时态归纳
时态和时间是两个不同的概念。时间是一种客观存在的形式,它不依赖于任何一种特定的语言,为所有的文化共有。时态是一种语言的手段,依语言的不同而有所区别,它是属于动词的语法范畴。英语动词时态是以动词形式变化来表示句子中谈到的动作、状态的时间关系和说话的时间。因此我们可以看到时态和时间两者间虽然有关系,但不可以混淆。
The plane leaves tomorrow morning. 飞机明晨起飞。
此句中的时态为一般现在时,但是它所表示的时间却为将来(明晨)
英语动词的常用时态总共有十六种:
一般现在时 现在进行时 一般过去时 过去进行时
一般将来时 将来进行时 现在完成时 过去完成时
将来完成时 现在完成进行时 过去完成进行时
1. 一般现在时
一般现在时的形式
是以动词的原形表示的,当主语为第三人称单数时,做谓语的动词原形后要加上词尾-s or –es, 其构成方式列表如下:
情况 构成 例词
一般情况 词尾加-s Reads, writes
以ch,sh,s,x,o结尾的词 词尾加-es Teaches,washes,guesses, fixes, goes
以辅音字母+Y 结尾的词 变Y为I,再加-es Tries, carries
但是,动词to be 和to have 的一般现在时的形式特殊如下:
一般动词的词形变化 To be 的词形变化 To have 的词形变化
I know it I am a student I have a pen.
You know it. You are a student You have a pen
He (she) knows it. He (she) is a student. He (she)has a pen.
We (you,they) know it. We (you,they) are students. We (you,they) have pens.
一般现在时的功用
1. 表示一直发生的事情,经常发生的动作:
Nurses look after patients in hospitals.
Excuse me, do you speak English?
I get up at 8 o’clock every morning.
It often rains in summer in Beijing.
2. 表示客观事实或者真理:
Birds fly.
The earth goes around the sun.
3. 谈论时间表、旅程表等,如:
What time does the film begin?
The football match starts at 8 o’clock.
Tomorrow is Thursday.
4. 谈论籍贯、国籍等,如:
Where do you come from?
I come from China. 你是哪国人?我是中国人。
Where do you come from?
I come from Guangzhou. 你是哪里人?我是广州人。
5. 询问或者引用书籍、通知或新近接到的信笺内容,如:
What does that notice say?
What does Ann say in her letter?
She says she’s coming to Beijing next week.
Shakespears says, “Neither a borrower or a lender be.”
莎士比亚说:“既不要向人借钱,也不要借钱给别人。”
一般过去时
一般过去时是表示在说话时间以前发生的动作或者状态的动词时态,它是英语时态体系中最重要的时态之一。
1) 一般过去时规则动词的构成形式:
规则动词在其原形后面加-ed:
to work-worked
以字母e结尾的规则动词,只加-d:
to love---loved
对所有人称均无词形变化。
否定式均由did not + 动词原形构成
I / you / he / she / they / we did not work.
疑问式均由 did + 主语 + 动词原形 构成
拼写注意:
情况 变化 例词
动词为单音节,以一个元音字母和一个辅音字母结尾 辅音字母双写,再加-ed Stop-stoppedAdmit—admitted
以y结尾的动词,在y 前为辅音字母时 Y 变为 I ,加 – ed Carry –carriedHurry –hurried
以y 结尾的动词,在y 前为元音字母时 加—ed Obey—obeyedEnjoy---enjoyed
在英语当中有一部分动词的过去式变化形式是不规则的,这类动词被称为不规则动词。总数大概不过200多个,但是使用频率很高。主要分成三类:
1》 第一类不规则动词的三种形式同形,如:
cost cost cost
cut cut cut
hurt hurt hurt
shut shut shut
set set set
注意,有些动词的过去式与过去分词有两中形式,如:
bet bet / betted bet / betted
wed wed / wedded wed / wedded
wet wet / wetted wet / wetted
2》 第二类不规则动词的过去式和过去分词同形,如:
bend bent bent
bring brought brought
catch caught caught
hide hid hid / hidden
get got got/ gotten(AmE)
lead led led
3》 第三类不规则动词的原形、过去式和过去分词都不相同,如:
原形 过去式 过去分词
begin began begun
break broke broken
forbid forbade forbidden
grow grew grown
ring rang rung
wake woke / waked woken / waked
此外还有少数不规则动词的过去分词与原形相同,如:
come came come
become became become
run ran run
一般过去时的功用
1) 表示一个没指明具体时间的过去的行动,如:
He worked in that bank for four years. (没说明起始时间,但是现在不在那里工作了)。
They once saw Deng Xiaopin.
Did you ever hear BackStreet Boy sing?
2) 表示在过去特定的时间结束的行动,如:
When did you meet him?
I met him yesterday.
When we lived in Phoenix, we studied at Arizona State University.
Where have you been?
I’ve been to the opera.
Did you enjoy it?
3) 表示过去的习惯
He always carried an umbrella.
They never drank wine.
现在完成时的形式
现在完成时由to have 的现在时+过去分词构成:
肯定式 否定式 疑问式 否定疑问式
I have worked I have not worked Have I worked? Have I not worked?
You have worked You havenot worked Have you worked? Have you not worked?
He (she)has worked. He(she)has not worked. Has he(she) worked? Has he(she) not worked?
We(you / they) have worked. We (you / they) have not worked. Have we (you / they) worked? Have we (you / they) not worked?
紧缩形式
现在完成时的功用
现在完成时可以说成是兼有现在与过去意义的一种复合时态。它与现在有密切联系,如:
------Oh,dear, I’ve forgotten her name.
和现在的联系就是 I don’t remember her name now.
------Fort has gone to Canada.
和现在的联系就是 He is not here. He is in Canada now.
1) 表示延续到现在的动作 (有时是总计做了多少次等)。
How many times have you been to the United States?
She really loves that film. She has seen it eight times.
Tom has lived in Now York all his life.
2) 表示开始与过去而在说话时刻结束的行动,如:
I haven’t seen you for ages. 我好久没见到你了。(说话时刻已经见到了)
This room hasn’t been cleaned for months. (也许从说话开始时刻就要打扫它了)
3) 表示过去的动作对现在造成的影响,如:
The window has broken.
4) 和最高级连用,表示到现在为止是最……的
What a boring film! It’s the most boring film I’ve ever seen.
Is it a thick book?------Yes, it is the thickest book I’ve ever read.
5) 和句型 This is the first time…, It’s the first time 连用,如:
This is the first time he has driven a car.
(相当于 he has never driven a car before.)
Is this the first time you’ve been in hospital?
Professor Johnson has lost his passport again. It’s the second time he has lost it.
6) 和ever, never, yet, just, already 等副词连用,如:
Have you ever eaten French cheese?
We have never had a private car.
Has it stopped raining yet? (yet 表示期待雨停止)
Would you like something to eat?
No, thanks. I’ve just had lunch.
Don’t forget to mail the letter, will you?
I’ve already mailed it. (already 表示比预料的要快)
7)与since 连用,since 表示与某一时刻或从句连用,表示“从那一刻到说话时为止”,它总是与完成时连用,如:
She has been here since 6 o’clock.
He hasn’t been himself since the accident. (那次事故后,他从未完全康复)
Since I was a child I have lived in England.
一般过去时与现在完成时的比较
1) 过去时仅仅表示过去,现在完成时还表示与现在的关系,如:
He has lost his key.
He lost his key.
2) 与现在无关的或者过去很久的历史事件不能用现在完成时
The Chinese invented printing.
Shakespear wrote Hamlet.
3)如果说明动作有特定的过去时间,就不能用现在完成时,如:
Did you see the film on television last night?
Tom lost his key yesterday.
询问某事发生的具体时间或者地点时(when , what time, where), when , what time, where), 用一般过去时,如:
What time did they arrive?
When and where were you born?
比较:
Have you see Ann this moring? ( 说话时仍为上午)
Did you see Ann this morning? ( 说话时为下午)
Jack has lived in London for six years. 还在伦敦住
Jack lived in London for six years. 先不住伦敦了
I have never played golf in my life.
I didn’t play golf when I was on holiday last summer.
现在进行时
现在进行时是由助动词to be 的现在时 + 现在分词构成:
肯定式 否定式 疑问式
I am working.You are working.He (she) is working.We (you,they) are working. I am not working.You are not working.He (she) is not working.We (you,they) are not working. Am I working?Are you working?Is he (she) working?Are we (you,they) working?
现在分词的构成,是在动词原形上加—ing, 但是应该注意:
情况 变化 例词
动词以单个e 结尾 去掉e, 加 ing Love _lovingArgue _ arguing
动词以 —ee结尾 直接加 ing Agree_ agreeingSee _ seeing
动词为单音节:以单一元音字母 + 单一辅音字母结尾 辅音字母双写,再加 ing Hit _ hittingRun _runningStop _ stopping
动词为双音节或者多音节:最后一个音节为重读音节,以单一元音字母 + 单一辅音字母结尾 辅音字母双写,再加 ing Be’gin be’ginningAd’mit ad’mitting
以 y 结尾的动词 直接加 ing Carry carryingEnjoy enjoying
现在进行时的功用
1) 表示说话时正在发生或者进行的动作
Please don’t make so much noise, I’m studying.
Let’s get out. It isn’t raining any more.
2) 表示在现在相对较长一段时间内正在进行的动作,但是说话一刻不一定在做的动作
Have you heard about Tom? He is building his own house.
David is teaching English and learning Chinese in Beijing.
这些动作,在说话时并不一定在发生或进行,而是在包括说话的一刹那在内的一段时间内发生、进行的。
3)表示最近的确定的安排
Ann is coming tomorrow.
Oh, is she? What time is she arriving?
At 10:15.
Are you meeting her at the station?
I can’t. I’m working tomorrow morning.
以上句子也可以用be going to (do) 的形式来表示。但是谈论已确定的安排时候,用现在进行时态显得更加自然,除非受到动词的功能的限制。在此,切不可用will, 如:
Alex is getting married next month. 不能用 will get married.
4) 和always 连用表示某种情绪,可能是厌烦也可能是赞扬,如:
Tom is always going away for weekends.
My husband is always doing homework.
有些动词是表示一种状态而不是动作,一般不用于进行时。例如,我们一般不说 I am knowing, 而说 I know. 常见的这类动词有:
want like hate know see hear believe understand seem
think(相信) suppose remember need love realize mean forget prefer have (拥有)belong
To understand is to accept. 理解就是接受
Do you like Beijing?
Do you see the rainbow?
I remember him very well.
I think I understand what he wants.
一般现在时和现在进行时的比较
一般现在时表示的是一般、重复的动作或者事情
现在进行时表示说话时或说话前后正在发生的动作或事情,如:
Tom plays tennis every Sunday.
Where’s Tom? -------He is playing tennis.
What do you do? 你是干什么工作的?
What are you doing here? 你在这里干什么?
一般现在时是表示经久的情况,而现在进行时表示的是暂时的,如:
My parents live in Shanghai. They have been there for 50 years.
She’s living with some friends until she can find an apartment.
过去进行时
过去进行时的构成形式为:
I / he /she was
We / they / you were + 动词的现在分词
过去进行时的功用
1) 表示在过去某个时间后者某段时间正在进行的动作,如:
When I rang him up, he was having dinner.
This time last year I was living in Shanghai.
What were you doing at 10 o’clock last night?
2) 过去进行时和一般过去时连用,表示在一个动作发生的过程中,发生了另一个动作,如:
It was raining when I got up.
I fell asleep when I was watching television.
3) 过去一般时所说明的动作是已经完成的,而过去进行时不表示正在进行的动作一定会完成,如:
Tom was cooking the dinner.
Tom cooked the dinner.
现在完成进行时
其构成形式如下:
I / we / they have
He / she / it has been + 动词的现在分词
功用如下:
1) 表示一个在过去开始而在最近刚刚结束的行动,如:
Ann is very tired. She has been working hard.
Why are you clothes so dirty? What have you been doing?
2) 表示一个从过去开始但仍在进行的行动,如:
It has been raining for two hours. (现在还在下)
Jack hasn’t been feeling very well recently.
3) 表示一个从过去开始延续到现在,可以包括现在在内的一个阶段内,重复发生的行动,如:
She has been playing tennis since she was eight.
4) 现在完成时强调动作行为的结果、影响,而现在完成进行时只强调动作行为本身,如:
Tom’s hands are very dirty. He has been repairing the car.
The car is going again now. Tom has repaired it.
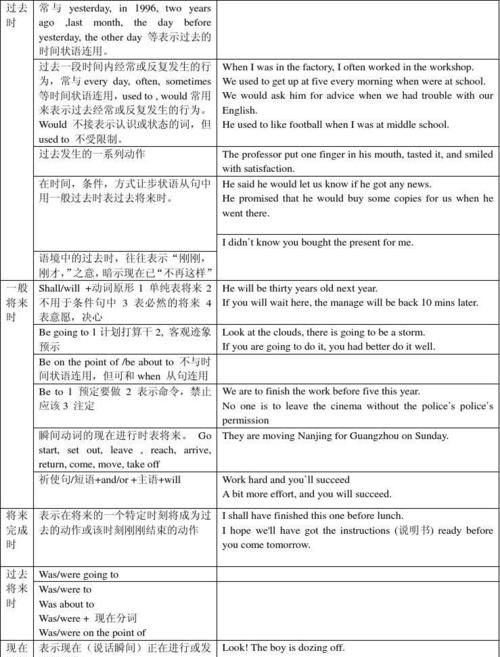
高中英语的时态有哪些
初中+高中英语语法
16种时态的详细介绍
一般现在时
1.表示现在习惯或经常反复发生的动作。常与always, usually, often, sometimes, every day (week, month)等连用。
He plays football twice a week.他每周踢两次足球。
I sometimes go to work on foot.我有时步行去上班。
2.表示现在的事实或状态。
It’s cold today.今天很冷。
You look tired now.你现在看起来很疲乏。
3. 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
I don't want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup.
I am doing my homework now.
第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。再如:Now watch me, I switch on the current and stand back. 第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。
4.表示格言或警句中。
Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round..
5.表示客观事实或普遍其理。
It’s far from the earth to the sun.地球与太阳间的距离很远。
Five and three makes eight.五加三得八。
5.表示已预先安排或计划好将来确定会发生的动作。
但主要用于go, come, leave, start, return, arrive等瞬间动词。
The train from London arrives at 7:00.从伦敦来的火车7:00到站。
He leaves on business the day after tomorrow.他后天出差。
6.在时间、让步及条件状语从句中表示将来的动作。
I’ll call you as soon as I get there.我一到那里就打电话给你。
I’ll come if he invites me.他如果邀请我我就来。
7.在以here, there开头的句子里,表示正在发生的动作。
Her comes the bus!汽车来了!
There goes the bell!铃响了!
当主语是代词时,代词必须放在动词之前。如:
There he comes!他来了!
8.某些表示心理状态和感觉的动词,如feel, love, hope, want, understand等表示现在发生的具体行为。
I feel pain in my head.我头疼。
I don’t understand what you mean.我不理解你的意思。
此时只用一般现在时而不用现在进行时。
9在由after,until,before,once,when,even if,in case,as long as,as soon as,the moment以及if,unless等引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,通常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如:
1)I will tell him the news as soon as I see him.
2)I will not go to countryside if it rains tomorrow.
10某些表示起始的动词,可用一般现在时表示按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,这类动词有:be,go,come,start,depart,arrive,begin,leave等。例如:
1)The plane leaves at three sharp.
2)The new teachers arrive tomorrow.
11在由why,what,where,whoever,who,that,as等引导的从句中,也常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如:
1)Free tickets will be given to whoever comes first.
2)You’ll probably be in the same train as I am tomorrow.
12一般现在时用于倒装句中可以表示正在发生的动作,动词以come, go为主。如:Here comes the bus. (车来了) / There goes the bell.(铃响了)。
13一般现在时常用于体育比赛的解说或寓言故事中。Now the midfield player catches the ball and he keeps it.
14一般现在时的特殊用法
a. 用于新闻标题或图片说明中
China Declares Manned Spaceflight Successful
中国宣布载人航天飞行圆满成功
Laura Bush Arrives in Moscow
劳拉·布什抵达莫斯科
b. 用于体育运动、表演等实况报道中
Francis slips past, passes the ball to Yao Ming, who jumps, catches and shoots it into the basket.
弗朗西斯穿过去,把球传给姚明,姚明跳起来,接住球投进篮里。
Now, look, I press the button and turn on the machine.
现在,看,我按下按扭,打开了这台机器。
c. 表示告诫或劝说
You mind your own business.
你不要管闲事!
If he does that again, he goes to prison.
如果他再那样的话,他就会进监狱的。
d. 表示现在瞬间的动作
Here comes the bus.
汽车来了。
There goes the bell.
铃响了。
一般过去时
1.表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去时间的副词如:yesterday, last week, two hours ago等连用。
My family moved here five years ago.我家五年前搬到了这里。
I was born in 1973.我生于1973年。
2.表示过去一段时间经常或反复发生的动作。这时可与频度副词如:often, usually, always等连用。
He always worked into night those days.那些日子他总是工作到深夜。
I often left on business in 1987.1987年我经常出差。
表示“过去经常,而今不再”时,要用used to。如:
I used to read newspaper after breakfast.
我过去经常早饭后看报纸。(意指现在已不是这样)
The children often swam in this river. 孩子们过去经常在这条河里游泳。
3.表示过去连续发生的一连串动作。
He put down the heavy box, took out the keys, and opened the door.
他放下这沉重的箱子,掏出钥匙开了房门。
过去发生的一连串动作,若用and, or, but等并列连词连接,则一律用过去式。
They moved the chairs to the table, sat down and began to have supper.
他们把椅子搬到桌边,坐下开始吃饭。
4.在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般过去时表示过去将来的动作。
He said that he would let me know as soon as he got the information.
他说他一得到消息就立即让我知道。
Mary told me that she would stay at home if it rained.玛丽告诉我如果下雨她就呆在家里。
5表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。例如:
We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film.
6表示过去习惯性动作。例如:
1)He always went to class last.
2)I used to do my homework in the library.
(注意与be used to doing短语的区别)
7,讲故事、对过去经历的回忆、双方都明白的过去事件等一般用过去时,而且经常省略时间状语。如:I happened to meet Rose in the street.(我正好在街上遇到露西)
8一般过去时的特殊用法
a. 在虚拟语气中表示现在或将来时间的动作或状态
It's time we went.
是我们该走的时候了。
I wish I were twenty years younger.
但愿我年轻20岁。
I would rather you didn't do anything for the time being.
我宁愿你暂时先不要采取什么措施。
b. 在口语中,一般过去时往往显示委婉客气。
I wondered if you could give me a hand.
我想请你帮个忙。
Might I come and see you tonight?
我想今晚来看你,好吗?
9句型:
It is time for sb. to do sth"到……时间了""该……了"
It is time sb. did sth. "时间已迟了""早该……了"
It is time for you to go to bed.你该睡觉了。
It is time you went to bed.你早该睡觉了。
would (had) rather sb. did sth.表示'宁愿某人做某事'
I'd rather you came tomorrow.
10 wish, wonder, think, hope 等用过去时,作试探性的询问、请求、建议等。
I thought you might have some. 我以为你想要一些。
比较:
一般过去时表示的动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在。
Christine was an invalid all her life.
(含义:她已不在人间。)
Christine has been an invalid all her life.
(含义:她现在还活着)
Mrs. Darby lived in Kentucky for seven years.
(含义:达比太太已不再住在肯塔基州。)
Mrs. Darby has lived in Kentucky for seven years.
( 含义:现在还住在肯塔基州,有可能指刚离去)
注意: 用过去时表示现在,表示委婉语气。
1)动词want, hope, wonder, think, intend 等。
Did you want anything else?
I wondered if you could help me.
2)情态动词 could, would.
Could you lend me your bike?
一般将来时
一般将来时是由“will / shall + 动词原形”构成的。shall只限于第一人称,主要见于英国英语,现在的趋势是第一、二、三人称的单复数形式均用will表示。在口语中,shall和will常缩写成“'ll”,紧接在主语之后。其否定式shall not 和will not 常简略为shan't 和won't。在状语从句中用一般现在时表示将来。在以第一人称为主语的问句中,常用 shall 表示提议和询问情况,在以第二人称作主语的问句中,用will 表示请求。当主语是第一人称时,用will 表示意愿.决心.允诺.命令等
(1)表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示将来的时间状语如next month, tomorrow, in a week, soon等连用。
I will go to the zoo next Sunday.下周日我将去动物园。
She’ll go to the cinema tonight.今晚她将去看电影。
注意:
在口语中,常用will / shall + be doing结构来代替will / shall + 动词原形,以表示生动。
I'll be seeing a friend off at the airport.
我要去机场给一个朋友送行。
He'll be going with us tomorrow.
他明天和我们一起去。
(2)表示将来经常发生的动作或某种必然的趋势
Some birds will fly away to the south when winter comes.
冬季来临时,一些鸟儿将飞往南方。
(3)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。例如:
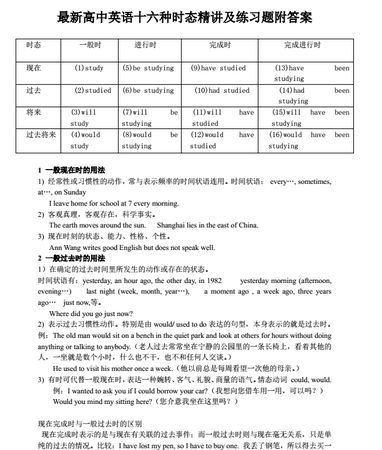
高中英语的时态有哪些
一 般
完 成
进 行
完 成 进 行
现 在
现在一般时
do
现在完成时
have done
现在进行时
is doing
现在完成进行时
have been doing
过 去
过去一般时
did
过去完成时
had done
过去进行时
was doing
过去完成进行时
had been doing
将 来
将来一般时
will do
将来完成时
will have done
将来进行时
will be doing
将来完成进行时
will have been doing
过去将来
过去将来一般时
would do
过去将来完成时
would have done
过去将来进行时
would be doing
过去将来完成进行时
would have been doing
注:构成时态的助动词be (is, am, are), have (has, have), shall, will 等需根据主语的变化来选择。
在这16种时态中,其中有8种时态是最重要的,也是用得最多的,是初学者必须要掌握的,它们是一般现在时(也称一般现在时)、一般过去时(也称一般过去时)、一般将来时(也称一般将来时)、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时、过去将来一般时(也称过去将来时),其余的时态相对用得较少。
1. 一般现在时
用法:
A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。
B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。)
D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持 主句、从句时态一致。
E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动 、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词 )可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用 。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.
(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。)
How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)
F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事 情。
例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。)
2. 现在进行时(be doing)
用法:现在正在进行的动作。
3. 现在完成时(have done)
用法:
A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses.
A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell
答案是C) haven't sold。
B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for 加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。
例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time.
A) are to challenge C) have been challenged
B) may be challenged D) are challenging
全句的意思是:“虽然牛顿是个伟大的人物,但他的许多见解直到今天还在受到挑战,并且被现代科学家的工作所修正。”challenge是及物动词,在本句中应当是被动语态;其动作延续到今天,所以要用现在完成时态。可见答案是C) have been challenged。A) are to challenge和D) are challenging都是主动语态,不可能是答案。B) may be challenged虽然是被动语态,但意思与全句内容不合,所以不对。
C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose等。
例:John has broken his left leg.(约翰摔断了左腿。)
注意事项
A) 现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带。现在完成时和过去时的区别在于:现在完成时强调动作的动态,或受动态的影响,是动态的结果,对现在有影响;过去时只表示过去的某个具体时间里发生的动作,与现在没有联系。
例:He worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他曾经在那家医院工作了8年。这只是讲述一个过去的事实,他现在已经不在那家医院了。)
He has worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他已经在那家医院里工作了8年。表示他从过去开始工作,一直工作到现在,现在仍在那家医院工作。)
B) 因为含有for加一段时间或since加一个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以不能使用终端动词或瞬间动词。
例:My sister has been married for 5 years.(过去分词做表语表示状态,可以延续)
My sister has married. Don't disturb her.(终端动词)
C) 在"this is the first/ second/ third…… time that……"句型里要求用完成时。
例:This is the second time that the products of our company have been shown in the International Exhibition.(这是我公司产品第二次参加国际展览会。)
D) 句型"It is/ has been……since"所使用的两种时态都正确。
例:It is/ has been 10 years since I last saw him.(从我上次见到他以来已经10年了。)
E) 在"no sooner than"、"hardly/ scarcely ……when"、"before"、"prior to"等句型中,主句要求完成时。
例:I haven't met that professor prior to today.(以前我从未见过那位教授。)
4. 现在完成进行时(have been doing)
用法:表示某一动作开始于过去某一时间,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。
例:We have been working on this project for over a month now.(到目前为止,我们一直在处理那个项目,已经花了一个多月时间了。)
注意事项:与现在完成时相比,现在完成进行时更强调:在从过去到现在的时间里,动作或状态一直持续或一直反复出现。
例:1997年6月四级第45 题
It seems oil ___________ from this pipe for some time. We'll have to take the machine apart to put it right.
A) had leaked B) is leaking
C) leaked D) has been leaking
从本题上下文看,这两个句子的意思是:“看来,这个管道漏油已有一段时间了,我们将不得不拆卸机器排除故障。”第二句表示将要采取的措施。第一句动作发生在第二句之前,并且延续到现在为止仍在继续。因此,空格中需用现在完成时或现在完成进行时。D) has been leaking是现在完成进行时,因此是本题的答案。有11%的考生误选了B) is leaking。由于本句有时间状语for some time,表示谓语动作延续,谓语不能用现在进行时,必须用和完成时有关的时态。有些考生误选了C) leaked或A) had leaked。是因为他们没有注意到本题第二句是一般将来时,所以第一句的谓语不能用过去时或过去完成时。
5. 一般过去时
用法:
A) 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。
B) 表示过去习惯性动作。特别是由would/ used to do表达的句型,本身表示的 就是过去时。
例:The old man would sit on a bench in the quiet park and look at others for hours without doing anything or talking to anybody.(老人过去常常坐在宁静的公园里的一条长椅上,看着其他的人,一坐就是数个小时,什么也不干,也不和任何人交谈。)
He used to visit his mother once a week.(他以前总是每周看望一次他的母亲。)
C) 有时可代替一般现在时,表达一种婉转、客气、礼貌、商量的语气。
例:I wanted to ask you if I could borrow your car?(我想向您借车用一用,可以吗?)
Would you mind my sitting here?(您介意我坐在这里吗?)
注意事项:
A) 注意时间状语的搭配。一般过去时的时间状语应该是表示过去某个时间的词或词组,如:yesterday, last month, in 1999, two days ago等,绝对不可与recently, in the past 10 years, this month等连用,因为这样的时间状语都与现在有关系,应该用现在完成时或一般现在时。
B) used to do的否定形式和疑问形式很特别:你怎么写都正确。以否定形式为例:used not to do, didn't used to do, didn't use to do都对。
Used to do经常与 be used to doing sth/ sth结构进行对比。前者表示"过去常常或过去曾经",要求加动词原形;后者表示"习惯于",要求加名词或动名词。
6. 过去完成时(had done)
用法:表示在过去的某个时间或动作以前已经发生的动作或已经存在的状态。就是我们常说的:表示"过去的过去的动作或状态"。
Until then, his family _________ from him for six months.
A) didn't hear C) hasn't heard B) hasn't been hearing D) hadn't heard
全句的意思是:“到那时为止,他家里已经有六个月没得到他的消息了。”由此可以看出,谓语动词的动作延续到过去的某一时刻才完成,因此谓语要用过去完成时。答案是D)。其它选项中:A) didn't hear,因为一般过去时只表示过去发生的事情或存在的状态,所以不能与时间状语for six months连用。B) hasn't been hearing,现在完成进行时表示过去某时刻继续到现在或现在还在进行的动作,与题意不符。C) hasn't heard,现在完成时表示从过去某一时刻到现在为止发生的动作。而题中的then只表示过去的某一时刻,不能表示现在时间。
注意事项:“过去的过去”这种逻辑关系常通过上下文体现出来,而不一定受某个时间状语的限制。
例:There had been some one in our room just now, because I noticed a burning cigarette end on the floor when we opened the front door.(刚才有人在我们的房间里,因为我们打开前门进来时,我注意到地板上有一支仍在燃烧的香烟。)
分析:虽然时间状语是just now,似乎应该使用一般过去时,但是“在房间里”这个状态是在"开门"和"注意"这两个过去的动作之前就存在的,所以应该用过去完成时。
7. 过去将来时(would/ should do)
用法:表示从过去的某个时间看将要发生的事。
例:I said on Thursday I should see my friend the next day.(我星期四说我将于第二天拜访我的朋友。)
注意事项:由于过去将来时是由过去时和将来时组合而成的,所以其注意事项可以参考过去时和将来时的相关注意事项。想学习更多英语知识,请关注口袋英语aikoudaiyy
8. 过去进行时(was/ were doing)
用法:
A) 表示在过去一个比较具体的时间正在发生的动作。
例:Mary was listening to light music 10 minutes ago.(10分钟前,玛丽正在听轻音乐。)
B) 如果when, while这样的时间状语引导词所引导的主从句之一是一般过去时,则另一个句子常用过去进行时。
例:I was washing my hair when you knocked at the front door.(你敲前门时我正在洗头发。)
注意事项:其它与将来时有关的事项请参见下面所讲的一般将来时。
9. 一般将来时
用法:
A) 基本结构是will / shall do。
例:We shall send her a glass hand-made craft as her birthday gift.(我们将送给她一个玻璃的手工制品,作为给她的生日礼物。)
B) 有些动词,如:arrive, be close, come, do, done, go, have, leave, open, play, return, sleep, start, stay等,用于一般进行时,并且通常与一个表示将来时间的时间状语连用,可以表示将来时。
例:My mother is coming to visit me next week and is staying here until May.(我妈妈下周将来看我,并会呆到5月。)
C) 表示“打算去……,要……”时,可用be going to do。
例:This is just what I am going to say.(这正是我想说的。)
D) 表示“即将、正要”时,可用be about to do。强调近期内或马上要做的事。
例:Don't worry, I am about to make a close examination on you.(别担心,我马上就给你做一次仔细的检查。)
E) "be to do"的5种用法:
a) 表示“按计划、安排即将发生某事或打算做某事”。
例:She is to be seen in the lab on Monday.(星期一你准会在实验室见到她。)
b) 该做或不该做的事情(语气上接近于should, must, ought to, have to),表示一种命令、规劝性语气。
例:You are to go to bed and keep quiet, kids. Our guests are arriving in less than 5 minutes.(孩子们,你们必须 上床睡觉,不准吵闹。我们的客人5分钟之内就要到了。)
c) 能或不能发生的事情(接近can, may)
例:How am I to pay such a debt?(我怎么可能还得起这么大的一笔债呢?)
d) 不可避免将要发生的事情,后来将要发生的事情。
例:I assure you that the matter _______ as quickly as possible. Have a little patience.
A. will be attended B. will be attended to
C. is attended D. is attended to
will be attended to关键的一点是:attend表示“处理,解决”时是不及物动词,必须与to连用。另外,从上下文看,事情显然尚未解决,所以应该用将来时的被动语态。答案是B。
e) 用于条件从句“如果……想,设想”(接近if ……want to,或if ……should)
例:Greater efforts to increase agricultural production must be made if food shortage ____________ avoided.
A) is to be B) can be C) will be D) has been
答案是A) is to be。全句的意思是:“如果要避免食品短缺,就必须作出更大努力来增加农业产量。”
F) 同样可以表示“正要、将要”的意思的句型是be on the point of doing。
例:The coach is on the point of giving up the game because our team has been scored 7 points.(教练想要放弃这场比赛了,因为对方已经射进了7个球。)
例:1999年6月四级第65题
I was _______ the point of telephoning him when his letter arrived.
A) in B) to C) at D) on
答案是D)。on the point of doing 是固定词组,意思是“正要、打算”。全句的意思是:“当他的信到的时候我正要打电话给他。”
注意事项:
在以if, when, as long as, as soon as, after, before, in case, until, unless等连词以及具有连词作用的副词(immediately, the moment, directly)等引导的状语从句,一般用现在时代替将来时。强调延续性或动态时,可用完成时。
例:I hope his health will have improved by the time you come back next year.(我希望到明年你回来的时候,他的身体已经好多了。)
10. 将来进行时(will be doing)
用法:强调在将来的某个具体时间正在发生的动作或事情。
例:Don't worry, you won't miss her. She will be wearing a red T-shirt and a white skirt at that time.(别担心,你不会认不出她的。她到时会穿一件红色的T恤衫和一条白色的短裙。)
注意事项:由于本时态是由将来时和进行时融合在一起的,所以关于本时态的注意事项,可参考"一般将来时"和"现在进行时"的有关注意事项。
11. 将来完成时(will have done)
用法:表示从将来的某一时间开始、延续到另一个将来时间的动作或状态,或是发生在某个将来时间,但对其后的另一个将来时间有影响的动作或状态。就好象把现在完成时平移到时间轴的将来时时段一样。其用法从和过去及现在有关,变成了和将来及将来的将来有关。
例:1997年1月四级第22题
The conference __________ a full week by the time it ends.
A) must have lasted B) will have lasted
C) would last D) has lasted
本题考核谓语动词的时态。全句的意思是:“会议从开始到结束将持续整整一个星期。”句中by the time it ends表示动作要延续到将来某一时刻,因此要用将来完成时。答案是B) will have lasted。如果选A),因为情态动词must后面接动词不定式的完成时形式表示对已经发生的事情的一种肯定推测,而本句的时间状语是by the time it ends而非by the time it ended,所以犯了时态不呼应的错误。Would虽可以表示推测或可能性,但would last不能表示延续到将来某一时刻的动作,所以C) would last错误。因为D) has lasted是现在完成时,表示到现在为止已经完成的动作,不能表示延续到将来某一时刻的动作,所以也不正确。
注意事项:由于本时态是由将来时和完成时融合在一起的,所以关于本时态的注意事项,可以参考“一般将来时”和“现在完成时”的有关注意事项。想学习更多英语知识,请关注口袋英语aikoudaiyy
12)将来完成进行时:shall have been doing ,will have been doing
例:By the end of next month, the project will have been being worked for 3 years. (到下个月底为止,这项工程就已经不停地进行了3年了。)(被动语态)
13)过去完成进行时:had been doing
例:The old clock had been being taken apart of and fixed up again for several times by my 10-year old son before I came back home.(我回到家之前,我10岁大的儿子已经把这个旧钟表拆卸并重新组装了好几回了。)(此处强调“拆卸”和“组装”这两个过去的过去的动作一直在反复进行。)(被动语态)
14) 过去将来进行时:should be doing , would be doing
例:The government promised that a new highway would be being built next July.(政府承诺说第二年7月将有一条新的高速公路正在修建。)(此句的时间状语是具体的将来时间,所以最好用将来进行时。)(此句为被动语态)
15) 过去将来完成时:should have done , would have done
例:I believed by the end of that year an advanced version of that software would have been developed, but I was wrong.(我坚信到那年年底为止,那个软件的新版本将被开发出来。但是我错了。)(此句为被动语态)
16) 过去将来完成进行时:should have been doing , would have been doing
例:They said that by the end of the following month, the project would have been being worked for 3 years. (他们说到第二个月底为止,这项工程就已经不停地进行了3年了。)
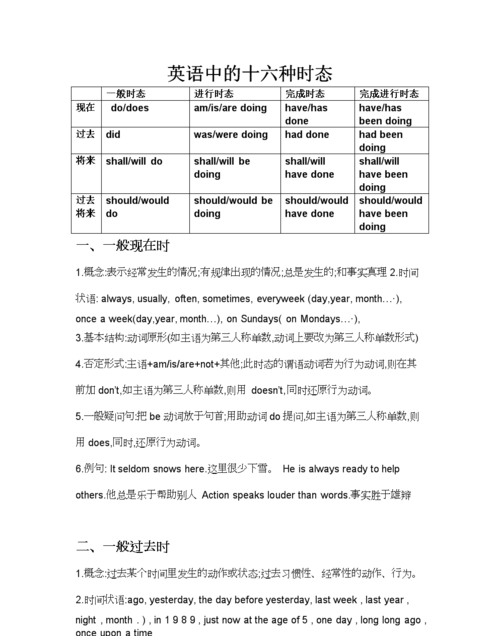
英语时态有几种
时态(Tense)是英语谓语动词的一种形式,表示动作发生时间(Time)和体态(Aspect)。所谓体态是指动作发生的方式或事物所处的状态。英语不同于汉语,表示动作发生在什么时间和以何种体态发生,主要是通过谓语动词形式本身的变化来实现的。英语中,表示动作发生的时间有四种:现在、过去、将来和过去将来;表示动作发生的体态也有四种:一般、进行、完成和完成进行。时间和体态的结合就构成了时态。英语有16种时态。但是较常用的只有十种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时和现在完成进行时。
具体的时态举例,如果16种全列上,是放不下的。建议你找比较厚一点的语法书看一下,一般都有介绍。
8.1 —般现在时(Present Indefinite Tense)
1. 表示习惯性的动作;讲话时,人或事物的特性或状态;以及客观真理等
谓语动词:除第三人称单数需要在动词后加-s外,其余人称均用原 形动词(be和have动词随着人称的不同有特殊形式)。该时态常跟有一个含有频度或现在概念的状语,如:always,never,every day等。例如:
We get up at six every morning. (习惯性动作)我们每天早上六点钟起床。
Everyone is in high spirits. (现在所处状态)大家都情绪高涨
Light travels more quickly than sound. (客观事实)光比声运行得更快。
2. 用于时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时
例如:
If it is fine tomorrow, we will go on a picnic. 如果明天是晴天,我们将去野餐。
When you come next time, bring me some magazines. 你下次来时,给我带几本杂志来。
3. 与某些具有“出发,到达”等含义的动词连用,表示按计划将要发生的动作
常用的这部分词包括:arrive,be,begin,go,leave,start,stay等。例如:
The delegation arrives in Beijing this afternoon.代表团将于今天下午到达。
There is a new film tonight.今天晚上有一个新电影。
4. 用于报刊的新闻标题中
例如:
Algerian Troops Fire on Anti-government Rioters 阿尔及利亚部队向反政府暴乱者开火
Wildlife Flourishes in Jilin Reserves 吉林保护区野生动物兴旺
8.2 —般过去时(Past Indefinite Tense)
表示过去某时间的动作或状态。谓语动词用过去式:规则动词的过去式是在原形动词后加-ed或-d;不规则动词的变化形式需要记忆(参见附录一)。该时态常跟有一个表示过去时间的状语,如:then,at that time,just now,three days ago,或一个由when,while等引导的表示过去的时间状语从句。例如:
The children went out just now. (不规则动词)孩子们刚才出去了。
She died ten years ago. (规则动词)她十年前就去世了。
【注】有时一个使用过去时的句子中并没有表示过去时间的状语,却有一个地点状语。这时,该地点状语往往暗示了动作是在过去某时间发生的。例如:
I lost my wallet at the theatre.我在剧院丢了钱包。
8.3 —般将来时(Future Indefinite Tense)
表示相对于讲话时间将要发生的动作或情况。谓语形式是shall或will加动词原形。(在英国第一人称用shall,其他人称用will;在美国各种人称均用will。)这种时态,通常跟有一个表示将来的时间状语,如soon,next week,tomorrow等。例如:
Next month, my sister will be nineteen. 下个月我妹妹将是十九岁了。
I will (或shall) return you the book as soon as possible. 我将尽快地把书还给你。
【注】表示将来时间的其他形式.
1) be going to do表示最近打算要做的事情。例如:
What are you going to do this evening? 你今天晚上干什么?
The wall is going to be painted green. 这堵墙将被漆成绿色。
有时,也用于天气情况。例如:
It is going to rain. 天要下雨了。
be going to可用于条件句表示将来时间,而will(shall)则不能。例如:
If you are going to play tennis this afternoon, you had better get your shoes prepared now. 如果你下午要打网球,最好现在就把鞋准备好。
2) be to do表示按计划要发生的事情。例如:
We are to meet at the school gate.我们约定在校门口见面。
3) be about to do结构表示“即将(正要)做某事”。例如:
Autumn harvest is about to start.秋收就要开始了。
4) 一般现在时表示根据规定、时间表要发生的动作(参见本讲 8.1-3)
5) 现在进行时表示按计划、安排即将发生的动作(参见本讲8.5-2)
8.4 一般过去将来时(Past Future Indefinite Tense)
表示在过去某一时刻之后将要发生的动作或情况。多用于主句谓语动词是一般过去时的宾语从句中。其形式由will或shall的过去式would或should加原形动词构成。例如:
He said that he would get married soon. 他说他不久就要结婚了。
I asked him when he would come here again. 我问他何时再到这儿来。
【注】和一般将来时一样,一般过去将来时也有其他相应的表达形式,如 was (were) going to do等。例如:
He said that he was going to try again. 他说他要再试试。
8.5 现在进行时(Present Continuous Tense)
由be的适当形式(am, is, are) +现在分词构成。主要用于:
1. 表示说话时,或现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的情况。
例如:
They are making an experiment now. 他们正在进行一个实验。
Professor Wang is attending a conference in Paris 王教授正在巴黎参加一个会议。
2. 表示一个按计划即将发生的动作。
但仅适用少数动词而且常跟有一个时间状语。常见的这类动词有:go,come,leave,arrive等。例如:
He is coming here next week and is staying here until August.
他将在下星期到这儿来,并且一直待到八月。
【注】 1)不用于进行时态的动词(Verb Not Used In Continuous Tenses)包括表示感觉、情感、心理状态、所有关系以及特征等状态动词一般不可用于进行时,(参见第七讲7.2)。例如:
agree(同意) belong(属于) have(有)
love(爱) remember(记得) want(想要)
appear(好像) see(看见) hear(听见)
notice(注意) seem(好像) be(是)
feel(感觉) know(知道) mind(介意)
think(认为) believe(相信) forget(忘记)
like(喜欢) realize(认识到) wish(希望)
然而,当这部分词转作其他意思使用时,有的就可以用于进行时态了。
例如:
I am seeing Mary tomorrow. 明天我将与玛丽会面。
He is thinking about the problem. 他正在考虑这个问题。
2) be的进行时态+动态形容词(Dynamic Adjective)(参见第五讲形容词5.1-2-2),有时可表示在某一相对短暂时刻人们的活动和行为。例如:
I’m just being curious. 我只是有点好奇。
Mary is being modest now. 现在玛丽倒谦虚起来了。
3) 习惯进行时(Habitual Continuous)
现在(或过去)进行时有时可与always,constantly,forever等词连用,含有感情色彩,常常用于表示某种令人不悦的情况。例如:
You are always finding fault with me. 你老是挑我的毛病。
John is forever losing things. 约翰总是丢三落四的。
8.6 过去进行时(Past Continuous Tense)
表示过去某时刻或某阶段正在进行的动作。谓语形式:由was (were) +现在分词构成。通常有一个表示过去时间的状语。例如:
We were talking about you a moment ago. 我们刚才谈到你呢。
I was playing the piano when she came in. 她进来的时候,我正在弹钢琴。
【注】过去进行时还常常用于对故事中情节的描述。例如:
It was a dark night and a strong wind was blowing.那是一个漆黑的夜晚,风在呼呼地刮着。
8.7 将来进行时(Future Continuous Tense)
谓语形式:由shall或will + be +现在分词构成。
1. 主要表示在将来某一时刻或某一段时间正在进行的动作。
例如:
What will you be doing this time tomorrow? 明天这个时候,你在干什么?
We will be having a meeting from 3 to 4 this afternoon. 今天下午三点到四点,我们要开会。
2. 有时也可表示预料不久就要发生或势必要发生的动作。
例如:
I believe he’ll be coming soon.我想他马上就会到的。
I will be seeing a friend off this afternoon. 今天下午我要去送一个朋友。
8.8 现在完成时(Present Perfect Tense)
谓语形式:由have(has)+过去分词构成。主要有两个用法:
1. 表示过去发生的但对现在有影响的动作。
这时,可以不用时间状语,也可和一些表示不定过去的时间状语连用,常见的有already,yet,never,before,recently,just,ever,once等。例如:
I have been to Peking many times. 我多次去过北京。
They have already published the results of their experiments. 他们已经发表了实验的结果。
2. 表示从过去某时间开始一直延续到现在(可能还要继续下去)的动作。
常用于含有延续意义的动词,并且一般要跟一个表示一段时间的状语,如since,for two years,so far,in recent years等。例如:
He has lived here since 1949. 自从1949年以来,他一直住在这儿。
I have studied English for two years. 我学英语已经两年了。
【注】 1) 含有界限意义的动词(Terminative Verb)如:begin,end,die,lose,find,fall,go,come,join等,以及含有瞬间意义的动词(Momentary Verb)如:knock,jump,strike,hit等,不能用于完成时的第二种用法。(参见第七讲7-2)例如:
不可说:He has joined the army for ten years.
应该说:He has been an armyman for ten years.
或者说:It is (has been) ten years since he joined the army.
或者说:He joined the army ten year ago.
译文:他参军已经有十年了。
2) It is (has been)... since这一结构也常用于现在完成时。例如:
It is (= has been) a long time since they last met each other. 自从他们上次见面以来,已有很长时间了。
3) 在“This is the first (second) time that... ”句型中,从句中常用完成时态。例如:
Is this the first time that you have visited Hong Kong? 这是你第一次参观香港吗?
This is the second time that I have broken a cup this year. 这是我今年第二次打坏茶杯了。
4) 在when和where引导的疑问句中,一般不用现在完成时(“Where have you been?”除外),因为这类句子询问的要点就是事情发生的具体时间和场合。例如:
----When did you see him? 你什么时间看见他的?
----I saw him an hour ago. 我是一小时以前看到他的。
----Where did you buy the book? 你在哪儿买的这本书?
----I bought the book at our school book store. 在学校书店买的。
5) 现在完成时和一般过去时的区别
(1) 两者都可表示过去发生过的动作,但是前者表示的是过去动作对现在的影响,而后者则是表示过去动作的事实。试比较:
He has gone to Peking.他到北京去了。 (意思是人已不在这里)
He went to Beijing (last week). 他(上星期)到北京去了。(意思是动作发生在上周,人现在或许已回来。)
(2) 两者都可表示过去开始并延续了一段时间的动作,现在完成时含义为该动作仍在继续,而一般过去时则说明该动作现早已终止。试比较:
My uncle has lived in Rome for four years. 我叔叔在罗马住了四年了。(现在仍在那儿住)
My uncle lived in Rome for four years. 我叔叔在罗马住了四年。(现在不住在那儿了)
8.9 过去完成时(Past Perfect Tense)
谓语形式:由had+过去分词构成,表示在过去某一时刻以前已经完成的动作,常用一个由by,before等介词或连词引导的、表示到过去某一时间为止的时间状语。这一时态,常用于宾语或定语从句中。例如:
John had learned some Chinese before he came to China. 约翰来中国以前,学过一些汉语。
By the end of last year, I had worked in this college for ten years. 到去年年底为止,我在这所学院工作已有十年了。
He found the book that he had lost. 他找到了他丢失的那本书。
过去完成时也常用在“no sooner…than”,和“ hardly…when (before)”等句型的主句中,从句中常用一般过去时。“no sooner”“hardly (scarcely)”移至句首表示强调时,要求用倒装语序(参见第十七讲17.2-2)。例如:
(1) We had no sooner reached home than it began to rain.
No sooner had we reached home than it began to rain.
译文:我们一到家,天就下雨了。
(2) He had hardly entered the office when (before) the phone rang.
Hardly had he entered the office when (before) the phone rang.
译文:他一进办公室,电话铃就响了。
【注】过去完成时和一般过去时的区别
两者都表示过去的动作,但是一般过去时表示的是相对于现在的过去时间,而过去完成时表示的是相对于过去某一时刻的过去,即过去的过去。注意不要在无过去相对时间的句子里误用过去完成时,也不要在有过去相对时间的句子里误用过去时。例如:
错误:They had finished that work yesterday.
正确:They finished that work yesterday.
译文:他们昨天完成了那项工作。
错误:All delegates arrived before 6 yesterday afternoon.
正确:All delegates had arrived before 6 yesterday afternoon.
译文:昨天下午六点以前,所有的代表都到了。
8.10 现在完成进行时(Present Perfect Continuous Tense)
现在完成进行时由have (has) + been+现在分词构成,表示动作从过去某一时间开始,一直延续到现在,可能还要继续下去,通常与表示一段时间的状语连用,如:for hours,since this morning...例如:
They have been watching television for two hours. 他们已经看了两个小时的电视了。
He has been working on this essay since this morning. 自从今天早上起他一直在写那篇文章。
【注】1) 现在完成进行时和现在完成时的区别
(1) 现在完成进行时和现在完成时的第二种(即表示动作延续)的用法相似并常常可以互换。它们的区别在于:现在完成进行时比现在完成时更强调动作的延续性,前者可以说是后者的强调形式。 试比较:
We’ve been living here for ten years.
We’ve lived here for ten years.
译文:我们在这儿住了十年了。
(2) 在不用时间状语的情况下,现在完成进行时表示动作仍在进行,而现在完成时则表示动作在过去已结束。例如:
The students have been preparing for the exam. (还在进行)学生们一直在准备考试。
The students have prepared for the exam. (已经结束)学生们对考试作了准备。
(3) 现在完成进行时一般不适用于状态动词(Stative Verb),要表示状态动词的延续,只可用现在完成时。例如:
They’ve known each other since 1970. 从1970年起,他们就相互认识了。
He has hoped that he has an opportunity to have college education. 他一直希望有机会上大学。
2) 现在完成进行时在过去场合中的变化形式是过去完成进行时(the Past Perfect Continuous Tense)。其形式为:had + been + 现在分词。例如:
She asked me what I had been doing these years. 她问我这些年在干些什么。
They were sweating all over because they had been playing basketball. 他们浑身是汗,因为他们一直在打篮球来着。
以上就是关于高中英语有几种时态和句型,高中英语时态8种基本时态归纳的全部内容,以及高中英语有几种时态和句型 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
