本文目录
初中英语从句的类型与用法
英语的复合句包括并列句和主从句两种.其中并列句是两句地位完全相同的简单句用表示并列关系的连词连接而成(例如and,or等).主从句虽然有两套主谓结构,但是其中一套是主要的,称为主句,另一套只是充当主句的某个成分,称为从句.英语从句分为宾语从句,定语从句,状语从句,主语从句,表语从句,同位语从句6种.
宾语从句和表语从句
宾语从句和表语从句是从句中较为简单的一种.这两种从句是以句子的形式代替了主句中的宾语或表语,也就是直接占据了谓语后宾语或表语的位置,比较明显.引导宾语从句或表语从句的引导词最常用的是that,以及关系代词what,which,who(whom),关系副词when,where,how,whether.
由于主从复合句中有两套主谓结构,因而要注意时态的搭配.时态搭配的原则是从句服从主句,但是可以根据情况灵活配置,不过主从句之间不出现时段断层.因而一般常见的配置组合为:
主句 现在时 过去时 将来时
从句 现在时,过去时,将来时 过去的时态 一般现在时
注:当从句的内容是客观真理时,无论主句是什么时态,从句永远用一般现在时,例:The teacher told the students that the light travels faster than the sound in the air.
定语从句
定语从句是从句充当定语的用法,引导词与时态搭配的规则与宾语从句相同.定语从句与宾语从句区分的要点是宾语从句充当主句的宾语,占据了主句中宾语的位置,而定语从句的主句结构完整,定语从句在引导词的引导下跟在被修饰的主句的主语或宾语(表语)之后,起修饰作用,而被修饰的词语称为先行词.例如:
①People don’t know who runs in the morning in the park everyday.人们不知道是谁每天早晨在公园里跑步.
②People don’t know the man who runs in the morning in the park everyday.人们不知道那个每天早晨在公园里跑步的人是谁.
在②中,主句部分People don’t know the man句子结构是完整的,the man是被从句修饰的成分,即先行词.
注意,that是引导短语从句的引导词中最灵活而且用法最多的,通常可以代替所有关系代词(which,what,who,whom),而且有几种情况必须使用that:A.先行词是不定代词时;B.先行词受形容词最高级修饰时;C.当先行词被any, few, little, no, all, much, some等词修饰时D.当先行词为序数词或被序数词所修饰时;E.当先行词被the very, the only, the last, the just, the same等修饰时;F.当先行词既包含人又包含物时当先行词是疑问代词who,which,what或主句以这些词开头时;G.当先行词为主句表语或关系代词为从句表语时.
以下两种情况一般只使用which:在“介词+关系代词”结构中先行词为“those+表事物的复数名词”时.
当先行词为时间,地点或方式名词时,就有是使用关系代词和关系副词的问题了.原则非常简单:如果从句主谓宾结构完整,就使用关系副词;如果从句主谓宾结构不完整,使用关系代词.例如:
①This is the place where they met each other for the first time.
这是他们第一次见面的地方.
②This is the place that they will never forgrt.
这是他们永远不会忘记的地方.
在①中,从句部分的主谓宾结构是完整的,因而主句中的“place”充当了从句的地点状语,所以使用了关系副词where;在②中从句中没有宾语,因而主句中的“place” 充当了从句的宾语,所以使用了关系代词that.
注意定语从句中有一类非限制性定语从句.非限制性定语从句是先行词的附加说明,去掉了也不会影响主句的意思,它与主句之间通常用逗号分开,例如:
This is the house which we bought last month. 这是我们上个月买的那幢房子.(限制性)
The house, which we bought last month, is very nice.这幢房子很漂亮,是我们上个月买的.(非限制性)
2) 当先行词是专有名词或物主代词和指示代词所修饰时,其后的定语从句通常是非限制性的,例如:
My house, which I bought last year, has got a lovely garden. 我去年买的的那幢房子带着个漂亮的花园.
3) 非限制性定语从句还能将整个主句作为先行词, 对其进行修饰, 这时从句谓语动词要用第三人称单数,例如:
He seems not to have grasped what I meant, which greatly upsets me. 他似乎没抓住我的意思,这使我心烦.
Liquid water changes to vapor, which is called evaporation. 液态水变为蒸汽,这就叫做蒸发.
说明:关系代词that和关系副词why不能引导非限制性定语从句.
状语从句
状语从句的种类最多,知识点比较零散,归纳之后有以下几种:
时间状语从句
引导词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since, till, until, the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day, the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than,hardly …when, scarcely … when
例:
I didn't realize how special my father was until I was 18.
While Tom was watching TV, his wife was reading.
No sooner had I arrived home than it began to rain.
Every time I take your advice, I get into trouble.
地点状语从句
引导词:where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere
Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
Wherever you go, you should bring the mp3 player with you.
原因状语从句
引导词:because, since, as, since, seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that, considering that, in as much as, in so much as
Now that everybody has come, let's begin our clas.
Considering that he is no more than 10 years old, his height of 1.60 m is not normal.
目的状语从句
引导词:so that, in order that, lest, in case, for fear that, in the hope that, for the purpose that, to the end that
The boss asked his secretary to give him the letter so that he could send it out himself.
The instructor raised his voice that the students at the back could hear more clearly.
结果状语从句
引导词:so … that, so… that, such … that, such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that,
He got up so early that he caught the first train.
It's such a good chance that we must not miss it.
条件状语从句
引导词:if, unless, as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, suppose that, in case that, on condition that
You will certainly succeed so long as you keep on trying.
Provided that there is no opposition, we shall call off the meeting.
让步状语从句
引导词:though, although, even if, even though, as(用在让步状语从句中 必须要倒装),while ( 一般用在句首 ),no matter …, in spite of ,the fact that, while, whatever, whoever, wherever,whenever, however, whichever
Much as I respect him, I can't agree to his proposal.
No matter how hard he tried, she could not change her mind.
比较状语从句
引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较), 特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than; not A so much as B
She is as bad-tempered as her mother.
The house is three times as big as ours.
The more you exercise, the healthier you will be.
Food is to men what oil is to machine. 食物之于人,犹如油之于机器.
方式状语从句
引导词:as, as if, how, the way
When in Rome, do as the Roman do.
She behaved as if she were the boss.
Sometimes we teach our children the way our parents have taught us.
应当注意的知识点有:
引导时间状语从句的连词
主要有when, while, as, by the time, before, after, since, till/until, as soon as等.其中when、while和as都可表示"当……时候",但用法有区别:
1) when意为"在……时;当……时",可表示"点时间"或"段时间",从句谓语可以 是终止性动词,也可以是延续性动词.例如: When I got home, he was having supper.
2) as意为"边……边……"或"与……同时",重在表示两个动作同时发生、伴随进行.as从句是终止性动词时,主句通常也必须是终止性动词.例如: They sang as they danced.
3) while只可表示"段时间",从句谓语只限于延续性动词.例如: While I was sleeping, my father came in.
引导原因状语从句的连词
原因状语从句一般由because, since, as, for引导. 注意as, because, since 和for的区别:
1) 如果原因是构成句子的最主要部分, 一般用because.because引导的从句一般不放在句子的开头.例如: I missed the train because I got up late.
注:对于以why开头的问句, 一般只能用because引导的从句来回答.
2) 如果原因已为人们所知, 或不如句子的其余部分重要, 就用as或since、since 比as稍微正式一些.as和since引导的从句一般放在句子的开头.例如:
As he was not well,I decided to go there without him.
Since this method doesn't work, let's try another.
3) for表示所说的理由是一种补充说明,因此,for引导的从句可以放在括号里,而
且for引导的从句一般不放在句子的开头.例如: I decided to stop and have lunch, for I was feeling quite hungry.
引导结果状语从句的连词
主要有so/such…that…,so that等.
1) so...that结构在某种情况下可以与enough to和too...to结构相互转换.例如:
She is so short that she can't reach the buttons of the lift.
=She is too short to reach the buttons of the lift.
2)so that也可以引导结果状语从句,意为"结果是;以致于".例如: They missed the bus so that they were late for class.
注:so that也可引导目的状语从句, 此时可用to或in order to替换, 将其改为简单句.
例如: He got up early so that he could get to school on time.
=He got up early to get to school on time.
=In order to get to school on time,he got up early .
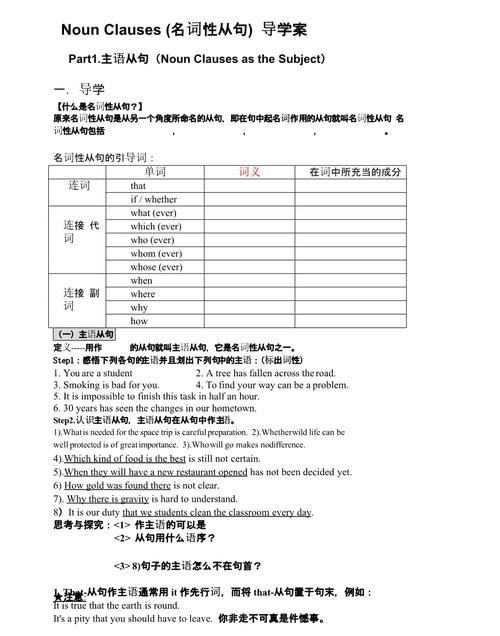
主语从句
主语从句主要有三类:
由连词that引导的主语从句. 例如:That you will win the medal seems unlikely.
你想获得奖牌看起来是不可能的.
用连接代词which或连接副词if, whether 引导的主语从句. 例如:
Which of them escaped from the prison is still a mystery.
他们哪一个是从监狱里逃跑的,仍然是个谜.
When they will come hasn’t been made pubic.
他们什么时候来还不知道.
Whether she is coming or not doesn’t matter too much.
她来不来都无关紧要.
用关系代词(what,whatever,who,whoerver)引导的主语从句.
主语从句可以直接放在主语位置上,也可以用it作形式主语, 而将从句放在句末(尤其是当谓语较短时).
当what引导的主语从句表示“…的东西”时,一般不用it作形式主语.
错:It is a book what he wants.
对:What he wants is a book. 他想要的是本书.
如果带主语从句的句子是疑问式,则必须用it作形式主语的结构.
例如:Has it been settled who will be sent to carry out the task ?
谁将被派去执行这项任务决定了吗 ?
固定用法:It is +名词+从句;It is +形容词+从句;It is +过去分词+从句;It +不及物动词+从句(当“及物动词 + 宾语”较短时,也可用这种结构);It +某些固定结构+ 主语从句.
同位语从句
在复合句中用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句.它一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容.如: I heard the news that our team had won.我听到了我们队获胜的消息.
可以跟同位语从句的名词通常有news,idea,fact,promise,question,doubt,thought,hope,message,suggestion,words(消息),possibility等.
英语中引导同位语从句的词有连词 that,whether,连接副词 how,when,where等.(注:if,which 不能引导同位语从句.)如:I have no idea when he will be back.我不知道他什么时候回来.
有时同位语从句可以不紧跟在说明的名词后面,而被别的词隔开.如:The thought came to him that maybe the enemy had fled the city. 他突然想起可能敌人已经逃出城了.
这是我教学中总结的,学生们反映还不错,有什么不明白的再问我.

八上英语unit1重点语法
一. 学习目标:
1. 学习一些单音节形容词,多音节形容词和特殊形容词的比较级和最高级形式;
2. 学习进行简单的比较,并表达自己的好恶;
二. 语言结构:
1. 用-est,the most表示最高级。
2. 不规则的形容词的比较级和最高级形式good, better, the best; bad, worse, the worst
三. 重点单词:
comfortable adj. 舒适的;安逸的
seat n. 座位
screen n. 屏;幕;荧光屏
close adj. 近的;接近的
close to 靠近;接近
quality n. 品质;特质
theater n. 剧院;戏院
cinema n. 电影院
jeans n. (pl.)牛仔裤
trendy adj. 时髦的;赶时髦的
funky adj. (俚)时髦的;极好的
radio n. 无线电;无线电广播
radio station 无线电台
FM abbr. (=Frequency Modulation)调频
AM abbr. (= Amplitude Modulation)调幅
teen n. (= teenager)(13-19岁的)青少年
bargain n. 特价商品;便宜货
delight n. 欣喜;高兴;愉快
by bus 乘坐公共汽车
positive adj. 积极的;建设性的;肯定的
negative adj. 消极的;否定的
dull adj. 乏味的;无聊的;单调的
performer n. 演员;演出者;演奏者
success n. 成功
without prep. 无;没有;缺少
province n. 省;地方
still adv. 还是;还;仍然
enough adj. 充足的;充分的
distance n. 距离;路程
farthest adj. & adv. (far的最高级)最远的(地)
四. 重点句子:
1. Town Cinema is the cheapest.
2. It has the friendliest service.
3. Movie Palace has the most comfortable seats.
4. Jason’s and Trendy Teens are good stores.
5. Trendy Teens has better service.
6. Jason’s has the best quality clothing.
7. Oldies 102.1 FM is pretty bad.
8. It’s worse than All Talk 970 AM.
9. It has the worst music.
五. 重点语法(形容词最高级)
1. 形容词比较级和最高级的规则变化:
构词法 原级 比较级 最高级
一般加er或est tall
young taller
younger tallest
youngest
以e结尾只加r或st nice
large nicer
larger nicest
largest
以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音字母时,双写该字母,再加er, est big
fat
hot bigger
fatter
hotter biggest
fattest
hottest
2. 形容词比较级和最高级的不规则变化:
原级 比较级 最高级
good better best
well better best
bad worse worst
badly worse worst
many more most
much more most
little less least
far farther
further farthest
furthest
old older
elder oldest
eldest
3. 基本用法
(1)形容词比较级用于两者(人或物)之间的比较表示其中一个“更……”或“较……”,常用连词than连接另一个所比较的人或物。如:Our classroom is bigger than theirs.
我们的教室比他们的更大。
(2)形容词最高级用于三者或三者以上的人或物之间的比较。表示其中一个在某一方面超过其他几个,其前用冠词the,后面带有in或of的短语说明比较。如:
He is the tallest in our class.
他是我们班上最高的一个。
4. 应注意的几个问题:
(1)表示“越来越……”用“比较级+and+比较级”,如:It is getting colder and colder.
天气变得越来越冷。
(2)比较级常用的修饰词有:a little, a bit, much, even, a lot 等。如:The boy is much taller than that one. 这男孩比那男孩高得多。
(3)表示“……中最……的一个”用“one of the +最高级+复数名词”。如:The river is one of the longest rivers in our coutry. 这条河是我国最长河流之一。
(4)“The +比较级……the+比较级……”表示“越……越……”。如:The more, the better. 越多越好。
(5)“the+序数词+最高级”表示“第几个最……”。如:The Yellow River is the second river in China.
黄河是我国第二长河。
(6)表示某事物之间在某一方面一样或不一样时,可以用as…as或not so (as)…as结构。如:
He is as busy as before.
他还是象以前那样忙。
My handwriting is not so good as yours.
我的书法不如你的好。
5. 参考练习:
(1)This stamp is ______ in my collection.
A. the elder B. the old C. the eldest D. the oldest
(2)The Summer Palace is _________ than Zhong Shan Park.
A. biger B. more big C. the biggest D. bigger
(3)Which is ________, Lesson Five or Lesson Nine?
A. interesting B. more interesting
C. most interesting D. the most interesting
(4)I think the movie “Titanic”is ________ one of all the movies.
A. the best B. best C. better D. a good
(5)The weather is _________ today than yesterday.
A. bad B. worse C. badder D. badly
答案:(1)D(2)D(3)B(4)A(5)B
六. 课文解析:
What do young people think about places in town? We did a survey of our readers and this is what we learned. All the movie theaters are good, but the Screen City is the best in our town. It has the biggest screens and the most comfortable seats. However, Town Cinema is the cheapest, and it has the friendliest service. The most popular clothing store is Jason’s. It has the best quality clothing. It’s also the cheapest. Funky Fashions is the worst. It has really bad service. As for radio stations, most people think that Jazz 107.9 FM is really great. It plays the most interesting music.
1. think about 表示“考虑”,“对…有某种看法”
eg: We have many things to think about.
They’re thinking about buying a new car.
What do you think about the film?
2. We did a survey of our readers and this is what we learned.
我们在读者中作了一个调查,以下是我们所得到的信息。
句中“what we learned”是“this is”的表语,是一个表语从句。
3. clothing 表示“衣服”,是衣服,服装的总称,只有单数形式,作主语时,谓语用单数形式。
eg: a factory that make children’s clothing.
Our clothing protects us from the cold.
它的同义词有: clothes, cloth.
clothes统指各种衣服,包括外套、西装、衬衣、裙、鞋等,不指单件衣服,它既不能用作单数,也不能和表示具体数目的数词连用,不能说,a clothes, six clothes,做主语时,谓语用复数形式。
eg: He had to buy many clothes.
These clothes are new.
All of her clothes were made by her mother.
cloth 指做衣服用的材料(布料,毛料,丝绸等),它是物质名词,不可数,没有复数形式。
eg: a piece of cloth “一块布料”
eg: How much cloth does it take to make a coat for the child?
七. 重难点解析:
1. close 的用法
(1)作动词,表示“关闭”,指关闭门,窗或闭合眼睛等。
turn off 也有“关闭”的意思,但指通过电键,开关或龙头来关闭电灯,电视,收音机,自来水和煤气等。
(2)作形容词,表示“近的”,“靠近的”
a cloth friend.
close to school.
Close the door, please.
2. success 是名词,表示“成功”“好结果”“及格”
eg: He met with success in his business.
I wish you success.
successful 是形容词,意思是“成功的”“顺利的”
a successful test.
They were successful in finding the way to go back home.
successfully 是副词,“成功地”,“顺利地”
He won the prize successfully in the speaking competition.
3. without 是介词,意思是“无”,“没有”,后面接名词、代词、动名词做宾语。
eg: We couldn’t finish the work without him.
He worked for 12 hours without stopping.
Can I take this book away without permission.

英语主语从句怎么写
首先在表语从句中缺主语、缺宾语、缺表语的时候是不能用which来引导从句的,此时应用what来引导.which只在宾语从句和定于从句中做引导词,在表语从句中不能做引导词
如:He has become a teacher.他已经成为一名教师.
He has become what he wanted to be ten years ago.他已经成为了他10年前想成为的.
这个时候的是become这个系动词引起的表语从句,在从句中可以这么看( )he wanted to be 这个时候从句缺少be这个词的宾语,所以应该用what而不用which,这是固定用法.
另外再告诉你一个技巧就是 【在主语从句,表语从句,宾语从句中缺主语缺宾语缺表语一律用what来引导.】这是我们老师告诉我们的,做题的时候很有帮助哦!
高中英语课堂教学设计方案
导语:高中英语课堂教学的顺利进行对于学生的升学考试,以及他们今后的英语学习和工作至关重要。教学方法的改进和创新对于提升高中英语课堂教学效果有着很大的帮助作用。然而,现阶段的高中英语课堂教学仍然存在着一些不足之处。
高中英语课堂教学的有效方法
一、用系统化进行词汇与短语教学
词汇和短语是英语学习的基础。但是大量的英语词汇给学生带去繁重的学习负担,他们甚至把词汇视为绊脚石。因为词汇和短语是零散的,所以我们可以在词汇和短语的教学过程中教授给学生一些学习方法,用联系的方法对词汇和短语进行系统化。
1.熟悉词性
我在教学过程中发现很多学生不熟悉词性,当然就搞不清短语与句子的使用了。就拿“成功”这个单词来说,它有名词success,动词succeed,形容词successful,副词successfully,这四种形式经常被同学们搞混。比如说“在某方面成功”,succeed in,可是很多学生说成success in。我们在教学的时候应该让学生们理清词性的概念。
首先,succeed是动词,而且是不及物动词,不及物动词后面不能直接加宾语,如果要加的话就加上相应的介词。还有的同学在写句子的时候也会因为词汇犯错,如翻译这样的一个句子:“汤姆是位很成功的领导。”很多同学写成:Tom succeed leader.这是个错误的句子。正确的是:Tom is a successful leader.没有把握词性就会把短语搞错,同时句子也会出错。让学生根据词性分类词汇是很有作用的,这样就可以正确使用词汇和句子。
2.用联系的方法进行短语教学
词汇可以生成短语,一词多个短语。在我们碰到学生们容易用错或记错的短语的时候,不妨它们归纳,把他们所熟悉的短语都归纳出来,便于其理解和记忆。比如当我们讲到go to school(去上学),go to the school(去学校,但不是学习)这一粗短语时,就可把和它类似的也列一些出来如:go to church(去做礼拜),go to the church(去教堂玩);at table(在桌子边吃饭),at the table(不是吃饭,坐在旁边)。又如in charge of,in the charge of;in control of,in the control of,这两组短语不带定冠词和带定冠词的意义都是一样的。
二、用具体的`公式把复合句简单化
复合句是学生理解句子和语篇的阻碍。我们可以让复合句回归到简单句的模式。我首先给学生一个简单的概念,即用从句去充当什么成分就叫什么从句,如用从句去充当定语,这个从句就叫定语从句。我还给同学们一些实例。从简单句慢慢过渡到一个复合句。
Lily is a student.
Lily is a student who works hard.
Lily is a student who is popular with all the students who are in China.
Lily is a student who is popular with all the students who are in China which is known to people all over the world.
上面的四个句子,我们可以把它进行具体的公式化,只要套用下面的结构就可以扩展定语从句,也可以把繁琐的定语从句简化成简单句。
S+LV+P
S+LV+P(S+Vi)
S+LV+P〔S+LV+P(S+LV+P)〕
S+LV+P【S+LV+P〔S+LV+P(S+LV+P)〕】
在教学过程中关于句子我总结了下面三条:
1.一个句子只能有一个谓语,谓语由动词构成。
2.如果一个句子有多个动词,只有一个是谓语动词,其他为非谓语动词。
3.如果一个句子有多个谓语,那么这个句子可能是并列句或者是复合句。如果有并列连词,就是并列句,如果没有就是复合句。且我们用谓语动词的个数减去一就是复合连词的个数。也就是说,如果有两个谓语动词那一定是一个连词出现,如果是三个谓语动词,就是两个连词出现。
例如:Who will make a decision is not important.
S=(S+Vt+O)+Vt+P
因为没有并列连词,所以是复合句。接下来,我们判断哪个是主句的谓语和从句的谓语。首先我们看到who,可是句末不是问号,所以who应该不是引导复合句的特殊疑问词而是关系词,因此who will make a decision 是从句,那么is就是主句的谓语,主句的句子结构是主系表结构,is前面就应该是句子主语。从句who will make a decision是主语,即主语从句。因此,整个句子简化成主系表结构:
The question is whether they will run out of money soon.
S+LV+P=(S+Vt+O)
因为没有并列连词,所以是复合句。接下来,我们必须判断哪个是主句的谓语和从句的谓语。首先,我们看到“whether”,它是引导名词性从句的关系词,那么“whether”引导的句子应该是名词性从句。那么“will run out of money”就是从句的谓语而“is”就是主句的谓语,即主句的句子结构是主系表结构。“is”前面的“the question”就是句子主语,后面的从句“whether they will run out of money”是表语,即表语从句。因此,整个句子还是主系表结构。
三、教会学生阅读理解的技巧
1.抓关键词
我一般要求学生在做阅读理解的时候,先把题目看一遍,这样对文章会有所了解,然后回到原文,带着问题去找答案。为了提高准确率,带着题目的关键词回到文章找答案,这样可以节省很多时间。题目的问题肯定有关键词出现,那么在关键词周围一定会有我们要找的答案。
2.找中心句
主题句一般出现在文章的开头和结尾。用归纳法撰写的文章,都是表述细节的句子在前,概述性的句子在后。此时,主题句就是文章的最后一句。通常用演绎法撰写的文章,大都遵循从一般到个别的写作程序,即从概述开始,后详细阐述。这时,主题句就是文章的第一句。有主题句往往对全文起提示、启迪、归纳的作用,主旨大意题、归纳概括题、中心思想题往往直接可从主题句中找到答案。
3.压缩句子
学生们经常会被一些很长的词和句困扰,其实很多复杂的名词是不会影响解题的,很多长的复合句也可以把它缩为简单句。如下面的句子是从一篇阅读理解中抽出来的:
Norm Pethrick,a 36-year-old man in Australia’s northern city Darwin,was praised on Thursday for jumping onto a crocodile’s back to save his wife Wendy at Litchfield National Park,a popular tourist spot southwest of Darwin.
一眼看来是非常繁琐的句子,其实个简单句。“a 36-year-old man in Australia’s northern city Darwin”是“Norm Pethrick”的同位语,“on Thursday”是说明表扬的时间,“for jumping onto a crocodile’s back to save his wife”是受表扬的原因,“at Litchfield National Park”是救人的地点,“a popular tourist spot southwest of Darwin”是“Litchfield National Park”的同位语。我们可以把它压缩成简单的句子:Norm Pethrick was praised.其他的成分都“枝叶”。
以上是我从高中英语教学中反思出的一些教学观点,只要我们在教学中不断去积累、不断去反思,我们可以把更多的教学难点简单化、具体化、系统化,让更多的学生学得轻松、学得更好。

以上就是关于表语从句导学案教学,初中英语从句的类型与用法的全部内容,以及表语从句导学案教学 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

