本文目录
英语中考必考语法知识点归纳
1.主动语态变为被动语态,主语变为介系词by的宾语,宾语变为主语,人称代名词的格也要变化。
Peter,
I
heard
he
was
hit
by
you.
(被)
Peter,
I
heard
you
hit
him.
(主)
彼得,我听说你打了他。
I
hit
him.(主)
He
was
hit
by
me.
(被)
我打了他。
2.主动语态变为被动语态,句子的时态保持不变。
I
will
give
him
a
pen.(主)
He
will
be
given
a
pen
by
me.(被)
我将给他一支笔。
3.一些与格动词的被动语态有两种形式;另一些与格动词如:write,
make,
bring等的被动语态则只能以直接宾语作主语。
A
toy
was
given
to
Tom
by
me.
(被)
Tom
was
given
a
toy
by
me.
(被)
I
will
give
Tom
a
toy.
(主)
我给汤姆一个玩具。
Tom
gave
me
a
pen.(主)
A
pen
was
given
to
me
by
Tom.(被)
I
was
given
a
pen
by
Tom.(被)
汤姆给我一枝笔。
A
big
cake
was
brought
to
me
by
you.
(被)
You
brought
me
a
big
cake.
(主)
你带给我一个大蛋糕。
She
wrote
me
a
letter.(主)
A
letter
was
written
to
me
by
her.(被)
她给我写了一封信。
write当述语动词,在此只能用直接宾语letter当被动语态的主语。
4.在感官动词或使役动词后作补语的原形动词,在被动语态中用不定词。
You
were
heard
to
talk
with
Peter.
(被)
I
heard
you
talk
with
Peter.
(主)
我听到你和彼得谈话。
I
saw
her
come
out
of
the
classroom.(主)
She
was
seen
to
come
out
of
the
classroom
by
me.(被)
我看见她出了教室。
5.主动语态中如用people,
somebody等作主语,被动语态中可省略宾语。
People
eat
watermelons
in
the
summer.(主)
Watermelons
are
eaten
in
the
summer.(被)
在夏天吃西瓜。
6.否定句的被动语态中,not放在第一个助动词后。
I
should
not
be
blamed
by
you.
(被)
You
should
not
blame
me.
(主)
你不应该责怪我。
You
should
not
write
this
letter.(主)
This
letter
should
not
be
written
by
you.(被)
你不应该写这封信。
7.疑问句的被动语态中,用BE的对应形式代替DO。
Does
she
drive
this
car?(主)
Is
this
car
driven
by
her?(被)
她开这辆车吗?
What
shall
we
do
next?(主)
What
will
be
done
by
us
next?(被)
我们下一步做什么?
8.祈使句的被动语态形式为:let+宾语+be+过去分词。
Open
the
door
please.(主)
Let
the
door
be
opened
please.(被)
请开门。
9.主动语态中有复合人称代名词时,被动语态的形式为:主动语态的主语+BE+过去分词。
Tom
was
hurt.
(被)
Tom
hurt
himself.
(主)
汤姆自己受的伤。
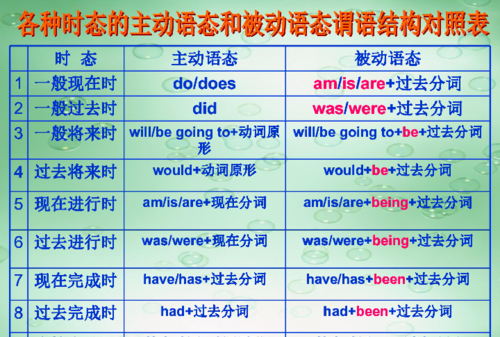
英语的被动语态结构be+过去分词
英语的被动语态结构如下:
(1)助动词+be+及物动词的过去分词
(2)情态动词+be+及物动词的过去分词
被动语态(Passive voice)是动词的一种形式,用以说明主语与谓语动词之间的关系。英语的语态共有两种:主动语态和被动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者。被动语态是动词的一种特殊形式

一般来说,只有需要动作对象的及物动词才有被动语态。汉语往往用"被""受""给"等被动词来表示被动意义 。被动语态由“be动词+及物动词的过去分词”构成。被动语态的时态变化只改变be的形式,过去分词部分不变。疑问式和否定式的变化也如此。
一般现在时、一般过去时用be +及物动词的过去分词,be有人称、时、数变。
完成时态have(has)done,被动将been加中间。一般将来shall(will)do,被动变do为be done。将来进行无被动,shall(will)be doing。现在完成时,被动 have(has)been done。现、过进行be doing,被动be加being done。
情、助、有、是妥安排,一律随新主语变。否定助后加not,疑问一助置主前。

主语恰是疑问词,直陈语序主在前。一般情助加be done,双宾多将间宾变。复合宾语宾变主,宾补、主补相应变。
英语中后面可直接加宾语的动词
有些动词可以有两个宾语,在用于被动结构时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一宾语仍然保留在谓语后面。通常变为主语的是间接宾语。 例His
mother
gave
him
a
present
for
his
birthday.
可改为
He
was
given
a
present
by
his
mother
for
his
birthday.当“动词+宾语+宾语补足语”结构变为被动语态时,将宾语变为被动结构中的主语,其余不动。 例Someone
caught
the
boy
smoking
a
cigarette.
可改为The
boy
was
caught
smoking
a
cigarette.
所以,有些动词的被动形式后边可以跟宾语,但是大部分词应该不可以跟
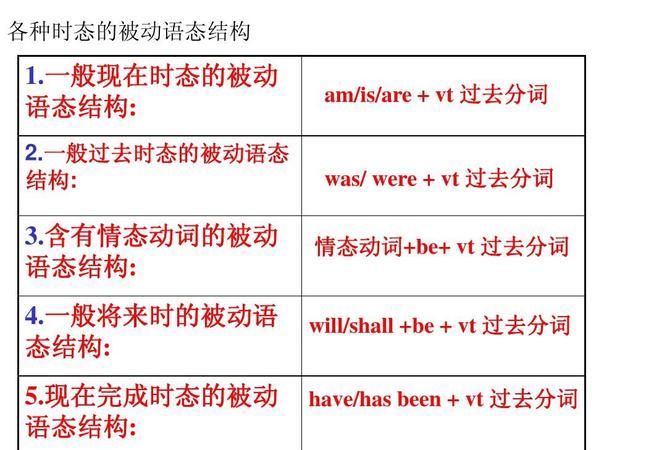
英语被动语态的结构
英语被动语态的结构
被动语态的句子是以《be动词+过去分词》的形式来表达,如果要特别强调动作或行为的执行者时,句子后面需接by,译为“被(由)……”。
1 被动语态的句型
肯定句:主语+be +过去分词+(by~).
否定句:主语+be not +过去分词+(by~).
一般疑问句:Be +主语+过去分词+(by~)?
特殊疑问句:疑问词+be +主语+过去分词+(by~)?
被动语态的时态是由be的时态决定的,be是什么时态,全句就是什么时态,be动词后面的过去分词不变。
2 被动语态的十种时态
以动词give为例,其被动语态的.各种时态构成如下:
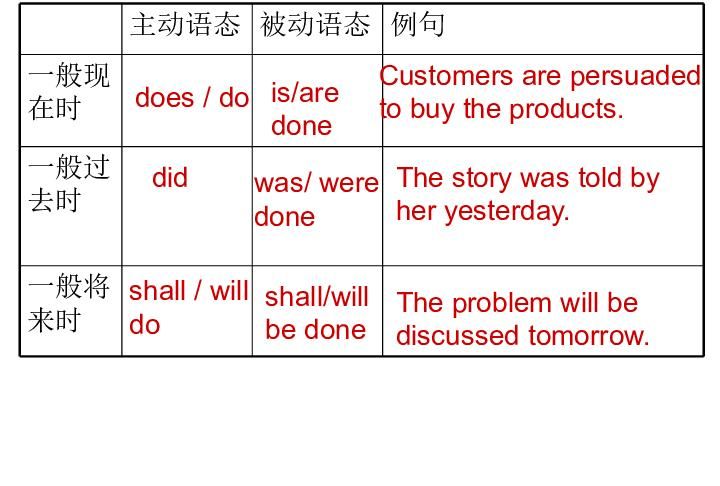
1.一般现在时
History is made by the people.
历史是人民创造的。
2.一般过去时
These new cars were made in Tianjing in 1994.
这些新车是1994年在天津生产的。
3.一般将来时
Li Ming will be asked to attend the lecture.
李明将被邀请参加讲座。
4.现在进行时
A new railway is being built.
一条新铁路正在修建。
5.过去进行时
The roads were being widened.
路那时正在加宽。
6.现在完成时
He has been sent to work in Shanghai.
他已经被派往去上海工作了。
7.过去完成时
A new hotel had been built when I got there.
我到那儿时,一座新旅馆已经建好了。
8.过去将来时
He said a new hotel would be built in two months.
他说两个月后新旅馆就会建好了的。
3 被动语态的否定句和疑问句
English is not used in European countries.
欧洲国家不使用英语。
Is English used in European countries?
欧洲国家使用英语吗?
1.否定句
凡是有be动词的句子,其否定句都是在be动词的后面加not,被动语态也不例外。
This song is not liked by young people.
这支歌不被年轻人所喜爱。
Rome was not built in a day.
罗马城不是一天建成的。
2.被动语态的疑问句
把Be动词放在句首,就构成了被动语态的一般疑问句;而疑问词+一般疑问句就构成了被动语态的特殊疑问句了。
Is Chinese used only in China?
汉语只是在中国使用吗?
Were these computers made in the U.S.A.?
这些计算机是美国制造的吗?
Yes,they were.是的。
No,they weren't.不是。
What language is spoken in China?
中国说什么语言?
Chinese.
汉语。
What was it made of?
它是什么制造的?
It was made of bamboo.
比较
各种含be动词的否定句型
I am not busy.
我不忙。(一般现在时)
She is not running.
她没在跑。(现在进行时)
There are not any books there.
那儿没有书。(一般现在时)
He is not going to visit his uncle.
他不准备去看他叔叔。(一般将来时)
Japanese is not spoken in China.
在中国不说日文。
初中英语被动语态的知识点详解
1.不及物动词没有被动语态
因为不及物动词没有宾语,所以若将其用于被动语态则没有主语,故不能用于被动语态。
但是值得注意的是,有些英语中的不及物动词,译成汉语时却可能是及物的,很容易出错,这类动词如:take place(发生),happen(发生),come about(发生),break out(爆发),appear(出现),disappear(消失),last(持续),arise(出现,发生)等:
A fire broke out during the night.夜间发生了火灾。
Influenza usually breaks out in winter.流感通常发生在冬季。
Use this money when the need arises.有需要时就使用这笔钱。
2.某些静态动词不用于被动语态
英语有些静态动词(如have, lack, fit, hold, suit, resemble等)通常不用于被动语态,如以下各句均不能变为被动语态:
My shoes dont fit me.我的鞋不合适。
The young man lacks experience.这个年轻人缺乏经验。
The hall holds 1000 people.大厅可容纳1000人。
3.宾语为相互代词和反身代词时不用于被动语态
由于相互代词和反身代词通常不能用作主语,所以当它们用作动词宾语时,句子不能转换成被动语态:
We should help each other.我们应该互相帮助。
英语被动语态知识
一、被动语态的构成形式
1. 被动语态的基本时态变化
被动语态通常为十种时态的被动形式, 被动语态由be+过去分词构成,be随时态的变化而变化。以do为例,各种时态的被动语态形式为:
1) am/is/are +done (过去分词) 一般现在时
例:Visitors are requested not to touch the exhibits.
2) has /have been done 现在完成时
例:All the preparations for the task have been completed, and we're ready to start.
3) am/is /are being done 现在进行时
例:A new cinema is being built here.
4) was/were done 一般过去时
例:I was given ten minutes to decide whether I should reject the offer.
5) had been done 过去完成时
例: By the end of last year, another new gymnasium had been completed in Beijing.
6) was/were being done 过去进行时
例:A meeting was being held when I was there.
7) shall/will be done 一般将来时
例:Hundreds of jobs will be lost if the factory closes.
8) should/would be done 过去将来时
例:The news would be sent to the soldier's mother as soon as it arrived.
9) shall/will have been done 将来完成时(少用)
例:The project will have been completed before July.
2. 被动语态的特殊结构形式
1)带情态动词的被动结构。其形式为:情态动词+be+过去分词。
例:The baby should be taken good care of by the baby-sitter.
2) 有些动词可以有两个宾语,在用于被动结构时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一宾语仍然保留在谓语后面。通常变为主语的是间接宾语。
例:His mother gave him a present for his birthday. 可改为 He was given a present by his mother for his birthday.
3) 当“动词+宾语+宾语补足语”结构变为被动语态时,将宾语变为被动结构中的主语,其余不动。
例:Someone caught the boy smoking a cigarette. 可改为The boy was caught smoking a cigarette.
4)在使役动词have, make, get以及感官动词see, watch, notice, hear, feel, observe等后面不定式作宾语补语时,在主动结构中不定式to要省略,但变为被动结构时,要加to。
例:Someone saw a stranger walk into the building. 可改为A stranger was seen to walk into the building.
5) 有些相当于及物动词的动词词组,如“动词+介词”,“动词+副词”等,也可以用于被动结构,但要把它们看作一个整体,不能分开。其中的介词或副词也不能省略。
例The meeting is to be put off till Friday.
3. 非谓语动词的被动语态
v.+ing 形式及不定式 to do 也有被动语态(一般时态和完成时态) 。
例I don't like being laughed at in the public.
二、 如何使用被动语态
学习被动语态时,不仅要知道被动语态的各种语法结构,还要知道在哪些情况中使用被动语态。
1. 讲话者不知道动作的执行者或不必说出动作的执行者 (这时可省 by 短语)。
例: My bike was stolen last night.
2. 借助被动的动作突出动作的执行者。
例:I was given ten minutes to decide whether I should accept the offer.
3. 为了更好地安排句子。
例:The well-known person got on the bus and was immediately recognized by people. (一个主语就够了)
三、 It is said that+从句及其他类似句型
一些表示“据说”或“相信”的动词如believe, consider, expect, report, say, suppose, think等可以用于句型“It+be+过去分词+that从句”或“主语+be+过去分词+to do sth.”。
有:
It is said that… 据说,It is reported that…据报道,It is believed that…大家相信,It is hoped that…大家希望,It is well known that…众所周知,It is thought that…大家认为,It is suggested that…据建议。
例:It is said that the boy has passed the national exam. (=The boy is said to have passed the national exam. )
四、谓语动词的主动形式表示被动意义
1.英语中有很多动词如break,catch,clean,drive,lock,open,sell,read,write,wash等,当它们被用作不及物动词来描述主语特征时,常用其主动形式 表达被动意义,主语通常是物。
例: This kind of cloth washes well.
注意:主动语态表被动强调的是主语的特征,而被动语态则强调外界作用造成的影响。
试比较:The door won't lock. (指门本身有毛病)
The door won't be locked. (指不会有人来锁门, 指“门没有锁”是人的原因)
2.表示“发生、进行”的不及物动词和短语,如:happen, last, take place, break out, come out, come about, come true, run out, give out, turn out等以主动形式表示被动意义。
例: How do the newspapers come out? 这些报纸是如何引出来的呢?
3. 系动词没有被动形式, 但有些表示感受、感官的连系动词feel, sound, taste, book, feel等在主系表结构中常以主动形式表示被动意义。
例Your reason sounds reasonable
五、非谓语动词的主动形式表被动意义
在某些句型中可用动名词和不定式的主动形式表被动意义 。
1. 在need,want,require, bear等词的后面,动名词用主动形式表示被动意义,其含义相当于动词不定式的被动形式。
例:The house needs repairing(to be repaired).这房子需要修理。
2. 形容词worth后面跟动名词的主动形式表示被动含义,但不能跟动词不定式;而worthy后面跟动词不定式的被动形式。
例:The picture-book is well worth reading.(=The picture-book is very worthy to be read.)
3. 动词不定式在名词后面作定语,不定式和名词之间有动宾关系时,又和句中另一名词或代词构成主谓关系, 不定式的主动形式表示被动含义。
例: I have a lot of things to do this afternoon. (to do与things是动宾关系,与I是主谓关系。)
试比较:I’ll go to the post office. Do you have a letter to be posted? ( 此处用不定式的被动语态作定语表明you不是post动作的执行者。)
4.在某些“形容词+不定式”做表语或宾语补足语的结构中,句子的主语或宾语又是动词不定式的逻辑宾语时,这时常用不定式的主动形式表达被动意义。
这些形容词有nice,easy,fit,hard,difficult,important,impossible,pleasant,interesting等。
例:This problem is difficult to work out .(可看作to work out省略了for me).
5. 在too… to…结构中,不定式前面可加逻辑主语,所以应用主动形式表示被动意义。
例:This book is too expensive (for me) to buy.
6. 在there be…句型中,当动词不定式修饰名词作定语时,不定式用主动式作定语,重点在人,用被动形式作定语,重点在物。
例:There is no time to lose(to be lost).(用 to lose可看成for us to lose;用to be lost,谁 lost time不明确。)
7. 在be to do结构中的一些不定式通常应用主动表主动,被动表被动。然而,由于古英语的影响,下列动词rent,blame,let等仍用不定式的主动形式表示被动意义。
例: Who is to blame for starting the fire?
以上就是关于英语被动语态宾语,英语中考必考语法知识点归纳的全部内容,以及英语被动语态宾语 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

