本文目录
wish后面加从句的话一定要用虚拟语气吗?
不一定的,要是wish表祝愿,祝福的话就用一般陈述句语气就可以了
如果表示与现在事情相反的话就用虚拟语气
wish后面加虚拟语气时的一般规则是什么?
wish后面所跟的宾语从句中的虚拟语气表示某种不能实现的愿望。
其主要形式有三种:
表示对现在情况的虚拟: wish + 主语 + 动词过去式或 were
表示对过去情况的虚拟: wish + 主语 + had + 过去分词
表示对将来情况的虚拟: wish + 主语 + would + 动词原形。
单词解析
1、wish
英 [wɪʃ];美 [wɪʃ]
n. 希望;祝福;心愿
vt. 祝愿;渴望;向…致问候语
vi. 愿望;需要
n. (Wish)人名;(英)威什
例:She was sincere and genuine in her wish to make amends for the past.
她诚恳而真心地希望弥补过去的错误。
例:It's a horrid experience and I wouldn't wish it on my worst enemy.
这是一次可怕的经历,我甚至不希望它发生在我仇敌的身上。

扩展资料
wish的用法
1、wish的基本意思是“希望”“想要”,指对未曾达到、难以达到或不可能达到的目标极其渴望。wish还可作“祝愿”解。
2、wish既可用作不及物动词,也可用作及物动词。用作及物动词时,后接名词、代词、动词不定式或that从句作宾语,从句中的谓语动词要用虚拟式。
3、当表示实现的可能性不大的主观设想时,从句中的谓语动词不用一般现在时,而须用一般过去时; 当表示与过去的事实相反时,从句中的谓语动词不用一般过去时,而须用过去完成时; 当表示对未来的设想时,从句中的谓语动词要用“would〔could,might〕+动词原形”结构。
4、wish引导的that从句中的主语是单数第一人称、第三人称或表示单数的名词词组时,其后的be既可以是was,也可是were。
5、wish用作不及物动词时,常与介词for连用。
6、wish是表示感情的动词,不用于被动结构。
7、wish用作名词时,意思是“渴望,希望,盼望,愿望”,指在心中形成对某物的追求,也可指“希望的事,想要的东西”。wish还可指为了达到某一目的而进行的“许愿,祈祷,祈求”。
8、wish后可接that引导的同位语从句和表语从句,从句中的谓语动词要用虚拟式,从句中可用should,也可省略should,而用动词原形。wish作“祝愿”解时,要用复数形式。
9、wish有时也可接双宾语,还可接以“(to be+) adj. ”、动词不定式或过去分词充当补足语的复合宾语。过去分词作宾语补足语时表示被动或完成意义。
wish后一定是虚拟语气吗
wish做“希望”解释的时候基本都是虚拟语气,只有做“祝福”解释的时候才有可能是标准语气。
wish从句可以不用虚拟语气吗
动词的语气——虚拟语气(The Subjunctive Mood)
一、语气的定义和种类
l、语气:语气是动词的一种形式,它表示说话人对某一行为或事情的看法和态度。
2、语气的种类:
(1)陈述语气: 表示动作或状态是现实的、确定的或符合事实的,用于陈述句、疑问句和某些感叹句。如:We are not ready. 我们没准备好。What a fine day it is!多好的天气啊!
(2)祈使语气: 表示说话人的建议、请求、邀请、命令等。如: Open the door, please。请打开门。
(3)虚拟语气: 表示动作或状态不是客观存在的事实,而是说话人的主观愿望、假设或推测等。如: If I were you, I should study English. 如果我是你,我就学英语了。May you succeed! 祝您成功!
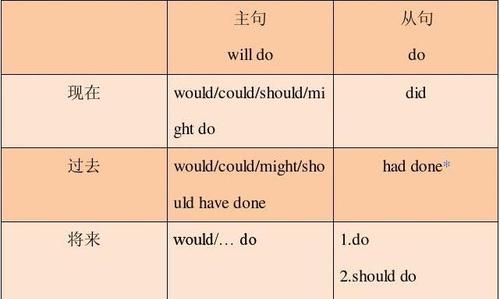
二、虚拟语气在条件从句中的用法
条件句有两类,一类是真实条件句,一类是虚拟条件句。如果假设的情况是有可能发生的,就是真实条件句。在这种真实条件句中的谓语用陈述语气。如: If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, we will go to the park. 如果明天不下雨,我们就去公园。
如果假设的情况是过去或现在都不存在的,或将来不大可能发生的,则是虚拟条件句。如: If he had seen you yesterday, he would have asked you about it. 如果他昨天见到你,他会问你这件事的。(事实上他昨天没见到你,因此也未能问你这件事。)
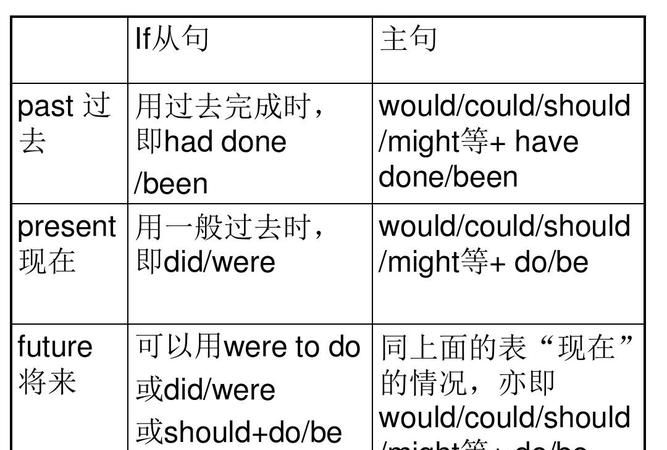
在含有虚拟条件句的复合句中,主句和从句的谓语都要用虚拟语气。现将虚拟条件从句和主句的动词形式列表如下:
与现在事实相反: 从句: 动词的过去式(be的过去式一般用were)
主句:would/ should/ could/ might + 动词原形
与过去事实相反 : 从句 :had + 过去分词
主句 :would/ should/ could/ might + have + 过去分词
与将来事实相反 : 从句:动词过去式,should + 动词原形,were to + 动词原形
主句 : would/ should/ could/ might + 动词原形
注: 主句中的should只用于I、we,但在美国英语中,should常被would代替;从句中的should可用于各种人称。
l、表示与现在事实相反的假设和结果。如: If my brother were here, everything would be all right. 要是我哥哥在这儿 ,一切都没问题了。
2、表示与过去事实相反的假设和结果。如: If you had taken my advice,you wouldn't (couldn’t) have failed in the exam. 如果你按照我的建议去做,你一定不会(不可能)考试不及格。
3、表示与将来事实可能相反的假设和结果。如: If it were Sunday tomorrow, I should (would,could,might) go to see my grandmother. 如果明天是星期天,我就 (可能)去看望我奶 奶。If it were to snow this evening, they would not go out. 如果今晚下雪,他们将不出去了。
4、有时条件从句中的动作和主句中的动作发生的时间不一致(表示错综时间的虚拟语气),这时动词的形式要根据它所表示的时间加以调整。例如: If you had listened to the doctor, you would be all right now. 如果你当初听了医生的话,身体现在就好了。(从句动作指过去,主句动作指现在)
5、虚拟条件句可以转换成下列形式:
(l)省略连词if。在书面语中,如果虚拟条件从句中有were,had 或 should,可以把if省略,把这几个词放到主语之前,构成主谓倒装。例如: Should he come (If he should come), tell him to ring me up. 他要是来了,让他给我打个电话。Were I you (If I were you), I would not do it. 我要是你,就不做这事。
(2)用介词短语代替条件状语从句。有时假设的情况并不用条件从句表示出来,而是通过介词短语来表示。如: Without air (If there were not air), there would be no living things. 如果没有空气的话,就不会有生物了。But for your help (If it hadn’t been for your help) I couldn’t have done it. 要是没有你的帮助,我就不可能完成这件事。
假设的情况有时可以通过上下文或其他方式表现出来。如: I was busy that day. Otherwise I would have gone there with them. (If I hadn’t been busy that day, I would have gone there with them.) 我那天很忙,否则,我就和他们一起去那儿了。(如果我那天不忙的话,我就……);I would have finished the work, but I have been ill. (If I hadn’t been ill, I would have finished the work.) 我本来该完成这项工作的,但我生病了。(如果我没生病的话,我就会完成……)
6、省去条件从句或主句:表示虚拟语气的主句或从句有时可以省略,但其含义仍可以推知。
(1)省去条件从句。如: You could have washed your clothes yourself. 你本可以自已洗衣服的。省去了"If you had wanted to")(事实是:你自己没洗衣服,因为你不想洗。)
(2)省去主句(常用以表示愿望)。如: If my grandmother were with me! 如果我的祖母与我在一起多好啊!(事实是:祖母已不在世。);If only she had not left! 如果她没走就好了!(事实是:她已经走了。)
三、虚拟语气的其他用法
l、虚拟语气在主语从句中的用法:在"It is important (strange,natural,necessary)that…"这类句型里,that所引导的主语从句中的谓语动词常用 “should+动词原形”结构,表示某事是"重要"、"奇怪"、"自然"、"必要"等意义。如: It is important that every member (should) inform himself of these rules. 重要的是每个成员知道这些规则。
2、虚拟语气在宾语从句中用法:
(1)在动词wish后的宾语从句中,表示与现在或过去的事实相反,或对将来的主观愿望,从句通常省略连词that。1)表示对现在情况的虚拟:从句动词用过去式或过去进行式(be动词一般用were)。如: I wish I knew the answer to the question. 我希望知道这个问题的答案。(可惜不知道);2)表示对过去情况的虚拟:从句动词常用"had+过去分词"。如: I wish (wished) I hadn’t spent so much money. 我后悔不该花那么多钱。(实际上已经花掉);3)表示对将来的主观愿望:谓语动词形式为"would+动词原形"。此时要注意,主句的主语与从句的主语不能相同,因为主句的主语所期望的从句动作能否实现,取决于从句主语的态度或意愿(非动物名词除外)。如: I wish it would stop raining. 但愿雨能停止;I wish you would come soon. 但愿你立刻来。
(2)在suggest,demand,order,propose,insist,command,request,desire等动词后的宾语从句中,谓语动词用“should + 动词原形”,表示建议、要求、命令等。如: I demand that he (should) answer me immediately. 我要求他立刻答复我。
(3)would rather之后的宾语从句,+主语+过去式表示与现在和将来的事实相反;+主语+had+动词过去分词表示与过去事实相反.
3、虚拟语气在状语从句中的用法
(1)在带有even if/ even though引导的让步状语从句的主从复合句中,主句和从句都用虚拟语气,动词形式与含有非真实条件句的虚拟语气相同。如: Even if he had been ill, he would have gone to his office. 即使生了病,他都去办公室。
(2)由as if或as though引导的状语从句表示比较或方式时。从句谓语形式为动词的过去式(be用were)或 “had+过去分词”。如: He treated me as if I were a stranger. 他那样对待我,好像我是陌
生人似的。She talked about the film as if she had really seen it. 她谈论那部影片,就好像她确实看过一样。
注:如果表示的事情可能会发生,那么方式状语从句中的谓语动词可用陈述语气。
(3)在in order that或so that引导的目的状语从句中,谓语动词多用 “could或might(有时也用should)+ 动词原形”。如: Mr green spoke slowly so that his students could (might) hear clearly. 格林先生说得很慢,好让学生听清楚。
4、虚拟语气在定语从句中的用法:在"It is time (that) …"句型中,定语从句的谓语动词常用虚拟语气表示将来,动词形式一般用过去式,意思是"该干某事的时候了"。如: It’s (high) time we did our homework. 我们该做作业了。
5、虚拟语气在简单句中的用法
(1)情态动词的过去式用于现在时态时,表示说话人的谦虚、客气、有礼貌,或委婉的语气,常见于日常会话中。如: It would be better for you not to stay up too late. 你最好别太晚睡觉。
(2)在一些习惯表达中。如: I would rather not tell you. 我宁愿不告诉你。
(3)用“may + 动词原形”表示"祝愿"、"但愿”,此时may须置于句首(多用于正式文体中)。如:May you be happy!祝你快乐!May good luck be yours.祝你顺利。
练习、虚拟语气
1. If I ____ where he lived, I ____ a note to him.
A. knew, would B. had known, would have sent
C. know, would send D. knew, would have sent
2. If they ____ earlier than expected, they ____ here now.
A. had started, would be B. started, might be
C. had started, would have been D. will start, might have been
3. I didn’t know his telephone number. ____ it, I ____ then.
A. Had I known, would ring him up B. Should I know, would have rung him up
C. If I knew; would ring him up D. Had I known; would have rung him up
4. Mary is ill today. If she _____ , she ____ absent from school.
A. were not ill; wouldn' t be B. had been ill; wouldn't have been
C. had been ill; should have been D. hadn't been ill; could be
5. Were I to do it, I ________ it some other way.
A. will do B. would do C. would have done D. were to do
6. I ________ him the answer ________ possible, but I was so busy then.
A. could tell; if it had been B. must have told; were it
C. should have told; had it been D. should have told; should it be
7. Without your help, we________ so much.
A. won ' t achieve B. didn ' t achieve
C. don't achieve D. wouldn't have achieved
8. You didn't take his advice. ________ his advice, you ________ such a mistake.
A. Had you taken; wouldn't have made B. If you had taken; would make
C. Were you lo take; shouldn t have made D. Have you taken; won t have made
9. We wish we ____ what you did when we were at high school.
A. did B. could have done C. have done D. should do
10. She wishes she ____ to the theatre last night.
A. went B. would go C. had gone D. were going
11. Tom is very short now. His mother wishes that he ________ be tall when he grows up.
A. could B. should C. would D. were able to
12. My sister advised me that I ________ accept the invitation.
A. could B. must C. should D. might
13. He asks that he ________ an opportunity to explain why he’s refused to go there.
A. is given B. must give C. should give D. be given
14. Do you think of Wang Fang's suggestion that he ________ Mr. Li to the party?
A. will invite B. have invited C. is invited D. invite
15. I insisted that he ________ at once.
A. be gone B. go C. would go D. might go
16. Li Ming insisted that he ________ anything at all.
A. hadn ' t stolen B. shouldn ' t steal C. doesn ' t steal D. steal
17. It is quite natural that my coming late again ________ them very angry.
A. had made B. would make C. makes D. make
18. He acted as if he ________ everything in the world.
A. knew B. knows C. has known D. won't know
19. Read it aloud so that I ________ you clearly.
A. may hear B. will hear C. hear D. have heard
20. They got up early in order that they ________ they first train.
A. caught B. will catch C. might catch D. shall catch
21. I am sorry that he ________ in such poor health.
A. are B. shall be C. were D. should be
22. That is a good book. You ________ it yesterday.
A. could buy B. should buy C. should have bought D. bought
23. It is high time we ________ home.
A. will go B. would go C. have gone D. went
24. I ' d rather that you ________ home.
A. went B. have gone C. will go D. had gone
25. If only I _________ to the lecture!
A. listen B. will listen C. am listening D. had listened
26. ---- If he_____ , he ______ that food. ---- Luckily he was sent to the hospital immediately.
A. was warned; would not take B. had been warned; would not have taken
C. would be warned; had not taken D. would have been warned; had not taken
27.I didn' t see your sister at the meeting. If she _________, she would have met my brother.
A. has come B. did come C. came D. had come
28. Without electricity, human life ________ quite different today.
A. is B. will be C. would have been D. would be
29. He ________ you more help, even though he was very busy.
A. might have given B. might give C. may have given D. may give
30. If city noises _______ from increasing, people _______ shout to be heard even at the dinner table 20 years from now.
A. are not kept; will have to B. are not kept; have to
C. do not keep; will have to D. do not keep; have to
31. Mike's father, as well as his mother, insisted that he ________ home.
A. stayed B. could stay C. has stayed D. stay
32. Mr. Smith insisted that he ________ the work all.
A. had done B. have done C. did D. so
33. Jane would never have gone to the party ________ that Mary would come to see her.
A. has she known B. had she known C'. if she know D. if she has known
34. If you had enough money, what ________ ?
A. will you buy B. would you buy C. would you have bought D. will you have bought
35. If you ________ that film late last night, you wouldn't be so sleepy.
A. didn't see B. haven't seen C. wouldn’t have seen D. hadn’t seen
36. Our monitor requested that ________.
A. all the class studied more carefully the problem
B. the problem was more carefully studied
C. with great care the problem could be studied
D. all the class study the problem more carefully
37. ---- Would you have called her up had it been possible?
---- Yes, but I ________. busy doing my homework..
A. was B. were C. had been D. would be
38. His tired face suggested that he ________ really tired after the long walk.
A. had been B. was C. be D. should be
39. It is important that we ________.
A. shall close the window before we leave B. will close the window before we leave
C. must close the window before we leave D. close the window before we leave
40. I didn't know his telephone number, otherwise I ______ him.
A. had telephoned B. would telephone C. would have telephoned D. telephone
如果您认为本词条还有待完善,需要补充新内容或修改错误内容,请 编辑词条
参考资料:
1.添加一些特殊的。。。比如had hope用于虚拟语气是。。从句要用would do 的形式。。还有in case of ..for fear of ...lest..等等。。

以上就是关于wish什么时候不用虚拟语气 ,wish后面加从句的话一定要用虚拟语气吗?的全部内容,以及wish什么时候不用虚拟语气 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
