本文目录
英语的定语从句的完整的句子50个
英语的定语从句的句子总结
导语:英语的定语从句的句子哟哪些重点知识呢?以下是我为大家整理的文章,欢迎阅读!希望对大家有所帮助!

知识总结归纳
(一)定语从句的结构:在复合句中,修饰某个名词或代词的句子(做这个名词或代词的定语)叫定语从句,定语从句一般放在被修饰的名词或代词后面,被修饰的名词或代词叫做定语从句的先行词,它与定语从句之间要有一个词连接,这个词指代先行词的内容叫做关系词(关系代词或关系副词:that, which, who, whose, when, where, why)。先行词在定语从句中充当主语,宾语,时间,地点,原因状语。
结构:先行词+关系词+定语从句。
1. There she saw a wall of water that was quickly advancing towards her.
2. In Japan, someone who sees another person making the gesture will think it means money.
3. A theme park is a collection of rides, exhibitions or other attractions that are based on a common theme.
4. The park has a conservation center that helps protect marine animals and their habitats in the rivers and coastal waters of Asia.
5. Visitors can go on exciting rides where they can feel what it is like to do the things they have seen their heroes do in the movie.
6. Oprah Winfrey is a black woman whose rise to fame is an inspiring story.
(二)定语从句分为限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句:
限定性定语从句:从句对先行词进行必要的描述或说明,缺少它,则句义显得不完整,从句与先行词紧密相连。
非限定性定语从句:对先行词进行补充说明,解释,它与先行词之间有逗号隔开。
1. Before she could move, she heard a loud noise, which grew to a terrible roar.
2. Tree after tree went down, cut down by the water, which must have been three meters deep.
3. Flora, whose beautiful hair and dress were all cold and wet, started crying.
4. Their talk includes rhythm and rhyming words as well as tongue twisters, which often make the audience applaud.
(三)关系词前面可以根据定语从句的内容加上一些介词,这些关系词在介词后面常用which 或whom.
1. There was a man with whom I would have to work together and finally the manager of the company.
2. Many people who saw the film were afraid to swim in the sea when they remembered the scenes in which people were eaten by the shark.
知识重点与难点
(一)当先行词有最高级,序数词修饰,是不定代词,或是all, no, only等形式时,关系代词一般用that,而不能用which。
1. The Titanic was the largest ship that had ever been built at that time.
2. There is one thing that keeps worrying me.
(二)当先行词是表示时间,地点,原因的词时,关系词用when, where, why 还有which, that
1. I'm very glad to return to my hometown where I had lived for 10 years.
2. This is my hometown which I used to talk about to you.
3. I think I can understand the reason why he didn't tell the truth to me.
4. No one believes the reason that he gave us about his absence at the meeting.
(三)定语从句的简化表达:
1. The man who is sitting on the platform is a professor from Wuhan University.
2. The letter that was mailed last night will reach him tomorrow.
3. The question that is being discussed is very important.
4. You are welcome to a party to be given in our class at 7:45.
说明:以上的定语从句部分可以用更加简单的非谓语形式表达出来:
1. The man sitting on the platform is a professor from Wuhan University.
2. The letter mailed last night will reach him tomorrow.
3. The question being discussed is very important.
4. You are welcome to a party to be given in our class at 7:45.
说明:修饰一个名词除了后面用定语从句以外,还可以用非谓语动词形式:doing短语,done短语,being done短语,to be done短语修饰。其结构和意思如下:
1. 被修饰名词+doing短语: 正在做….的人/正在发生的事。
2. 被修饰名词+ done短语: 被…..的'人/事
3. 被修饰名词+being done短语:正在被…..的人/事
4. 被修饰名词+ to be done短语:将要被…..的人/事
(1)Do you know the man talking to my sister ?
(2)The "crazy" gesture, moving the index finger in a circle in front of the ear, means "you have a phone call" in Brazil.
(3)Did you see that car being repaired ?
(4)In a camera, the lens must be focused on the object to be photographed.
(5)The students to attend the meeting will arrive here tomorrow.
(6)Goods imported from abroad are not always better than those made in China.
(7)The Yellow River, said to be "the mother river" runs across China like a huge dragon.
总结:以上做定语的那些短语就是英语语法中所说的分词,不定式的各种形式作定语。
1. 这些短语作定语应放在被修饰名词的后面。如果单独一个V-ing或V-ed形式作定语,则可以放在被修饰名词前面。
2. 分词作定语时,其动作应与全句动作同时发生。V-ing表示主动意义和正在做,V-ed表示被动意义。being done表示正在被做的
3. 不定式作定语表示将要发生的,to be done表示将要被做的
存现句定语从句用that
不属于。
定语从句是作定语的句子,要和主语在一起,构成主从复合句。
存现句属于简单句句型的一种。
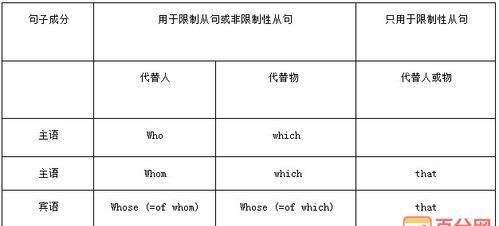
包含定语从句的英语句子
英语句子定语从句的用法
导语:英语句子定语从句的用法是什么?以下是我为大家整理的文章,欢迎阅读!希望对大家有所帮助!

一、定语从句的引导词
1、一共有9个:who, whom , whose, that, which, when,where, why, as
与名词从句相比:定从不能由what和how引导;which的含义改变;定从内部的介词可以放引导词前。
2、引导词的功能有哪些?
(1)引导定语从句
(2)代替先行词在定语从句中充当一个成分。(先行词在从句中不再出现)
二、定语从句的关键
1、首先,要能判断出该从句是什么从句:
(1)放句首没有用逗号分开的,一般是主语从句,也有可能是状语从句,但从句结束后若有体现时态变化的动词,则一定是主语从句。
(2)放及物动词后,若及物动词不是被动语态,后面一定是宾语从句;若该及物动词是被动语态,后面一般是主语从句(It+ is + adj/n./done+that/whether/when…)或状语从句。
(3)放be动词后,后面一定是表语从句,但 “It is/was + 从句(被强调成分) + that”是强调句(强调句中“非谓语”)。
(4)放名词后,一般是定语从句,但若该名词有“内涵/内容”(fact/truth/news/information/ problem/suggestion), 则很可能是同位语从句。
(5)用逗号分开的从句,一般是状语从句或 as/which引导的定语从句,也要注意用放在句中用逗号分开的“插入语”(however, for example,believe it or not等)。
2、其次,判断出是定语从句后可以用“三个优先”法做题:
(1)优先选择含whose的选项,能与空格后的名词构成“某人的某物”搭配,一般就是答案;
(2)优先选择含介词的选项,然后看该介词与从句中的谓语是否能构成符合逻辑的搭配;
(3)用逗号分开的定从,优先考虑as和which,若该空能翻译为“一件事”而从句意思是通顺的,则放句首就用as,句末用which(若该空能翻译为“如同”“像…一样”则应用as)
3、再次,做定语从句题可以用“三问法”来检测是否出错:
(1)先行词本身是否为特殊的词?
way+ in which/that/省略
指物的不定代词:anything, one, some,many, a lot, all, both, that等 + that
指人的不定代词或数词:one, those, anyone, two等 + who
既有人又有物: + that
“抽象的地点”condition, situation,case, point + where
“抽象的时间”one’s stay/visit + when
在特定语境中可以作“地点/位置”理解的词:trousers/ sleeves + where
(2)先行词前面有无特殊的词?
有不定代词修饰:all/every/little/much+ …+ that
有最高级/序数词修饰:the best/second … + that
有just the/ the very/ the only/ the last等修饰:+ that
有who/which疑问词:+ that(避免重复)
有the same/ such/ as修饰:一般+ as
(注意: ①第一个as是否为一个以as结尾的搭配,如regard…as;
②区分such…as(定从)与such …that“如此…以至于”)
(3)先行词在定语从句中充当什么成分?
注意:从句中spend后的“时间”,以及visit后的“地点”,不是状语,而是宾语,应该用不定代词
4、只能用that引导定语从句有哪些情况?
先行词前为all, everything, nothing,something, anything, little, much等不定代词时;
先行词前有:all, every, no, some, any,little, much, few等不定代词修饰时;
先行词被序数词修饰时;
先行词被形容词最高级修饰时;
先行词前only, just, very, last有等修饰时;
先行词是表示人和物混杂的两个名词时;
主句是以who, which,开头的疑问句或先行词是疑问代词时;
在修饰时间、地点等先行词时,只有用that代替when, where等引导词;
【例】I'll never forget the Sunday (that) you first arrived.
Do you know anywhere (that) I can get a drink ?
先行词为reason, way (意为“方法”)时,常用that 代替why,which, in which,也可省略。
引导词在定语从句中作表语时,多用that引导。
先行词是主句表语时;
【例】It is a dictionary that will help you a lot.
当主语以there be 开头时;
当先行词是数词时;
同一个复合句里有两个定语从句,一个用which,另一个通常用that。
5、reason后面用什么引导?way 后面用什么引导?
reason后面的定语从句用why引导。
way 后面定语从句用in which 或 that引导that可以省略。
6、when引导的定语从句等于什么引导的`定语从句?
when引导的定语从句等于介词+ which引导的定语从句。
7、where 引导的定语从句等于什么引导的定语从句?
where 引导的定语从句等于介词+which引导的定语从句。
★8、one of 和 the (only) one of引导的定语从句在主谓一致问题上应注意什么?
前者引导的定语从句谓语动词用复数;后者用单数。
9、限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句有和区别?
限制性定语从句是主句不可缺少的一个部分,缺少后主句意思不完整。非限制性定语从句是对主句的进一步说明,不要从句对主句意义无多大影响;非限制性定语从句前后有逗号隔开。而且非限制性定语从句中不能用that。
10、as 和which引导的非限制性定语从句在用法上有什么区别?
as和 which 都可以引导非限制性定语从句.都可以代替主句中的整个内容或某一成分。
as 引导的非限制性定语从句可以位于句首,并常和know, see, expect等词连用,意为:“正如……”,而which不能位于句首。
11、as 可以用于哪些结构中引导定语从句?
such... as; the same... as; so ...as..
12、the same…as和 the same…that 引导的定语从句如何区别?
the same…as 引导的定语从句指的是相同事物,强调同类。
the same…that引导的定语从句指的是同一物。
13、such…as …和 such…that…如何区分?
such…as…引导的是定语从句,as必须代替先行词在其引导的从句中充当成分。
such…that…引导的从句是状语从句,that只是引导从句并不在其引导的从句中充当成分,在选择填空首先看从句中是否缺句子成分,如果缺成分就要考虑是定语从句;如果不缺成分就要考虑是状语成分。
★14、whose 引导定语从句有那些注意点?
whose 作定语,后面跟名词。一般有三种表示形式:
【例】This is the dictionary whose cover has come off.
= This is the dictionary the cover of which has come off.
= This is the dictionary of which the cover has come off.
★★★15、 “介词 + 关系词” 开头的定语从句有哪几种情况?
注意:引导定从的介词后不能加who/that
(1)先行词在从句中做状语,用来替换when/where/why的:in/on/from/for/in front of + which/whom:
(2)“of所有格”: the+名词+ of + which/whom; of + which/whom +… the+名词
(3)“某个范围中的多少”: some/both/the former + of + which/whom; of + which/whom … some…
(4)偶尔可用“介词+ whose”和“介词+where”
三、关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词所代替的先行词是人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。
1、who指人,在从句中做主语
The boys who are playing football are from Class One.
2、whom指人,在定语从句中充当宾语,常可省略。
Mr. Liu is the person (whom)you talked about on the bus.
【注意】关系代词whom在口语和非正式语体中常用who代替,可省略。
The man who/whom you met just now is my friend.
3、which指物,在定语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略
Football is a game which is liked by most boys.
4、that指人时,相当于who或者whom;指物时,相当于which。在定语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略。
The number of the people that/who come to visit the city each year rises one million.
5、whose通常指人,也可指物,在定语从句中做定语
He has a friend whose father is a doctor.
whose指物时,常用以下结构来代替:
The classroom whose door is broken will soon be repaired.
=The classroom of which the door is broken will soon be repaired.
Do you like the book whose cover is yellow?
=Do you like the book the color of which is yellow?
(注意:the + 名词 + of which/whom常考!)
英语中定语修饰什么语
定语从句就是一个从句在整个句子中充当定语的成分
宾语从句就是一个从句在整个句子中充当宾语的成分
状语从句就是一个从句在整个句子中充当状语的成分
定语从句
(一)、定义:在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫做定语从句。
定语 定语用来限定、修饰名词或代词的,是对名词或代词起修饰、限定作用的词、短语(动词不定式短语、动名词短语和分词短语)或句子,汉语中常用‘……的’表示。主要由形容词担任,此外,名词,代词,数词,分词,副词,不定式以及介词短语也可以来担任,也可以由一个句子来担任。单词作定语时通常放在它所修饰的词之前,作前置定语。短语和从句作定语时则放在所修饰的词之后,作后置定语。
定语从句是指在一个句子中作定语的句子,定语从句要放在所修饰的词后。
如:1) The man who lives next to us is a policeman.
2) You must do everything that I do.
上面两句中的man和everything是定语从句所修饰的词,叫先行词,定语从句放在先行词的后面。
引导定语从句的词有关系代词that, which, who(宾格who, 所有格whose)和关系副词where, when、why
关系词常有三个作用:1、引导定语从句 2、代替先行词 3、在定语从句中担当一个成分
(二)、关系代词引导的定语从句
1.who指人,在从句中做主语
(1)The boys who are playing football are from Class One.
(2)Yesterday I helped an old man who lost his way.
2. whom指人,在定语从句中充当宾语,常可省略。
(1) Mr. Liu is the person (whom) you talked about.
注意:关系代词whom在口语和非正式语体中常用who代替,可省略。
(3) The man who/whom you met just now is my friend.
3. which指物,在定语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略
(1) Football is a game which is liked by most boys. ( which 在句子中做主语)
(2) This is the pen (which) he bought yesterday. ( which 在句子中做宾语)
4. that指人时,相当于who或者whom;指物时,相当于which。
在宾语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略。
(5) The people that/who come to visit the city are all here. (在句子中做主语)
(6) Where is the man that/whom I saw this morning? (在句子中做宾语)
5. whose通常指人,也可指物,在定语从句中做定语
(1) He has a friend whose father is a doctor.
(2) I lived in a house whose roof has fallen in.
whose指物时,常用以下结构来代替
(3)The classroom whose door is broken will soon be repaired.
=The classroom the door of which is broken will soon be repaired.
(5)Do you like the book whose color is yellow?
=Do you like the book the color of which is yellow?
注:that 用法
(1)不用that的情况
(a) 在引导非限定性定语从句时。
(错)The tree, that is four hundred years old, is very famous here.
(b) 介词后不能用。
We depend on the land from which we get our food.
We depend on the land that/which we get our food from.
(2) 只能用that作为定语从句的关系代词的情况
(a) 在there be 句型中,只用that,不用which。
(b) 在不定代词,如:anything, nothing, the one, all等作先行词时,只用that,不用which。
(c) 先行词有the only, the very,the same,the last,just修饰时,只用that。
(d) 先行词为序数词、数词、形容词最高级时,只用that,不能用which。.
(e) 先行词既有人,又有物时。
(f) 先行词指物,在主句中作表语时.
(g) 为了避免重复.
(h)先行词是the way或the reason时,that可作关系副词,也可省略
(i) 主句的主语是疑问词who /which时
举例:
Is this the book that you borrowed in the library?
这是你在图书馆借的那本书吗?
Who that break the window should be punished.
谁打碎了窗户都要受到惩罚.
All that is needed is a supply of oil.
所需的只是供油问题。
Finally, the thief handed everything that he had stolen to the police.
那贼最终把偷的全部东西交给了警察。
(三)、关系副词引导定语从句
关系副词 关系副词:在句中作状语
关系副词=介词+关系代词
why=for which
where=in/ at/ on/ ... which (介词同先行词搭配)
when=during/ on/ in/ ... which (介词同先行词搭配)
1. where指地点,在定语从句中做地点状语用来表示地点的定语从句。
(1) Shanghai is the city where I was born.
(2) The house where I lived ten years ago has been pulled down.
2. when引导定语从句表示时间。在定语从句中做时间状语也可做连接词用
(1) I still remember the day when I first came to the school.
(2) The time when we got together finally came.
[注]表示时间“time"一词的定语从句只用when引导,有时不用任何关系代词,当然也不用that引导。
By the time you arrived in London, we had stayed there for two weeks.
到你到达伦敦的时候,我们在那里已经待了两个星期。
I still remember the first time I met her. 我仍然记得我第一次见到她。
Each time he goes to business trip, he brings a lot of living necessities, such as towels, soap, toothbrush etc。
每一次他去出差,他带来了生活必需品,如毛巾,肥皂,牙刷等,很多。
3. why指原因 在定语从句中做原因状语
(1) Please tell me the reason why you missed the plane.
(2) I don’t know the reason why he looks unhappy today.
注意:关系副词引导的从句可以由“介词+关系代词”引导的从句替换
(1) The reason why/ for which he refused the invitation is not clear,
(2) From the year when/in which he was going to school, he began to know what he wanted when he grew up.
注:1)介词后面的关系代词不能省略。
2)that前不能有介词。
3) 某些在从句中充当时间,地点或原因状语的"介词+关系词"结构可以同
关系副词when ,where和why 互换。
This is the house in which I lived two years ago.
This is the house where I lived two years ago.
Do you remember the day on which you joined our club?
Do you remember the day when you joined our club?
This is the reason why he came late.
This is the reason for which he came late.
宾语从句
(一) 宾语从句的种类
宾语从句是一种名词性从句,在句中作及物动词的宾语,或介词的宾语,或形容词的宾语。根据引导宾语从句的不同连词,宾语从句可分为三类。
1. 由that引导的宾语从句。that只有语法作用,没有实在的意义,在口语
和非正式文体中可以省略。例如:
He said (that) he wanted to stay at home.
She doesn’t know (that) she is seriously ill.
I am sure (that) he will succeed.
2. 由连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which和连接副词when, where, why, how引导的宾语从句。这些连接代词和连接副词在宾语从句中充当某个成分。例如:
Do you know who (whom) they are waiting foe?
He asked whose handwriting was the best.
Can you tell me where the No.3 bus stop is?
I don’t know why the train is late.
3. 由if或whether引导的宾语从句。if和whether在句中的意思是“是否”。例如:
I want to know if (whether) he lives there.
He asked me whether (if) I could help him.
(二)宾语从句的语序
宾语从句的语序应为陈述句的语序。例如:
I hear (that) physics isn’t easy.
I think (that) you will like this school soon.
Can you tell me how I can get to zoo?
Please tell me when we’ll have the meeting.
(三)宾语从句的时态
1. 如果主句的时态是一般现在时,宾语从句该用什麽时态就用什麽时态。
如: I don’t think (that) you are right.
Please tell us where he is.
Can you tell me how I can get to the railway station?
2. 如果主句的时态是一般过去时,宾语从句只能用相应的过去时态(一般过去时, 过去进行时, 过去将来时,过去完成时)。例如:
He asked what time it was.
He told me that he was preparing for the sports meet.
He asked if you had written to Peter.
He said that he would go back to the U.S. soon.
3. 如果宾语从句所陈述的是客观真理,其时态常用一般现在时。例如:
Our teacher said that January is the first month of the year.
Scientists have proved that the earth turns around the sun.
状语从句
状语从句
状语从句用来修饰主句中的动词,副词和形容词的从句叫状语从句。根据其含义状语从句可分为时间状语从句,地点状语从句,条件状语从句, 原因状语从句,结果状语从句,比较状语从句,目的状语从句,让步状语从句。
1. 时间状语从句
(1)时间状语从句常用when, as, while, before, after, since, till, until, as soon as等连词来引导。例如:
It was raining hard(rain hard 下大雨) when got to school yesterday.
While he was doing his homework, the telephone rang.
As he walked along(沿着走) the lake, he sang happily.
He had learned a little Chinese before he came to China.
After he finished middle school, he went to work in a factory.
(2)在时间状语从句里,通常不用将来时态,用现在时态表示将来的动作或状态。例如:
I’ll ring you up as soon as I get to New York.
I will tell him everything when he comes back.
He won’t believe it until he sees it with his own eyes.
(3)在带有till或until引导的时间状语从句的主从复合句里,如果主句用肯定式,其含义是“一直到……时”,谓语动词只能用延续性动词。如果主句用否定式,其含义是“直到……才……”, “在……以前不……”, 谓语动词可用瞬间动词。例如:
The young man read till the light went out(熄灭).
Let’s wait until the rain stops.
We won’t start until Bob comes.
Don’t get off(从下来) until the bus stops.
【Till是指直到某一特定事件发生的时候,而在那个时刻之后,该事情或状况仍将持续。 Until是指直到某一特定事件发生的时候,而讲话的人在自己心里认为,在那个时刻之后,该事情或该状况将中止(不怎么可能持续)。固定组合里from morning till night,till/until是不能替换的,】
2. 条件状语从句
(1)条件状语从句通常由if, unless引导。例如:
What shall we do if it snows tomorrow?
Don’t leave the building unless I tell you to.
(2)在条件状语从句里,谓语动词通常用现在时态表示将来的动作或状态。例如:
I’ll help you with your English if am free tomorrow.
He won’t be late unless he is ill.
(3)“祈使句 + and (or)+ 陈述句” 在意思上相当于一个带有条件状语从句的复合句。例如:
Hurry up, or you’ll be late. =If you don’t hurry up, you’ll be late.
Study hard and you will pass the exam. =If you study hard, you will pass the exam.
3. 原因状语从句
(1)原因状语从句通常由because, since, as引导。例如:
He didn’t come to school because he was ill.
As it is raining, we shall not (不得;不应该)go the zoo.
Since you can’t answer the question, I’ll ask someone else.
(2)because表示直接原因,语气最强。Because引导的原因状语从句多放在主句之后。回答由why提出的问题,只能用because。As和since语气较弱,一般用来表示明显的原因。由as和since引导的原因状语从居多放在句首。例如:
------Why aren’t going there?
------Because I don’t want to.
As he has no car, he can’t get there easily.
Since we have no money, we can’t buy it.
(3)because和so不能同用在一个句子里。
4. 结果状语从句
(1)结果状语从句由so…that, such…that, so that引导。例如:
He is so poor that he can’t buy a bike for his son.
She is such a good teacher that everybody likes her.
My pencil fell under the desk, so that I couldn’t see it.
(2)so…that语such...that可以互换。例如:
在由so...that引导的结果状语从句中,so是副词,与形容词连用。其结构是: “...so + 形容词(副词)+ that + 从句”。例如:
He was so glad that he couldn’t say a word.
The hall is so big that it can hold 2,000 people.
Mother lives so far away that we hardly ever(几乎不,从来不) see her.
在由such…that引导的结果状语从句中,such是形容词,它修饰的可以是单数或复数可数名词,也可以是不可数名词;名词前面可以带形容词,也可不带。如果是单数可数名词,前面需加不定冠词a或an。例如:
It was such a hot day that nobody wanted to do anything.
He had such long arms that he could almost touch the ceiling.(天花板)
He made such rapid progress that he did very well in the mid-term.
有时上述两种结构是可以互换的。例如:
It was such a wonderful film that all of us wanted to see it again.
=The film was so wonderful that all of us wanted to see it again.
It is such an important match that nobody wants to miss it.
=The match is so important that nobody wants to miss it.
(3)如果名词前由many, much, little, few等词修饰时,只能用so, 不用such。例如:
Soon there were so many deer that they ate up all the wild roses.
He has so little time that he can’t go to the cinema(去看电影) with you.
5. 比较状语从句
比较状语从句通常由as…as, 比较级 + than…等连词引导。例如:
Tom runs faster than John does.
This classroom is as big as that one.
6. 目的状语从句
(1)目的状语从句通常由 so that, in order that(为了,以便)引导。例如:
We started early so that we could catch the first train.
He studies hard so that he could work better in the future.
We used the computer in order that we might save time.
(2)so that既可引导目的状语从句,又可引导结果状语从句。区别这两种从句的办法有两个:1)目的状语从句里往往带有情态动词can, could, may, might等。2)从意思上看,目的状语从句往往表示的目的很明确。例如:
Speak clearly so that they may understand you. (目的状语从句)
Jack is badly ill so that he has to rest. (结果状语从句)
7. 让步状语从句
(1)让步状语从句通常由although, though等连词引导。例如:
Though he is young, he knows a lot.
Although I am tired, I must go on working.
(2)although(though)不能用在同一个句子中。例如:
我们不能说:Though it was raining hard, but he still went out.
应该说:Though it was raining hard, he still went out.或It was raining hard, but he still went out.
8. 地点状语从句
地点状语从句常常由where来引导。例如:
Go where you like.
Where there is a will, there is a way.
总结:状语从句分类及常用连词:
类别 连 词
时间状语从句 when, whenever, while, as, before, after, since, till, once(一旦)
地点状语从句 where, wherever
原因状语从句 because, since, as, for, now that(既然,由于)etc. (et cetera,等于and so on)
目的状语从句 in order that(为了,以便), so that, that, etc.
结果状语从句 so…that, so that, such…that, that, etc.
条件状语从句 if, unless, as(so)long as, etc.
让步状语从句 though, although, even if, even though, however, whatever, as, etc.
比较状语从句 as…as, so…as, than, etc.
方式状语从句 as, as if, as though, etc.

以上就是关于英语存现句定语从句,英语的定语从句的完整的句子50个的全部内容,以及英语存现句定语从句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

