本文目录
状语从句从属连词分类
高中英语状语从句用法解析
一、 定义:
在句中作状语的从句是状语从句,修饰主句中的动词、形容词或副词等。状语从句由从属连词引导,从属连词在句中不充当句子成分,只起连接作用,状语从句放在句首时,要用逗号,放在句尾时不用。
二、 分类
根据意义上的不同,状语从句可分为:
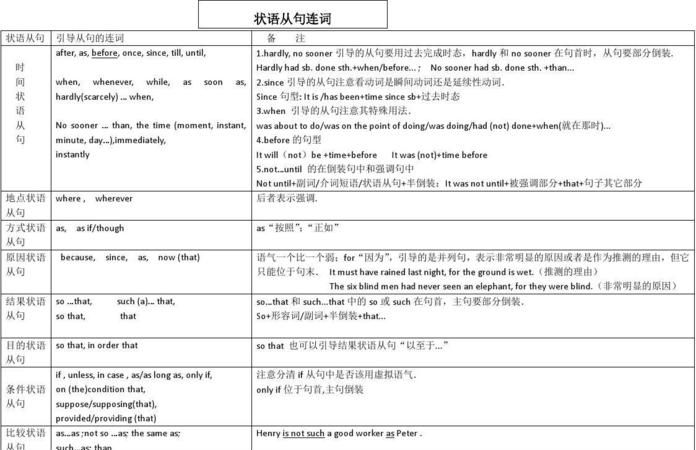
①时间状语从句 ②地点状语从句 ③原因状语从句
④目的状语从句 ⑤条件状语从句 ⑥结果状语从句
⑦让步状语从句 ⑧方式状语从句 ⑨比较状语从句
三、 时间状语从句
主句是一般将来时,时间状语从句用一般现在时表将来;主句是过去将来时,从句用一般过去时表示过去将来时;主句是一般过去时,从句用一般过去时。记忆:“主将从现”
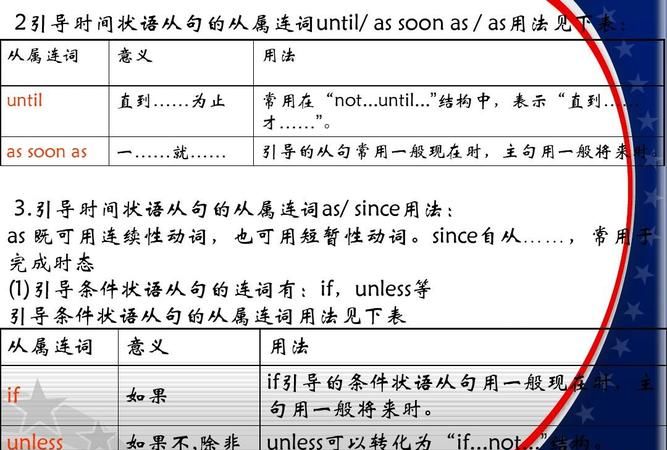
引导时间状语从句的连词有:
as, when (whenever), before, after, as soon as, until (till), since, every time, once.
特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
4、 地点状语从句
地点状语从句用where, wherever引导
特殊引导词:wherever, anywhere, everywhere
五、 原因状语从句
原因状语从句用because(因为),since(既然), as(由于)引导
特殊引导词:seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that, considering that
六、 目的状语从句
目的状语从句用so(常用于口语), that, so that, in order that引导
目的状语从句的谓语常含有may, might, can, could, should, would等情态动词。
特殊引导词:lest, in case, for fear that,in the hope that, for the purpose that, to the end that
七,条件状语从句
条件状语从句由if, unless, (so) as long as(只需)引导
在条件状语从句中要用一般时表示将来时(与时间状语从句相同)
特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, suppose that, in case that, on condition that
八、 结果状语从句
结果状语从句由such…that, so….that, so that, that 引导
特殊引导词:such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that,
9、 让步状语从句
although, though
even though = even if, whether…or
however = no matter how
whatever = no matter what
whoever = no matter who
whenever = no matter when
wherever = no matter where
特殊引导词: as(用在让步状语从句中必须要倒装),while ( 一般用在句首 ),no matter …, in spite of the fact that,
10、 方式状语从句
方式状语从句由as(如同,按照),as if (though)引导
*as和like都有“像”的意思,as是连词,后面连接句子,like是介词后面可加名词、代词或名词性短语。
十一、比较状语从句
比较状语从句由as…as, not as(so)…as, than, the+比较级,the+比较级引导
特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than; not A so much as B

条件状语从句的用法及规则
条件状语从句的用法及规则:
1、引导条件状语从句最常用的连词是if,由if引导的条件状语从句表示在某种条件下某事很可能发生。
2、if从句还表示不可实现的条件或根本不可能存在的条件,也就是一种虚拟的条件或假设,从句多用一般过去时或过去完成时。
3、在条件状语从句中,要注意“主将从现”的规定,即主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表示将来时。
4、if既可以引导条件状语从句,表示“如果”,也可以引导宾语从句,表达“是否”。一站式出国留学攻略 ***ing.com

状语从句的讲解和用法
状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。其实状语从句也是有一定的使用 方法 的。下面我就给大家介绍状语从句的用法讲解。
状语从句的概说状语从句即指在主从复合句用作状语的从句。按照其意义,状语从句可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句等。状语从句是 英语学习 中的一个语法重点,也是历年重点考查的内容之一。学习状语从句主要应注意引导状语从句的从属连词的用法与区别,以及从属连词在一定的语言环境中的意义与用法。
时间状语从句的介绍1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词很多,常见的有before, after, when, while, as, since, till, until, as soon as 等。
2. 表示“当…时候”的 while, when, as 的用法区别是:while从句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词;表示带有规律性的“每当”或当主、从句谓语动词的动作发生有先后时,只能用when;当表示“一边…一边…”或“随着”时,只能用as。另外,用于此义的 as 所引导的时间状语从句谓语只能是动作动词,不能是状态动词。如下面一道高考题的答案是B 而不能是A:
“I’m going to the post office.” “_____ you’re there, can you get me some stamps?”
A. As B. While C. Because D. If
3. until 在肯定句中通常只连用延续性动词,表示相应动作结束的时间;在否定句中通常连用非延续性动词,表示相应动作开始的时间,意为“直到…才”。如:
He waited until she was about to leave. 他等着一直到她准备离开。
I did not begin to work till he had gone. 他走了后我才开始工作。
4. 表示“一…就”除用as soon as 外,还可用 the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, no sooner…than, hardly…when 等。如:
I came immediately you called. 你一来电话我就来了。
Hardly had she arrived when it began to snow. 她刚到就下起雪来了。
The moment I have finished I'll give you a call. 我一干完就给你打电话。
5. every time, each time, (the) next time, (the) last time, by the time, the first time, any time 等以time 结尾的词语也可用作连词,引导时间状语从句。如:
Next time you come in, please close the door. 下次你进来,请关门。
He didn’t tell me anything the last time I saw him. 上次我见到他时他什么也没告诉我。
By the time I got home, she had already gone to bed. 我到家时她已睡觉了。
条件状语从句的介绍1. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词主要有 if, unless, as [so] long as等。如:
Don’t come unless I telephone. 除非我打电话,否则你别来。
If you watch carefully you will see how to do it. 如果你仔细瞧你会看出该怎样做。
As long as you do your best, we’ll be happy. 只要你尽力,我们就满意了。
2. in case 也可引导条件状语从句,其意为“如果”、“万一”。如:
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 如果我忘了,请提醒我。
让步状语从句的介绍1. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词主要有 although, though, however (=no matter how), even if (即使), whether…or (不论…还是)等连词。如:
The speech is good, though it could be better. 这次演讲不错,虽然还可以再好一点。
He went out even though it was raining. 尽管下雨,他还是出去了。
2. as 也可引导让步状语从句,但要将名词、形容词或副词等提到as 前,若提前的是单数可数名词,要省略a / an。如:
Teacher as he is, he can’t know everything. 虽然是老师,他也不可能什么都懂。
3. 连词while 有时也可表示“尽管”、“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。如:
While we don’t agree we continue to be friends. 尽管我们意见不同,我们还是朋友。
4. whatever, whoever, however, whenever, wherever 等引导让步状语从句。如:
Don’t lose heart whatever you do. 不管你做什么,都不要灰心。
Whoever you are, you can’t pass this way. 不管你是谁,你都不能从这里通过。
注:表示“虽然”的 though, although 不可与 but 连用,但可与 yet, still 连用。
点击下页还有更多 >>>原因状语从句的介绍
条件状语从句的从属连词有哪些
条件状语从句
通常由以下连词引导:if, unless, on condition that, suppose, in case(如果,万一), as /so long as(只要)等 如:
①If you are thirsty, water far away can’t help you.
远水不解近渴。
②So long as we do not divorce ourselves from the masses, we are certain to be victorious.
只要我们不脱离群众,我们就一定会胜利。
③You can’t expect the reception to be clear unless the radio set is properly tuned it.
如果不把收音机调好,你不可能指望收到清晰的播音。
④Suppose we can’t get the necessary equipment, what shall we do?
假设我们弄不到必要的设备,那我们怎么办?
⑤We’ll let you use the room on condition that you keep it clean and tidy.
我们可以让你们用这个房间,如果你们能保持整洁的话。
⑥Send us a message in case you have any difficulty.
万一有什么困难请给我们一个信。
unless作连词,表示“如果不”,“除非”,在意义上等于if…not, 在有些场合主要是指真实条件句,它引导的肯定式的条件状语从句可以和if引导的否定式的条件状语从句互换。
如:Unless you change your mind, I won’t be able to help you.
= If you don’t change your mind, I won’t be able to help you.
除非你改变你的想法,否则我不能帮助你。
unless不可用于假想的事情,因此,当if…not引导非真实条件状语从句时,一般不可改用unless.
如:
If she weren’t so silly, she would understand.
如果她不那么傻,她就会懂了。
以上就是关于状语从句的连词和用法 ,状语从句从属连词分类的全部内容,以及状语从句的连词和用法 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
