本文目录
怎么判断一个句子是不是独立主格
1.独立主格转换成状语从句,当状语从句的主语与主句的主语不是指同一个对象时,可用独立主格结构取代状语从句,但不再保留连词。如:After
class
was
over
(=Class
being
over
/
Class
over),
the
students
soon
left
the
classroom.下课后,学生很快离开了课室。
2.
不能省略being
(having
been)的情形:在下列两种情况下,独立主格结构中的being(或having
been)不能省略。
(1)
独立主格的逻辑主语是代词时。如:It
being
Sunday,
we
went
to
church.因为是星期天,我们去做了礼拜。
(2)在There
being+名词的结构中。如:There
being
no
bus,
we
had
to
go
home
on
foot.因为没有公共汽车,所以我们不得不步行回家。
3.
在“名词(或代词)+介词短语”构成的独立主格结构中,一般不用形容词性物主代词和冠词。如:
Miss
Smith
entered
the
classroom,
book
in
hand.史密斯小姐走进了课室,手里拿着一本书。比较with的复合结构。如:Miss
Smith
entered
the
classroom,
with
a
book
in
her
hand.
4.
独立主格结构没有所有格形式The
chief-editor
arriving,
we
began
the
meeting.
主编来了,我们开始开会。(比较动名词复合结构。)
我认为,一般看可能是“主格”的那个小分句的意思,一般表示条件或者假设的小分句,就有可能是考察独立主格的。
至于怎么找出答案,这个还真不好说,最好还是多练习,然后遇到这样的句子就会很自然地选出答案了。

独立主格结构逻辑主语跟主语的关系
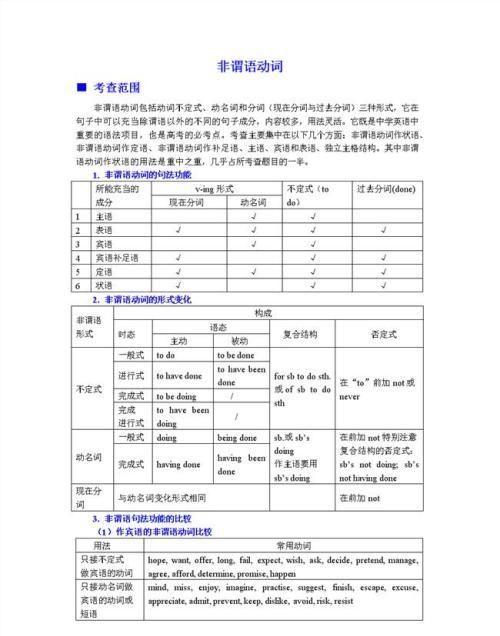
由“名词(代词)+现在分词”构成的独立主格 独立主格由“名词或代词+形容词、副词、分词不、不定式等” 构成,其中的“名词或代词”用主格形式,起逻辑主语的作用,其后的“形容词、副词、分词不、不定式等”起逻辑谓语的作用。注意,独立主格结构与主句之间不能使用任何连接词。本文主要介绍“名词或代词+现在分词”的用法。The children playing in the room, I couldn’t get down studying. 孩子们在屋里玩,我没法学习。Mothing being ill, I had to stay at home looking after her. 母亲病了,我只好呆在家里照顾她。There being no bus, we had to walk home. 由于没有公共汽车,我们只好走回家。Night enshrouding the earth, nobody could make out what the dark mass was from a distance.黑夜笼罩大地,谁也看不清远处黑压压的一片是什么东西。

独立主格的语法知识点
一、什么是独立主格结构
所谓独立主格结构就是一个与句子相对独立的带有逻辑主语的结构。
由于这个逻辑主语与它所支配的行为状态表达的是辅助主要句子的另一层独立的意思,加之要用代词和名词的主格形式(现代英语中名词的主格与宾格是一致的)表示,因此这种逻辑主语就称作独立主格。逻辑主语加上它所支配的行为状态就构成了一种语法结构,这种语法结构称为独立主格结构。如下列例句中的括号部分:
* (Everyone being ready), the teacher began his class. 每个人都准备好后,老师开始上课。
独立主格(即逻辑主语):Everyone
独立主格的行为状态:being ready
起到的辅助作用:表示 the teacher began his class 发生的时间
* (It being National Day today),the streets are very crowded. 由于今天是国庆节,街上很拥挤。
独立主格:It
独立主格的行为状态:being National Day today
起到的辅助作用:表示 the streets are very crowded 的原因
The manager looks relaxed, (many things settled). 由于许多事情已经处理好了,经理看上去很轻松。
独立主格:many things
独立主格的行为状态:settled
起到的辅助作用:表示 The manager looks relaxed 的原因
二、独立主格结构的构成
独立主格由两部分组成——
1、逻辑主语(即独立主格):由代词的主格或名词充当独立主格
2、叙述语:用来陈述逻辑主语的行为状态。
其中叙述语是独立主格的重点。
三、能够构成独立主格结构中叙述语的词语
1、现在分词(-ing 非谓语动词)
——用作时间状语
The chairman began the meeting , everyone being seated. 每个人坐好后,主席开始开会。(相当于一个时间状语从句after everyone was seated)
——用作原因状语
Many eyes watching him, he felt a bit nervous. 许多眼睛看着他,他感到有点儿紧张。(相当于一个原因状语从句As many eyes were watching him)
——用作条件状语
Time permitting, we will have a picnic next week. 时间允许的话,我们下星期将进行一次野炊。(相当于一个条件状语从句If time permits)
My health allowing, I will work far into the night. 我的健康许可的话,我愿工作到深夜。(相当于一个条件状语从句If my health allows)
——用作伴随方式的状语
The boy lay on the grass, his eyes looking at the sky. 男孩躺在草地上,眼睛看着天空。(相当于一个并列分句and his eyes were looking at the sky)
2、过去分词(-ed非谓语动词)
* The book written in simple English, English beginners were able to read it. 该书是用简单英语写的,英语初学者也能看懂(原因状语 , = As the book was written in simple English,English beginners were able to read i)
* He was listening attentively in class, his eyes fixed on the blackboard. 他上课专心听讲,眼睛紧盯着黑板。(方式状语,= He was listening attentively in class, and his eyes were fixed on the blackboard. )
* The task completed, he had two months' leave. 任务完成以后,他休了两个月的假(时间状语。=When the task had been completed,he had two months' leave. )
3、不定式(to do)
* I send you 100 dollars today, the rest to follow in a year. 现寄给你100美元,其余部分将在一年以后再寄。(方式状语,= I send you 100 dollars today, and the rest is to follow in a year.)
* The manager looks worried,many things to be settled. 经理看上去很着急, 有这么多的事情要处理。(原因状语,= The manager looks worried because many things will be settled)
.
4、形容词短语
* He turned to me, his eyes sleepy. 他睡眼惺忪地转向我。(= He turned to me, and his eyes were sleepy.)
* He stood there, his mouth wide open. 他站在那里,嘴张得大大的。(= He stood there, and his mouth was wide open.)
5、小品副词 .
* School over, we all went home. 放学了,我们都回家了。(= School was over, and we all went home.)
* He sat at his desk, his shoes off. 他坐在课桌旁,没穿鞋子。( = He sat at his desk and his shoes were off.)
6、介词短语
* He is standing in front of the blackboard, his back towards us. 他站在黑板面前,背对着我们。( = He was standing in front of the blackboard, and his back was towards us.)
* The new teacher came in, a smile on her face. 新老师面带微笑走了进来。( = The new teacher came in and she had a smile on her face.)
* The teacher came into the classroom,a rule in his hand. 老师走进教室,手里拿着一把直尺。( = The teacher came in and a ruler was in his hand.)
高考考独立主格结构吗
高考肯定要考独立主格结构的,这个是基本的英语知识的,这是必考的。
成人高考和普通高考的区别:
1,年龄规定不同。成人高考是面向成人的高校入学考试,年龄在这卡着,必须年满18周岁。
普通高考是只要是合格的高中毕业生或者具有同等学力的考生参加的考试,这个年龄没有要求,只要你高中毕业或同等学历就可以报名参加。
2,考试时间不同。成人高考是每年10月底考试,普通高考一般在每年的6月7日、8日考试。
3,考试难度不同。成人高考是面对成人的,并且是远离课本,远离校园多年的成年人考试,所以考试题型简单,并且必须按照《考试大纲》要求来的。而普通高考考试难度很难,不只是考基础,并且中等和难度题型占比分数很大。
4,出题不一致。成人高考考试题全国统一,但普通高考则是每个省都不一样,有的用的地方卷,有的用的全国卷。
5,录取分数线要求不同。成人高考录取分数线非常低,总分450分,600分,录取分数线每年平均在100-150分左右。这个和科目有关。但普通高考录取分数线和学校有关,本科比专科高,一本比三本高,985/211院校比一本高。
6,学习形式不同。普通高考必须在学校上课考试,学分不够需要继续学习,并且无法毕业。而成人高考不需要去学校上课,不需要修学分,每半年考试一次,在函授站报名的通过他们举办的期中考试考过即可。
7,学费不同。普通高考录取院校学费从4000/年-10000/年不等。而成考则从2200/年-5000/年不等。
8,毕业证书不同。成人高考毕业证书标明“函授”,普通高考毕业证书标明“全日制”。

以上就是关于独立主格高考考点 ,怎么判断一个句子是不是独立主格的全部内容,以及独立主格高考考点 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

