本文目录
状语从句的九种常见类型
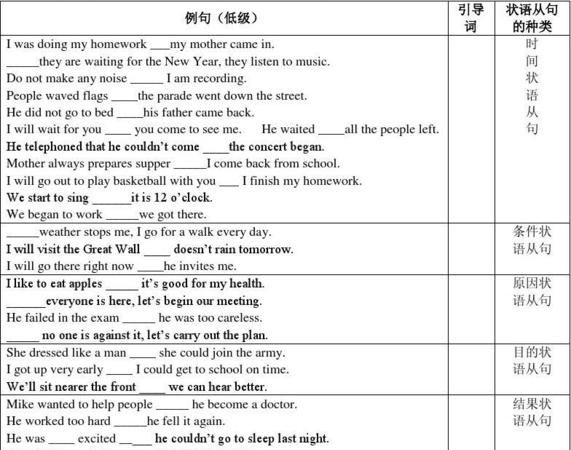
一、时间状语从句:
1、 连接词when、while、as
⑴when ①正当…时候 be about to…ving…
②从句动词先于或后于主语动作
⑵while: 可表示对比(从句只用连续性动词)
⑶as: “一边一边”“随着”
省略句中: eg: As time goes on…随着时间的推移
As a boy,hewao hopeless at English.
2、 before,after
before常用句型:It is/was/will be…before
eg: It will be 5 years before we meet again.
3、 till,until
①用于肯定句中“直到…为止”,主句谓语为持续性动词
②用于否定句中“直到…才”,主句谓语为短暂性动词(until,till可用before代替)
③Not until位于句首 倒装
④强调句型只用until
二、地点状语从句:where,wherever,everywhere
也可引导定语从句:
状语从句:We shall go where the condition are poor.
定语从句:We shall go the place where the condition are poor.
三、原因状语从句
1、because\since\as
⑴①用why提问
②强调句中
③关联词“not…but”
④与“just”等副词连用 eg:You shouldn’t any only because you had much.
⑵since引导从句常放句首,往往表示对方已知的让步原因关系,主从时态一般相同
⑶as从句放句首
2、now(that) 既然
3、considering that,seeing (that):与since,now that意相近: “鉴于…”“考虑到…”
4、not that…,but that…“不是因为…而是因为…”
四、目的状语从句
1、that,so that,in order that“为了,以便”
⑴从句中往往出现情态动词:can\could\may\might
⑵当主从句的主语一致时,可转换为相应动词不定式结构:so as to\in order to
2、in case,for fear that,lest“以防、以免、万一..”从句是肯定句
五、结果状语从句
1、so,that,so that
so that可以引导结果状语从句和目的状语从句,区别在于:目的状从中有情动(结果状从前有“,”号)
2、so…that
such a\an +形+单名=so+形+a\an+单名 “如此…以至于”
3、such…that
such…that(状从)
such…as(定从)
4、such that (是这样…以致)
六、条件状语从句:主句中用一般将来时,从句中用一般现在时或一般过去时
1、if正面条件“如果”
2、unless. 反面条件=if not 主句为否定意味,从句为肯定句(从句也可用否定结构)
unless做介词 “除非,如果不”
3、so\as long as,on condition that “条件是…”“只要..”
4、in case既可引导目的状,又可引导条件状=”if it happened that…”
5、providing,provided that, suppsing,suppose (that),given (that) “如果,只要,假如”
七、方式状语从句
1、as,just as
“如…”“正如…一样”Do just as you like
2、as if, as though (虚拟语气)
八、比较状语从句
1、as…as,the same as. 否定句用not so\as…as,not the same as
从句中常用省略句: eg:He runs as fast as he can.
2、than
3、the more…the more…“越…越…”
4、more than
九、让步状语从句
1、 although,though.句中不出现but,可出现still\yet(副词)
though的位置较灵活,可倒装
2、even if,even though“即使” even if表主观,时态往往用于将来
even though通常表客观上的,往往表过去事实
3、 no matter wh…只用于让步状语从句
wh..ever 让步状从/名词性从句
4、as特殊倒状
5、while,whereas突出对比
6、if(=even if) 强调部分(n.\adj.\adv.\v.) +as+主+谓(可以是情动)
1. I get to Pairs, I’ll call you up at the airport.
A.Since B.While C.Once D.Although
2. the headmaster comes, we won’t discuss this plan.
A. Unless B.If not C.Except D.Whether
3.Bill must have been away from the office. how many times I phoned him, nobody answered it.
A.Whatever B.No matter
C.In spite of D.Though
4.I had been to Beijing long you visited it. A.before B.till C.after D.when
5. , he is good at drawing.
A.To be a child B.A child as he is
C.As a child D.Child as he is
6.Don×t be discouraged you have fallen behind others.
A.whether B.as if C.even if D.however
7. We can get there on time the car doesn’t break down.
A. while B. as long as C. so that D. even if
8. The vase on the left is than the one on the right,and not .
A. more nicer;so expensive
B. much more better;as expensive
C. nicer;as expensive
D. better;such expensive
9. It wasn’t long he joined the job.
A.that B.before C.until D.and
10. These planes can fly than the old ones.
A.as fast three times B.three times as fast
C.three times fast D.three times faster
11. had the bell rung the students took their seats.
A.Hardly;when B.No sooner;when
C.Hardly;than D.No sooner;then
12. many times,but he still couldn’t understand it.
A.Having been told B. Though had been told
C. He was told D. Having told
13. we have come, let’s stay and enjoy it.
A. For B.As C. Because D. Since
14.You’d better do you are required.
A. like B.which C.that D.as
15. that none of us could follow him.
A. He spoke very fast B. So fast he spoke
C. Too fast he spoke D. So fast did he speak
16.I’ll start early, it may be dark.
A. however B.whether C.if D.though
17. the baby fell asleep the room.
A. After;did the mother leave
B. Not until;did the mother leave
C. Not until;the mother left
D. Soon after;the mother had left
18. the day went on, the weather got worse.
A. With B. Since C. As D. While
19. He can×t have gone out, the light is still on.
A. because B. since C. as D. for
20. I was walking along the river I heard a cry for help.
A. while B. since C. when D. as
21. We shouldn’t do that dangerous experiment ______________the teacher is with as.
A. if not B. if C. unless D. as long as
22. He has little education he is unable to find a job.
A. such;that B. so;and
C. so;that D. such;and
23.The soldier was wounded, he pushed on.
A. for B. and C. so D. yet
24. The full letter reads follows.
A.like B.as C.that D.which
25.Will you go our motherland needs us most after graduation?
A. that B. where
C. in which D. to the place which
26. This is a revision paper. When you do it, you’d better make a mark you have questions.
A. where B. the place C. as if D. since
27. Water power station are built big water falls.
A. where there are B. where there have
C. which has D. which are
28. I am sure I’ll meet a kind-hearted man I go.
A. where B. to the place where
C. wherever D. the place
29. She is so good at playing table-tennis that she can hit the ball she wants it to go.
A. the place where B. that
C. in which D. where
30. It was his mother came in to prepare his lessons.
A. not until;did the boy begin
B. until;that the boy began
C. until;did the boy begin
D. not until;that the boy began
状语从句专练答案:
1-5 CABAD 6-10 CBCBD
11-15 ACDDD 16-20 DBCDC
21-25 CCDBB 26-30 AACDD
状语从句九大类型及例句
一、时间状语从句 常用引导词:when(在…时), as(当…时), while(在…期间), as soon as(一……就……), before(在…之前), after(在...之后), since(自从...以来) , not...until(直到…才)untill/till(直到…时)等 特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant( 瞬间,顷刻), immediately , directly(不久,立即), no sooner … than(一...就...), hardly …when(刚一...就...) , scarcely … when(刚...就.../一...就...) 当用no sooner … than,hardly …when,scarcely … when作为引导词的时候,从句要部分倒装。 I didn’t realize how special my mother was until I became an adult.
直到我成为了一个成年人我才意识到我的母亲是多么的特殊。
While John was watching TV, his wife was cooking.
当约翰看电视时,他的妻子正在做饭。
The children ran away from the orchard(果园), the moment they saw the guard.
孩子们一看到守卫就逃出了果园。
No sooner had I arrived home than it began to rain.
还没等我到家就开始下雨了。(<--- This translation is wrong. No sooner...than... means something happened right after something happened. )(我一到家就开始下雨了。)
Every time I listen to your advice, I get into trouble.
每当我听取你的建议时,我就会惹上麻烦。
二、地点状语从句
常用引导词:where
特殊引导词:wherever, anywhere, everywhere
Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
一般来说,有工厂的地方空气污染就严重。
Wherever you go, you should work hard.
无论你去哪里,你都应该努力工作。
地点状语从句一般由连接副词where, wherever等引导,已经形成了固定的句型,例如:
Where there is no rain, farming is difficult or impossible.
在没有雨水的地方,耕作是困难的或根本不可能的。
They were good persons. Where they went, there they were warmly welcomed.
他们都是好人。因此他们走到哪里都受到热烈欢迎。
You should have put the book where you found it.
你应该把书放回原来的地方。
Where the Communist Party of China goes, there the people are liberated.
哪里有了中国共产党,哪里的人民就得解放。
Wherever the sea is , you will find seamen.
有海就有海员。
三、原因状语从句
常用引导词:because, since, as,
特殊引导词:seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that.
My friends dislike me because I’m handsome and successful.
我的朋友都不喜欢我,因为我又英俊又成功。
Now that everybody has come, let’s begin our conference.
既然每个人都到了,让我们开始我们的会议吧。
The higher income tax is harmful in that it may discourage people from trying to earn more.
更高的收入税是有害的,因为它或许会阻碍人们努力赚钱。
四、目的状语从句
常用引导词:so that, in order that
特殊引导词:lest, in case, for fear that,in the hope that, for the purpose that, to the end that
The boss asked the secretary to hurry up with the letters so that he could sign them.
老板要求秘书快写函件以便他能在上面签字。
The teacher raised his voice on purpose that the students in the back could hear more clearly.
为了让后面的学生听得更清楚,老师有意地提高了他的声音。注意,由for引导的是一个并列句,不是原因状语从句,但有表原因的意思,是并列连词
五、结果状语从句
常用引导词:so … that, such … that,
特殊引导词:such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that,
He got up so early that he caught the first bus.
他很早起床以便赶上第一班公共汽车
It’s such a good chance that we must not miss it.
这是一个好机会,千万不能错过它
To such a degree was he excited that he couldn’t sleep last night.
他激动到这个程度,以至于他昨晚睡不着
六、条件状语从句
常用引导词:if, unless,whether(whether...or not)
特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, supposing that, in case(美语中表条件,英语中表目的), on condition that
We’ll start our project if the president agrees.
如果总统同意,我们将开始我们的项目
You will certainly succeed so long as you keep on trying.
只要你继续努力,你一定会成功的。
Provided that there is no opposition, we shall hold the meeting here.
如果没有人反对,我们就在这里开会。
七、让步状语从句
常用引导词:though, although, even if, even though
特殊引导词: as(用在让步状语从句中必须要倒装),while ( 一般用在句首 ),no matter …, in spite of the fact that, whatever, whoever, wherever, whenever, however, whichever
Much as I respect him, I can’t agree to his proposal.
尽管我很尊敬他, 但是我却不同意他的建议。
The old man always enjoys swimming even though the weather is rough.
老人都很喜欢游泳,即使天气很恶劣。
No matter how hard he tried, she could not change her mind.
不论他如何努力,她都不会改变她的主意。
He won’t listen whatever you may say.
他不会听你说什么。
八、比较状语从句
常用引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较)
特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what/as X is to Y; no … more than; not so much A as B
She is as bad-tempered as her mother.
她和她妈妈一样脾气很坏。
The house is three times as big as ours.
这房子是我们的三倍大。
The more you exercise, the healthier you will be.
你运动的越多,你就越健康。
Food is to men what oil is to machine.
食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。。
九、方式状语从句
常用引导词:as, as if, how
特殊引导词:the way
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
入国问禁,入乡随俗。
She behaved as if she were the boss.
她表现得好像她是老板。
Sometimes we teach our children the way our parents have taught us.
有时,我们用父母教导我们的方式教导我们的孩子。
十、状语从句的省略
状语从句同时具备下列两个条件:①主句和从句的主语一致,或从句主语为it;②从句主要动词是be的某种形式。从句中的主语和be动词常可省略。例如:
When ( the museum is ) completed , the museum will be open to the public next year .
当博物馆完成,该博物馆将于明年向公众开放。
He’ll go to the seaside for his holiday if (it is ) possible.
如果可能,他将去海边度假的话
另外,比较状语从句经常省略。例如:
I’m taller than he (is tall ).
我比他高
The higher the temperature (is), the greater the pressure (is ).
温度越高,压力越大
就状语从句而言,有时为了使语言言简意赅,常常将状语从句进行简化。状语从句的简化现象在口语中较为普遍,而且在高考中的复现率也较高。因此,有必要对其进行全面、透彻的了解。
状语从句的简化现象常存在于以下五种状语从句中:①由if, unless等引导的条件状语从句;②由although, though, even if / though等引导的让步状语从句;③由when, while, as, before, after, until / till等引导的时间状语从句;④由as, as if等引导的方式状语从句;⑤由as, than等引导的比较状语从句。下面针对这五种情形作一归纳。
(1)当状语从句的主语是it,且谓语动词是be时,it和be要完全简化掉。例如:
If (it is) possible, he will help you out of the difficulty.
如果可能的话,他会帮你摆脱困境。
You must attend the meeting unless (it is) inconvenient to you。
除非情况对你来说不方便,否则你必须出席这次会议。
(2)当状语从句的主语和主句的主语一致时,从句可以将主语和be动词简化掉。常用于以下几种情形:
连词+形容词
As (he was) young, he learned how to ride a bike.
他小时候就学会了骑自行车。
Whenever (she is) free, she often goes shopping.
她有空就去逛商店。
Work hard when (you are) young, or you'll regret.
少壮不努力,老大徒伤悲。
连词+名词
While (he was) a young boy, he was always ready to help others.
他在孩子时代就乐于助人。
Although (he was) a farmer, now he is a famous director.
尽管他曾是个农民,但现在他是位著名的导演了。
连词+现在分词
As (she was) walking along the river bank, she was singing a pop song.
她沿着河堤边走边唱着流行歌曲。
Although (he is) doing his best in maths these days, he has still got no good marks.
尽管近来他一直在学数学,但他仍然没有取得好成绩。
连词+过去分词
He won't go there with us unless (he is) invited.
除非受到邀请,否则他不会和我们一道去那里。
The concert was a great success than (it was) expected
.这场音乐会出乎意料地取得了巨大成功。
连词+不定式
He stood up as if (he were) to say something.
当时他站起来好像要说什么。
He wouldn't solve the problem even if (he were) to take charge.
即使他来负责,他也解决不了这个问题。
连词+介词短语
She looked anxious as though (she was) in trouble.
她看上去很焦急,好像遇到了麻烦。
He had mastered the English language before (he was) in the USA.
他到美国之前就懂英语了。
注意:当从句主语和主句主语不一致时,从句部分要么用完全形式,要么用独立主格结构来表达。例如:
When the meeting was over, all the people went out of the meeting-room.
当会议结束时,人们都走出了会议室。(=The meeting over)

地点状语从句的例句有哪些
地点状语从句例句如下:
1、We must camp where we can get water.我们必须在能找到水的地方露营。

2、Go back where you came from.(where引导地点状语从句)你从何处来到何处去。
3、Go back to the village where you came.(where引导定语从句,修饰village)回到你来的那个村子里去。
4、you can go where you want to go .你可以去你想去的地方。
5、With a car,a person can go where he pleases and when he pleases.有了汽车,人可以想去哪儿就去哪儿,想什么时候去就什么时候去。
9大状语从句例句标志词
一、时间状语从句
While John was watching TV, his wife was cooking.
当约翰看电视时,他的妻子正在做饭。
二、地点状语从句
Wherever you go, you should work hard.
无论你去哪里,你都应该努力工作。

三、原因状语从句
Now that everybody has come, let’s begin our conference.
既然每个人都到了,让我们开始我们的会议吧。
四、目的状语从句
The boss asked the secretary to hurry up with the letters so that he could sign them.
老板要求秘书快写函件以便他能在上面签字。
五、结果状语从句
It’s such a good chance that we must not miss it.
这是一个好机会,千万不能错过它。
六、条件状语从句
You will certainly succeed so long as you keep on trying.
只要你继续努力,你一定会成功的。
七、让步状语从句
He won’t listen whatever you may say.
他不会听你说什么。
八、比较状语从句
The house is three times as big as ours.
这房子是我们的三倍大。
九、方式状语从句
She behaved as if she were the boss.
她表现得好像她是老板。

以上就是关于状语从句典型例句00句 ,状语从句的九种常见类型的全部内容,以及状语从句典型例句100句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
