本文目录
比较级的八种句型结构加举例
比较级的结构及例句整理如下:
1)A=B同程度比较:as+原级+ as表示“和……一样。
the apple is as big as the pear.
2)A≠B不同程度的比较:not so/ as+原级+as 表示“不如……”。
the bridge is not so/as long as one.
3)A>B比较级+ than表示“比……”。
many more+原级+名词+ than修饰可数名词。
much more+原级+名词+ than修饰不可数名词。
I can run faster than you.
this test is more difficult than that one.
I make much more money than you.
4)A<B less+原级+ than表示“少于。
this book is less difficult than that one.
5)more/ fewer+可数名词+ than,和more/ less+不可数名词+ than.
li ming eats more apples than wang hua .
I spend more money on candies than brother.
6)the+比较级+主谓,the+比较级+主谓表示“越……越……”。
the more money you make, the more you spend.
the busier I am, the happier I feel.
7)比较级+ and+比较级表示“越来越……”。
单音节形容词:形容词比较级+形容词比较级。
多音节形容词:more and more+形容词原形。
it's getting cooler an cooler.
you are become more and more beautiful.
8)no+比较级+ than表示对两个比较对象进行否定,可用“neither……nor……”结构改写。
I no more selfish than you. (neither I nor you are selfish).
比较级的句型总结6条
比较级的用法和句型
2019-12-17 11:32:20
文/叶丹
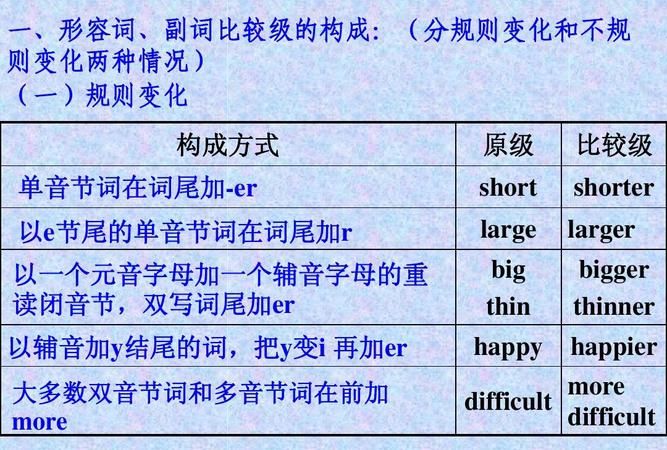
比较级的用法一般句式的构成:A+is/are+形容词比较级+than+B。比较级等级有三个:原级,比较级和最高级。
比较级用法
1.表示"比…更",用比较级形容词+than+比较成分,than后主词的述语动词往往省略,非正式用法的than后的人称代名词可用受格。
2.表示"较…低; 不及…"用less+原级形容词+than+比较成分。
3.表示两者之中"较…",用the+比较级+of the two。
4.定冠词或指示形容词+比较级+名词表示比较。
5.有少数以ior结尾的形容词,如inferior(次于),junior(年幼的;下级的),posterior(之后),prior(之前),senior(年长的,上级的),superior(优于)等本身就有比较的意思,常与介系词to连用。
6.比较形容词可以被副词如a little(一点),much(得多),even(更加),still(更加),far(…的多)等修饰,但不可用very修饰。
比较级基本句型
同级比较
1.由“…as+形容词原型+as…”或“…as+形容词+名词+as…”构成。
My grandpa is as energetic as a young man.
I try to find as much information as I can about what happened.
2.由“…not so (as)+形容词或副词原型+as…”或“…not so (as)+形容词+名词+as…”构成。
Luckily,the weather is not so wet as it is today.
降级比较
1.由“…形容词比较级+than…”构成。
He is more concerned about others than about himself.
2.由“…many/much more+可数/不可数名词+than…”
My friend earned much more money than I did last year.
比较级句型结构
常用形容词比较级结构小结
1.当as… as 中有名词时
as +形容词+ a +单数名词 /as + many/much +名词
This is as good an example as the other is.
I can carry as much paper as you can..
2. 倍数+ as + adj. + as= 倍数+ the+ of,表示倍数的词或其他程度副词做修饰语时放在as前
This room is twice as big as that one. (Your room is the same size as mine.)
This bridge is three times as long as that one. (This bridge is three times the length of that one. )
Your room is twice as large as mine.( Your room is twice the size of mine.)
3.可修饰比较级的词 a bit, a little, much, a lot, still, even,far等
4.many,old 和 far
1) 如果后接名词时, much more +不可数名词 ;many more +可数名词复数
2) old 有两种比较级和最高级形式: older/oldest 和elder/eldest,elder,eldest 只用于兄弟姐妹的长幼关系。My elder brother is an engineer.
3) far 有两种比较级,farther,further. 在英语中两者都可指距离。在美语中,father 表示距离,further表示进一步。I have nothing further to say.
5.the + 最高级 + 比较范围
The Sahara is the biggest desert in the world.
形容词最高级前通常必须用定冠词 the,副词最高级前可不用。
形容词most前面没有the,不表示最高级的含义,只表示"非常"。
It is a most important problem. =It is a very important problem.
6.“the + 形容词”的两种用法
“the+形容词”既可以等同于复数普通名词,也可以等同于抽象名词,代表一类人或事。
The rich are apt to look down upon the poor.富人常常轻视穷人。
The poet had an yearning for the supernatural.诗人憧憬超自然的东西。
这种用法也可以适用于“the+现在分词”及“the+过去分词”。
The unexpected always happens. 天有不测风云。
The wounded and the dying were rushed to hospital. 受伤的人和垂死的人被急送到医院去了。
7. “the+ 比较级+理由”
该句型具有“更加”的意思。常以“all (或much) the+ 比较级”的形式出现。例如:
I am the more inclined to help him because he is poor. 因为他穷,我更想帮他。
It is all the more dangerous for not being generally recognized as such.
一般不认为危险的,反而更加危险。
8.“the+比较级...,the+比较级...”。该句型的意思为“越……越……”。例如:
The more he flatters me,the less I like him.他越是迎合我,我越不喜欢他。
The higher the mountain is, the more people like to climb it; the more dangerous the mountain is, the more they wish to conquer it.山越高,人越想爬;山越危险,人越想征服它。
这种句型常用省略说法,The sooner,the better.越快越好。 More haste,less speed. 欲速则不达。
9.“the last+不定式/形容词从句”。意思是“最不大可能的、最不适的”。
Money is the last thing he wants, and you won’t succeed by offering it.
他决不要钱,你想用钱去买动他是决不可能的。
The author should be the last person to talk about his work.作者最不宜讨论他的作品。
10.序数词通常只修饰最高级。 Africa is the second largest continent.
11.否定词语+比较级","否定词语+ so… as"结构表示最高级含义
Nothing is so easy as this=Nothing is easier than this. =This is the easiest thing.
12.. more词组
1) the more… the more… 越……就越……
The harder you work,the greater progress you’ll make.
2) no more… than…不比……多/ no less… than… 不如 ……
The officials could see no more than the Emperor.
He is no less diligent than you.
3) more than不只是,非常 She is more than kind to us all.
13.“so+形容词/副词+that”
在“so”后接形容词和副词表示因果关系,“that”之前表示原因,“that”之后表示结果。例如:
Those ponds and streams are so small that they cannot be shown in your maps.
那些池塘和小溪太小,所以你的地图上没有。
He had lived so long in Asia that he had forgotten his English way of life.
他在亚洲住得太久,所以英国的生活习惯都已经忘记了。
14. “so much so that” 理解为“如此……以至于”
The patient was very tired when he returned from the ride, so much so that he could not sit up.
病人坐车回家时非常疲倦,疲倦得甚至不能坐起来。
He is poor, so much so that he can hardly get enough to live.他很穷,穷得几乎难以生活下去。
15.“more+原级+than”
这种句型一般将不同性质加以比较,可以理解为“与其说……不如说”。例如:
He is more witty than wise.与其说他聪明,不如说他机智。
He is more dead than alive. 与其说他活着,不如说他死了。
16.“much more”和“much less”
以上两种表达法都有“更加”的意思。“much more”用于肯定句,表示程度加强;“much less”用于否定句,表示程度减少。例如:
I like music, much more dancing.我喜欢音乐,更喜欢跳舞。
I don't like music, much less dancing.我不喜欢音乐,更不喜欢跳舞。
17..“would sooner(rather)...than”和“ would as soon...as” 均可理解为“宁愿……也不”。
He would rather(sooner) resign than take part in such dishonest business deals.
他宁可辞职也不干这种不正当的勾当。
I would as soon die as disgrace myself.我宁死不受辱。
18.“no sooner...than”、“hardly...when”和“scarcely... before”
以上三个句型的意思是“一……就”。应当注意的是,在以上句型中,句子的前半部分一般用过去完成时,而后半部则用一般过去时。该句型通常采用倒装语序。
No sooner had I opened the cage than the little bird flew out.=Scarcely(Hardly) had I opened the cage before (when ) the little bird flew out.我一开笼小鸟就飞出去了。
19.“anything but”、“nothing but”和 “all but”
英语中,“anything but”=never,“ nothing but”=only, “all but”=almost, nearly。
He is anything but a scientist.他决不是科学家。
I am nothing but a student.我不过是个学生。
He is all but a fool.他几乎是个傻瓜。
20.prior、superior 、inferior 、senior 和junior 表示比较时后面用“to”不用“than”
“prior to”意思是早于,比……重要; “superior to”意思是优于,高于;
“inferior to”意思是次于 ; “senior to ”意思是年长于,地位高于;
“junior to”意思是年幼于,地位低于,迟于。
The task is prior to all others.这项任务比其他所有的任务都重要。
In maths he felt superior to John. 他觉得自己数学比约翰强。
These apples are inferior in flavor to those. 这些苹果的味道不如那些。
He is two years senior to me. 他比我大两岁。
21.much,more,most
(1) more和most的用法相当自由:
You should ride more.你必须多骑马。I use this room most.这个房间我用得最多。
(2)当much是原级时,使用范围较小,意为a lot(许多)时可修饰表示否定意思的动词:
He doesn’t ride much nowadays.现在他不太骑马了。
(3)在表示疑问的句子里much主要与how连用。在没有how的疑问句中可用much,但a lot更常见:
How much has he ridden?他骑马多吗?
(4)在肯定句中as/so/too+much是可以的。在没有as/so/too的情况下,肯定句中用a lot/a good deal/a great deal会更好:
He shouts so much that… 他叫喊的太厉害了,以至于……
I talk too much.我说得太多了。
但是说:He rides a lot/a great deal.他常骑马。
(5) very much意为greatly(非常)时,在肯定句中使用比较广泛。
常和它一起用的词有blame(责备),praise(赞扬),thank(感谢)及一些表达感情的动词:admire(钦佩),amuse(使娱悦),approve(赞成),dislike(不喜欢),distress(使烦恼),enjoy(喜爱),impress(使有深刻印象),like(喜欢),object(反对),shock(震惊),surprise(使惊奇)等等:
Thank you very much.非常感谢你。
They admired him very much.他们很钦佩他。
She objects very much to the noise they make.她非常反对他们弄出的噪音。
(6)much(=greatly非常)可以和very连用,也可以省去very而与下列分词连用:admired(受钦佩的),amused(娱悦的),dis-liked(不受喜欢的),distressed(烦恼的), impressed(留有……印象的),liked(受喜欢的),shocked(被震惊的),struck(受巨大影响的),upset(心烦意乱的)。
He was(very) much admired.
She was (very)much impressed by their good manners.
(7) much意为a lot(许多)时能够修饰形容词的比较级和最高级及动词:
much better好多了
much the best最最好
much more quickly快多了
(8)much too可与形容词的原级连用:
He spoke much too fast.他说话说得太快了。
(9) most在形容词或副词之前,有“很”的意思。主要与双音节或多音节形容词/副词连用:
He was most apologetic.他已表示十分的歉意了。
She behaved most generously.她的行为非常慷慨大度。
22.可修饰比较级的词
much, many, a lot, even, far, a bit, a little, still, yet, by far, any, a great deal
23.表示“最高程度“的形容词没有最高级和比较级。

总结比较级句型结构
◇句型一:形容词或副词比较级+than…
□注意事项:
该句型为比较级的最基本句型。只要看到than,即可确定前面使用比较级。
He is taller than I am.
他比我高。
The boy does his homework more carefully than the girl.
这个男孩做作业比这个男孩认真。
◇句型二:less + 形容词的原级 + than
□注意事项:
该句型表示“不如、不及”,特别需要注意的是,less本身就是little的比较级,后面必须跟形容词的原级,否定就造成了比较级的重复使用。
This computer is less expensive than that one.
这台电脑比那台便宜。
◇句型三:as +形容词或副词的原级+ as
□注意事项:
该句型表示对比的两者程度相当,as之间必须跟形容词或副词的原级,决不能使用比较级。此外,还要确定使用形容词还是副词。确定的依据就是根据第一个as前的动词,如果是系动词(如be,感官动词look, sound, smell, taste, feel等),那么就用形容词的原级,如果前面的动词是一般的实义动词,那么就必须用副词的原级修饰动词。
This lesson is as easy as that one.
这节课和那节课一样容易。
Lucy talks with old people as politely as her sister.
露西和老人交谈和与他妹妹交谈一样礼貌。
特别提醒:as…as之间也可以跟名词,句型如下:
☆as +形容词+ a/an +单数名词+as
He is as kind a person as his father.
他和他爸爸一样都是善良的人。
☆as + many/much+不可数名词/可数名词复数+as
I can carry as much paper as you can.
你能搬多少纸,我也能。
I have as many books as you do.
我的书和你的一样多。
We’ll give you as much help as we can.
我们将尽我们所能给你帮助。
其它几个关于as…as的句型:
☆as … as one can:尽其所能
He began to run as fast as he could.
他尽其所能跑得快。
☆as … as possible:尽可能
Please help us as quickly as possible.
请尽可能地帮助我们。
☆as soon as…一……就……
He will call me as soon as he comes here.
他一来这儿就会给我打电话。
◇句型四:not as/so +形容词或副词的原级+ as
□注意事项:
该句型表示“前者不如后者……”,往往可以与句型一和句型二替换。第一个as可以换为so。
This classroom is not as bright as yours.
这个教室没有你们的明亮。
I cannot run as fast as you.
我跑步不如你快。
◇句型五:the +形容词或副词最高级+ in / of / among +比较范围
□注意事项:
如果这里为副词最高级,前面的the常常省略。介词in和of的用法完全不一样。in表示“在某一范围内”,如:in the classroom,in the world。of表示“在同类之间”,of后面的词与主语同类,另名词前一般有冠词the。among表示“在(三者或三者以上)之间”,among后接代词或没有修饰语的名词。
The Yangtze River(The Changjiang River) is the longest river in our country.
长江是我们国家中最长的河流。
Peter is the tallest of the six students.
皮特是六个学生中最高的一个。
This picture is the most beautiful among these.

以上就是关于比较级的句型结构 ,比较级的八种句型结构加举例的全部内容,以及比较级的句型结构 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
