本文目录
现在分词在什么时候用
现在分词在现在进行时的时候用。
作用:现在分词(present participle)(又称-ing形式,现在进行时),是分词的一种,分词又分为现在分词和过去分词,它们都是非限定动词。
怎么用:现在分词在句子里面不能单独充当谓语,但能充当其它的一些成分(定语,表语,补语,状语),并且它们具有动词的性质。
否定结构
现在分词的否定式由“not+现在分词”构成。如:
Not knowing where to go, she went to the police for help.
她不知道该往哪儿走,就去请警察帮助。(现在分词一般式的否定结构)。
Not seeing John, I asked where he was.
我看不见约翰,于是问他在何处。(现在分词一般式的否定结构)。
动词的现在分词是怎样构成的
现在分词(present participle)(又称-ing形式,现在进行式) ,是分词的一种, 分词又分为现在分词和过去分词,它们都 是非限定动词,现在分词在句子里面不能 单独充当谓语,但能充当其它的一些成分 (定语,表语,补语,状语)
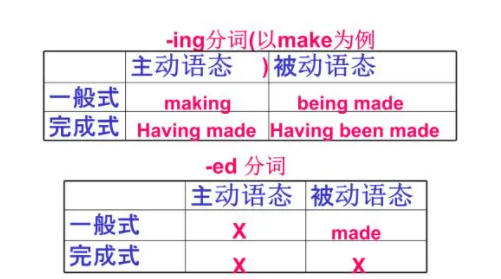
具有动词的性质,所以又是类动词的一 种。一般式:doing; 一般被动式: being done; 完成式:having done; 完 成被动式:having been done。
定式都是在-ing前面加not ,包括独立主 格形式。
比如seeing,asking,going
现在分词变化规则的题
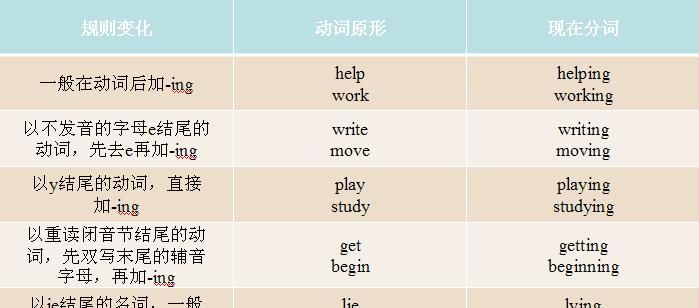
现在分词变化规则是:
1、一般情况直接加-ing;
2、以不发音的e、ue结尾的动词去e, 加-ing;
3、以重读闭音节结尾的动词,并且末尾只有一个辅音字母,最后一个字母不是x的动词ut ----- cutting
put ----- putting
begin ------ beginning
,双写最后一个字母,再加ing;
run——running

注意:rain——raining(不要问我为什么,因为词典上就这么写的)
4、以ie结尾的动词变ie为y,再加-ing;
lie ----- lying
tie ----- tying
die ----- dying
5、以c结尾的动词变c为ck,再加-ing;
6、以l结尾的动词 如果动词原形以非重读音节结尾,则末尾的字母l双写与不双写均可;
7、部分以-p结尾的动词同样遵循第6条,这类词多由“前缀+名词”构成。 如果动词原形以非重读音节结尾,则末尾的字母p双写与不双写均可。
英语上现在分词是什么意思
现在分词的基本用法: 现在分词表示主动的意义;表示一般性的或正在进行的动作;在表现形式上有“一般式”和“完成式”与“主动式”和“被动式”之分, 1)作表语 现在分词作表语通常表示主语所具有的特征.例如: This story is quite interesting. The journey without you will be boring. 2)作定语 现在分词可以单独作定语,也可以构成合成词作定语,但在更多情况下是分词短语作定语,包括限定性和非限定性(用逗号与其他部分分开),在意义上相当于一个定语从句.现在分词作定语通常带有主动意义和未完成意义.例如: The man following was obviously in a hurry.(现在分词单独作定语) They acted just like a conquering army.(现在分词单独作定语) Do you know the man standing over there by the door? (分词短语作限定性定语) Last night,we caught a thief stealing John’s bike.(分词短语作限定性定语) The name Nebraske comes from the Oto Indian word “ebrathka”,meaning flat water.(分词短语作非限定性定语) 3)作宾语补足语 a.表示感觉和心理状态的动词,如hear,feel,find,listen to,look at,watch,notice,observe,smell,see等词的宾语可以用现在分词作宾语补足语.例如: I noticed him slipping away before the end of the meeting. I can smell turkey roasting,and it's making me hungry. b.表示“致使”等意义的动词,如catch,get,have,keep,leave,set等词的宾语可以用现在分词作宾语补足语.例如: What I saw just now set me thinking of my childhood in the countryside. Please don't keep the machine running while you are away. 4)作状语 现在分词作状语表示主语在进行一动作的同时所进行的另一动作,它对谓语动词起修饰或陪衬的作用.这时要注意现在分词与其逻辑主语在时态和意义上的统一.例如: Rushing out of the room,he was knocked down by a car.(作时间状语) = When he rushed out of the room,he was knocked down by a car. Working harder,you will pass the entrance exam. (作条件状语) = If you work harder,you will pass the entrance exam. She sat at a window,reading a book.(作伴随状语) =She sat at a window and read a book. Having won the championship,he was awarded a million dollars.(作原因状语) = Because he had won the championship,he was awarded a million dollars. Even if taking a taxi,I will still be late for the meeting.(作让步状语) = Even if take a taxi,I will still be late for the meeting. The road is under construction,thus causing the delay. (作结果状语) = The road is under construction,and thus caused the delay. 注意,当现在分词作让步状语时,一般放在句首,常常由although,though,even if, unless等连词引入;作结果状语时,一般放在句末,前面可以加so,thus,hence,thereby等副词. 过去分词的基本用法: 与现在分词不同,过去分词表示被动的意义,表示已经完成和被动的动作.在表现形式上,只有一种形式. 1)作表语 过去分词作表语表示主浯所处的状态.用作表浯的过去分词大多来自及物动词;不及物动词的过去分词能作表语的只限于少数表示位置转移的动词,如go,come,assemble等,它们用在连系动词之后,表示完成意义,无被动意义.例如: The man looked quite disappointed. He is greatly discouraged by her refusal. His hair is nearly all gone. 已经形容词化了的过去分词大多可作表语,常见的有:accomplished,amazed,amused,astonished,broken,closed,completed,complicatcd, confused,crowded,devoted,disappointed,discouraged,drunk,excited,frightened,hurt,interested,lost,satisfied,surprised, worried等. 做定语 a) 前置定语的过去分词通常来自及物动词,带有被动意义和完成意义.例如: We like skating in the frozen lake in the winter. = We like skating in the lake which has been frozen in the winter. How many finished products have you got up to now? = How many products that have been finished have you got up to now? 来自不及物动词的过去分词很少能单独用作前置定语,能作这样用的仅限以下几个词,这时仅表示完成意义,不表示被动意义: a retired worker = a worker who has retired an escaped prisOner= a prisoner who has escaped a faded/withered flower = a flower that has faded the risen sun = the sun that has just risen a returned student = a student who has returned vanished treasure = treasure that has vanished b)用作后置定语的过去分词通常也来自及物动词,表示被动意义和完成意义.这时相当于一个定语从句.例如: Things seen are better than things heard. = Things which are seen are better than things which are heard. The lobster broiled over charcoal was delicious. = The lobster which was broiled over charcoal was delicious. 做宾语补足语 a) see, hear, feel,find,think等表示感觉和心理状态的动词可以带过去分词作宾语补足语.例如: Tom found himself involved in an awkward situation. I saw Tom dressed like a beggar in the street. Everybody thought the match lost until the last minute. d) make, get, have, keep 等表示“致使”意义的动词可以带过去分词作宾语补足语.例如: I have my clothes washed everyday. Don't get your schedule changed;stay with us in the class. He’s trying to make himself understood. Please keep us informed of the latest price. c)like,want,wish,order等表示希望、要求、命令等意义的动词可以带过去分词作宾语补足语.例如: We don't like such topics (to be) discussed in class. I wish this problem (to be) solved this week. 4)作状语 用作状语的过去分词通常来自及物动词.过去分词用作状语时,修饰主句的谓语动词,意义上相当于状语从句,表示时间、条件、原因、伴随状况等.过去分词作状语,前边往往可以加when, while, if,as if, though.一般说来,这种结构的逻辑主语必须与主句的主语一致.例如: Whenever praised,she blushes.(作时间状语) = Whenever she is praised,she blushes. United,we stand;divided,we fall.(作条件状语) = If we are united,we stand;If we are divided,we fall. Written in great haste,this book is full of errors.(作原因状语) = Because this book is written in great haste,it is full of errors. Mary was reading a love story,completely lost to the romantic life.(作伴随状浯) = Mary was reading a love story,and was completely lost to the romantic life. Although born in Germany,John lives and works in U.S.A. (作让步状语) = Although John was born in Germany,he lives and works in U.S.A. 3.分词的完成式及被动式 前面提到过,过去分词只有一种形式,所以这里所讲的完成式及被动式均指现在分词的完成式及被动式. 如果现在分词表示的是一般性动作,不表明动作的先后或与谓语动作同时发生,这时要用现在分词的一般形式.例如: Living in the downtown,we found a lot of amusements. 如果现在分词所表示的动作先于句子谓语发生,就要用现在分词的完成式“(not) having+过去分词”.例如: Having heard from my father,I was relieved. Not having received any letter from my family,I was worried. 如果现在分词的逻辑主语是现在分词所表示的动作的对象,则要用现在分词的被动形式,包括其一般形式“(not) being+过去分词”和其完成形式“(not) having been+过去分词”.例如: Upon being questioned,he denied having robbed the bank. The new method,having been widely used abroad,can increase the working efficiency. 4.分词独立结构 如果过去分词或现在分词带有与句子主语不同的主语,这就构成了独立结构,也叫独立主格结构或垂悬结构,通常在句中起状语丛句的作用,表示原因、时间、条件、方式或伴随状况.例如: The holidays being over,they began to get down to do their work again.(原因状语) = As the holiday was over,they began to get down to do their work again. All things considered,her paper is of greater value than yours.(条件状语) = All things are considered,her paper is of greater value than yours. His homework done,Johan went out to play. (时间状语) = After his homework had been done,Johan went out to play. The girl was smiling sweetly,her long hair flowing in the breeze.(伴随状语) 当独立结构表示伴随状况时,可变为由with引导的介词词组, 而表示否定意义的类似结构便可由without引导.例如上例可变为: The girl was smiling sweetly with her long hair flowing in the breeze. Without anyone noticing,I slipped out of the room. 独立结构的位置比较灵活,它可以置于句首、句中或句末.另外,独立结构中用作主语的名词之前的限定词有时可以省略.例如: The manager sat quietly in his office,(his) eyes closed. He stood in the doorway,(his) wet cloak dripping water on the rug,and waited for some sign of recognition.
详细的你可以看大法。

以上就是关于怎么样的现在分词 ,现在分词在什么时候用的全部内容,以及怎么样的现在分词 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

