本文目录
定语从句的用法归纳总结视频讲解
定语从句是高中英语的重要语法项目之一,它的结构和用法比较复杂。我们应从哪些方面有效地复习定语从句呢?下面就是我给大家带来的定语从句的用法讲解,希望大家喜欢!
[定语从句的种类]
定语从句分为限制性和非限制性两种。限制性定语从句是 句子 不可缺少的部分,如去掉主句意思就不完整或失去意义;非限制性定语从句是先行词的附加说明,去掉也不会影响主句的意思。它与主句之间通常用逗号分开,一般不用that引导,关系词不可省略。如:
This is the book that I want to read. (限制性)
Tom’s father, who arrived just now, is a famous scientist. (非限制性)
非限制性定语从句的先行词成分可以是整个主句,非限制性定语从句常用which引导,修饰整个句子。定语从句的谓语动词要用第三人称单数。例如:
The weather turned out to be very good, which was more than we could expect.
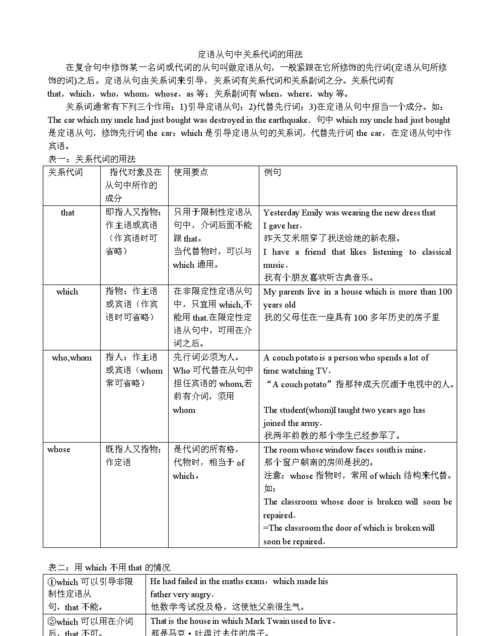
关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词所指代的先行词是表示人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。
在定语从句中,who和that既可作主语又可作宾语,whom只可作宾语(作宾语时可以省略)。如:
Is he the man who/that wants to see you? (who/that在从句中作主语)
The man (whom/who/that) you spoke to just now is our English teacher. (whom/who/that在从句中作宾语,可省略)
[whose]
在定语从句中作定语,可用来指人或物,表示物时相当于“the+名词+of+which”或“of+which+the+名词”。如:John, whose wife is ill, can’t come to the party.
[which & that]
which和that指代的先行词是表示事物的名词或代词,在定语从句中可作主语、宾语等。如:
Please show me the radio that/which you have just bought. (that/which在从句中作宾语,可省略)
This is the film that/which created a great sensation. (that/which在从句中作主语)
只能用that而不能用which的情况:
1. 先行词是最高级或被最高级修饰时。如:This is the best dictionary that I’ve ever used.
2. 先行词是序数词或被序数词修饰时。如:The first thing that we should do is to get some food.
3. 当先行词是anything, everything, nothing, something, few, all, none, little, some等不定代词时,或是由every, any, all, some, no, little, few, much等词修饰时。如:Tom told his father all that had happened.
There is little that I can do for you.
4. 先行词既有人又有物时。如:They talked about the teachers and the schools that they knew.
5. 先行词被the only,the very,the right等修饰时。如:This is the very book that I want to have.
6. 在which,who,whom引起的问句中,为避免重复。如:Who is the girl that talked to you yesterday?
7. 关系代词在定语从句中作表语时。如:China is not the country that it was.
只能用which,不能用that的情况:
1. 在非限制性定语从句中。如:Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a very long histroy.
2. 在介词后面,即“介词+which(指物)”。如:This is the house in which we lived three years ago.
[as]
关系代词as代替的先行词是人或物的名词, 在从句中作主语、宾语和表语。
as引导限制性定语从句时,常和such, the same, as(so)连用, 构成such ... as, the same ... as, as/so ... as等结构,在从句中可作主语、宾语和表语。如:
Don’t trust such men as praise you to your face. (在定语从句中作主语)
I have the same trouble as you have. (在定语从句作宾语)
It’s as pleasant a film as I have ever seen. (在定语从句作宾语)
但是当先行词被the same修饰时,that也可以引导定语从句,但意义有所不同。the same ... as(指同样或同类的), the same ... that(指同一个)。例如:
This is the same watch as I lost.
This is the same watch that I lost.
as也可单独使用,引导非限制性定语从句,修饰整个主句或主句中的一部分,放在句首、句中或句末。如:
As is known to us all, smoking is harmful to one’s health. (指代整个主句,在从句中做主语)
He is late, as is often the case. (指代整个主句,在从句中做主语)
Light, as everybody knows, travels much faster than sound. (指代整个主句,在从句中做宾语)
as和which作关系代词的用法比较:
which引导的非限定性定语从句只能放在主句之后,which指代前面的一个句子或主句中的某一成分;as引导的非限定性定语从句能放在主句之前、中、后,既可指前面已经提到的情况,也可指后面提到的情况。
as引导从句时,有“为人所熟知”的含义,which则没有这层意思。as引导的从句往往表示的是一种附加说明,which引导的从句一般是较为重要的陈述。如:
His mother is ill, which makes him very sad.
As is expected, the England team won the football match.
[关系副词引导的定语从句]
关系副词when, where, why可代替的先行词是时间、地点或理由的名词,在从句中作状语, 相当于“介词+which”结构。例如:
I’ll never forget the time when/during which we worked in the factory.
This is the village where /in which he was born.
I don’t know the reason why/for which she looks unhappy today.
[判定用关系代词还是用关系副词]
关系代词与关系副词的选用,应看先行词在定语从句中充当什么成分:若作主语、宾语或定语,则用关系代词who,whom,that,which,whose,as等;若作状语, 就用where, when, why等关系副词。如:
The reason why I’m writing is to tell you about a party on Sunday. (状语)
The reason that/which he gave us sounded reasonable. (宾语)
Pisa is a city, which has a leaning tower. (主语)
Pisa is a city, where there is a leaning tower. (状语)
[介词+关系代词]
当关系代词作介词宾语时,就出现了“介词+关系代词”的结构引导定语从句的现象。当先行词指物时用“介词+which”,指人时用“介词+whom”,且关系代词不能省略。而这种结构中较难解决的问题是介词的选择问题:
1. 介词的确定可以根据整个句意来确定。
Oxygen is a kind of gas, without which we couldn’t live.
2. 介词可以根据与先行词的搭配来确定。
He gave me the book for which he paid a lot of money. (动词与介词搭配)
1949 was the year in which the P.R.C. was founded. (名词与介词搭配)
The snake, of which she used to be afraid, is her favorite animal now. (形容词与介词搭配)
定语从句的用法讲解相关 文章 :
1. 英语中as引导的定语从句的相关讲解
2. 定语从句中关系词的用法讲解
3. 英语定语从句的用法
4. 英语数词的分类和用法
5. 高中英语语法知识总结:定语从句
6. 考点初中英语定语从句的用法
7. 非限制性定语从句的用法讲解
8. 英语语法:定语从句
9. 定语从句语法知识点汇总
定语从句的用法
有关定语从句的用法:
一、定义
用来修饰句子中的名词或代词或其短语的从句,就叫做定语从句。其实,就是拿句子来做名词、代词或是其短语的定语。如:
It's a book.
I bought the book yesterday.
以上两句话中,都有book一词,所以可以用定语从句把两句话连起来。即:
It's the book that I bought yesterday.
这句话中that引导的I bought yesterday就是一个定语从句,用来修饰the book。
二、两个概念
要想学好定语从句,得先弄清楚两个基本概念,即:先行词和关系词。
(一)先行词
所谓先行词,就是指定语从句所修饰的成分。这个名称倒是挺形象的,为什么?因为先行词永远出现在定语从句的前面,总是先走一步的,呵呵!
(二)关系词
所谓关系词,就是指用来连接定语从句的词语。关系词可以分为关系代词和关系副词。需要注意的是,关系代词或关系副词都要在从句中充当成分的,所以是不可或缺的',尽管当关系代词在从句中作宾语时,经常可以省略(本文会继续讲到这个情况)。
我们在来看一下在第一节里出现的句子:
It's the book that I bought yesterday.
句中的the book就是先行词,被后面的从句I bought yesterday所修饰。而that就是关系代词,用来连接I bought yesterday,同时又在从句作bought的宾语,而且可以省略。
定语从句的学习,其实就是有关根据先行词的特点选择合适的关系词的学习。
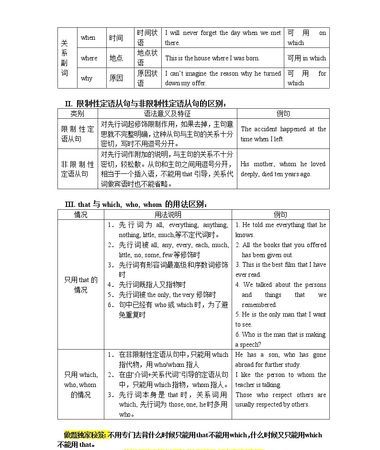
三、分类
按照定语从句与先行词的关系紧密与否,可以分为限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句。
(一)限定性定语从句
限定性定语从句对先行词起着修饰限定作用,是不可或缺的。如:
These are the apples that/which they sent us two days ago.
(二)非限定性定语从句
非限定性定语从句对先行词起着补充说明作用,可要可不要。非限定性定语从句都会被逗号与先行词隔开。如:
They have to walk to the South Pole, which is out of a plane's reach.
【注意】
1、当先行词具有唯一性的时候,就只能采用非限定性定语从句,否则就会产生歧义或误解。如:
限定性定语从句:His wife who is now in Paris is one of my old classmates.
非限定性定语从句:His wife, who is now in Paris, is one of my old classmates.
因为限定性定语从句对先行词起着修饰限定作用,所以具有特指功能,所以第一句中的限定性定语从句意味着是特指他在巴黎的妻子,其潜台词就是他不只一个妻子,也许在上海或者在纽约等其他地方还有妻子。
而非限定性定语从句只对先行词起着补充说明作用,没有特指功能,所以第二句中的非限定性定语从句只是用来补充说明他的妻子现在人在巴黎这个事实。
2、that和why不能用来引导非限定性定语从句
that不能用来连接非限定性定语从句,具体的请看下一节的内容。
而why因为总是紧跟先行词reason,所以也不能用于引导非限定性定语从句。如:
That's the reason why he was late for school this morning.
在reason和why之间,不能插入逗号。
四、关系代词
英语里能够用来连接定语从句的关系代词主要有:
that:表人或物
which:表物
who:表人(主格或宾格)
whom:表人(宾格)
whose:表人或物(所有格)
that引导的定语从句
that引导定语从句时,其先行词既可能是人,也可能是物。如:
This is the photo that I took during the trip in France.
He is the man that will visit our school next week.
【注意】
1、当that的先行词表物时,可以用which来替换。此外,当that在从句中作宾语时,可以省略。如:
This is the photo that/which I took during the trip in France.
This is the photo I took during the trip in France.
句中的先行词the photo在从句I took during the trip in France中作took的宾语,所以可以省略。
2、不能用that的情况
1)当定语从句以介词开头时,一般不用that,而要用which或whom。如:
This is the pet dog for which I paid five hundred pounds.
She is the girl to whom I talked just now.
两句话的定语从句分别以介词for和to开头,所以后面不能再用that,而要采用which和whom。
2)当先行词是that时,往往用which来替换。如:
We have that which we need.
此时,that which往往可以用what来替换,因此我们可以把上面的句子改为:
We have what we need.
3)在非限定性定语从句中。如:
错误:His aunt, that is our maths teacher, often gives us candies as gifts.
正确:His aunt, who is our maths teacher, often gives us candies as gifts.
3、只能用that的情况
1)当先行词为everything、all,little、much等不定代词时。如:
All that glitters is not gold.
2)当先行词被all、every、no、any、some、little、much、one修饰时。如:
Don't waste any water that is reusable.
3)当先行词被the only、the very、the same、the last修饰时。如:
They are the only students that will attend the meeting.
4)当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。如:
This is the first time that I have ever heard about a ghost.
5)当先行词是be的表语或there be 的主语时。如:
There are five pens that will be on display tomorrow.
6)当先行词有人又有物时。如:
We don't like the teacher and his lessons that are not interesting at all.
7)当主句是以who或which及其-ever结构开头的特殊疑问句时。如:
Whoever that breaks the law will be punished.
4、多用who、不用that的情况
1)当先行词为anyone、one、ones时。如:
He is the one who will teach us English.
2)当先行词为those、he和people时。如:
Those who want to ask questions need to write them down first.
定语从句的规则
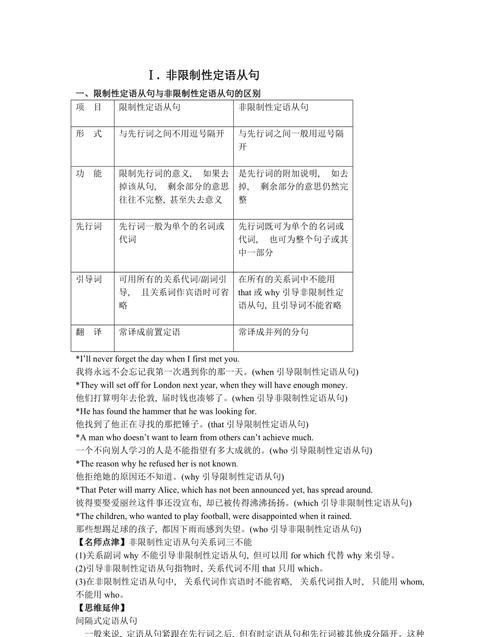
语法专题:定语从句
定语从句和形容词是近亲,都喜欢修饰n.或pron.
1. 先行词 :被定语从句修饰的n.或pron。
2. 限制性定语从句 和 非限制性定语从句 的区别。
Those who want to go, please sign their names here.(限制性定语从句)
This note was left by John, who was here a moment ago.(非限制性定语从句)
3.从句不完整,用 关系代词 ;从句完整,用 关系副词 。
1.That:
指人或物. 在定语从句中作主语,宾语,表语。作宾语时可省略。指人时,可与who, whom互换,指物时有时可与which互换。
I know the inventor that attended the meeting.(作主语)
He is the adviser(that)you are looking for. (作宾语)
【注意】
只能用that而不用which的情况:
第一种讲解方法:
(1)先行词为everything, something, anything, nothing,all, none, some,few, little,much,the one 等不定代词时;
I mean the one that was bought yesterday.
That is all that I have.
(2)先行词被形容词最高级或被only, any, few, little, no, all, one of 等修饰时;(如果先行词指人,可用关系代词who)
It is the most important taskthatshould be finished soon.
Don’t tell me any words that have nothing to do with me.
(3)先行词为数词或被序数词(含last)修饰时;
Look at these flowers. You can see the two thatyou gave me.
The first thing that my brother is going to do this afternoon is to write a letter.
(4)先行词被the only(唯一), the very (正是),the same (同一个)等词修饰时。
This is the very book that I want.
(5)先行词中既有人又有物时:
We were deeply impressed by the teachers and schools that we had visited.
(6)先行词在主句中作表语,或关系代词在从句中作表语时;
It’s a book that will help you a lot.
My home town is no longer the place that it used to be.
第二种讲解方法:
两:先行词既有人又有物
代:先行词为everything, anything, nothing, all等指物的代词时
限:先行词被the only, the very, the last,以及much,little, few, no等限定词修饰时
形:先行词被形容词最高级修饰时
数:先行词为数量词
特:特殊疑问句
有:There/Here is句型中
重:多重定语从句中已经有了which,为避免重复
表:关系词在从句中作表语
序:先行词被序数词修饰
口诀:两代限形数,特有重表序
2.Which:
指物,在定语从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时可省略。引导非限制性定语从句,可指代主句全句内容。
The tornado which happened last week was violent. (作主语)
He set the bird free, which made him happy. (作主语,指代主句全句)
Is that the entertainment program (which)you want to watch? (作宾语)
【注意】
只能用which不能用that 的情况:
(1)关系代词前有介词且指物时;
This is the room in whichLu Xun lived.
(2)非限制性定语从句中:
He has a daughter, whoworks in a hospital.
(3)先行词本身是that:
The clock is that which tells the time.
1. Who:
指人,在定语从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时可以省略。
The man who is sitting in the front row is an architect.
The old man (who/whom)you saw yesterday is a thinker.
2. Whom:
指人,在定语从句中作宾语,可用who代替。
Is that the teacher (whom/who)you referred to ?
【注意】关系代词在从句中作宾语时常可省略,但介词提前时,关系代词只能用which或whom,且不能省略。
3. Whose:
既可指人可也指物,在定语从句中作定语。
They live in a house whose window faces south.
4. As:
既可指人也可指物,在定语从句中作主语,宾语或表语。
(1)引导限制性定语从句,用于such...as,so...as, the same...as,as many(或as much)...as 结构中:
The houses are sold at such a low price as people expected.
This is the same book as I read last week.
(2)引导非限制性定语从句,说明这个主句;从句的位置可在主句前,主句中或主句后,常用逗号和主句隔开。
As you know, our band was formed in a very unusual way.
As is often the case, Mary was late for school.
【补充】
as和which 的区别:
相同点:as, which 在非限制性定语从句中,都可指代整个句子,都可作主语,宾语,表语。
不同点:
1. 位置:as的位置灵活句首,句中都可以;which只放在句中。
2. 语义:as“正如”。
3. 固定搭配:as be done.
二.关系副词
1. Where:
当定语从句修饰地点名词,且关系词在从句中作地点状语时。相当于in/at/on...+which
Ancient China was a place where(=in which) states were often at war with each other.
【注意】先行词为表地点含义的抽象名词situation,case, position, point等,且从句缺少状语时,常用where引导定语从句。
It’s helpful to put children in a situation where they can see themselves differently.
2. when:
当定语从句修饰时间名词,且关系词在从句中作时间状语时。相当于in/at/on/during...+which,先行词常为day, week, time 等表时间的名词。
But it was a time when there were many great philosopher.
Between the two parts of the concert is an interval,when(=during which)the audience can buy ice-cream.
3. Why:
当先行词是the reason,且关系词在从句中作原因状语。相当于for which.
This is the reason why=(for which)I’ve changed so much.
【注意】
先行词reason如在从句中作主语或宾语,其后的定语从句用that 或which 引导。
The reason that/which he explained to me is unreasonable.
【误区警示】
先行词表示时间或地点时,关系词不总是用when或where。如果关系词在定语从句中作主语或宾语,就要用which 或that.
I will never forget the days that we spent together.
三.介词+关系代词
【注意】
有这种用法的关系代词主要是which 和whom
1. 一先:介词根据先行词的习惯搭配来确定。
I remember the day on which I joined the party.
the days during which I lived here.
the month in which I stayed here.
1.二动:介词根究从句中谓语动词的习惯搭配来确定。
This is the book on which I spent five dollars.
for which I paid five dollars.
from which I learnt a lot.
about which Tom often talks.
2.三意义:介词根据句子意义来确定。
This is the book from which I got the story.
【注意】
在非限制性定语从句中表“所有关系”或“整体中的一部分”时常用介词of。
The musicians were to play jokes on each other as well as play music, most of whichwas based loosely on the Beatles.
三.定语从句中的几个注意点
1.先行词为way:
(1)若引导词在从句中作主语,宾语或表语时,用关系代词which 或that 引导。
The way (that/which)you came up with at the meeting yesterday is well worth trying.
(2)若从句缺少方式状语,相当于“用这种方式/方法(=in this way)”
时,用that或in which 来引导,可省略。
Is this the way (that/in which)you deal with the garbage?
2.先行词为time:
(1)作“次数”讲,用that来引导。
I could hardly remember how many times (that) I’ve failed.
(2)作“一段时间”讲。
情况一:关系词在从句中作主语,宾语等,用that/which来引导。
I will never forget the time which/that we spent on the farm.
情况二:关系词在从句中作状语,用when或at/in/during which来引导。
He lived in a time when/during whichthere were no cars.
3.whose
可以与the +n.+of+which/whom互换。
We study in a room whosedoor faces south.=We study in a room the door of whichfaces south.
4.定语从句中的主谓一致
(1)关系代词在句中作主语,从句谓语动词单复数与先行词保持一致。
Children who are not active or whose diet is high in fat will gain weight quickly.
(2)先行词为one of +复数名词时,从句谓语动词用复数形式;先行词为the (only/very/right)one of +复数名词 时,从句谓语动词用单数形式。
That is one of the most expensive dictionaries that have come out in recent years.

以上就是关于定语从句用法规则 ,定语从句的基本语法规则的全部内容,以及定语从句用法规则 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

