本文目录
英语被动语态的特殊用法初三
① 有些动词在主动结构中,后面接不带to的不定式,但如果改为被动,则需把省略的to加上,这类动词有 [let, make, have,help]和感官动词[feel,see,hear,watch,look at,listen to],如:The boss made my grandfather work 10hours a day.改成My grandfather was made to work for 10 hours a day. ② 含有宾语从句的主动结构变为被动,通常用it作为被动结构的先行主语,从句放在句子后面/也可采用另一种形式,这类动词有:know, say, believe, find, think, report等 ③ 不是所有的主动句都可以变换成被动句,更不是所有的被动句都可以自由变换成主动句。虽然语法原则上允许主动和被动句的互相转换,但有的句子转换后会变成不通顺或不地道的英语句子。因此,在某些题目里,这也成为判断应该用主动还是用被动的依据。 例:At 5:05 p.m. on Saturday 19th July , there was an accident at the junction of the Main Street and Panda Road when a boy was knocked down off his bicycle by a delivery van. The boy was sent to St. Maria Hospital where he was treated for shock and a broken arm. 在这段文章里,a boy was knocked down off his bicycle by a delivery van这句被动句强调出读到文章的人最关心的事故的受害者。The boy was sent to St. Maria Hospital这句话则说明了孩子被送到医院的事实,至于是由谁(某个过路人?或肇事司机?)送的不重要。he was treated for shock and a broken arm这句被动句无须说出treat这个动作的发出者,因为在医院,伤病员自然由医务人员处理,无须罗嗦。这样,这段文章就重点突出,条理清楚了。 ④ 有些动词可以有两个宾语,在用于被动结构时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一个宾语仍然保留在谓语后面。多是把间接宾语变为主语。这样句子自然些。直接宾语变为主语时,间接宾语要变为某个介词的宾语,介词to可以省略。如His father left him this house.改为This house was left (to) him by his father. ⑤ 有些动词虽为及物,但宾语并非是动作承受者,不能转换,这些动词有have, hold(容纳),suit, fit, lack, become(适合)contain, cost, last, mean, suffice(足够)等。 ⑥ 当直接宾语为反身代词、相互代词或宾语前有指代主语的物主代词时不用被动,如I shook my head.我摇摇头。 ⑦ 当宾语为同源宾语(与主句指同一人),动名词,动词不定式或一个从句时不用被动。如John enjoyed seeing the fil,. ⑧ 在一些固定说法中,有些名词和动词结合的固定说法,不能改We Chinese always keep our word. ⑨ 某些从不及物动词转化来的及物动词,直接宾语在表示动作的方式或效果时,这些动词在意思上起状语的作用,没有被动The girl kissed her boyfriend good night=The girl said good night to her boyfriend by kissing him.(这个女孩说了晚安并且亲了他的男朋友) ⑩ 表地点\处所\组织\长度\大小\数量\程度\抽象名词的词做宾语时不用被动. ⑪ 某些“不及物动词+介词”短语,walk into, listen to, sleep in, agree with, shake hands with, belong to, take part in, keep up with不能用被动。 ⑫ 某些词用主动表被动:sell, miss, build, grow, look, smell, taste, sound, feel等

雅思阅读中的NB是什么意思
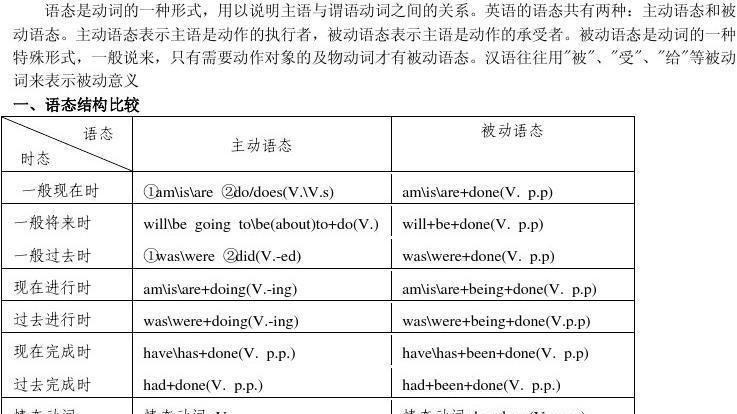
被动语态是由助动词“be”+过去分词构成的。这里的“be”既要表示出与主语的人称和数一致,也要表示出时、体的形式。被动语态有几种特殊用法。
(1)主动形式表示被动意义
1)常见的这类动词有:“act,add up,clean,compare,count,cook,draw,fill,iron,keep,let,look,make up,milk,kill,open,photograph,prove,read,sell,smoke,spoil”等。
The window won’t open.(这扇窗户打不开。)
The cow milks well.(这头牛出奶率很高。)
Damp wood will not fire.(湿木不易燃烧。)
She doesn’t photograph well.(她不上相。)
His judgment proved wrong.(他的判断是错的。)
The banana peels easily.(香蕉皮剥起来很容易。)
Flies kill easily in autumn.(秋天苍蝇容易死亡。)
It turned out fine that day.(结果那天天气很好。)
How did his coat catch on a nail? (他的衣服怎么钩到钉子上了?)
2)实用动词“need/want/deserve/require +V-ing(动名词)”形式表示被动意义。
My hair needs cutting。.
The bike wants repairing.
It doesn’t deserve mentioning.
Hamlet is required reading for the course.(《哈姆雷特》为本课程指定读物。)
3)一些固定句型如:"be worth doing sth. have/get sth.(sb.)done",以及to be under(in)+抽象名词等表示被动意义:
Beijing is a big city in China and worth visiting.(北京是中国的一个大城市,值得浏览。)
Mr..Wilson had his wallet stolen the day before yesterday.(威尔逊先生前天丢了一个钱包)。
The bike is under(in)repair.(自行车正在修理中。)
This tape recorder is in use.(这种录音机正在使用中。)
4)一些不定式的主动态表示被动意义:
①There be句型:
There are a lot of things to do.
There is nothing to worry about.
②不定式修饰want, have等动词的宾语,而句中的主语同时又不是不定式的逻辑主语时:
I want some clothes to wash.
Do you have anything to say for yourself?
③不定式修饰buy,get,give等动词的直接宾语,而句中的间接宾语又是不定式的逻辑主语时:
His sister gave him a bike to ride.
My father get me a book to read.
5)少数动词的进行时,有时表示被动意义:
Her works are printing.
The drum is beating.
My new house is building.
(2)“It is+V-ed+that-··"结构表示被动
常用的这类结构有:“it is said that…”(据说);It is supposed that…(据推测);It is well known that"…(众所周知);It is believed that"…(据信);It is reported that"…(据报导);It is hoped that"…(人们希望);It is generally considered that"…(有人认为);1twill be seen that"…(由此可以看出);It must be admitted that…(必须承认);It must be pointed out that…(必须指出)”等。
It is believed/thought that this medicine works well.
It is required(of)him that he give the evidence.(要求我提供证据)
It is feared that he could not come here.
It is estimated that a flight to Shanghai would take more than one hour.
It is often realized that women held a high social position in the Southern European societies in the 10th and llth centuries.
(3) “get + p.p.(动词的过去分词)"表示被动:
这种结构往往用来强调动作的结果,也可用来表示突然发生的事态,或最终出现的某种事实,是一种非正式语体。
Did the question get answered?
A Boeing 747 got crashed last week.
The house is getting painted/repaired.
The building got damaged in the flood.
Thousands of soldiers got killed in the war.
As I passed by, my coat got caught on a nail.
[注]在下列句子中,不能使用“get + p.p. (动词的过去分词)”结构。
误:He got born in 1976.
正:He was born in 1976.
误:The stow got written by him.
正:The story Was writ.ten by him.
误:The conference got being held in London.
正:The conference is being held in London.
(4) 注意以下被动语态的几种情况
1)短语动词变为被动语态后,其后的介词或副词应紧随其后。
Frank was brought up by his aunt.
The babies are well looked after.
The meeting Was put off.
The salesman was put out by Mr..Wilson’s question.
(威尔逊先生的问题把那位售货员惹火了。)
2)“Verb+宾语+宾补”变为被动语态后,宾语转化为主语,宾补转化为主补。
The wall Was painted white.(We painted the wal1 white.)
He is regarded as smart (We regarded him as smart.)
The house was found empty.(We found the house empty.)
He Was heard to play the guitar in the next door.
(I heard him play the guitar in the next door)
It is believed/thought that this medicine works well.
It is required(of)him that he give the evidence.(要求我提供证据)
It is feared that he could not come here.
It is estimated that a flight to Shanghai would take more than one hour.
It is often realized that women held a high social position in the Southern European societies in the 10th and llth centuries.
(3) “get + p.p.(动词的过去分词)"表示被动:
这种结构往往用来强调动作的结果,也可用来表示突然发生的事态,或最终出现的某种事实,是一种非正式语体。
Did the question get answered?
A Boeing 747 got crashed last week.
The house is getting painted/repaired.
The building got damaged in the flood.
Thousands of soldiers got killed in the war.
As I passed by, my coat got caught on a nail.
[注]在下列句子中,不能使用“get + p.p. (动词的过去分词)”结构。
误:He got born in 1976.
正:He was born in 1976.
误:The stow got written by him.
正:The story Was writ.ten by him.
误:The conference got being held in London.
正:The conference is being held in London.
(4) 注意以下被动语态的几种情况
1)短语动词变为被动语态后,其后的介词或副词应紧随其后。
Frank was brought up by his aunt.
The babies are well looked after.
The meeting Was put off.
The salesman was put out by Mr..Wilson’s question.
(威尔逊先生的问题把那位售货员惹火了。)
2)“Verb+宾语+宾补”变为被动语态后,宾语转化为主语,宾补转化为主补。
The wall Was painted white.(We painted the wal1 white.)
He is regarded as smart (We regarded him as smart.)
The house was found empty.(We found the house empty.)
He Was heard to play the guitar in the next door.
(I heard him play the guitar in the next door)
详解雅思阅读被动语态的几种特殊用法英语
被动语态是由助动词“be”+过去分词构成的.这里的“be”既要表示出与主语的人称和数一致,也要表示出时、体的形式.被动语态有几种特殊用法.每个人的情况不同,也可以登录文都国际教育官网进行一对一的咨询。
(1)主动形式表示被动意义
1)常见的这类动词有:“act,add
up,clean,compare,count,cook,draw,fill,iron,keep,let,look,make
up,milk,kill,open,photograph,prove,read,sell,smoke,spoil”等.
The window won’t open.(这扇窗户打不开.)
The cow milks well.(这头牛出奶率很高.)
Damp wood will not fire.(湿木不易燃烧.)
She doesn’t photograph well.(她不上相.)
His judgment proved wrong.(他的判断是错的.)
It turned out fine that day.(结果那天天气很好.)
How did his coat catch on a nail? (他的衣服怎么钩到钉子上了?)
2)实用动词“need/want/deserve/require +V-ing(动名词)”形式表示被动意义.
My hair needs cutting..
The bike wants repairing.
There is nothing to worry about.
②不定式修饰want, have等动词的宾语,而句中的主语同时又不是不定式的逻辑主语时:
I want some clothes to wash.
Do you have anything to say for yourself?
③不定式修饰buy,get,give等动词的直接宾语,而句中的间接宾语又是不定式的逻辑主语时:
His sister gave him a bike to ride.
It is believed/thought that this medicine works well.
It is required(of)him that he give the evidence.(要求我提供证据)
It is feared that he could not come here.
It is estimated that a flight to Shanghai would take more than one hour.
It is often realized that women held a high social position in the Southern European societies in the 10th and llth centuries.
初中被动语态知识点归纳
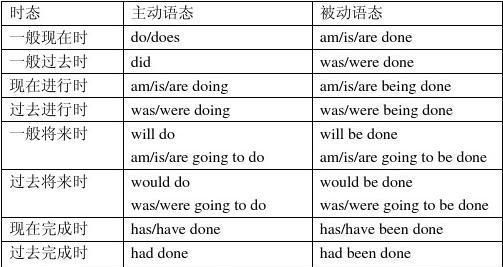
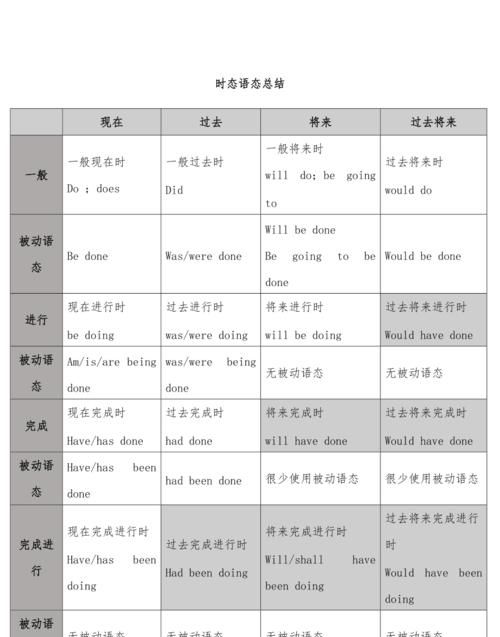
动语态复习“三步曲” 被动语态是动词语态的一种形式,表示主语是动作的承受者。在历年的中考题中,都有一定数量的考查被动语态的题目。因此,有必要对被动语态进行系统复习。 第一曲:掌握被动语态的结构 被动语态由"助动词+及物动词的过去分词"构成。不同时态的被动语态的差异主要体现在助动词be的变化上,同时助动词be还要在人称和数上与主语保持一致。现将初中阶段常见的几种时态的被动语态总结如下: 1.一般现在时的被动语态:am/is/are+done(指及物动词的过去分词,下同)如: English is used all over the world. 2.一般过去时的被动语态:was/were+done如: The picture was painted two years ago. 3.现在进行时的被动语态:am/is/are+being+done如: The flowers are being watered by them now. 4.现在完成时的被动语态:have(has)+been+done如:The room has been cleaned. 5.一般将来时的被动语态:will/be going to+be+done如: The work will be finished tomorrow. 6.含有情态动词的被动语态:情态动词+be+done如:Your homework must be handed in today. 其它几种特殊句型: It is said that …….. It is well known that ……. It is reported that…….. have sth done 第二曲:掌握主动语态变被动语态的方法 把主动语态变为被动语态时,应走好以下三步:1)主动语态的宾语变为被动语态的主语; 2)主动语态的谓语动词由主动语态形式变为被动语态形式; 3)主动结构的主语变为介词by的宾语,组成介词短语,放在被动结构的谓语动词之后。在无须说明动作的执行者或只强调动作的承受者时,by短语可以省略。请看示范: 主动语态:My brother repaired that bike yesterday. 主语 谓语动词 宾语其余部分 被动语态:That bike was repaired (by my brother) yesterday. 主语 谓语动词 by+宾语其余部分 对于主动语态变为被动语态方法的考查,主要在句型转换题目中出现。只要能够按照上面介绍的方法去做,一般是能够做对的。 第三曲:注意主动语态变为被动语态的几种特殊句型 1.含有短语动词的被动语态 一般来说,只有及物动词才有被动语态。另外,许多不及物动词
以上就是关于被动语态6种特殊情况 ,英语被动语态的特殊用法初三的全部内容,以及被动语态6种特殊情况 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

