本文目录
英语句子成分分析
版本一
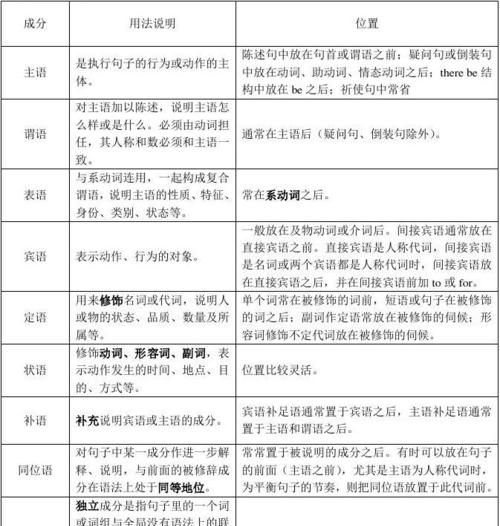
一、句子成分
(一)句子成分的定义:构成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。句子成分有主要成分和次要成分;主要成分有主语和谓语;次要成分有表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语和同位语。
(二)主语:主语是一个句子所叙述的主体,一般位于句首。但在there be结构、疑问句(当主语不疑问词时)和倒装句中,主语位于谓语、助动词或情态动词后面。主语可由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等表示。例如:
During the 1990s, American country music has become more and more popular.(名词)
We often speak English in class.(代词)
One-third of the students in this class are girls.(数词)
To swim in the river is a great pleasure.(不定式)
Smoking does harm to the health.(动名词)
The rich should help the poor.(名词化的形容词)
When we are going to have an English test has not been decided.(主语从句)
It is necessary to master a foreign language.(it作形式主语,真正的主语为后面的不定式)
(三)谓语:谓语说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态。动词在句中作谓语,一般放在主语之后。谓语的构成如下:
1、简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成。如:He practices running every morning.
2、复合谓语:(1)由情态动词或其他助动词加动词原形构成。如:You may keep the book for two weeks. He has caught a bad cold. (2)由系动词加表语构成。如:We are students.
(四)表语:表语用以说明主语的身份、特征和状态,它一般位于系动词(如be, become, get, look, grow, turn, seem等)之后。表语一般由名词、代词、形容词、分词、数词、不定式、动名词、介词短语、副词及表语从句表示。例如:
Our teacher of English is an American.(名词)
Is it yours?(代词)
The weather has turned cold.(形容词)
The speech is exciting.(分词)
Three times seven is twenty one?(数词)
His job is to teach English.(不定式)
His hobby(爱好)is playing football.(动名词)
The machine must be out of order.(介词短语)
Time is up. The class is over.(副词)
The truth is that he has never been abroad.(表语从句)
(五)宾语:宾语表示动作的对象或承爱者,一般位于及物动词和介词后面。例如:
They went to see an exhibition(展览)yesterday.(名词)
The heavy rain prevented me form coming to school on time.(代词)
How many dictionaries do you have? I have five.(数词)
They helped the old with their housework yesterday.(名词化形容词)
He pretended not to see me.(不定式短语)
I enjoy listening to popular music.(动名词短语)
I think(that)he is fit for his office.(宾语从句)
宾语种类:(1)双宾语(间接宾语+直接宾语),例如:Lend me your dictionary, please.
(2)复合宾语(宾语+宾补),例如:They elected him their monitor.
(六)宾语补足语:英语中有些及物动词,除有一个直接宾语以外,还要有一个宾语补语,才能使句子的意义完整。带有宾语补足语的一般句型为:某些及物动词(如make等+宾语+宾补)。宾补可由名词、形容词、副词、不定式、分词、介词短语和从句充当。例如:
His father named him Dongming.(名词)
They painted their boat white.(形容词)
Let the fresh air in.(副词)
You mustn’t force him to lend his money to you.(不定式短语)
We saw her entering the room.(现在分词)
We found everything in the lab in good order.(介词短语)
We will soon make our city what your city is now.(从句)
(七)定语:修饰名词或代词的词、短语或从句称为定语。定语可由以下等成分表示:
Guilin is a beautiful city.(形容词)
China is a developing country; America is a developed country.(分词)
There are thirty women teachers is our school.(名词)
His rapid progress in English made us surprised.(代词)
Our monitor is always the first to enter the classroom.(不定式短语)
The teaching plan for next term has been worked out.(动名词)
He is reading an article about how to learn English.(介词短语)
(八)状语:修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,说明动作或状态特征的句子成分,叫做状语。可由以下形式表示:
Light travels most quickly.(副词及副词性词组)
He has lived in the city for ten years.(介词短语)
He is proud to have passed the national college entrance examination.(不定式短语)
He is in the room making a model plane.(分词短语)
Wait a minute.(名词)
Once you begin, you must continue.(状语从句)
状语种类如下:
How about meeting again at six?(时间状语)
Last night she didn’t go to the dance party because of the rain.(原因状语)
I shall go there if it doesn’t rain.(条件状语)
Mr. Smith lives on the third floor.(地点状语)
She put the eggs into the basket with great care.(方式状语)
She came in with a dictionary in her hand.(伴随状语)
In order to catch up with the others, I must work harder.(目的状语)
He was so tired that he fell asleep immediately.(结果状语)
She works very hard though she is old.(让步状语)
I am taller than he is.(比较状语)
练习一
一、指出下列句子划线部分是什么句子成分:
1. The students got on the school bus.
2. He handed me the newspaper.
3. I shall answer your question after class.
4. What a beautiful Chinese painting!
5. They went hunting together early in the morning.
6. His job is to train swimmers.
7. He took many photos of the palaces in Beijing.
8. There is going to be an American film tonight.
9. He is to leave for Shanghai tomorrow.
10. His wish is to become a scientist.
11. He managed to finish the work in time.
12. Tom came to ask me for advice.
13. He found it important to master English.
14. Do you have anything else to say?
15. To be honest; your pronunciation is not so good.
16. Would you please tell me your address?
17. He sat there, reading a newspaper.
18. It is our duty to keep our classroom clean and tidy.
19. He noticed a man enter the room.
20. The apples tasted sweet.
二、用符号划出下列短文各句中的主语(—)、谓语(=)、宾语(~):
I hope you are very well. I'm fine, but tired. Right now it is the summer vacation and I'm helping my Dad on the farm. August is the hottest month here. It is the time of year for the rice harvest, so every day I work from dawn until dark. Sometimes we go on working after dark by the lights of our tractors. We grow rice in the south of the States, but in the north where it is colder they grow wheat. We have a lot of machines on the farm. Although the farm is large, my Dad has only two men working for him. But he employs more men for the harvest. My brother takes care of the vegetable garden. It doesn't often rain in the summer here. As a result, we have to water the vegetable garden. Every evening we pump water from a well. It then runs along channels to different parts of the garden.
三、用符号划出下列短文各句中的定语(—)、状语(=)、补语(~):
Most Saturday evenings there is a party, even at harvest time. These parties often make us very happy. We cook meat on an open fire outside. It's great! Americans eat a lot of meat — too much in my opinion. Some of my friends drink beer. I don't, because I have to drive home after the party. In your letter you asked about the time in different areas of the States. There are five different time areas in the States. In my state we are fourteen hours behind Beijing time. How many different time areas do you have in China? Well, I must stop and get some sleep. Please give my best regards to your parents.
四、选择填空:
( )1. ____ will leave for Beijing.
A. Now there the man B. The man here now
C. The man who is here now D. The man is here now
( ) 2. The weather ____.
A. wet and cold B. is wet and cold C. not wet and cold D. were wet and cold
( ) 3. The apple tasted ____.
A. sweets B. sweetly C. nicely D. sweet
( ) 4. He got up ____ yesterday morning.
A. lately B. late C. latest D. latter
( )5. The actor ______at the age of 70.
A. dead B. died C. dyed D. deaded
( )6. ____ were all very tired, but none of ____ would stop to take a rest.
A. We, us B. Us, we C. We, our D. We, we
( )7. He found the street much ______.
A. crowd B. crowding C. crowded D. crowdedly
( ) 8.I think _____necessary to learn English well.
A. its B. it C. that D. that is
( ) 9. The dog ____ mad.
A. looks B. is looked C. is being looked D. was looked
( )10.I will never forget the day ______ I joined the army.
A. that B. when C. in which D. where
句子结构
简单句的五个基本句型
主语 + 不及物动词 She came./ My head aches.
主语 + 及物动词 +宾语 She likes English.
主语 + 系动词 +主语补语 She is happy.
主语 + 双宾动词 +间接宾语 +直接宾语 She gave John a book She bought a book for me.
主语 + 宾补动词 + 宾语 + 宾语补语 She makes her mother angry.
The teacher asked me to read the passage.
( There +be There lies a book on the desk. )
分析下列句子成分
1. Our school is not far from my home.
2. It is a great pleasure to talk with you
3. All of us considered him honest.
4. My grandfather bought me a pair of sports shoes.
5. He broke a piece of glass.
6. He made it clear that he would leave the city.
7. ---I love you more than her,child .
8. Tees turn green when spring comes.
9. They pushed the door open.
10. Grandma told me an interesting story last night.
11. He wrote carefully some letters to his friends.
12. All the students think highly of his teaching
13. We need a place twice larger than this one.
14. He asked us to sing an English song.
15. Don't get nervous,help yourself to what you like.
16.We will make our school more beautiful.
17. He didn't come.That is why he didn't know.
18. She showed us her many of her pictures.
19. The old man lives a lonely life.
20. Luckily the 1989 earthquake did not happen in the center of town.
21. The cars made in Japan are better than those in Germany.
22. There are so many people in the hall that it's hard for me to find him.
23. No matter how difficult the task may be, we must fulfill it this month.
24. Go back where you came from.
25. We must do whatever the people want us to do.
26. At last he got home, tired and hungry.
27. Would you please pass me the cup?
28 Mary handed her homework to the teacher.
29. Do you know the latest news about him?
30. I’ll get my hair cut tomorrow.
英语句子成分分析
摘要
主要成分有主语和谓语;
次要成分有表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语和同位语。
一、主语
主语(subject):主语是一个句子所叙述的主体,一般位于句首。
主语可由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等表示。
1.Jane is good at playing the piano.
2.She went out in a hurry.
3.Four plus four is eight.
4.To see is to believe.
5.Smoking is bad for health.
6.The young should respect the old.
7.What he said is true.
8. It is necessary to master a foreign language. (it作形式主语,真正的主语为后面的不定式)
二、谓语
谓语说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态,即说明主语做什么或怎么样。通常由动词充当.
动词常分为实义动词,系动词,情态动词和助动词.
He ate two eggs this morning.
She cleans her room every day.
She came.
The bird died
三、宾语
宾语表示动作的对象或承受者,一般位于及物动词和介词后 面,分别称为动宾和介宾。
1.We study English.
2.He is looking at them.
3.He has refused to helpthem.
4. She enjoys reading.
5. I don't believe what he said.
6. She found itnecessary to learn a foreign language.
△双宾语:指人的是间接宾语,指物的是直接宾语。
He gave me two books.
四、表语
表语位于系动词之后,用以说明主语的身份、特征和状态。表语一般由名词、代词、形容词、分词、数词、不定式、动名词、介词短语、副词及表语从句表示。
1.Our English teacher is an American.
2. The weather has turned cold.
3. The speech is exciting
4.Hi
咨询记录 · 回答于2021-04-30
英语句子成分分析
主要成分有主语和谓语;
次要成分有表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语和同位语。
一、主语
主语(subject):主语是一个句子所叙述的主体,一般位于句首。
主语可由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等表示。
1.Jane is good at playing the piano.
2.She went out in a hurry.
3.Four plus four is eight.
4.To see is to believe.
5.Smoking is bad for health.
6.The young should respect the old.
7.What he said is true.
8. It is necessary to master a foreign language. (it作形式主语,真正的主语为后面的不定式)
二、谓语
谓语说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态,即说明主语做什么或怎么样。通常由动词充当.
动词常分为实义动词,系动词,情态动词和助动词.
He ate two eggs this morning.
She cleans her room every day.
She came.
The bird died
三、宾语
宾语表示动作的对象或承受者,一般位于及物动词和介词后 面,分别称为动宾和介宾。
1.We study English.
2.He is looking at them.
3.He has refused to helpthem.
4. She enjoys reading.
5. I don't believe what he said.
6. She found itnecessary to learn a foreign language.
△双宾语:指人的是间接宾语,指物的是直接宾语。
He gave me two books.
四、表语
表语位于系动词之后,用以说明主语的身份、特征和状态。表语一般由名词、代词、形容词、分词、数词、不定式、动名词、介词短语、副词及表语从句表示。
1.Our English teacher is an American.
2. The weather has turned cold.
3. The speech is exciting
4.Hi
the biggest gender difference is at the lowest post-school level,where 90% of those who held a skilled vocational diploma were men,compared with only 10% of women
请分析此句
语法结构方面,文章虽然也有各种各样的从句,但并不是每个句子都很复杂。关键在于句子结构各不相同。灵活使用各种非谓语动词,状语前置来展现句子的多样性。
请具体分析此句
就是这句

一个简单的英语句子
词类和句子成分
一、词类
能够自由运用的最小语言单位叫词。根据词的形式、意义及其在句中的作用所作的分类叫词类(parts of speech)。
英语的词通常分为十大类,即名词、冠词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、动词、介词、连词和感叹词。现分别叙述如下:
(一)名词
名词(noun)是表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。例如:
foreigner外国人 soap 肥皂 Newton牛顿
law 法律 freedom自由 peace 和平
英语名词可分为两大类:
1。普通名词(common noun)是某一类人、事物、某种物质或抽象概念的名称。例如:
teacher 教师 market市场 rice 大米
magazine杂志 sound 声音 production生产
2。专有名词(proper noun)是特定的某人、地方或机构的名称。专有名词的第一个字母必须
大写。例如:
Hemingway海明威 Russia 俄罗斯
New York 纽约 United Nations联合国
名词又可分为可数名词(countable noun)与不可数名词(uncountable noun)两种。可数名词有单、复数之分。绝大多数名词的复数形式的构成是在单数名词的后面加-s或-es。例如:
shop→shops商店 bus→buses 公共汽车 library→libraries图书馆
toy→toys 玩具 leaf→leaves树叶
英语中有一些名词的复数形式是不规则的。例如:
man→men男人 tooth→teeth牙齿 datum→data数据
有关名词复数形式构成的具体规则,请参阅有关的英语语法书。
(二)冠词
冠词(article)放在名词之前,帮助说明该名词所指的对象。冠词分为不定冠词(indefinite article)和定冠词(definite article)两种。
不定冠词为a/an,用在单数名词之前,表示某一类人或事物的“一个”。a用在以辅音开头的名词之前,an用在以元音开头的名词之前。例如:
a hotel 一家旅馆 a chance 一次机会
a double room一个双人间 a useful book 一本有用的书
an exhibition一次展览 an honest man一个诚实的人
冠词只有一个,既the,表示某一类人或事物中特定的一个或一些。可用于单数或复数名词前,也可用于不可数名词前。例如:
the TV programs 那些电视节目 the house那座房子
the Olympic Games奥运会
(三)代词
代词(pronoun)是用来指代人或事物的词。代词包括:
1。 人称代词,如:I, you, they, it等;
2。 物主代词,如:my, his, their, our, mine, hers等;
3。 反身代词,如:myself, yourself, itself, ourselves, oneself等;
4。 相互代词,如:each other, one another等;
5。 指示代词,如:this, that, these, those, such, same等;
6。 疑问代词,如:who, whom, whose, which, what等;
7。 关系代词,如:who, whom, whose, which, that等;
8。 不定代词,如:some, any, no, all, one, every, many, a little, someone, anything等;
(四)数词
数词(numeral)是表示“数量”和“顺序”的词。前者称为基数词,例如:one(一),twenty
(二十),thirty-five(三十五),one hundred and ninety-five(一百九十五)等;后者称为序数词,例如:first(第一),twentieth(第二十),fifty-first(第五十一等。
(五)形容词
形容词(adjective)是用来修饰名词,表示名词属性的词。例如:yellow(黄色的),wonderful(惊人的),strong(强大的)。形容词一般放在它所修饰的名词之前,例如:busy streets(繁华的街道),public relations(公共关系),young men(年轻人)等。
形容词的比较等级可分为三种,既原级、比较级和最高级。原级,既未变化的形容词原形,例如:great, big, difficult等;比较级,既形容词+后缀-er或more+形容词,例如:greater, bigger, more difficult等;最高级,既形容词+后缀-est或most+形容词,例如:greatest, biggest, most difficult等。
(六)副词
副词可分为四种,包括:
1。普通副词,例如:together(一起),well(好),carefully(仔细地)等;
2。疑问副词,例如:when(何时),where(何地),how(如何),why(为什么)等;
3。连接副词,例如:therefor(因此),then(然后),however(然而),otherwise(否则)等;
4。关系副词,例如:where, when, why等。
副词的比较等级的构成和形容词一样。
(七)动词
动词(verb)是表示动作或状态的词,例如:sign(签字),support(支持),have(有),exist(存在)等。
动词根据起意义和作用可分为实义动词、系动词、情态动词和助动词。
实义动词有完全的词义,并能独立作谓语,例如:explain(解释),stay(停留),have(有)等。系动词作谓语时,后面需接表语。常见英语系动词有:be(是),seem(似乎),look(看起来),become(变成),appear(显得),get(变得),feel(感到),turn(变成),remain(仍然是)等。
情态动词表示能力、义务、必要、猜测等说话人的语气和情感。情态动词只能和原行动词一起构成谓语动词。英语情态动词主要有can(能够),may(可以,也许),must(必须)及其过去形式could, might等。
助动词常和主要动词一起构成各种时态、语态、语气等动词形式,以及用于否定和疑问等结构中。英语助动词主要有shall, will, have, be, should, would, do等。
实义动词还可根据是否需要宾语分为及物动词和不及物动词。
及物动词(transitive verb)后面要跟宾语,意义才完整。例如:
You muxt consider the matter carefully.
你一定要仔细考虑这件事。(the matter是及物动词consider的宾语)
Have you received the letter?
你受到了那封信吗?(the letter是及物动词receive的宾语)
不及物动词(intransitive verb)本身意义完整,后面不需跟宾语,例如:
The old man walked very slowly.
这老人走的很慢。(walked是不及物动词)
He didn't sleep well last night.
他昨晚睡的不好。(sleep是不及物动词)
动词有四中基本形式,即动词原形、过去式、过去分词和现在分词。例如:
原形 过去式 过去分词 现在分词
live lived lived living
build built built building
have had had having
动词过去式和过去分词的构成有规则和不规则两种。规则动词(regular verb)的过去式和过去分词,在原形动词后面加词尾-ed或-d构成。不规则动词(irregular verb)的过去式和过去分词的形式是不规则的,如eat, ate, eaten。这些动词数量虽不多,但都是比较常用的,必须熟记。
现在分词在动词原形后面加-ing构成。关于动词原形加-ed和-ing的方法和读音以及不规则动词的变化,请参阅相关词典或语法书。
(八)介词
介词(preposition)又叫前置词,放在名词、代词或相当于名词的词前面,表示它后面的词与句子中其它成分之间的关系。
介词在句中一般不重读,也不能单独作句子成分。
介词根据其构成,可分为简单介词,如:in, at, for, since等;复合介词,如:into(进入), as for(至于), out of(出自);二重介词,如:until after(直至...之后), from among(从...当中);短语介词,如:according to(根据), because of(因为), in front of(在...之前), in the event of(如果);分词介词,如:regarding(关于), considering(考虑到), including(包括)。
介词后面的名词或代词叫做介词宾语。介词和介词宾语合称为介词短语(prepositional phrase)。
(九)连词
连词(conjunction)是连接词、短语、从句或句子的词。连词是虚词,在句中一般不重读,也不能在句中单独作句子成分。
根据连词本身的含义及其所连接的成分的性质,可分为并列连词和从属连词。
并列连词是连接并列关系的词、短语、从句或句子的连词,例如:and(和), or(或者、否则), but(但是), for(因为), not only...but also(不仅...而且), neither...nor(即不...也不)。从属连词是连接主从复合句的主句和从句的连词,例如:that, if(如果), whether(是否), when(当...时候), although(虽然), because(因为), so that(结果)。
从连词本身的结构形式看,又可分为:简单连词,如:but, because, if;关联连词,如:not only...but also, as...as(和...一样);分词连词,如:supposing(假如), provided(倘若);短语连词,如:as if(好象), as soon as(一旦...就), in order that(以便)。
(十)感叹词
感叹词(interjection)是表示喜怒哀乐等感情的词,例如:oh, well, why, hello等。
上述十大词类中,名词、代词、形容词、副词、动词、数词等都有实义,故称为实词(notioal word);而介词、冠词、连词、感叹词等没有实义,故称为虚词(form word)。
不少词可以属于几个词类,例如:smoke(名词) (烟尘),(动词) (吸烟);own(形容词) (自己的),(动词) (拥有);just(副词) (刚才),(形容词) (正义的);key(名词) (钥匙),(形容词) (主要的),等。
二、句子成分
由不同词类的单词,按照一定的语法规则组合在一起,能表达一个完整意思的语言单位叫做句子。一个句子由各个功能不同的部分构成,这些部分叫做句子成分(members of the sentence)。英语的句子成分有八种:主语、谓语动词、表语、宾语、定语、状语、主语补足语和宾语补足语。现分述如下:
(一)主语
主语(subject)是句子所要说明的人或事物,是句子的主体。主语的位置通常在句首,一般不省略。可以担当主语的有名词、代词、数词、动词不定式、动名词和主语从句。例如:
Walls have ears.
隔墙有耳。(名词做主语)
He will take you to the hospital.
他会带你去医院。(代词做主语)
Three plus four equals seven.
三加四等于七。(数词做主语)
To see is to believe.
眼见为实。(动词不定式做主语)
Smoking is not allowed in public places.
公共场所不允许吸烟。(动名词做主语)
Whether or not they will come depends on the weather.
他们来不来取决与天气。(从句做主语)
(二)谓语动词
谓语动词(predicate verb)是说明主语的动作或状态的句子成分。谓语动词的位置一般在主语之后。谓语动词由实义动词或系动词担任。助动词或情态动词加其他动词的适当形式也构成谓语动词。例如:
Action speaks louder than words.
百说不如一干。
The chance may never come again.
这样的机会恐怕不会再来。
Tom was very sick at heart.
汤姆心里非常难过。
Mary has been working at the dress shop since 1994.
自1994年以来,玛丽一直在那家服装店工作。
(三)表语
表语(predicative)是用来说明主语的身份、特征和状态的,它的位置在系动词之后。可作表语的有名词、代词、形容词与分词、数词、动词不定式、介词短语、副词以及表语从句等。例如:
My father is a professor.
我父亲是一位教授。(名词作表语)
Who's that? It's me.
是谁呀?是我。(代词作表语)
Everything here is dear to her.
这里的一切她都感到亲切。(形容词作表语)
The match became very exciting.
比赛变得很紧张。(分词作表语)
The story of my life may be of help to others.
我的生活经历对别人可能有帮助。(介词短语作表语)
Three times five is fifteen.
三乘五等于十五。(数词作表语)
His plan is to seek work in the city.
他的计划是在城里找工作。(动词不等式作表语)
My first idea was that you should hide your feelings.
我最初的想法是你应当掩饰你的感情。(从句作表语)
(四)宾语
宾语(object)表示动作的对象,是动作的承受者。宾语一般放在及物动词之后。英语介词后也会跟宾语。可作宾语的有名词、数词、代词、动名词等。不定式也可作及物动词的宾语。例如:
she covered her face with her hands.
她用双手蒙住脸。(名词短语作宾语)
We haven't seen her for a long time.
我们好长时间没看到她了。(代词作宾语)
Do you mind opening the window?
打开窗户你介意吗?(动名词作宾语)
Give me four please.
请给我四个。(数词作宾语)
He wants to dream a nice dream.
他想做一个好梦。(动词不定式短语作宾语)
We need to know what others are doing.
我们需要了解其他人都在干什么。(从句作宾语)
I lived in Japan in 1986.
我1986 年住在日本。(名词和数词作介词的宾语)
(五)定语
定语(attribute)是修饰名词或代词的词、短语或句子。单词作定语时通常放在它所修饰的名词之前;短语和从句作定语时则放在它所修饰的名词之后。作定语的有名词、形容词、数词、分词及其短语、不等式及其短语、介词短语以及定语从句等。例如:
They are woman workers.
她们是女工。(名词作定语)
Tom's father didn't write home until yesterday.
汤姆的父亲直到昨天才给家里写信。(所有格名词作定语)
Equal pay for equal work should be introduced.
应当实行同工同酬。(形容词作定语)
The play has three acts.
这出戏有三幕。(数词作定语)
This is her first trip to Europe.
这是她首次欧洲之行。(代词、数词和介词短语作定语)
China is a developing country.
中国是一个发展中国家。(分词作定语)
You haven't kept your promise to write us often.
你没有遵守给我们经常写信的诺言。(动词不定式短语作定语)
My cat has a good nose for milk.
我的猫对牛奶嗅觉灵敏。(介词短语作定语)
Those who want to go to Tibet are to sign their names here.
想去西藏的人须在此签名。(从句作定语)
(六)状语
状语(adverbial)是修饰动词、形容词、副词等的句子成分。状语表示地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、程度、方式、伴随情况等。作状语的有副词、名词、介词短语、分词及其短语、动词不定式及其短语、状语从句等。例如:
These products are selling quickly.
这些产品现在十分畅销。(副词作状语)
He is knee deep in snow.
他踩在齐膝深的雪里。(名词作状语)
The best fish swim near the bottom.
好鱼居水底。(有价值的东西不能轻易得到。)(介词短语作状语)
She sat there doing nothing.
她坐在那里无所事事。(分词短语作状语)
We'll send a car over to fetch you.
我们将派一辆车去接你。(动词不定式短语作状语)
She was slow to make up her mind.
她迟迟不能下决心。(动词不定式短语作状语)
Strike while the iron is hot.
趁热打铁。(从句作状语)
There is no such a word in English so far as I know.
据我所知,英语里没有这样一个词。(从句作状语)
(七)宾语补足语和主语补足语
英语有些及物动词,除了要有宾语之外,还要加上宾语补足语(object complement),才能使句子的意义完整。宾语和宾语补足语一起构成复合宾语。如果上述结构变成被动语态,原宾语成为主语,原宾语补足语相应地变为主语补足语(subject complement)。可以担当补足语的有名词、形容词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词等。例如:
They elected me captain of the team.
他们选我当队长。(名词短语作宾语补足语)
He made me ashamed of myself.
他使我感到惭愧。(形容词短语作宾语补足语)
We found everything there in good order.
我们发现那里的一切井井有条。(介词短语作宾语补足语)
I should advise you not to miss the chance.
我劝你不要错过机会。(不定式短语作宾语补足语)
I could feel my heart beating fast.
我可以感觉出自己的心跳得很快。(分词短语作宾语补足语)
Some goods are left unsold.
有些货物剩下未出售。(分词做主语补足语)
She was elected director of public relations.
她被选为公关部主任。(名词短语做主语补足语)
动词中的实义动词和系动词可以担当谓语。动词不定式、分词和动名词形式不能独立担当谓语。介词是虚词的一种,不能独立担当句子成分,但介词加上其后的宾语所构成的介词短语,可在句中担当多种成分。
高中英语复杂句子成分分析例句
前面我们主要讲了五种简单句的结构,今天开始我们将进入复杂句的学习,即多重句。顾名思义,多重句是由多个句子组成的长句。大家在开始多重句的学习之前,希望能复习回顾一下我们所学的简单句,因为多重句是在简单句的基础上加上相应的连接词组合而来,这些多重句就是我们平时所接触的长难句。
核心讲解:
我们曾经讲过,句子和短语最大的区别在于句子必须有谓语动词,即“老婆”。那将句子分成简单句和多重句的话,两者的区别是什么呢?简单句是一个“家庭”,只有一个谓语动词,一个“老婆”;而多重句是一个“家族”,包含多个“家庭”,有多个谓语动词,多个“老婆”。
多重句又可以分为三类:并列句、复合句和并列复合句。
并列句其实就是两个简单句的组合,为方便理解,我们可以将其比喻成两家人,即由“哥哥和嫂子+弟弟和弟妹”组合而来,其属于“同辈人”关系。
复合句是一个“大家族”,我们可以看作是一个爷爷奶奶生出了多个儿子,多儿子又生出来多孙子,其相当于一个树形的大家族,其属于“从属”关系。
并列复合句相当于“两个爷爷奶奶”分别繁衍了两个大家族,由两个或两个以上并列的复合句构成。
要点拓展:
我们可以通过一些例子来进一步了解多重句:
一、并列句:
1、 简单句1:Mike likes yellow.(麦克喜欢黄色。)
简单句2:Lucy likes blue.(露西喜欢蓝色。)
并列句:Mike likes yellowbutLucy likes blue.(麦克喜欢黄色,但露西喜欢蓝色。)
大家观察这三个句子可知,该并列句是由简单句1+连接词but+简单句2组成,即我们上文说到的,两个老公(Mike和Lucy)和老婆(两个likes),这两个简单句是“同辈”的关系,一般同等重要。
2、 简单句1:My grandfather bought me a watch.(我爷爷给我买了手表。)
简单句2:I liked it very much.(我非常喜欢它。)
并列句:My grandfather bought me a watchand I liked it very much.(我爷爷给我买了手表,我很喜欢。)
这个例子中的并列句由简单句1+连接词and+简单句2连接而成。因为这两个简单句是顺承关系,所以连接词为and;而上面的句中,两个简单句为转折关系,所以连接词是but。

以上就是关于英语复杂句子成分分析举例子 ,英语句子成分分析的全部内容,以及英语复杂句子成分分析举例子 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

