本文目录
高中英语状语从句思维导图
相信很多高中的同学们都傻傻分不清楚状语从句的用法,经常在考试中失分,接下来我给大家带来高中英语状语从句,希望能帮到大家。
高中英语状语从句
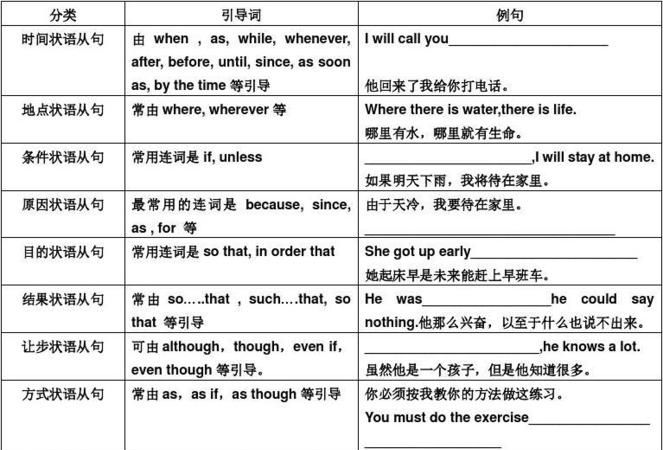
一、时间状语从句
1、when的用法
(1)when既可引导一个持续性动作,也可引导一个短暂性动作,可用于表示主句和从句动作同时发生或从句动作先于主句动作,有时还可表示从句动作后于主句,意为“当。。。时候”。
(2)when在be about to do。。。when。。。,be doing。。。when。。。,had done。。。when。。。,be on one’s way。。。when。。。,be on the point of doing。。。when。。。等结构中,作“那时突然”讲。
(3)when “既然、鉴于;尽管,虽然(位于主句之后);如果”
2、while的用法
(1)表示“当。。。时候”,引导的动作必须是延续性的。
(2)用作并列连词,表示相对关系“然而”。
(3)引导让步状语从句,相当于although,意为“虽然”,位于主句前。
(4)引导条件状语从句,相当于as/so long as,意为“只要”。
3、as 的用法
(1)表示“当。。。时候”,强调同时发生,不指先后。
(2)说明两种正在发展或变化的情况,表示“随着”,表示时间的推移。
(3)表示“一边。。。一边。。。”。
(4)强调两个动作紧接着发生。
(5)表示“虽然,尽管”。
(6)其他含义“正如,正像”,“作为”,“由于,因为”。
4、before的用法
(1)一般意为“在。。。之前”“。。。才”,“。。。就”“还没有。。。”“免得”“不知不觉”“宁可,宁愿”,“否则,要不然”。
(2)It + will be/was + 时间段+before+一般现在时/一般过去时。在肯定句中,意为“多长时间之后才”;在否定句中,意为“用不了多长时间就”。
5、until和till
(1)与肯定句连用,必须是延续性动词。
(2)与否定句连用,必须是非延续性动词,表示“直到。。。才,在。。。之前不。。。”。
注意:not until可用于强调句和倒装句
强调句:It is/was not until…that…倒装句:not until 放句首时,主句要部分倒装。
6、since的用法
(1)since后是非延续性动词,时间起点从该动作发生算起,意为“做某事多久了”;since后是延续性动词,时间起点从该动作结束算起,意为“不做某事已有多长时间”。
(2)It is/has been +时间段+since+一般过去时
7、表示“一......就......”的句型
(1)as soon as, once,immediately,directly,instantly,the moment,the minute等引导的从句都表示从句的动作一发生,主句的动作随即发生,常译作“一。。。就。。。”,这类从句中,经常用一般现在时态代替将来时态。
(2)on doing sth.或“on one’s+名词”作时间状语。
8、有些名词和副词可以起连接词的作用,引导时间状语从句。
注意:时间状语从句中不用将来时态。若要表示将来时间,可用一般现在时态表示。但when引导名词性从句时,从句中要使用将来时。
二、地点状语从句
1、地点状语从句由where,wherever引导。
注意:where与where的区别:Where表特定的地点,而wherever表示非特定的地点。
Wherever=to/at any place where
2、地点状语从句与定语从句的区别
Where引导定语从句时,从句前应有一个表示地点的名词作先行词;而状语从句前则无先行词。
三、原因状语从句
引导词:because, since,as, now that, not that…, but that…, seeing that, considering that, in that
注意:for也可以表示原因,属并列连词,但不是说明直接原因,而是对某种情况加以推断,用于表示补充说明理由。
四、目的状语从句
引导词:so, so that, in order that, that, to the end that(以便,为了),in case,for fear that,lest(以免,以防),
目的状语从句中通常有情态动词can,could,may,might,should,would等。
注意:1、in case 还可表示“万一,假如”。
2、目的状语从句可以用so as to, in order to 等不定式代替,但主句和从句的主语必须一致。
五、结果状语从句
引导词:so...that(如此。。。以至于。。。),such...that(如此。。。以至于。。。),so that(结果是),with the result that(所以,结果是)
注意:(1)so...that与such...that的区别
So+形容词such+a/an+形容词+单数名词
So+形容词+a/an+单数名词such+形容词+复数名词
So+副词such+形容词+不可数名词
So many/few+复数名词
So much/little+不可数名词
(2)so that引导的目的状语从句与so that 引导的结果状语从句
目的状语从句一般使用情态动词,结果状语从句一般不使用情态动词;
结果状语从句常常用逗号与主句分开。
(3)so...that与so...as;such...that与such...as
So...that/such...that为结果状语从句;so...as/such...as为定语从句。
六、条件状语从句
引导词:if(如果),unless(除非),if only(只要,但愿),only if(只有),in case(万一),suppose/supposing(that)
(假设),provided/providing(that)(只要,假若),on condition that(要是,在。。。条件下),so/as long as(只要),(let's/let us)say(假设)
七、方式状语从句
引导词:as(像。。。一样,正如。。。),as if/as though(好像,宛如)
注意:1、固定句型A is to B what C is to D.意为“A对B而言正如C对D一样”。
2、as if, as though引导的从句若与事实相反,用虚拟语气;若与事实相符,不用虚拟语气。
八、让步状语从句
引导词:though/although/as(虽然,尽管),even if/though(即使,尽管),whether/no matter whether...or(not)
(不管。。。是否,不管是。。。还是)wh-ever/no matter wh-(无论。。。)
注意:(1)though,although,as的区别
A、Though,although的主句中可以用yet, still, nevertheless,但不可使用but。
B、though引导的从句可以倒装,也可以不倒装;as引导的从句必须倒装;although引导的从句不能倒装。
其结构为:形容词/分词/副词/动词原形/名词(无冠词)+as/though+主语+谓语……
(2)though可用作副词,放在句末,意为“不过,但是”。Although无此用法。
(3)某些短语也引导让步的从句或短语,意为“尽管”,如:in spite of the fact that, despite the fact that, regardless of(the fact that)
九、比较状语从句
引导词:as...as(和。。。一样),not as/so...as(和。。。不一样),than(比),the more...the more...(越。。。越。。。)
十、状语从句中的省略问题
1、在状语从句中如果主语与主句的主语一致,同时从句中又含有系动词be,则通常可省去从句的主语和系动词be,留下其余部分。
2、若状语从句中主语是it, 动词是系动词be, 则通常可省去主语it及系动词be,留下其余部分。
高中英语名词性从句
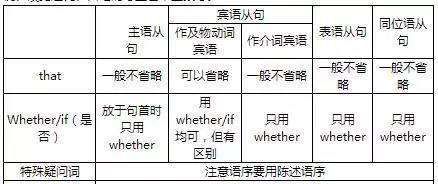
一、that 从句
1、主语从句
(1)that从句作主语时,常用it作形式主语,常见的句型有:
It+be+形容词(obvious, true, natural, surprising,good,wonderful,funny,possible,likely,certain,probable,etc.)+that从句
It+be+名词词组(no wonder, an honor, a good thing, a pity, no surprise, etc.)+that从句
It+be+过去分词(said, reported, thought, expected, decided, announced, arranged, etc.)+that从句
(2)that可以省略,但that从句位于句首时,that不能省略。
2、宾语从句
(1)常见的可以接that从句作宾语的动词有see, say, know, imagine, discover, believe, tell, show, think, consider, be sure, be afraid等。在可以接复合宾语的动词之后,如think, make, consider等,可以用it作形式宾语。
(2)That从句一般不能充当介词宾语,偶尔可作except, in 的宾语。
3、表语从句(that不可省略)
4、同位语从句
连词that引导同位语从句时,应在某些抽象名词之后,如:fact, hope, desire, thought, suggestion, idea, news, problem, possibility等,对前面的名词起补充说明的作用,that在从句中不担当任何成分,不能省略。
二、whether/if从句
1、在表语从句和同位语从句中只能用whether不能用if;当主语从句放于句首时,只能用whether不用if;当it作形式主语,主语从句放在句末时用whether或if均可;discuss后引导宾语从句时,必须用whether。
2、在宾语从句中:
(1)及物动词后:whether从句中不能有否定式,宾语从句为否定句时用if;if不能与or not连用,但可以用whether or not;whether后可以加不定式。
(2)介词后:只能用whether,不用if。
三、特殊疑问词引导的从句
1、主语从句:特殊疑问词引导主语从句时,常用it作形式主语。
2、宾语从句
(1)常见的能接特殊疑问词引导的宾语从句的动词有see, tell, ask, answer, know, decide, find out, imagine, suggest, doubt, wonder, show, discuss, understand, inform, advise等。
(2)作介词宾语。
3、同位语从句、表语从句
四、名词性关系从句
What=the thing(s) which/that, whoever=anyone who, whichever=anyone/anything that, whatever=anything that, where=the place where, when=the time when
五、名词性从句的几个难点
(一)that不可省略的情况
1、主语从句,that从句置于句首时;
2、当一个句子有两个或多个并列的宾语从句时,引导第二和以后几个从句的that不可省略;
3、由it作形式宾语时,that引导的宾语从句中,that不可以省略。
(二)wh-ever与no matter wh-的用法区别
Wh-ever既可引导名词性从句,又可引导让步状语从句;而no matter wh-只能引导让步状语从句。
(三)as if/though, because, why可以引导表语从句
注意:because引导的表语从句,主语不能是reason或cause,而且since,as不能引导表语从句。
(四)that引导的同位语从句与关系代词that引导的定语从句的区别
That引导的同位语从句成分是完整的,that在从句中不担当任何成分;that引导的定语从句成分是残缺的,that在从句中充当主语、宾语或表语。
高中目的状语从句连词
高中英语状语从句用法解析
一、 定义:
在句中作状语的从句是状语从句,修饰主句中的动词、形容词或副词等。状语从句由从属连词引导,从属连词在句中不充当句子成分,只起连接作用,状语从句放在句首时,要用逗号,放在句尾时不用。
二、 分类
根据意义上的不同,状语从句可分为:
①时间状语从句 ②地点状语从句 ③原因状语从句
④目的状语从句 ⑤条件状语从句 ⑥结果状语从句
⑦让步状语从句 ⑧方式状语从句 ⑨比较状语从句
三、 时间状语从句
主句是一般将来时,时间状语从句用一般现在时表将来;主句是过去将来时,从句用一般过去时表示过去将来时;主句是一般过去时,从句用一般过去时。记忆:“主将从现”
引导时间状语从句的连词有:
as, when (whenever), before, after, as soon as, until (till), since, every time, once.
特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
4、 地点状语从句
地点状语从句用where, wherever引导
特殊引导词:wherever, anywhere, everywhere
五、 原因状语从句
原因状语从句用because(因为),since(既然), as(由于)引导
特殊引导词:seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that, considering that
六、 目的状语从句
目的状语从句用so(常用于口语), that, so that, in order that引导
目的状语从句的谓语常含有may, might, can, could, should, would等情态动词。
特殊引导词:lest, in case, for fear that,in the hope that, for the purpose that, to the end that
七,条件状语从句
条件状语从句由if, unless, (so) as long as(只需)引导
在条件状语从句中要用一般时表示将来时(与时间状语从句相同)
特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, suppose that, in case that, on condition that
八、 结果状语从句
结果状语从句由such…that, so….that, so that, that 引导
特殊引导词:such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that,
9、 让步状语从句
although, though
even though = even if, whether…or
however = no matter how
whatever = no matter what
whoever = no matter who
whenever = no matter when
wherever = no matter where
特殊引导词: as(用在让步状语从句中必须要倒装),while ( 一般用在句首 ),no matter …, in spite of the fact that,
10、 方式状语从句
方式状语从句由as(如同,按照),as if (though)引导
*as和like都有“像”的意思,as是连词,后面连接句子,like是介词后面可加名词、代词或名词性短语。
十一、比较状语从句
比较状语从句由as…as, not as(so)…as, than, the+比较级,the+比较级引导
特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than; not A so much as B
比较状语从句
状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。比较状语从句是其中的一种,主要运用于形容词和副词的原级、比较级及最高级的句子之中。原级:as…as(和……一样),not so(as)…as …(和不一样);比较级:more…than(更);最高级:The most…in/of, the + 形容词+est…of/in。常用引导词:as(同级比较),than(不同程度的比较);特殊引导词:the more … the more … ;just as …, so…;A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than;not A so much as B。
比较状语从句通常由as或than引起,这类从句和大多数状语从句不同,它们不修饰动词,而是修饰as,so,less,more等副词,或其他比较级的词,如 taller, harder.在这里讨论它们,不是作为动词修饰语,而是作为一种状语从句。包含这类从句的句子通常为L,即从句在后: She is as tall as I(or me). He works as hard as his brother(does). He does not work as hard as his brother. He does not work.so hard as his brother. No other men work as(or so) hard as his brother (does). No other men work as hard as does his brother. She is taller than I(or me). She is taller this year than(she was tall)last year. She is more shy than unsocial. She thinks more about her appearance than(she thinks about) her personality. She finds it easier to read than to write. She is not taller than I.(Both are tall.) She is no taller than I.(Both are short.) I cannot persuade him any more than your persuade a pillar.(= I am unable to persuade him,just as you are unable to persuade a pillar.) I can forget her no more than she(forgets)me. Nothing is more dangerous than that you (should) make friends with him. I will help you rather than that you(should)have any trouble. It is better that we should die rather than that we(should)be slaves. He is only less silly than(= almost as silly as)John. Than him nobody is more clever.(= He is the cleverest man.)(than在这里的作用更接近介词) Than this there are no better places.(This is the best place.) I know John,than whom I have never seen a sillier man. 比较状语从句(adverbial clause of comparison)从某种角度上说,它也是一种方式状语从句,它通常可和以下关联词来引导as(或so)...as, than, according as, in proportion as等。如: as...as... He woke up as suddenly as he had fallen asleep. 他醒来得和入睡一样突然。(第一个as是副词) I have never seen so much rain as fell that February. 我从未见过像那个二月那么多雨。(否定结构常用so…as, 也可用as... as) than Man developed earlier than people think. 人类的出现比人们所想的要早。 He moves more slowly than his sister does. 他行动起来比他妹妹慢。 The youth of today are better off than we used to be. 今天的年轻人比我们过去的境况要好。 according as You may go or stay, according as you decide. 是去是留由你自己决定。 You will be praised or blamed according as your work is good or bad. 你受表扬还是责备得看你的工作好坏决定。 in proportion as Men are happy in proportion as they are virtuous. 人之幸福与德行成正比。 Some people are happy in proportion as they are noticed. 有些人越受到注意就越高兴。 The most…in/of This book is the most interesting of the three.这本书是三本中最有趣的。 the + 形容词+est…of/in This road is the busiest street in our city. 这条路是我们城市最繁忙的街道。 no more than只不过(嫌少的意思) I have no more than two pens.我只有两支笔。 It’s no more than a mile to the shops.去商店不过一英里。 not more than不如。。。;(前者不如后者) Jack is not more diligent than John.捷克不如约翰勤奋。 one of the + 名词(复数)….之一(用于最高级) Han Mei is one of the best students in our school. 韩梅是我们学校最好的学生之一。 来自百度百科
以上就是关于比较状语从句用法 ,状语从句的具体知识及用法了大神帮忙的全部内容,以及比较状语从句用法 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
