本文目录
英语中什么是状语
一、英语中什么是状语
英语中修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子是状语,状语一般由副词、介词短语、分词和分词短语、名词、不定式或相当于副词的词或短语来担当。
二、英语状语作用
状语的作用:状语说明地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、方向、程度、方式和伴随状语等。
状语一般由副词、介词短语、分词和分词短语、名词、不定式或相当于副词的词或短语来担当。其位置一般放在句末,但也可放在句首或句中。
副词是一种用来修饰动词,形容词,副词或全句的词,说明时间,地点,程度,方式等概念。
1.副词一般在句子中做状语
He speaks English very well. 他英语说得非常好。
其中的“very”是程度副词,用来修饰“well”。“very well”是修饰“speak”的程度状语。
2. 不定式在句子中可以作目的状语
I come specially to see you. 我专门来看你。
3.介词短语
Ten years ago, She began to live in Dalian.
从十年以前开始,她开始住在了大连。
The boy was praised for his bravery.
这个男孩因为他的勇敢而被夸奖。
4.从句作状语
When she was 12 years old, she began to live in Dalian.
她12岁的那一年开始居住于大连。
If I am not busy tomorrow, I will play football with you.
如果我明天不忙,我就会陪你踢足球。
5.动词ing形式作状语
①表示时间
Seeing its mother, the baby smiled. (see和smile同时发生)
看到它的母亲,婴儿笑了。
Having studied English for 3 years, he can communicate with foreigners.(先study 然后才能communicate)
学了3年英语,现在他能与外国人交流了。
②表示原因
Not knowing anything about the accident, he went to work as usual.
(=Because he didn't know anything about the...)
Not having received any news from home for a long time, she is becoming more and more homesick.
(=As she hasn't received any news from home...)
③表示结果
It rained heavily, causing severe flooding in that country.
大雨滂沱,造成了那个国家洪水泛滥。
European football is played in 80 countries, making it the most popular sport in the world.
80个国家都有足球这项运动,使它成为世界上最受欢迎的运动。
The snow lasted a week, leading to a serious traffic jam in the whole area.
雪持续了一个星期,导致了整个地区的严重交通堵塞。
④表示方式
He earns a living driving a truck. 他靠开卡车谋取生计。
⑤表示伴随
She sat at the desk reading a newspaper.(reading是伴随着sat进行的)
她坐在书桌前看报纸。
“Can't you read?”Mary said angrily pointing to the notice.(pointing是伴随着said进行的)
“你自己不会看吗?”玛丽指着那个告示牌并愤怒地说道。
I offered them something to eat, thinking they might be hungry.
我给了他们一些东西吃,心想着他们可能饿了。
6.名词作状语
We must get together again some day.
将来某天我们必能再相聚.
we should serve people heart and soul.
我们应该全心全意地服务
7、过去分词作状语
Faced with the situation, what are we supposed to do?
三、英语中状语有什么类型
一、时间状语
She is to be married next month. 她预定在下个月结婚。
I’ll meet you at 4 o’clock. 我将在4点钟和你见面。
A lot of students missed my lecture yesterday. 昨天许多学生误了我的课。
二、地点状语
He lives over the mountain. 他住在山的那一边。
I first met him in Paris. 我初次见到他是在巴黎。
The children are swimming in the river. 孩子们正在河里游泳。
注:地点状语除表位置外,还可以表“出发”“去向”“距离”等。如:
Are you glad to be going back to school? 返回学校你感到高兴吗?
They lived many miles from the town. 他们住的地方离镇子好几英里远。
三、方面状语
She is very weak in physics. 她物理很不行。
China is very rich in natural resources. 中国自然资源丰富。
This is better in every way than that. 这个在哪一方面都比那个要好。
The bridge is 2500 meters in length and 150 meters in height. 这座桥长2500米,高150米。
四、原因状语
He was surprised at what she said. 听到她说的话,他很吃惊。
He succeeded by hard work. 他由于努力工作而成功。
He was sent to prison for robbery. 他因为抢劫而坐牢。
Last week she fell ill from cold. 上星期她着凉生病了。
We’re proud of our motherland. 我们为祖国感到骄傲。
五、结果状语
He talked his wife into buying a car. 他说服他妻子买一辆小汽车。
The box is too heavy for me to lift. 这个箱子太重了,我提不动。
It rained heavily, causing severe flooding in that country. 大雨滂沱,造成了那个国家洪水泛滥。
He went to Africa in 1963, never to come back. 他在1963年到非洲,然后就再也没回来过了。
六、目的状语
They went out for a walk. 他们出去散步了。
He saves on behalf of his son. 他为儿子存钱。
He stood aside for her to pass. 他靠边站让她过去。
He cupped his ear to hear better. 他的手捂着耳朵,以便听得更清楚。
He went to the south in search of a better life. 他去南方寻求更好的生活。
I went to France not to study French, but to study architecture. 我去法国不是为了学法语,而是为了学建筑。
七、条件状语
Can you see without your glasses? 你不戴眼镜能看得清东西吗?
United, we stand;pided, we fall. 团结则存,分裂则亡。
With more moneyI would be able to buy it. 钱多一点的话,我就买得起。
To look at himyou could hardly help laughing. 看到他你就会忍不住笑起来。
We must be losing at least a third of our staff under new technology. 在新的技术条件下,我们必定要解雇至少三分之一的员工。
Weather permitting, we’ll have the match tomorrow. 天气允许的话,我们将于明天进行比赛。
八、让步状语
For all his money, he’s a very lonely man. 他虽然富有,可是非常寂寞。
Carol went to work in spite of feeling ill. 卡洛尔尽管感到不舒服仍去上了班。
With all his efforts, he lost the match. 虽然尽了全力,他还是输了那场比赛。
You couldn’t do that to save your life. 你即使为了救自己的命也不能那样做。
Laughed at by everybody, he had my sympathy. 人人都嘲笑他,但我却同情他。
Knowing all this, they made me pay for the damage. 他们尽管了解这一切,还是要我赔偿损失。
九、程度状语
I don’t like coffee very much. 我不太喜欢咖啡。
To a great extent, it is not fair. 在很大程度上,这是不公平的。
The system which is used in this school is very successful. 这个学校所施行的制度是非常成功的。
十、方式状语
We came on the bus. 我们坐公共汽车来的。
You must pay the bill in cash. 你必须用现金付账。
I watched the game on television. 我在电视上收看了那场比赛。
We see with our eyes, and hear with our ears. 我们用眼睛看,用耳朵听。
I heard of the job through a newspaper advertisement. 我从报上的广告中知道了这个工作。
十一、伴随状语
I slept with the window open. 我开着窗睡觉。
She said good-bye with tears in her eyes. 她含着泪水说再见。
He ran up to her breathing heavily. 他气喘吁吁地跑到她跟前。
He rushed into the room, his face covered with sweat. 他满脸是汗跑进屋来。

英语中时间状语放在什么位置
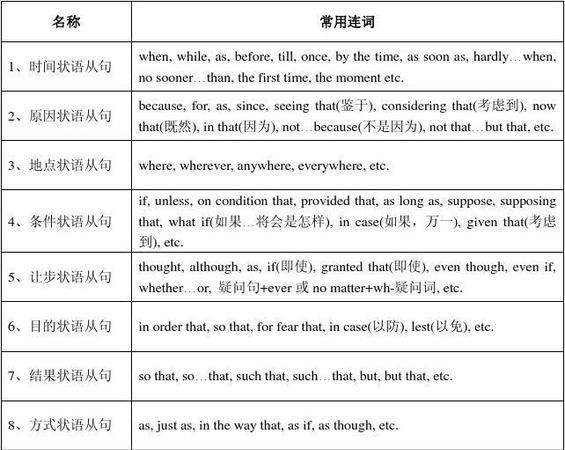
1、时间状语
常用引导词:when,as,while,before,after,since,not...until,until/till 等
特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant( 瞬间,顷刻), immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when , scarcely … when(刚...就.../一...就...),as soon as(一…就…)。
I didn’t realize how special my mother was until I became an adult.
直到我成为了一个成年人我才意识到我的母亲是多么的特殊。
2、地点状语
常用引导词:where
特殊引导词:wherever, anywhere, everywhere
Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
一般来说,有工厂的地方空气污染就严重。
3、原因状语
常用引导词:because, since, as,
特殊引导词:seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that.
My friends dislike me because I’m handsome and successful.
我的朋友都不喜欢我,因为我又英俊又成功。
4、条件状语
常用引导词:if, unless,whether(whether...or not)
特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, supposing that, in case(美语中表条件,英语中表目的), on condition that
We’ll start our project if the president agrees.
如果总统同意,我们将开始我们的项目。
5、目的状语
常用引导词:so that, in order that
特殊引导词:lest, in case, for fear that,in the hope that, for the purpose of , to the end that
The boss asked the secretary to hurry up with the letters so that he could sign them.
老板要求秘书快写函件以便他能在上面签字。
6、让步状语
常用引导词:though, although, even if, even though
特殊引导词: as(用在让步状语从句中必须要倒装),while (一般用在句首),no matter …, in spite of the fact that, whatever, whoever, wherever, whenever, however, whichever
Much as I respect him, I can’t agree to his proposal.
尽管我很尊敬他, 但是我却不同意他的建议。
7、比较状语
常用引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较)
特殊引导词:the more … the more …(越来...越...) ; just as …, so…; A is to B what/as X is to Y; no … more than; not so much A as B,the 比较级 ,the 比较级.
She is as bad-tempered as her mother.
她和她妈妈一样脾气很坏。
8、方式状语
常用引导词:as, as if
特殊引导词:the way
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
入国问禁,入乡随俗。
9、结果状语
常用引导词:so … that, such … that, so that...
特殊引导词:such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that,
He got up so early that he caught the first bus.
他很早起床以便赶上第一班公共汽车
英语中的状语是指什么
状语用来修饰动词,形容词或副词。他表示行为发生的时间,地点,目的,方式,程度等意义,一般由副词,介词短语,不定式(to+动词原形)来表示,位置不定。
宾语,就是在谓语之后的那部分,说明主语怎么样。如He likes English中,He是主语,likes是谓语,Ehglish就是宾语。
谓语在主语后,是动词。主语一般在句首,是名词或代词,
定语是用来修饰名词或代词的成分。如The black bick is mine,black是定语。
表语在系动词之后。(系动词是Be动词,感官动词等,如:sound听起来,is,are,am)
动词做主语,用ing或to do形式方可
问一个关于英语状语的问题怎么问
状语从句一共有九种, 分别有时间,地点,原因,结果,目的,让步,条件,比较,方式
时间 When i was young, I lived in the countryside.
地点 Where there is a will, there is a way.
原因 Becasue I got up late, I missed the bus.
结果 He worked so hard that he passed the exam easily.
目的 He went early so that he could find a good seat.
让步 Although I didn't like it, i had to take it.
条件 If you think this is not a problem, you can forget about it.
比较 He is as tall as she is.
方式 He had no choice but do as he was told.
以上就是关于十一种状语,英语中什么是状语的全部内容,以及12种状语 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

