本文目录
定语从句的思维导图及例句
定语从句的思维导图
一、定语从句的概念
在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词,定语从句一般放在先行词的后面。
二、定语从句的关系词
引导定语从句的关系词有关系代词和关系副词,常见的关系代词包括that, which, who(宾格whom,所有格whose)等,关系副词包括where, when, why等。关系代词和关系副词放在先行词及定语从句之间起连接作用,同时又作定语从句的重要成分。
三、定语从句的分类
根据定语从句与先行词的关系,定语从句可分为限制性定语从句及非限制性定语从句。限制性定语从句紧跟先行词,主句与从句不用逗号分开,从句不可省去,非限制性定语从句主句与从句之间有逗号分开,起补充说明作用,如省去,意思仍完整。
限制性关系从句
从语义上看,限制性关系从句主要起限定作用,修饰特定的人或事物,如果去掉限制性定语从句,整个句子表意会不完整甚至不通顺;从结构上看,限制性关系从句常紧跟先行词,并且同先行词之间一般不加逗号分隔(但不是绝对的)。
限制性关系从句的关系词包括:that, which, who, whom, whose, as, than等。
非限制性关系从句
从语义上看,非限制性关系从句主要起补充说明的作用,有时相当于一个并列分句或状语从句,可以表达原因、目的、结果、条件、让步等意义。
例如:Dr Lee, who had read through the instructions carefully before doing his experiments, did not obtain satisfactory results. (非限制性关系从句表示让步的意义,相当于though Dr Lee had read through the instructions...)
非限制性定语从句的关系词包括:which, who, whom, whose, as等,另外that在非限制性关系从句中并非绝对不可使用。
四、关系代词的用法
1. that 既可以用于指人,也可以用于指物。在从句中作主语或宾语,作主语时不可省略,作宾语可省略。例如:
Mary likes music that is quiet and gentle.玛丽喜欢轻柔的音乐。(that作主语)
The coat (that) I put on the desk is blue.我放在桌子上的那件外套是蓝色的'。(that作宾语)
2.which用于指物,在句中作主语或宾语,作主语不可省略,作宾语可省略。例如:
The building which stands near the train station is a supermarket.位于火车站附近的那座大楼是一家超市。(作主语)
The film (which) we saw last night was wonderful. 我们昨天晚上看的那部电影很好看。(作宾语)
3.who, whom用于指人,who 用作主语,whom用作宾语。在口语中,有时可用who代替whom,也可省略。例如:
The girl who often helps me with my English is from England.经常在英语方面帮助我的那个女孩是英国人。(作主语)
Who is the teacher (whom) Li Ming is talking to?正在与李明谈话的老师是谁?(作宾语)
注意:(1)当定语从句中含有介词,介词放在句末时,who, that, which可省略,但介词在关系代词前时,只能用“介词+which/whom”结构。例如:
This is the house in which we lived last year.这是我们去年居住的房子。
Please tell me from whom you borrowed the English novel.请告诉我你从谁那借的这本英文小说。
(2)含有介词的固定动词词组中,介词不可前置,只能放在原来的位置上。例如:
This is the person whom you are looking for. 这就是你要找的那个人。
(3)that 作介词的宾语时,介词不能放它的前面,只能放在从句中动词的后面。例如:
The city that she lives in is very far away.她居住的城市非常远。
(4)关系词只能用that的情况:
a. 先行词被序数词或形容词最高级所修饰,或本身是序数词、基数词、形容词最高级时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
He was the first person that passed the exam. 他是第一个通过考试的人。
b.被修饰的先行词为all, any, much, many, everything, anything, none, the one等不定代词时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
Is there anything that you want to buy in the shop?你在商店里有什么东西要买吗?
c.先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last, little, few 等词修饰时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
This is the same bike that I lost.这就是我丢的那辆自行车。
d. 先行词里同时含有人或物时,只能用that, 而不用which.例如:
I can remember well the persons and some pictures that I saw in the room.我能清楚记得我在那个房间所见到的人和一些照片。
e.以who或which引导的特殊疑问句,为避免重复,只能用that.例如:
Who is the girl that is crying? 正在哭泣的那个女孩是谁?
f.主句是there be 结构,修饰主语的定语从句用that,而不用which.例如:
There is a book on the desk that belongs to Tom. 桌子上那本书是汤姆的。
(5)关系词只能用which,而不用that 的情况:
a.先行词为that, those时,用which, 而不用that.例如:
What’s that which is under the desk? 在桌子底下的那些东西是什么?
b.关系代词前有介词时,一般用which,而不用that.例如:
This is the room in which he lives. 这是他居住的房间。
c.引导非限制性定语从句,用which, 而不用that.例如:
Tom came back, which made us happy. 汤姆回来了,这使我们很高兴。
五、关系副词的 用法
(1)when指时间,其先行词表示时间,在句中作时间状语。例如:
This was the time when he arrived.这是他到达的时间。
(2)where指地点,其先行词表示地点,在句中作地点状语。例如:
This is place where he works.这是他工作的地点。
(3)why 指原因,其先行词是原因,起原因状语作用。例如:
Nobody knows the reason why he is often late for school. 没人知道他为什么上学总迟到。
六、关系构成
关系从句的句法功能主要是充当定语。在英语中,关系从句通常位于它所修饰的词(组)之后。被关系从句修饰的词(组)叫做先行词(英语:antecedent),引导关系从句的词称为关系词,关系词指代先行词并在关系从句中充当一定的成分。
例如:This is the book which interests me.(“which interests me”是关系从句,修饰先行词“book”,而关系词“which”指代先行词“book”并在关系从句中充当主语。这句话可以拆分为两个句子来理解:“This is the book.”和“The book interests me.”)
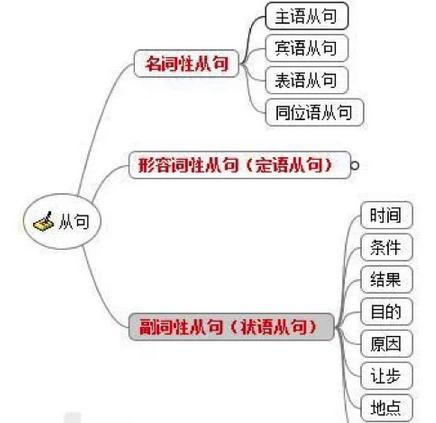
七、特殊的关系从句
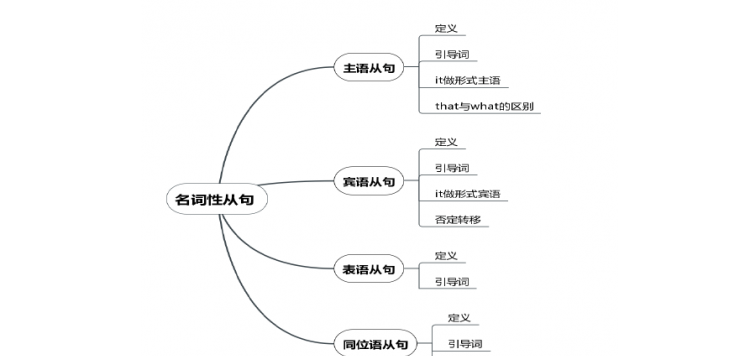
名词性关系从句
名词性关系从句(英语:nominal relative clause)又叫自由关系从句(英语:free relative clause),名词性关系从句在结构上不含有先行词,它的关系词同时扮演了关系词和先行词的角色,因此名词性关系从句的关系词又叫缩合连接代词。
例如:I like what I see.(“what I see”是名词性关系从句,它没有先行词,与此同时缩合连接代词“what”又直接充当了“like”的宾语。)
缩合连接代词“what”可以根据语义解释为“the thing(s) that”或“the person(s) that”。
嵌入式关系从句
嵌入式关系从句(英语:embedded relative clause)是一种较复杂的关系从句,它既是先行词的后置定语,又是另一结构的宾语。
例如:She has an adopted child who she says was an orphan. (关系从句修饰“an adopted child",同时又是“she says”的宾语)
双重关系从句
双重关系从句(英语:double relative clause)是指两个关系从句修饰同一个先行词的语法现象。
例如:You can easily find us;just look for a house whose windows need washing andwhosefence needs repairing!
宾语从句和定语从句的思维导图
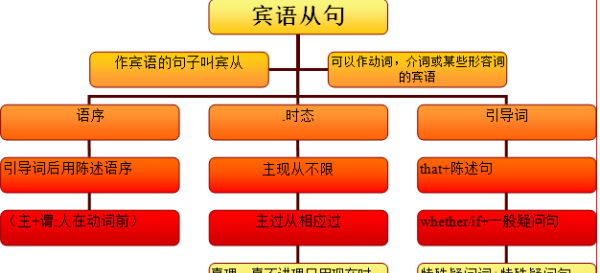
在句子中起宾语作用的从句叫作宾语从句,分为动词宾语从句、介词宾语从句和形容词宾语从句。
1.动宾从句
(1)大多数及物动词都可以带宾语从句
We all expect(that)they will win, for members of their team are stronger.我们都预料他们会赢,因为他们的队员更强壮。
(2)部分“动词+副词”结构也可以带宾语从句
I have found out(that)all the tickets for the concert have been sold out.我发现这场音乐会的所有票都卖光了。
(3)可运用形式宾语it代替的宾语从句
①动词find, feel, consider, make, believe, think等后面有宾语补足语的时候,则需要用it作形式宾语而将that宾语从句后置。
I think it necessary that we take plenty of drinks every day. 我认为我们每天多喝饮料是有必要的。
②有些动词带宾语从句时需要在宾语与从句前家it(双宾语)。
因为动词的原因,即动词需要有两个宾语才能将句子的意思表达清楚,it充当间接宾语,从句充当直接宾语。
I hate it when they say with their mouths full of food. 我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话。
(4)若宾语从句是以wh-等疑问代词或疑问副词引导的,则不可用it代替
We all consider what you said to be unbelievable. 我们都认为你所说的是不可信的。
2.介宾从句
I know nothing about my new neighbor except that he used to work in a company. 对于我的新邻居我只知道他曾在一家公司上班,其他一无所知。
3.形容词+宾语从句
有些形容词具有动词的含义,所以也可以带一个宾语从句,常用来引导宾语从句的形容词有:sure, certain, glad, please, happy, sorry, afraid, satisfied, surprised。
Are you sure his answer is right? 你确定他的回答是正确的吗?
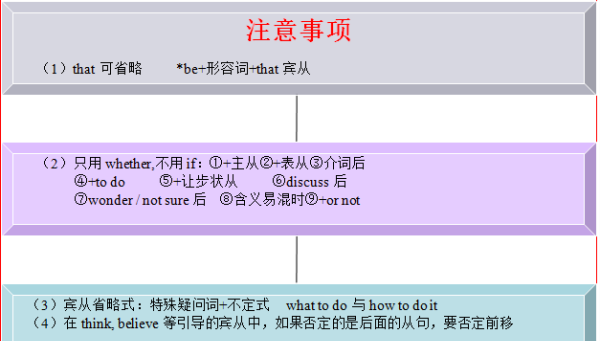

名词性从句,形容词性从句,副词性从句
英语的复合句一般分为三大类型:名词性从句、形容词性从句和副词性从句。 (一)名词性从句 在整个复合句中起名词作用,充当主语、宾语、表语和同位语等的各种从句,统称为名词性从句。名词性从句主要有以下几种: 1. that引导的从句e.g. It is reported that one third of Guangzhou citizens plan to buy a private car. (据报道,三分之一的广州市民打算购买私家车。) 2. whether/if引导的从句e.g. Whether motorcycles should be banned in Guangzhou has become an issue of controversy.(广州是否禁摩托车成了有争议的话题。) 3. how/why/when/where引导的从句e.g. This essay aims to explore why so many white collar workers suffer from insomnia. (本文将探讨为什么这么多白领失眠的原因。) 4. who/whom/whose/what/which引导的从句e.g. Who should be responsible for the environmental degradation is still unknown.(谁对环境恶化负责还不清楚。) (二)形容词性从句 具有形容词功能,在复合句中做定语的从句被称之为形容词性从句或定语从句。被修饰的名词、词组或代词被称为先行词。形容词性从句分为两种类型: (1)由关系代词who, whom, whose, that, which, as引导的从句。例如: People who are strongly against human cloning claim that it is immoral and unethical. (强烈反对克隆人的人们认为这样做不道德和不合伦理) (2)由关系副词when, where, why引导的从句。例如: I would like to analyze the reasons why a growing number of teenagers are addicted to gambling.(我将分析为什么越来越多的青少年沉迷于赌博的原因。) (三)副词性从句 副词性从句也称为状语从句,主要用来修饰主句或者主句的谓语。大致分为九大类,分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。 (1)时间状语从句e.g. When everyone is fully aware of the severity of fresh water scarcity and takes effective measures, I am convinced that we will tackle this problem constructively.(当每个人充分意识到淡水短缺的严重性,并采取有效措施,我相信我们一定能妥善解决好这个问题。) (2)地点状语从句e.g. Where there is smoke, there is fire.(无风不起浪)(3)原因状语从句e.g. Pets should be forbidden because they may spread diseases and damage the cityscape.(应该禁止饲养宠物,因为它们可能会传播疾病和有损市容。) (4)目的状语从句e.g. Old people should be encouraged to live in a nursing house so that they can enjoy professional care and first-rate facilities. (应当鼓励老人到敬老院居住,这样他们可以享受到专业的照料和一流的设施。) (5)结果状语从句e.g. Some government officials fail to recognize the potential hazards of improper waste disposal, so that the environment in some cities is deteriorating.(一些政府官员未能认识到垃圾处理不当带来的潜在危害,因此一些城市的环境不断恶化。) (6)条件状语从句e.g. If we continue to overlook the increasing waste in Guangzhou, it is likely that Guangzhou will become a huge landfill site sooner or later.(如果我们继续无视广州日益增多的垃圾,有可能不久的将来广州将成为巨大的垃圾填埋场。) (7)让步状语从句e.g. While I admit that smoking has some side-effects, I still feel that it is ridiculous to ban smoking in public places.(虽然我承认吸烟有副作用,我依然觉得公共场所禁烟是荒唐的。) (8)比较状语从句e.g. Red is two times as much as Blue.(红色是蓝色的两倍。) (9)方式状语从句e.g. Just as we protect less able human beings, so we should safeguard the welfare of other weaker species.(正如我们保护弱者一样,我们也应该保护弱势物种的福利。)

高中英语定语从句思维导图高清
一、定语从句的定义。
用作定语的从句叫做定语从句(attributive clause)。定语从句通常皆置于它所修饰的名词(或代词)之后,这种名词(或代词)叫做先行词(antecedent)。引导宾语从句的关联词为关系代词和关系副词。关系代词在定语从句中可用作主语、宾语、定语等;关系副词在定语从句中只用作状语。如:
The student who answered the question was John. 回答问题的那个学生是约翰。(who answered the question是关系代词who引导的定语从句,用以修饰who先行词student,who在从句中用作主语)
I know the reason why he was so angry. 我知道他这么生气的原由。(why he was so angry是关系副词引导的定语从句,用以修饰why的先行词reason,why在从句中用作原因状语)
定语从句一般紧跟其先行词之后。如:
The room which served for studio was bare and dusty. 这个用作工作室的房间空荡荡的,布满灰尘。(关系代词which引导的定语从句紧跟其先行词room之后)
有时亦可与先行词分离。如:
A new master will come tomorrow who will teach you German. 明天要来一位新教师教你们德语了。(关系代词who引导的定语从句与其先行词master分离)
二、关系代词的用法。
用作关联词的关系代词有who,whom,whose,that,which等。who,whom,whose指人,who是主格,在从句中用作主语(在非正式英语中亦可用作宾语);whom是宾格,在从句中用作宾语;whose是属格,在从句中用作定语(有时亦可指物)。如:
The man who was here yesterday is a painter. 昨天在这里的那个人是位画家。(主格关系代词who在从句中用作主语)
The man who I saw is called Smith. 我见到的那个人名叫史密斯。(在非正式英语中who 代替了whom,亦可省去不用)
I know the man whom you mean. 我认识你指的那个人。(宾语关系代词whom在从句中用作宾语)
A child whose parents are dead is called an orphan. 失去父母的孩子叫做孤儿。(属格关系代词whose在从句中用作定语,指人)
I’d like a room whose window looks out over the sea. 我想要一个窗户面临大海的房间。(属格关系代词whose在从句中用作定语,指room,可代之以of which,但后者较为正式)
that在从句中既可用作主语,亦可用作宾语(在非正式文体中可省去);既可指人,亦可指物,但在当代英语中多指物。如:
A letter that is written in pencil is difficult to read. 用铅笔写的信很难读。(关系代词that在从句中用作主语,指物)
The letter that I received from him yesterday is very important. 昨天他来的信很重要。(关系代词that在从句中用作宾语,指物)
Is he the man that sells eggs? 他是卖鸡蛋的那个人吗?(关系代词that在从句中用作主语,指人)
关系代词which在从句中可以用作主语和宾语,一般皆指物,在非正式文体中可以省去。
This is the book which has been retranslated into many languages. 这就是那本有多种译本的书。(关系代词which在从句中用作主语)
Where is the book which I bought this morning? 今天上午我买的那本书在哪儿?(关系代词which在从句中用作宾语,可省去)
which在从句中亦可用作定语和表语。如:
We told him to consult the doctor, which advice he took. 我们叫他去看医生,他听取了我们的劝告。(关系代词which在从句中用作定语)
The two policemen were completely trusted, which in fact, they were. 那两个警察完全受到信任,事实上真是如此。(关系代词which在从句中用作表语)
as,than,but亦可用作关系代词。如:
The two brothers were satisfied with this decision, as was agreed beforehand. 两兄弟对这个决定都满意,它事先已经他们同意了。(关系代词as在从句中用作主语,其先行词是this decision)
He was a foreigner, as I knew from his accent. 他是个外国人,我是从他的口音知道的。(关系代词as在从句中用作宾语,其先行词是前面的整个句子)
I never heard such stories as he tells. 我从未听过他讲的这类故事。(关系代词as与指示代词such连用,在从句中用作宾语,其先行词是such stories)
Her attitude to him was quite the same as it had always been. 她对他的态度同她惯常的态度完全一样。(关系代词as与指示代词same连用,在从句中用作表语,其先行词是same)
You spent more money than was intended to be spent. 你花的钱超过了预定的数额。(关系代词than在从句中用作主语,其先行词是money)
There are very few but admire his talents. 很少人不赞赏他的才干的。(关系代词but在从句中用作主语,其先行词是few,but=who don’t)
关系代词在定语从句中用作介词宾语时,介词既可置于从句之首,亦可置于从句之末。但以置于从句之首较为正式。如:
This is the book for which you asked. 这是你所要的书。(关系代词用作介词for宾语,之首,即which之前)
This is the book which you asked for. 这是你所要的书。(介词for置于从句之末,which在此可省去)
关系代词who和that用作介词宾语时,介词须置于句末。如:
The people you were talking to are Swedes. 你与之谈话的那些人是瑞典人。(关系代词主格who用作介词to宾语时,介词to须置于从句之末,who中口语中可省去)
Here is the car that I told you about. 这儿就是我和你谈过的那辆汽车。(关系代词that用作介词about宾语,介词about须置于从句之末)
有时从句还有其它成分,介词则置于从句之中。如:
This is the boy who he worked with in the office. 那就是与他一道办公的那个男孩。
先行词指人时,关系代词既可用who,亦可用that。但关系代词在从句之中用作主语时,多用主格who。如:
Persons who are quarrelsome are despised. 好争吵者遭轻视。(除外persons,还有people,those,等皆多用who)
All who heard the story were amazed. 听到这个故事的人都感到吃惊。(代词如he,they,any,all,one等之后多用who)
I will pardon him who is honest. 我愿意宽恕他,他是诚实的。(描述性定语从句用who)
I think it is you who should prove to me. 我认为是你应该向我提出证据。(在强调结构中多用who,who在此可省去)
Who is not for us is against us. 谁不赞成我们就是反对我们。(缩合连接代词who为可代之以that)
在下列一些情况中则多用that。如:
)He was the man that the bottle fell on. 他就是瓶子落在其身上的那个人。(此处常用that作宾语指人,亦可用whom)
He is a man that is never at a loss. 他是一个从未一筹莫展的人。(that常用于泛指人)
He was watching the children and parcels that filled the car. 我望着塞满车的孩子和包裹。(兼指人与物时须用that)
Who that you have ever seen can beat him in chess? 你曾见过谁能在棋艺上打败他?(避免与先行词who重复时应用that)
That’s the same man that asked for help the day before yesterday. 这个与前天求援的是同一个人。(先行词前有指示代词same时应用that)
He is not that man that he was. 他已不是过去的他了。(that常用作表语)
I knew her father for the simplest, hardest working man that ever drew the breath of life. 我早知她的父亲是一个世上最简朴最努力工作的人。(先行词前有形容词最高级、序数词或only等词时应用that)
先行词指物时,关系代词that与which往往可以互换。但在下列情况中多用that。如:
All that glitters is not gold. 闪光的东西不都是金子。(不定代词包括复合词something等多后接that)
It was the largest map that I ever saw. 那是我所看见过的最大的地图。(前有形容词最高级等的先行词之后多用that)
It was liberation that brought about a complete change in his life. 是解放给他的生活带来了彻底的改变。(强调结构用that)
There is a house that has bay windows. 有一栋房子有凸出的窗户。(that在此表固有的特点)
The distance that you are from home is immaterial. 你离家的距离是不足道的。(在限制性定语从句中关系代词用作表语应用that,在描述性定语从句中则应用which)
Which was the hotel that was recommended to you? 哪一个是推荐给你的旅馆?(这里用that显然是为了避免重复which)
在下列情况中则多用which。如:
Larry told her the story of the young airman which I narrated at the beginning of this book. 拉里把我在书本开关叙述过的那个关于一个青年飞行员的故事讲给她听。(离先行词较远时常用which)
A store should keep a stock of those goods which sell best. 商店应存在最畅销的货物。(“those+复形名词”之后多用which)
I have that which you gave me. 我有你给我的那个。(which比较正式,在非正式英语中也可用that)
Beijing, which was China’s capital for more than 800 years, is rich in cultural and historic relics. 北京曾是八百多年的中国首都,有很丰富的历史文物。(描述性定语从句一般皆用which)
This is the one of which I’m speaking. 这就是我所讲的那个。(介词之后须用which)
用作关联词的关系副词有when,where,why等。when在从句中用作时间状语,其先行词须是表时间的名词。如:
We will put off the picnic until next week, when the weather may be better. 我们打算把野餐推迟到下周,那时天气可能转好。(关系副词when的先行词是next week)
He came last night when I was out. 他昨晚来时我出去了。(关系副词when的先行词是last night)
since,before,after亦可用作表时间的关系副词。如:
Every hour since I came has been most enjoyable. 我来之后的每一个小时都是非常好玩的。(since用作关系副词)
On the day before we left home there came a snowstorm. 在我们离家的前一天,下了一场暴风雪。(before用作关系副词)
The year after she had finished college she spent abroad. 她大学毕业后的一年是在国外度过的。(after用作关系副词)
that有时亦可用作表时间的关系副词。如:
It happened on the day that I was born. 那件事是在我出生的那一天发生的。(that=when)
Little do I remember the day that I first met her. 我几乎不记得与她初次见面的日子。
where在从句中用作地点状语,其先行词须是表地点的名词。如:
They went to the Royal Theatre, where they saw Ibsen’s “The Doll’s House”. 他们去皇家剧院看了易卜生的《傀儡家庭》。
The place where Macbeth met the witches was a desolate heath. 麦克白遇见女巫的地方是一片荒原。
where的先行词亦可是有地点含义的抽象名词。如:
He has reached the point where a change is needed. 他已到了需要改弦易辙的地步。(where的先行词point是抽象名词)
why在从句中用作原因状语,其先行词只有reason。如:
That is no reason why you should leave. 那不是你必须离开的原因。(why先行词是reason)
He refused to disclose the reason why he did it. 他拒绝透露他做那件事的原因。(why先行词是reason)
有时why可以省去。如:
That’s one of the reasons I asked you to come. 那是我要你来的原因之一。(reasons后省去why)
有时why可用that代替。如:
The reason that he died was lack of medical care. 他死于缺乏医疗。(why由that代替)
当先行词为the way的时候,关系副词也可以用that,例如:
This is the way that he solved the problem. 这是他解决问题的方法。
I don't like the way that he talks. 我不喜欢他说话的样子。
定语从句可分为限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句。限制性定语从句与先行词关系密切,对它有限制作用。因此不可缺少,否则会影响全句的意义。限制性定语从句前一般不用逗号。如:
What is the name of the boy who brought us the letter? 给我们带信的那个男孩叫什么名字?
There is much which will be unpleasing to the English reader. 有许多东西将会使英国读者不愉快。
The teacher told us that Tom was the only person that was reliable. 老师告诉我们,汤姆是惟一可依赖的人。
I shall never forget the day when we first met in the park. 我永远不会忘记我们在公园相见的那一天。
Is there a store around where we can get fruit? 附近有可以买到水果的商店吗?
Do you know the reason why I came late? 你知道我迟到的原故吗?
非限制性定语从句(non-restrictive)只与先行词有一种松散的修饰关系,用逗号与先行词分开。因此从句中的关系代词不能省略。that一般不引导非限制性定语从句。如:
I like to chat with John, who is a clever fellow. 我喜欢与约翰交谈,他是个聪明人。
Water, which is a clear liquid, has many uses. 水是一种清澈的液体,有许多用途。
Once more I am in Boston, where I have not been for ten years. 我又一次来到了波士顿,我有十年没有到这里来了。
非限制性定语从句形式上是从句,其功能实质上相当于一个分句。如:
Then he met Mary, who invited him to a party. 后来他遇到玛丽,玛丽邀请他去参加晚会。(who实际上=and she)
When he was seventeen he went to a technical school in Zurich, Switzerland, where he studied mathematics and physics. 他17岁时,到瑞士苏黎世一专科学校上学,他在那里学习数学和物理学。(where=and there)
有时描述性定语从句的含义相当于一个状语从句。如:
We don’t like the room, which is cold. 我们不喜欢那个房间,它很冷。(which is cold=since it is cold)
He said he was busy, which was untrue. 他说他很忙,其实不然。(which was untrue=though it was untrue)
I want him, who knows some English. 我要他,他懂得些英语。(who knows some English=for he knows some English)
以上就是关于形容词性从句思维导图ppt ,定语从句的思维导图及例句的全部内容,以及形容词性从句思维导图ppt 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

