本文目录
英语中什么是副词
您好!
副词
定 义:
副词是一种用来修饰动词,形容词,全句的词,说明时间,地点,程度,方式等概念。
分 类:
1) 时间和频度副词:
now,then,often,always,usually,early,today, lately, next,last,already,generally,frequently, seldom,ever,never,yet,soon,too, immediately, hardly,finally,shortly, before, ago,sometimes, yesterday.
2) 地点副词:
here, there, everywhere, anywhere, in, out, inside, outside, above, below, down, back, forward, home, upstairs, downstairs, across, along, round , around, near, off, past, up, away, on.
3) 方式副词:
carefully, properly, anxiously, suddenly, normally, fast, well, calmly, politely, proudly, softly, warmly
4) 程度副词:
much,little, very,rather,so,too,still, quite, perfectly, enough, extremely, entirely,almost, slightly.
5) 疑问副词:
how, when, where, why.
6) 关系副词:
when, where, why.
7) 连接副词:
how, when, where, why, whether.
用 法:
副词在句中可作状语,表语,补语。
He works hard.
他工作努力。
You speak English quite well.
你英语讲的很好。
Is she in ?
她在家吗?
Let's be out.
让我们出去吧。
Food here is hard to get.
这儿很难弄到食物。
位 置:
1) 多数副词都可以放在动词的后面,如果动词带有宾语,副词就放在宾语后面。
I get up early in the morning everyday.
我每天早早起床。
He gave me a gift yesterday.
他昨天给了我一件礼物。
She didn't drink water enough.
她没喝够水。
The train goes fast.
火车跑得快。
We can go to this school freely.
我们可以免费到这家学校学习。
They left a life hardly then.
当时他们的生活很艰难。
He has a new hat on today.
他今天戴了一顶新帽子。
I have seen this film twice with my friends.
这部电影我和朋友看过两次。
2) 副词修饰形容词,副词时,副词在前面,而被修饰的词在后面。
It's rather easy, I can do it.
这很容易,我能做到。
He did it quite well.
他做得相当好。
It's rather difficult to tell who is right.
很难说谁是对的。
It's so important that I must tell my friends.
这件事太重要了,我得告诉我的朋友。
It's much better.
好多了。
3) 频度副词可放在实义动词的前面,情态动词和助动词的后面。
I often help him these days.
这些日子我经常帮助他。
I always remember the day when I first came
to this school.
我常常记得我第一次来学校的那一天。
You mustn't always help me.
你不能老是帮助我。
He seldom comes to see us.
他很少来看我们。
We usually go shopping once a week.
我们通常一周买一次东西。
The new students don't always go to dance.
新学生并不时常去跳舞。
4) 疑问副词,连接副词,关系副词以及修饰整个句子的副词,通常放在句子或从句的前面。
When do you study everyday?
你每天什么时间学习?
Can you tell me how you did it?
你能告诉我你如何做的吗?
First, let me ask you some questions.
先让我来问几个问题。
How much does this bike cost?
这辆车子多少钱?
Either you go or he comes.
不是你去就是他来。
The students were reading when the teacher came into the classroom.
当老师进教室时,学生们正在读书。
5) 时间副词和地点副词在一个句中, 地点副词在前面时间副词在后面。
We went shopping in the supermarket at 9 o'clock yesterday.
昨天九点钟我们到超市买东西了.
What were you doing in the classroom yesterday afternoon?
昨天下午你在教室里干什么?
The accident took place in the Eleven Avenue one hour ago.
一小时前十一号大街发生了一场事故。
比较等级:
副词和形容词一样,也有它的比较级和最高级形式. 可以参考形容词的变换形式。但以词尾 -ly 结尾的副词(除 early )须用 more 和 most 。
hard harder hardest
fast faster fastest
early earlier earliest
much more most
warmly more warmly most warmly
单音节副词的比较级是在副词后面加上 -er 构成的,最高级是在副词后面加上 -est 构成的。
near nearer nearest
hard harder hardest
多音节副词的比较级是在副词的前面加上 -more 构成的。 最高级是在副词前面加上 -most 构成的。
warmly more warmly most warmly
successfully more successfully most successfully
有些副词的比较级和最高级形式是不规则的。
well-better - best little - less - least
Much- more - most badly - worse - worst
far-farther(further)-farthest(furthest)
副词的比较级和最高级用法同形容词的比较级用法基本一样。 最高级形式句中 the 可以省略。
He works harder than I.
他比我工作努力。
Lucy gets up earlier than Lili.
露西比丽丽起床早。
He runs fastest in our class.
他在我们班跑地最快。
He dives deeper than his teammates.
他比他的队员潜水深。
It's true that he speak English more fluently than any of us.
他英语讲的确实比我们任何人都好。
Our school team play football best in our region.
我们校队在我们地区足球踢得最好的。
副词比较级和最高级的形式
副词比较级和最高级的变化形式与形容词基本上一样
一般 副词
hard→harder →hardest
fast→faster →fastest
late→later →latest
early→earlier →earliest
特殊 副词
well →better →best
much →more →most
badly →worse →worst
little →less →least 但是,开放类副词即以后缀�ly结尾的副词不能像形容词那样加�er或�est,如
quickly →more quickly →most quickly quietly →more quietly →most quietly
〔注〕: early与slowly中的�ly不是后缀,故可以把�y变�i再加�er和�est
比较级和最高级的基本用法
一、原级比较的基本用法
1. 原级比较由“as+形容词或副词(或再加名词或短语)+as ”构成“原级相同”比较句,表示两者比较;其否定式,即“程度不及”比较句型为“not so(as) +形容词或副词+as”,而且as…as结构前可用just, almost, nearly, quite等表示程度的词修饰
1) Walking briskly for thirty minutes will burn as many calories as .
〔A〕 to run for fifteen minutes
〔B〕 running for fifteen minutes
〔C〕 you run for fifteen minutes
〔D〕 fifteen�minute walking
2) The gorilla(大猩猩), while 〔A〕 not quite as curious than 〔B〕 the chimpanzee(黑猩猩), shows more persistence 〔C〕 and memory retention(记忆力) in solving 〔D〕 a problem.
3) Alaska is twice 〔A〕 as larger 〔B〕 as 〔C〕 the next largest 〔D〕 state, Texas.
2. “as (so)+名词+as+名词”进行名词比较,这时一般情况下有一个表示原级的比较词,但如果第一名词前出现了形容词修饰该词或出现副词修饰谓语,应当用so而不用as
4) Thomas Jefferson’s achievements as an architect rival his contributions a politician.
〔A〕 such
〔B〕 more
〔C〕 as
〔D〕 than
5) I should say Henry is not much a writer as a reporter. (88年考题)
〔A〕 that
〔B〕 so
〔C〕 this
〔D〕 as
二、比较级
1. 比较级由“形容词(副词)比较级+than+…,”构成表示在两者中间一方比另一方“更加…”。连词than后可接句子,也可接名词、代词、名词短语、介词短语、动词、动词不定式、�ING结构和�ED结构,有时也可省去than。
6) Natural mica(云母) of 〔A〕 a superior 〔B〕 quality is cheapest 〔C〕 to obtain than synthetic 〔D〕 mica.
7) She is older than .
〔A〕 any other girl in the group
〔B〕 any girl in the group
〔C〕 all girls in the group
〔D〕 you and me as well as the group
8) Josephine McCrackin joined 〔A〕 the “Santa Cruz Sentinel” in 1905 and, until her death fifteen years late 〔B〕 , remained 〔C〕 active in journalistic 〔D〕 work.
2. 注意than前后两项相比较的人或事物要一致
9) The purpose of the research had a more important meaning for them than .
〔A〕 ours
〔B〕 with us
〔C〕 for ours it had
〔D〕 it did for us
10) Sound travels air.
〔A〕 faster through water than through 〔B〕 faster than through water and
〔C〕 through water faster and〔D〕 where it is faster through water than through
11) Gerbrand von den Feckhout, one of Rembrand’s pupils, followed 〔A〕 the style of his teacher so implicitly that 〔B〕 his paintings 〔C〕 are sometimes confused with his master 〔D〕 .
三、最高级
1. 最高级用于三者以上比较,形容词的结构形式是“定冠词+形容词最高级+名词+表示范围的短语或从句”(如all, of all, of the tree, in the world, that has ever taken place等)
12) The more 〔A〕 fearsome of all the 〔B〕 animals in 〔C〕 the Western 〔D〕 Hemisphere is the grizzly bear.
13) Of all economic 〔A〕 problems, inflation continues to be 〔B〕 a 〔C〕 most significant in its daily impact on 〔D〕 people and business.
14) , the most familiar to general public is the criminal jurisdiction.
〔A〕 All the activities
〔B〕 The activities
〔C〕 Of all the activities
〔D〕 It is the activities
2. 副词的最高级与形容词最高级的区别在于最高级前没有定冠词the
[编辑本段]例题解析
1) B为正确答案。
2) B错。改为 as ,和前面的as和形容词原形curious 一起构成同程度比较。
3) B错。 改为as large。
4) C对。动词rival(胜过、匹敌)前后是两个相比较的成分achievements(成果)和 contributions(贡献),由于前面的名词后出现了短语 as an architect,故空白处也应用as,使前后对比成分一致。
5) B为正确答案。
6) C错。应改为比较级cheaper。比较级后并不一定跟接连词than,有时在其间有名词或名词短语(被形容词所修饰),介词短语,不定式或其他成分隔开。
7) A为正确答案。“She”作为单个不能跟全组比(C和D不对),也不能跟全组所有相比,因为“她”也是其中一员,自然“她”不能跟自己相比。这里“She”比较的是“这组中的任何一个”,所以A对。
8) B错。应改为比较级later,因此处实为与1905年相比晚15年,故应使用比较级。
9) D为正确答案。
10) A为正确答案。
11) D错。 改为his master’s。
12) A错。 改为most。
13) C错。改为the, significant是多音节形容词,在此处应用最高级形式(在前面加 the most),注意句中的“of all… ”。
14) C为正确答案。本句空白处缺状语,A和B全为名词短语,不符合条件;D为句子,和空白后面的句子没有任何联系,故亦应排除。只有C正确,和后面的最高级the most familiar前后呼应。
[编辑本段]特殊表达法
一、形容词与副词的同级比较: 由“as(so)…as”引出,其否定式为“not so…”或“not as…as”,考生还应注意下列含有“as”结构或短语的句子
1. as such:表示上文所指明的事或人
He is a child,and must be treated as such. 他是个孩子,必须被当作孩子对待。
2. as much:表示“与…同量”
Take as much as you like. 拿多少都行。
I would gladly have paid twice as much for it. 就是价格再贵一倍,我也会愿意把它买下的。
He as much as admitted the whole story. 他几乎全部承认了。
3. as many:表示“与…一样多”
I found six mistakes in as many lines. 我在六行中发现了六个错。
二、表示“几倍于”的比较级:用twice (两倍),four times (四倍),ten times (十倍)加上as … as 结构
This one is four times as big as that one. 这个是那个的四倍大。(这个比那个大三倍。) / Our campus is three times as large as yours. 我们的校园比你们的大两倍。 / He has books twice as many as she does. 他的书比她多一倍。
1) The five�year deal obligates 〔A〕 the country to buy nine million tons 〔B〕 of grain a year 〔C〕 , three million more as 〔D〕 the old pact’s minimum.
三、“the same +名词+as”表示同等比较
2) The lens of a camera performs the lens of the eye.
〔A〕 in the same function 〔B〕 the same function as
〔C〕 the function is the same as 〔D〕 and has the same function
3) The elimination of inflation would ensure that the amount of money used in repaying a loan would
have as the amount of money borrowed.
〔A〕 as the same value 〔B〕 the same value
〔C〕 value as the same 〔D〕 the value is the same
四、比较级前可用a little, a bit, slightly, a great deal, a lot,many, much等词语表示不定量,far, completely,still表示程度或更进一步
4) There are now methods for studying color vision in infants than there once were.
〔A〕 more sophisticated than
〔B〕 much more sophisticated
〔C〕 much sophisticated
〔D〕 sophisticated
5) The photographs of Mars taken by satellite are than those taken from the Earth.
〔A〕 clearest
〔B〕 the clearest
〔C〕 much clearer
〔D〕 more clearer
6) Common porpoises(海豚) are usually not considered 〔A〕 migratory, although 〔B〕 some do move 〔C〕 to more warmer 〔D〕 waters in winter.
兼有两种形式的副词
1) close与closely
close意思是"近"; closely 意思是"仔细地"
He is sitting close to me.
Watch him closely.
2) late 与lately
late意思是"晚"; lately 意思是"最近"
You have come too late.
What have you been doing lately?
3) deep与deeply
deep意思是"深",表示空间深度;deeply时常表示感情上的深度,"深深地"
He pushed the stick deep into the mud.
Even father was deeply moved by the film.
4) high与highly
high表示空间高度;highly表示程度,相当于much
The plane was flying high.
I think highly of your opinion.
5) wide与widely
wide表示空间宽度;widely意思是"广泛地","在许多地方"
He opened the door wide.
English is widely used in the world.
6) free与freely
free的意思是"免费";freely 的意思是"无限制地"
You can eat free in my restaurant whenever you like.
You may speak freely; say what you like.
副词有加a或ly的 区别在于通常加a 的副词描述一种状态,而加ly 的副词则倾向于感觉。
可修饰比较级的词
1)a bit, a little, rather, much, far, by far, many, a lot, lots, a great deal, any, still, even等
2)还可以用表示倍数的词或度量名词作修饰语。
3)以上词(除by far)外,必须置于比较级形容词或副词的前面。
典型例题:
1) ---- Are you feeling ____?
---- Yes,I'm fine now.
A. any well B. any better C. quite good
D. quite better
答案:B. any 可修饰比较级,quite修饰原级,well的比较级为better.
2)The experiment was____ easier than we had expected.
A. more B. much more C. much
D. more much
答案:C. much可修饰比较级,因此B,C都说得通,但easier本身已是比较级,不需more,因此C为正确答案。
3)If there were no examinations, we should have ___ at school.
A. the happiest time B. a more happier time
C. much happiest time D. a much happier time
答案:D。
中国语文中的副词
副词是一类用以修饰名词以外词语和整个句子的词,修饰名词的词一般为形容词。
一般而言中文在一个词的后面加「的」使其成形容词,加「地」使其成副词,但是现在一般已经不太常做这种区别了。
以副词修饰的句子举例:「一只非常小的虫轻易地钻进了那个洞穴里」,其中[非常]和[轻易]地为副词,小为形容词,虫为主词,钻进为动词,洞穴里指明前往地点。
一些问问题时的所用的词,像如何、谁、何时、什么等在某方面也可视为副词。
副词口诀:
副词修饰动与形,范围程度与时间。肯否估计与情态,语气频率用法全。
稍微没有全都偏,简直仅仅只永远,已经曾经就竟然,将要立刻刚偶然,
渐渐终于决忽然,难道连续又再三,也许必须很非常,最太十分更马上,
越极总挺常常再,屡次一定也不还。时名副名看加在,名前可加副不来。
前很后名都不行,单独回答更不能。
英语中连词有哪些单词
英语中是副词的单词有很多,比如now 现在、then 然后、often 经常、always 总是、usually 经常、early 早些、today 今天、here 这里、there 这里、everywhere 任何地方、in 在...里面、along 一直、round 环绕地、near 旁边,等等。

单词解析:
一、now
1、读音:英 [naʊ] 美 [naʊ]
2、翻译:
adv. 现在;立刻
conj. 既然(与that连用)
n. 现在;此刻
adj. 目前的;现存的
3、例句:It is now possible to put a man on the moon.
目前已能将人送到月球上。
二、often
1、读音:英 ['ɒfn] 美 ['ɔːfn]
2、翻译:adv. 经常;时常;屡次
3、例句:I often take my children to play in the park.
我经常带我的孩子们去公园玩。
三、always
1、读音:英 ['ɔːlweɪz] 美 ['ɔːlweɪz]
2、翻译:adv. 总是;一直;始终;永远;随时;无论如何
3、例句:I'm always at home in the evenings.
晚上我总是在家里。
四、here
1、读音:英 [hɪə(r)] 美 [hɪr]
2、翻译:
adv. 这里;这时;在这点上
n. 这里
int. 嘿;喂(用于引起注意)
3、例句:It is neither hot nor cold in winter here.
这里冬天既不热也不冷。
五、today
1、读音:英 [tə'deɪ] 美 [tə'deɪ]
2、翻译:
n. 今天;当今
adv. 今天;当今
adj. 现在的
3、例句:I feel my fingers are all thumbs today.
我觉得我今天笨手笨脚。
参考资料来源:百度百科-英语副词
英语副词有哪些
常见的副词有now现在、out外面、in里面、often经常、always总是、carefully小心地、fast飞快、along一直、early早一些、today今天、here这里、in在…里面等。
副词可分为:时间副词、频率副词、地点副词、方式副词、程度副词、疑问副词、连接副词、关系副词、表顺序的副词以及表完成的副词。
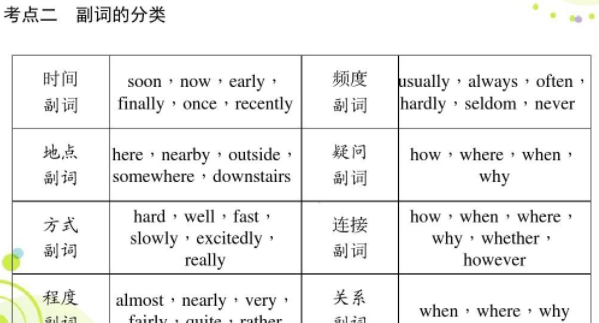
副词的用法
1、方式副词
方式副词能够表达出某人完成某事的方式,它最常与行为动词搭配使用。方式副词可以放在句末,或者直接放在动词后。
2、时间与频率副词
时间副词能够表达出某事发生的时间。它可以表达出一个具体的时间.虽然时间副词有时引导一个句子,但它常常放在句末。
3、程度副词
程度副词通常表示某事完成的程度。它们通常位于句末。
英语中副词是什么意思
副词(adverb,简写为adv)是一种用来修饰动词、形容词、全句的词,说明时间、地点、程度、方式等概念的词。副词是一种半虚半实的词。副词可分为:地点副词、方式副词、程度副词、疑问副词和连接副词。副词连用顺序:程度副词+方式副词+地点副词+时间副词。
以上就是关于其中副词英语 ,英语中什么是副词的全部内容,以及其中副词英语 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
