本文目录
初中英语时间状语从句归纳总结
列举英语语法状语从句的归纳总结
在复合句中修饰主句或主句中的某一成分的从句叫状语从句。状语从句通常由从属连词或起连词作用的词组引导,有时甚至不需要连词直接和主句连接起来。状语从句根据它表达的意思不同,可分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等九类。

一、 时间状语从句
时间状语从句是表示时间关系的从句。可以引导时间状语从句的.连词很多,根据意义和主从句之间的时间关系,通常可分为以下几种情况:
A. when, while, as, whenever
when, while, as表示主句谓语作和从句的谓语动作同时发生或几乎同时发生。
1.when
①when表示点时间时,从句中用短暂性动词;表示段时间时,用持续性动词。 When I got home, my family were already having dinner.
我到家的时候,全家已在吃晚饭。
(when表示点时间)
When they were still talking and laughing, the teacher came in.
当他们还在说笑的时候,老师进来了。(when表示段时间)
He waved ahello when he saw her.
当他看见她的时候,就挥手打了个招呼。(when表示点时间)
When you think you know nothing, you begin to know something.
当你认为自己一无所知的时候,就开始知道一些事情了。(when表示段时间)
注意:
当when意思是正当……时候(and at that moment)时,when只能跟在前一分句之后。 He was about to go to bed when the doorbel rang.
他正要上床,忽然门铃响了。
They were watching the World Cup when suddenly the lights went out.
他们正看着世界杯比赛,突然灯灭了。
They had just arrived home when it began to rain.
他们刚到家,天就开始下雨了。
②有时when表示虽然,尽管的含义,相当于although或since。
He walks when he might take a taxi.
尽管可以打的,但他还是步行。
How can you hope for mercy yourself when you show none
既然你不宽恕别人,你自己又怎能希望得到别人的宽恕呢?
2.while
①while通常表示一段时间,从句中宜用持续性动词作谓语。
Strike while the iron is hot.
趁热打铁。
She fell asleep while she was reading the newspaper.
她在看报的时候睡着了。
②while有时可以作并列连词,表示对比,可译成……而……。
I am fond of English while he likes maths.
我喜欢英语而他却喜欢数学。
We slept while the captain kept watch.
我们睡觉而上尉担任警戒。
③while有时可引导让步状语从句,意思是虽然。
While they love te children, they are strict with them.
虽然他们都爱他们的孩子,但却对他们要求严格。
提示:
虽然during 与 while 意思很相近,但是during是介词,不能引导从句。
3.as
①as表示点时间时,从句中用短暂性动词;表示段时间时,用持续性动词。as和when两者经常可以通用。
The thief was caught as when he was stealing in the supermarket.
小偷在超市行窃时被逮住了。
I saw Jim as when he left the meeting room.
吉姆离开会议室时候我看到了他。
②as表示 一边……一边……,强调从句和主句中两个动作交替进行或同步进行。 They talked as they walked.
他们边走边聊。
He looked behind from time to time as he went.
他一边走,一边不时地往后看。
③as表示随着
As time goes on, it's getting warmer and warmer.
随着时间的推移,天气变得越来越暖了。
As spring warms the earth, al flowers begin to bloom.
随着春回大地,百花开始绽放。
4.when, while, as的用法区别
①只有当从句表示的是段时间,即其谓语动词有持续性特征时,这三者可以通用互换。 I got the news on the radio when while as I was having breakfast.
我在吃早饭的时候从收音机里获悉这一消息。
②在下列情况下,三者彼此之间不能替换使用:
a.as更强调同一时间或紧接的一前一后或伴随着的变化。
We listened to the singer sing as he played the guitar.
我们听着歌星边弹吉它边演唱。
I thought of it just as you opened your mouth.
你一张嘴我就知道你要说什幺
As he grew older, he became less and less active.
随着他年龄的增长,他变得越来越不活泼了。
提示:
状语从句可放在主句之前或之后,放在主句之前时一般用逗号与主句分开。有时可置于主句中间,前后用逗号。
b.when更强调特定时间,还可表示从句中的动作先于或后于主句的动作。
When I had given Mary the spare ticket, I found my own already gone.
当我把多余的票给了玛丽时,我才发现我自己的票已不知去向。(从句动作发生在主句之前,注意主从句的时态)
When I finally got there, he meeting had been on for ten minutes.
当我最终赶到那里时,会议已开始十分钟了。(从句动作发生在主句之后,注意时态) c.while从句只能表示延续的动作或状态或主从句中动作的对比。
She thought I was talking about her daughter, while in fact, I was talking
about my daughter.
她以为我在谈论她女儿,而事实上,我在谈论我的女儿。
d.若表示两个短促动作几乎同时发生时,用as场合多于when。
As he finished his speech, the audience burst into applause.
他结束讲话时,观众爆发出雷鸣般的掌声。
5.whenever
whenever是when的强势语,它描述的不是一次性动作,而是经常发生的习惯性动作。 You are always welcome whenever you come.
无论你何时来都欢迎。
Whenever we met with diffiulties, they came to help us.
每当我们遇上困难的时候,他们就来帮我们。
B. before, after
1.before
before表示在一段时间之前。
I must finish all the work before go home.
回家之前我必须干完所有的活。
You must first learn to walk before you try to run.
在想要跑以前,你得先学会走。
He had learned English for three years before he went to London.
他去伦敦之前已学了三年英语。
提示:
before 从句往往带有否定的含义。
He ran off before I could stop him.
我还没来得及阻止他,他就跑掉了。
Thke it down berore you forget it.
趁着还没忘记的时候就记录下来。
必背:
before 常用句型 It is was will be
;英语高手来列举最基本最常用的语法句型
过去时+ed,不过有些是不规则的,还有第三人称单数+S,不过有些是不随主语的变化2变化的
many+可数,much+不可数 ,这个你应该知道吧,

英语中省略的语法归纳
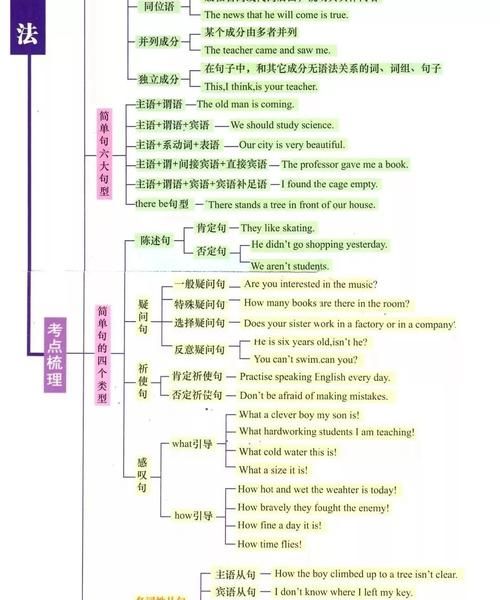
简单说说吧:非限定动词 非限定动词又称非谓语动词,即在句中不能单独作谓语,不受主语的人称和数的限制。非谓语动词有三种,即不定式、分词和动名词。本单元要求学员掌握三种非谓语动词的基本形式和用法;掌握不定时的被动式;不带to 的不定式;三种非谓语动词的复合结构(即带逻辑主语的不定式、分词和动名词)的形式及用法;现在分词与过去分词的区别;动名词与不定式的比较;现在分词与不定式的比较等。虚拟语气 语气是一种动词形式,用以表示说话者的意图或态度。虚拟语气表示所说的话只是一种主观的愿望、假设或建议等。虚拟语气可以用在非真实条件句、主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句和定语从句中。本单元要求学员掌握虚拟语气的基本形式和用法;掌握情态动词用于虚拟语气;了解含蓄条件句;掌握虚拟时态与谓语动词时态的关系等。介词 我们经常在名词或名词短语、代词或动名词前用介词表示人物、事件等与其它句子成分的关系。介词后面的名词或相当于名词的词语叫介词宾语。介词可表示地点、时间、比较、反对、原因、手段、所属、条件、让步、关于、对于、根据等。介词及其宾语构成介词短语,在句中担任后置定语、状语、表语等语法成分。本单元要求熟记常用介词及介词与其它此类的搭配。基本句型结构 句子按其结构可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。只存在一个主谓关系的句子叫简单句,即一个主语部分和一个谓语部分组成。当我们需要把几个意思连在一起时,可用标点符号或等立连词或连接副词把几个简单句连接成一个并列句。它们之间的关系是同等的。当一个句子由一个逐句和一个或从句构成时,这就是复合句。复合句的主语往往可以独立存在,从句则只作一个句子成分。本单元重点掌握疑问句,弄清楚各种疑问句的结构及用法,能正确完成附加疑问句部分,能回答各种疑问句。掌握简单句、并列句及复合句的句型结构;学会简单句与并列句、简单句与复合句、并列句与复合句的转换;学会将直接引语变为间接引语;掌握名词从句的用法。 摘自 ***/view/328219.htm
常见的英语语法错误有哪些
时态讲解
一、一般现在时主要用于:
1 、表示经常性或习惯性动作。 e.g. It seldom snows here.
2 、表示现在的特征或状态。 e.g. He is always ready to help others.
3 、普遍真理。 e.g. Action speaks louder than words.
4 、剧情图片介绍,背景说明,动作解说。 e.g. (Tom enters the room and sits at the table)
Doctor : What's your trouble, young man?
Tom : I've caught a cold, doctor.
5 、时间、条件、让步、方式状语从句表将要发生的动作时。
e.g. Tomorrow we shall go for an outing unless it rains.
与这种时态连用的时间状语常有: always, often, never, seldom, usually, once, a week, now 等。
二、一般过去时主要用于:
1 、表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况(包括习惯性的动作或状态)
e.g. When did you read the novel? She often came to help us in those days.
2 、谈到过去的情况时 e.g. I didn't know you were so busy.
3 、谈到已死人的情况时 e.g. Lei Feng was a great communist fighter.
与这个时态连用的时间状语常有:
yesterday, last night, the other day, two months ago, in 1985, then, just now, when, after, as soon as 引导的时间状语从句,表示主句动作开始的时间。
三、现在完成时主要用于:
1 、表示到现在为止这一时期中发生的动作或情况,即多次动作的总和。
e.g. We have learnt four English songs this month. How many times have you read the novel?
For many days we haven't seen each other.
2 、表示对现在有影响的某一已发生的动作。
e.g. The delegation has left 代表团已经走了(说明现在不在这里) Look, what you have done. 看你干的事。
与这一时态连用的时间状语有: already, yet, just, ever, never, by now, so far, recently, by the end of this month, since, for 短语,连词 since 引导的时间状语从句。
一般过去时与现在完成时的区别:
一般过去时:重在说明动作在过去发生时的具体情况(时间、地点、方式、对象、细节等)。
现在完成时:只提起已发生的动作(事实)及其影响,不说明动作发生时的具体情况。
cf. Have you had your lunch? What did you have for lunch?
I have ever been to the Great Wall, and I went there last summer with my father.
注:现在完成时表达的动作常具有反复性,故下面一句是错的:
Have you seen the six thirty's news program? 应改为: Did you see the six thirty's news program?
四、现在完成进行时主要用于:表示过去开始的某一动作一直持续到现在,以至延伸到将来,它强调动作延续时间之长久。e.g. I've been writing an article. 我一直在写一篇文章。(还在写)
cf. I've written an article. 我写了一篇文章。(已写完)
It has been raining these days. 这些天一直在下雨。
五、过去完成时
1 、过去完成时是一个相对时态,表示过去的过去,只有在两个过去发生的动作相比较时才可显示出来。
e.g. As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.
注:主从句表达的动作紧接时,即两动作发生的时间没有明显时间上的悬殊或空档时,主从句都可用一般过去时。 e.g. Where did your brother study before he joined the army?
2 、过去完成时可表示截止过去某一时间动作的总或动作的结束。
e.g. By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books By eight o'clock, he had finished his homework.
与这个时态连用的时间状语常有: by 1985, by eight o'clock, by then, by the end of last month, by the time when, when, as soon as, before 等连词引导的时间状语从句,表示主句动作结束的时间。
(六)现在进行时主要用于:
1 、表示现在或现阶段正在进行的动作。 e.g. Listen, someone is crying. What are you doing these days?
2 、代替一般现在时,表示经常性动作或状态,而含有某种感情色彩。
e.g. How are you feeling today? 你今天感觉怎样?(显得亲切)
He is doing well in his lessons. 他的功课很好。(赞扬)
You are always boasting. 你老爱吹牛。(厌烦)
3 、动词 go, come, leave, arrive 等表将要发生的动作时。 e.g. They are leaving for Shanghai.
与这种时态连用的时间状语常有: now, these days, recently, this week 等。
七、过去进行时主要用于: 表示过去某个时刻或阶段正在进行的动作。
e.g. At that time she was working in a PLA unit. 那时她在解放军某部工作。
What were you doing this time yesterday?
与这个时态连用的时间状语常用: at nine o'clock, this time last night, these days, at that time 等。
用 when 引导的时间状语从句表示主句的动作正在进行的时间。
e.g. When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
注:
1 、 while 引导时间状语从句叙述过去的动作时,从句常用过去进行时。
e.g. I read a magazine while I was waiting for the bus.
2 、 when 用作并列连词,意为“这时”,连接两分句时,第一句多用过去进行时。
e.g. I was reading a newspaper when he came in.
一般过去时与过去进行时的区别:
一般过去时:强调过去某一时间开始或完成的动作。
过去进行时:强调过去某一时间正在进行的动作。
试区别下面两句:
We were building a reservoir last winter. 去年冬天我们在修建一座水库。(可能尚未建成)
We built a reservoir last winter. 去年冬天我们修建了一座水库。(已经建成)
八、一般将来时主要用于: 表示将要发生的动作或情况
e.g. Tom will have a bike of his own.
与这个时态连用的时间状语常用: tonight, tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next week, in three hours, two days later 等。
一般将来时态与其它结构表将来情况的区别:
一般将来时态 :主要从时间的角度表将要发生的动作或情况。
be going to 结构 :①表(主观上)打算或准备做某事时。 ②表有发生某事的预兆时。
e.g. They are going to have a competition with us in studies. It is going to rain.
据以上区别,故下面一句是错的:
I am going to be eighteen years old next year. 应改为: I shall be eighteen years old next year.
be about to do sth 结构 :意为“刚要做某事”、“马上要做某事”强调时间之紧迫性。
e.g. We are about to discuss this problem. 我们将马上讨论这个问题。
be to do sth 结构: 表示按计划、安排、规定将实施某事或表示注定会发生某事。
e.g. When is the train to leave. All these things are to be answered for.
及物动词与不及物动词
英语中按动词后可否直接跟宾语,可把动词分成及物动词与和及物动词。
1.及物动词: 字典里词后标有vt. 的就是及物动词。及物动词后必须跟有动作的对象(即宾语),可直接跟宾语。see 看见 (vt.) +宾语 I can see a boy.
2.不及物动词:字典里词后标有vi. 的就是不及物动词。不及物动词后不能直接跟有动作的对象(即宾语)。若要跟宾语,必须先在其后添加上某个介词,如to,of ,at后方可跟上宾语。
具体每个动词后究竟加什么介词就得背动词短语了,如listen to,look at…..
3. 宾语(动作的对象):是名词或代词,或相当于名词的词或短语(如动名词)。其它词不看作动作的对象呢。
4.举例:“看”
(1)see 看见 (vt.) +宾语 I can see a boy.
(2)look 看 (vi.) x宾语(即不能直接加宾语). Look! She is singing.
Look carefully! (注意:carefully 是副词,不是名词,故不作宾语哟)
(3)look at 看…….+宾语 Look at me carefully! (me是代词,作宾语了)
连系动词
连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。
表语通常由名词、形容词,或相当于名词或形容词的词或短语等充当,说明主语是什么或怎么样。
一、 连系动词的类型有:
1. "存在"类:表示存在或具有某种特征或状态.这类连系动词强调"存在"。常见的有:be(是),look(看起来),feel(摸上去),seem(似乎是),appear(似乎、显得),prove(证明是),smell(闻起来),taste(尝起来),sound(听起来)等。例如:
The story sounds true.
Those oranges taste good.
2. "持续"类:表示某种情况或状态的持续。这类连系动词强调"持续"。常见的有:remain(依然),keep(保持),stay(保持),continue(继续、仍旧),stand(处于某状况或情形)等。例如:
Why don't you put the meat in the fridge? It will stay fresh for several days.
It's already ten in the morning. The store remains closed. What's the matter?
3. "变化"类:表示由一种情况或状态变化成另一种情况或状态。这类连系动词强调"变化"后的情况或状态.常见的有:become(变成), turn(变成), grow(变得), go(变得)等。例如:
Put the fish in the fridge, or it will go bad in hot weather.
二、注意事项
1. 有些连系动词通常不用于被动语态和进行时态中。如:feel, taste等词。例如:
-Do you like the material?
-Yes, it feels very soft.
2. 一般情况下,连系动词主要跟形容词或分词作表语。例如:
Be careful when you cross this very busy street. If not, you may get run over by a car.
3. 能跟名词作表语的连系动词常见的有:be, become, appear, seem, prove, remain和turn等.注意:turn后跟(表示主语身份的)名词作表语时,不加冠词。例如:
Twenty years later, he turned teacher.
The population growth in China remains a problem.
4. 连系动词也可跟不定式(to do / to be),常见的有:appear, seem, remain, prove, look等。例如:
Having a trip abroad is certainly good for the old couple, but it remains to be seen whether they will enjoy it.
On the long journey, Peter proved to be a most interesting guide. We all had a wonderful time.
终止性动词与延续性动词
终止性动词指不会持续一段时间的动作,即动作在瞬间或短时间内完成。 例如:get arrive 这类动词不与一段时间连用
终止性动词:表示不能延续的动作,即动作发生后立即结束。如:begin,arrive, borrow, ...终止性动词的肯定式是不能持续的,所以不能和表示一段时间的状语连用,而终止性的否定式就可以和表一段时间的状语.
一、延续性动词和终止性动词的概念
英语中,动词按其动作发生的方式、动作发生过程的长短,可分为延续性动词和终止性动词。
延续性动词表示能够延续的动作,这种动作可以延续下去或产生持久影响。如:learn, work, stand, lie, know, walk, keep, have, wait, watch, sing, read, sleep, live, stay等。
终止性动词也称非延续性动词、瞬间动词或短暂性动词,表示不能延续的动作,这种动作发生后立即结束。如open, close, finish, begin, come, go, arrive, reach, get to, leave, move, borrow,buy等。
二、延续性动词的用法特征
1.延续性动词可以用于现在完成时,其完成时态可与表示"段时间"的状语连用。表示"段时间"的短语有:for two years, during the past three years, since last year, how long等。如:I have learned English since I came here.自从我来到这儿就学英语了。
2.延续性动词不能与表示短暂时间的"点时间"状语连用。如:It raind at eight yesterday morning.(误) rain为延续性动词,而at eight表示"点时间",前后显然矛盾。如果用延续性动词表示一瞬间的动作,可以借助come, begin, get等终止性动词来表示。上句可改为:It began to rain at eight yesterday morning.(正)又如:
-When did you get to know Jack?
-Two years ago.
-Then you've known each other for more than two years.
-That's right.
三、终止性动词的用法特征
1.终止性动词可用来表示某一动作完成,因此可用于现在完成时。如:
The train has arrived.火车到了。
Have you joined the computer group?你加入电脑小组了吗?
2.终止性动词表示的动作极其短暂,不能持续。因此,不可与表示一段时间的状语连用(只限肯定式)。如:
(1)他死了三年了。
误:He has died for three years.
正:He has been dead for three years.
正:He died three years ago.
正:It is three years since he died.
正:Three years has passed since he died.
(2)他来这儿五天了。
误:He has come here for five days.
正:He has been here for five days.
正:He came here five days ago.
正:It is five days since he came here.
正:Five days has passed since he came here.
(1)、(2)句中的die、come为终止性动词,不能与表示"段时间"的状语连用。那么,应如何正确表达呢?可以采用下面的四种方法:
(1)将句中终止性动词转换为相应的延续性动词,如上面两例中的第一种正确表达方式。下面列举几例:leave→be away, borrow→keep, buy→have, begin/start→be on, die→be dead, move to→live in, finish→be over, join→be in/be a member of, open sth.→keep sth. open, fall ill→be ill, get up→be up, catch a cold→have a cold。
(2)将句中表示"段时间"的状语改为表示过去确定时间的状语,如下面两例中的第二种正确表达方式。
(3)用句型"It is+段时间+since..."表达原意,如上面两例中的第三种正确表达方式。
(4)用句型"时间+has passed+since..."表达原意,如上面两例中的第四种正确表达方式。
3.终止性动词可用于现在完成时否定式中,成为可以延续的状态,因而可与表示一段时间的状语连用。如:
He hasn't left here since 1986.
I haven't heard from my father for two weeks.
4.终止性动词的否定式与until/till连用,构成"not+终止性动词+until/till ..."的句型,意为"直到……才……"。如:
You can't leave here until I arrive.直到我到了,你才能离开这里。
I will not go to bed until I finish drawing the picture tonight.今天晚上直到我画完画,我才上床睡觉。
5.终止性动词可以用于when引导的时间状语从句中,但不可以用于while引导的时间状语从句中。when表示的时间是"点时间"(从句谓语动词用终止性动词),也可以是"段时间"(从句谓语动词用延续性动词)。而while表示的是一个较长的时间或过程,从句谓语动词用延续性动词。如:
When we reached London, it was twelve o'clock. (reach为终止性动词)
Please look after my daughter while/when we are away. (be away为延续性动词短语)
6.终止性动词完成时不可与how long连用(只限于肯定式)。如:
误:How long have you come here?
正:How long have you been here?
正:When did you come here?

以上就是关于列举英语语法 ,初中英语时间状语从句归纳总结的全部内容,以及列举英语语法 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

