本文目录
虚拟语气在特殊句型中的用法
最低0.27元/天开通百度文库会员,可在文库查看完整内容>
原发布者:我是木头人970
虚拟语气一、if引导的虚拟条件句(表示与事实相反的假设):现在:If+主语+过去式/were,主语+should/would/could/might+动词原形过去:If+主语+had+过去分词,主语+should/would/could/might+have+过去分词过去式/were将来:If+主语+should+动词原形,主语+should/would/could/might+动词原形wereto+动词原形另外:有些词,如:or/otherwise(否则);without(没有);butfor(要不是……)等,表示一个隐含的条件,所用的虚拟语气与if引导的虚拟条件句结构相同注意:if引导的虚拟条件句中,谓语部分含有were/had/should,可将引导词if省略,并将were/had/should提到句首。二、wish之后接的宾语从句(表示不可能实现的愿望):过去式/were(现在)Wish+(that)had+过去分词(过去)would/could/might+动词原形(将来)三、asif/asthough常与seem/look/appear等动词连用,表示“看起来似乎……好象……”;以及ifonly表示“要是……该多好啊”所用的虚拟语气结构与wish结构相同;四、虚拟语气在名词从句中的运用:1、表示“命令”、“建议”、“要求”、“坚持”等词后所带的名词从句用虚拟语气,结构都是:Array,其中should可以省略。记忆口诀:insist2、动词 order+(that)+主语+Arrayadvise/suggest/recommend(宾语从句)require 3、名词:advice/suggestion/order/request之后

宾语从句要用虚拟语气的动词
虚拟语气分三种情况来掌握:
1、虚拟条件句。
2、名词性虚拟语气。
3、虚拟语气的其他用语。
一、虚拟条件句:
条件状语从句是非真实情况,在这种情况下要用虚拟语气。
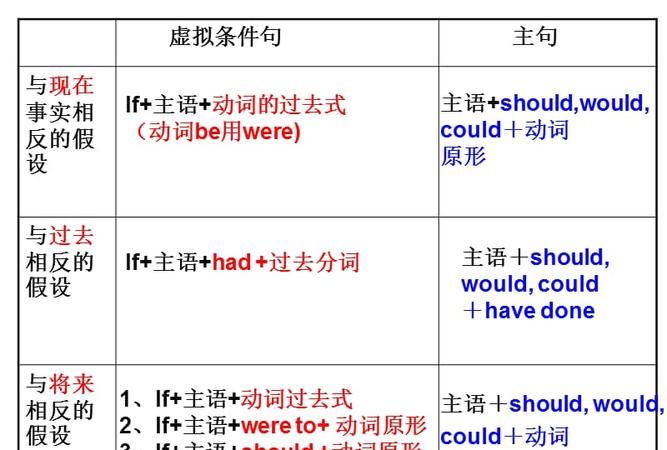
1、条件从句与现在事实不一致,其句型为:
If 主语+过去时,主语+should(could, would, 或might)+动词原形,如:
If I were you, I would study hard.
If it rained, I would not be here now.
2、条件从句与过去事实不一致,句型为:
If 主语+had+过去分词,主语+should(could, would, 或might)+have+过去分词,如:
If the doctor had come last night, the boy would have saved.
If I had not studied hard, I would have failed in the exam last term.
3、条件从句与将来事实不一致,句型为:
+do,主语+should(could…)+ 原形 do
过去时(与现在事实条件句一样)。
If it should rain tomorrow, we would stay at home.
If I were to go to the moon one day, I could see it with my own eyes.
If you missed the film to night, you would feel sorry.
注意问题:
1、If条件句中绝对不可出现“would”。
2、根据句中的时间状语,有时可能出现“混合虚拟”的情况,即主句可能是现在的情况,条件句也许是发生在过去的情况,但都是遵守上述句型。
3、在条件句中如果出现were, had, should可省去if,将主语与这些词倒装,例如:
Had the doctor come last night, the boy would have saved.
Were I to go to the moon one day, I would see it with my own eyes.
Should it rain tomorrow, we would stay at home.
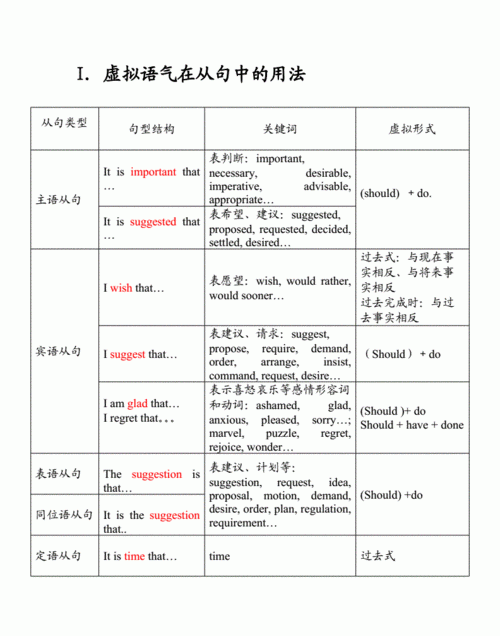
二、名词性虚拟语气:
在表示命令、建议要求、惊叹时的名词性从句中需用虚拟语气,基本句型:
主语+(should)+动词原形,如:
Mother insisted that John go to bed at 9 o’clock.(宾语从句)
We suggested that the meeting should not be held.
It was required that the crops should be harvested at once.(主语从句)
The suggestion that he be invited was rejected.(同位语从句)
That is their demand that their wages be increased.(表语从句)
注意:在这种句子中绝不出现“would”“must”“could”等。
三、虚拟语气在一些特殊词中的使用或含蓄条件句:
1、wish后的宾语从句:
与现在愿望不一致 主语+过去时;
与过去愿望不一致 主语+had+过去分词;
与未来愿望不一致 主语+would(could)+原形。
I wish I were you.
I wish I had visited the white House when I was in the states.
I wish I met you tomorrow at the party.
2、It’s time句型:当It’s time后用that从句时应该为:
主语+should+原形 或 主语+过去时,例如:
It’s time that you went to school. 或
It’s time that you should go to school.
3、If only引起的感叹句相当于“How I wish+宾语从句”
If only he could come! 他要能来就好了。
If only I had known the answer! 我要早知答案就好了。
4、would rather, as if(though)引导的句子也需使用虚拟,表示过去的情况用过去完成时,表示现在与将来的情况用过去时,如:
I’d rather you posted the letter right away.
I’d rather you had returned the book yesterday.
She loves the children as if they were hers.
Alan talked about Rome as if he had been there.
5、without, but, but for, otherwise引起的短语或句子常暗含着含蓄条件。
Without you, I would never know him.
But for your cooperation, we wouldn’t have done the work so well.
But that she was afraid, she would have said no.
I would be most glad to help you, but I’ am busy now.
I would have come to the party yesterday, but I was working.
I am busy now, otherwise I would do you the favor!
虚拟语气有哪几种句型英语
虚拟语气
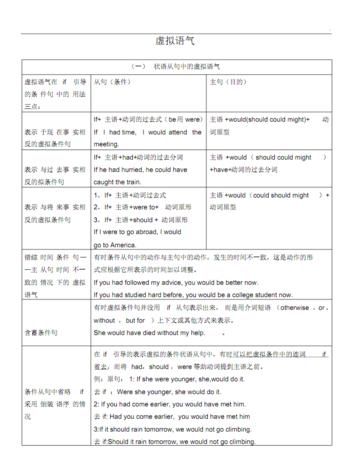
虚拟语气(Subjunctive Mood)这一语法项目是各类英语考试中心测试的重点之一.虚拟语气是一种特殊的动词形式,用来表示说话人所说的话并不是事实,而是一种假设、愿望、怀疑或推测.判断是真实条件句还是非真实条件句.只有在非真实条件句中才使用虚拟语气.通过句子意思,看假设的条件是否能够实现,能够实现是真实条件句,不能使用虚拟语气;假设的条件不能实现则是非真实条件句,要用虚拟语气.判断这个假设是与哪个事实相反.通常有三种情况:①与过去事实相反.②与现在事实相反.③与将来事实可能相反
I: 最基本的虚拟语气句型:
1. 虚拟现在时表示与现在事实相反的假设,其if 从句的谓语形式用动词的过
去式(be 一般用were),主句用would/ should/ could/ might +动词原形.
If places were a like, there would be little need for geographers.
如果各个地方都一样,就不需要地理学家了.
2. 虚拟过去时是表示与过去事实相反的假设,if 从句的谓语形式用过去完成时
即had+过去分词,主句用would / should / could / might + have +过去分词.
If he had known your address yesterday, he would have telephoned you.
3. 虚拟将来时是表示对将来实现的可能性很小的或不确定的假设.If从句的谓
语形式用一般过去式或用were to / should +动词原形,主句用would / should
/could/ might +动词原形.
If he were to leave today, he would get there by Friday
4. 省略if 采用倒装语序的条件句.
有时可以把含有助动词、情态动词、be或have的虚拟条件句中的连词if 省去,而将had , should, were 等 词
提到主语之前,即用倒装结构.
Had he worked harder, he would have got through the exams.
Were he to leave today, he would get there by Friday.
Were I in your place, I wouldn’t do that
5. 有时虚拟条件句并没来if 从句表示出来,而是用介词短语(otherwise, or, without, but for)、上下文或其它方 式来表示.
We didn't know his telephone number; otherwise we would have telephoned him.
Without you help, I wouldn’t have achieved so much.
But for your help, I would not have succeeded.
II: 虚拟语气在从句中用should的情况:
1. 在建议,要求,命令,想法后的动词后的从句里, 用should + 动词原形, should 可以省略. 如 advise, agree, command, decide, demand, determine, grant, indicate, insist, order, prefer, propose, request, require, stipulate, suggest, urge, vote. 常考到的是: suggest, advise, demand, require, propose, insist, order, request.
His doctor suggested that he (should) take short leave of absence.
The author proposed that TV (should) be turned off at least one hour every day.
2. 在建议,要求,命令,想法后的名词后的从句里, 用should + 动词原形, should可以省略. 如 advice, agreement, command, decision, decree, demand, determination, indication, insistence, order, preference, proposal, request, requirement, stipulation etc.
It was Bill’s suggestion that everyone (should) have a map.
His suggestion was that everyone (should) have a map.
He gave us a suggestion that everyone (should) have a map.
3. 在It is/was +形容词后的that 从句中用should的结构, should 可以省略. 这类形容词常见的有: advisable, anxious, compulsory, crucial, desirable, eager, essential, fitting, imperative(绝对必要), impossible, improper, important, natural, necessary, obligatory, possible, preferable, probable, recommended, urgent, vital etc.
It‘s natural that she (should) do so.
It is essential that we (should) tell her the news.
4. 在 lest 和 for fear that( 以免) , in case (以防)从句中用should, should 可以省略.
She walked quietly lest she (should) wake up her roommates.
Have your gun ready in case we should need it.
III: wish 后的 that 从句中:
1. 表示现在或将来的愿望,从句中过去式.
I wish I knew his address.
I wish I were young.
2. 表示过去没有实现或不可能实现的愿望, 从句用过去完成式或would, could, might + have + 过去分词.
I wish you had written to him.
I wish I could have slept longer this morning, but I had to get up and come to class.
3. 如果将wish改成wished, 其后that 从句中的动词形式不变.
4. 如果that 从句中用would , 一般表示 对现状不满或希望未来有所改变 或请求
I wish he would answer my letter.
I wish prices would come down.
I wish you would help me.
I wish you would stop asking silly questions.
IV: 在 It’s about/ high/ first(second, third etc) time 后的that 从句中, 用过去式. 表示 “该是做什么的时候了”
It is about time you were in bed.
It is high time we left.
It is the first time I came here.
V: 在would rather, would sooner, would just as soon 后的that从句中, 用过去式或过去完成式, 表示”宁愿做什么”
I would rather he came tomorrow than today.
John would rather that she had not gone to the party yesterday evening.
VI: 在if only 感叹句中, 谓语动词与wish宾语从句的虚拟形式相同.
If only he didn’t drive so fast! (现在)
If only she had asked someone’s advice.(过去)
If only the rain would stop.(将来)
VII: 在as if / as though 从句中, 表示和现在事实相反或对现在情况有所怀疑, 用过去式; 表示过去想象中的动作或情况, 用过去完成式.
He speaks as if he were on the spot.
She spoke to me as if I were deaf.
This device operated as though it had been repaired.
注: 1. 在 as if / as though 句中, 如果有可能成为事实, 用陈述语气.
He looks as if he is going to be ill.
2. 在 insist 后的从句中, 如果是坚持自己, 用陈述语气, 坚持别人做什么事情, 用虚拟语气.
she insists that she is right.
she insisted that I should finish the work at once.
虚拟语气能在哪几种从句中使用呢
主句都一样,只是从句有区别。请看:与现在事实相反:从句动词用:did/were; 主句动词用:would do/ be 与将来事实相反:从句动词用:should(were to) do /be 主句动词用:would do/ be 用在以if引导的非真实条件状语从句中,从句和主句皆须用虚拟语气。从句和主句动词的搭配形式,通常为:与现在事实相反:从句动词用:did/were; 主句动词用:would do/ be 与过去事实相反:从句动词用:had done/been 主句动词用:would have done/ been 与将来事实相反:从句动词用:should(were to) do /be 主句动词用:would do/ be 三种基本形态(这是基础,建议牢记下面的例句,争取能脱口而出) 与现在事实相反:If I had enough money, I would buy a book. 与过去事实相反:If I had had enough money, I would have bought a book. 与将来事实相反:If I were to have enough money, I would buy a book. If I should have enough money, I would buy a book.
以上就是关于从句用虚拟语气的句型有哪些 ,虚拟语气在特殊句型中的用法的全部内容,以及从句用虚拟语气的句型有哪些 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
