谈到怎么判断主句和从句before 想必大家都想知道。那么,就有必要说一下了,英语中主句和从句的语态怎么判断,详细一点,最好举例说明和如何区分when.while.as.before after.as soon as until时间状语从句的主句和从句怎么判断主句和从句before 的内容,让您更清楚知道如何判断一个句子中的从句和主句,来深入了解。
怎么判断主句和从句before :before 和after 在句里面 看主句从句
Before是在……之前,after是在……之后.
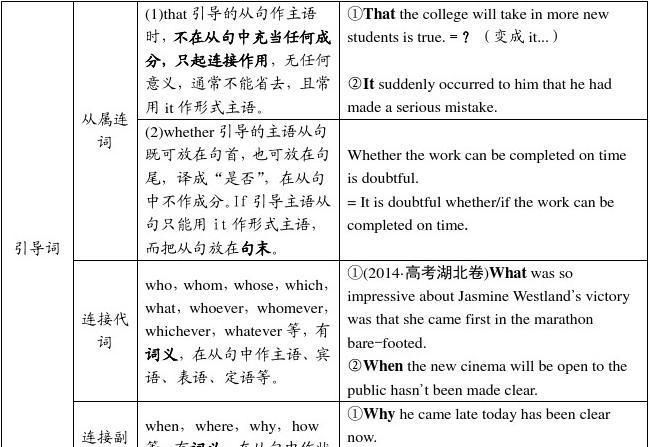
怎么判断主句和从句before :怎样区分主句和从句
英语中六大从句用法总结1.主语从句 1)主语从句可直接位于主语的位置,如果从句较长,谓语又较短,可用it作形式主语,而将从句放在句末。常见的句型有: *It is a fact\a pity\a question\good news that... *It seems\appears\happened\has turned out that... *It is clear\important\likely\possible that... *It is said\reported\estimated\has been proved that... It is said that comic books create a connection between people of the same generation. It seems that the performance is very useful. 2)what引导的主语从句表示“...的东西时”,一般不用it作形式主语。 What we lack is experience. 3)what,who,when,why,whether等词含有各自的疑问意义,但它们引导的主语从句,都用陈述语序。 How the plan is to be carried out should be discussed again. I did know why I felt like crying. 2.宾语从句 1)宾语从句可位于及物动词、介词和某些形容词后。连词that常可省略。介词后一般接疑问词引导的宾语从句。in that(因为),except that(除了),but that(只是)已构成固定搭配,其他介词后一般不接that引导的宾语从句。 *I promised that I would change the situation. *All this is different from what American young people would say about friendship. *He is certain that watching so much television is not good for children. *This article is well-written except that it is a bit too long. 2)宾语从句后如有宾补,要用形式宾语it来代替,而把宾语从句移至宾补之后。 He has made it clear that he would not change his mind. 3)在think,believe,suppose,expect等动词后的宾语从句中,如果谓语是否定的,一般将否定词移至主句谓语上,宾语从句则变成肯定形式。 He didn't think that the money was well spent. 3.表语从句 表语从句出现在结构为“主语+系动词+表语从句”的句子中。表语从句除可用that,what,when,why,whether,how等引导外,还可由because,as if(though)等引导。that常可省略。如主句主语为reason,只能用that引导表语从句,不可用because. Perhaps the most important thing to remember is that there is no one common type of life in America. The reason why so many people died there is that there were not enough food supplies. It looks as if successful international cultural communication will make the world smaller. 4.同位语从句 同位语从句用于对前面出现的名词作进一步说明,一般用连词that引导,由于先行名词的意义不同,也可用whether,who,when,where,what,why,how等引导。常见的先行名词有fact,idea,belief,news,hope,conclusion,evidence,suggestion,order,problem,report,decision.有时由于谓语较短,将同位语从句位于谓语之后。 She finally made the decision that she would join the fashion show. I had no idea how many books I could borrow at a time. The news came that their team had won the championship. 5.定语从句 定语从句所修饰的先行词可以是名词或代词,也可以是一个句子。定语从句通常位于先行词之后,由关系代词或关系副词引导。 *限制性定语从句 限制性定语从句修饰先行词,对先行词起修饰作用,紧接先行词之后,无逗号,若省去,原句意思不完整。引导定语从句的关系代词有who,whom,whose,which,that等。who,whom,whose用于指人,whose有时也可指物,相当于of which;which用于指物;that既可指人也可指物,但只用于限制性定语从句中。关系代词除了引导定语从句,替代先行词外,还在从句中担任主语、宾语、定语等。 The computers and cables which make up the Internet are owned by people and organizations. Those who live alone or who are sick may have trouble in getting close to other people. The girl whose parents died in an accident is living with her grandmother. 1)当先行词是all,anything,everything,something,nothing等不定代词或先行词前有first,last,any,few,much,some,no,only以及形容词最高级修饰时,只能用关系代词that引导从句。 That is all that I've heard from him. He's the first person that I'm going to interview this afternoon. 2)关系代词的省略 在从句中作宾语的关系代词常可省略。关系代词紧跟介词,作介词宾语时不可用that,只可用which或whom引导从句,并且不可省略,但当介词位于宾语从句句末时,作为介词宾语的关系代词仍可用that,也可省略。 This is one of those things with which we have to put up. This is one of those things (which\that) we have to put up with. 3)引导定语从句的关系副词有when,where,why等。关系副词在从句中作状语,意义上相当于一个“介词+which”的结构。 Even in comic books where(=in which) there are no words,the stories are fully expressed through the drawings. No one knows the reason why(=for which) he was so angry that day. 5.定语从句 *非限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句既可修饰先行词,也可修饰整个主句,起补充说明作用,与主句之间有逗号隔开,若省去,原句意思不受影响。不可用that引导非限制性定语从句。关系词不可省略。 Every object has a gravitational pull,which is rather like magnetism. *“介词+which\whom\whose”引导的定语从句 “介词+which\whom\whose”可引导限制性定语从句,也可引导非限制性定语从句,该结构中介词的选择取决于从句谓语动词的固定搭配,或先行词的习惯搭配。 This is the computer on which he spent all his savings It is written by a person with whom we are all familiar. *as引导的定语从句 as引导的定语从句主要用于“such...as”及“the same...as”的结构中,代替先行词是人或物的名词。as引导非限制性定语从句时,代替整个主句,从句可位于主句之前、之后或中间。 These are not such problems as can be easily solved.(as代替先行词problems) As is mentioned above,no single company or group can control what happens on the Internet.(as代替主语) 6.状语从句 *时间状语从句 引导时间状语从句的从属连词和词组有: 1)when,whenever,while,as,after,before,since,till,until,once等。 We have learnt quite a lot about it since we came here. 2)as soon as,hardly(scarcely)...when,no sooner...than,each(every) time,the moment,immediately(that)等。 As soon as I sent an e-mail message,I received positive responses. The moment he heard the good news,he jumped with joy. *地点状语从句 引导地点状语从句的连词是where,wherever. Wherever she went,she took her little daughter with her. *原因、结果和目的状语从句 1)引导原因状语从句的从属连词有:because,as,since,now(that),seeing that,considering that,in that等。 Considering that he is a freshman,we must say he is doing well. 2)引导结果状语从句的连词有:so...that,such...that,so that,that,so等。 Mickey Mouse is so attractive that the children are reluctant to leave. 3)引导目的状语从句的连词有:so that,in order that,for fear that,lest等,从句常使用may,might,can,could,would等情态动词。 We got up early this morning so that we could catch the first bus to the railway station. *条件和让步状语从句 1)引导条件状语从句的连词和词组有if,unless,as(so) long as,on condition that,in case,provided(providing) that,supposing等。 As long as you have the right equipment,you can use a telephone line to transmit computer data. 2)引导让步状语从句的连词和词组有though,although,whether,even though,even if,no matter what(when,how...),whatever(whenever,wherever,however....)等。though,even if等引导状语从句可转换成含有as的部分倒装结构,具有强调意义。其结构为“形容词(副词、动词、名词)+as+主语+谓语”。 No matter what you may say,I would not change my mind. Young as he is,he is quite experienced in this work.(=though he is young) Child as he is,he can speak English fluently.(=though he is a child) *方式状语从句 引导方式状语从句的连词有as,just as,as if,as though等。as if,as though引导的状语从句中,谓语动词常用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反。 The young man made the experiment just as the teacher had taught him. Everything went on as usual as if nothing had happened.
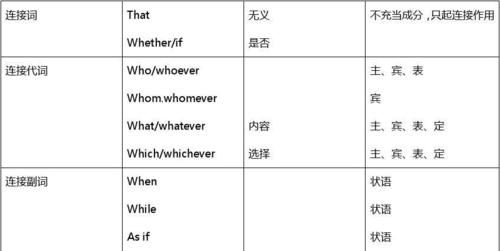
怎么判断主句和从句before :如何判断一个句子中的从句和主句
这简单,只要找到从句的关系词,就能判定。不管是限定从句还是非限定从句,关系词后就足从句部分,之前那就是主句部分。而所有的关系词引导的从句,都是主句在前的。

怎么判断主句和从句before :主句和从句怎么区分
主句是主要表达的,从句是补充说明的,如果你能看明白意思,可以从这方面入手
如果你知道是什么从句并且知道连接词,连接词在中间,前面的是主句,后面的是从句,反正从句是紧跟着连接词的。如果连接词在开头,会有逗号把主句和从句隔开,前面是从句,后面是主句。

以上就是关于怎么判断主句和从句before ,如何判断一个句子中的从句和主句的全部内容,以及怎么判断主句和从句before 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
