本文目录
什么是被动语态
被动语态,即不知道动作执行者或强调动作承受者的一种语态。英语的语态是通过动词形式的变化表现出来的。英语中有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的对象。
例如:Many people speak Chinese. 谓语:speak的动作是由主语many people来执行的。 例如:Chinese is spoken by many people. 中文Chinese是动词speak的承受者。 被例如中文常说:我被他打,这就是一种被动。但有时由于句子结构上的需要也要用被动,例如It is not unusual for workers in that region to be paid more than a month it 在句中作形式主语。而不定式to be paid more than a month是句子的逻辑主语。结合选项全句的意思是:“那个地方的工人一个多月后才得到工资是常有的事”。
主动语态变为被动的几个特殊情况
① 有些动词在主动结构中,后面接不带to的不定式,但如果改为被动,则需把省略 的to加上,这类动词有 [let, make, have,help]和感官动词[feel,see,hear,watch,look at,listen to],如:The boss made my grandfather work 10hours a day.改成My grandfather was made to work for 10 hours a day. ② 含有宾语从句的主动结构变为被动,通常用it作为被动结构的先行主语,从句放在句子后面/也可采用另一种形式,这类动词有:know, say, believe, find, think, report等 ③ 不是所有的主动句都可以变换成被动句,更不是所有的被动句都可以自由变换成主动句。虽然语法原则上允许主动和被动句的互相转换,但有的句子转换后会变成不通顺或不地道的英语句子。因此,在某些题目里,这也成为判断应该用主动还是用被动的依据。 例:At 5:05 p.m. on Saturday 19th July , there was an accident at the junction of the Main Street and Panda Road when a boy was knocked down off his bicycle by a delivery van. The boy was sent to St. Maria Hospital where he was treated for shock and a broken arm. 在这段文章里,a boy was knocked down off his bicycle by a delivery van这句被动句强调出读到文章的人最关心的事故的受害者。The boy was sent to St. Maria Hospital这句话则说明了孩子被送到医院的事实,至于是由谁(某个过路人?或肇事司机?)送的不重要。he was treated for shock and a broken arm这句被动句无须说出treat这个动作的发出者,因为在医院,伤病员自然由医务人员处理,无须罗嗦。这样,这段文章就重点突出,条理清楚了。 ④ 有些动词可以有两个宾语,在用于被动结构时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一个宾语仍然保留在谓语后面。多是把间接宾语变为主语。这样句子自然些。直接宾语变为主语时,间接宾语要变为某个介词的宾语,介词to可以省略。如His father left him this house.改为This house was left (to) him by his father. ⑤ 有些动词虽为及物,但宾语并非是动作承受者,不能转换,这些动词有have, hold(容纳),suit, fit, lack, become(适合)contain, cost, last, mean, suffice(足够)等。 ⑥ 当直接宾语为反身代词、相互代词或宾语前有指代主语的物主代词时不用被动,如I shook my head.我摇摇头。 ⑦ 当宾语为同源宾语(与主句指同一人),动名词,动词不定式或一个从句时不用被动。如John enjoyed seeing the fil,. ⑧ 在一些固定说法中,有些名词和动词结合的固定说法,不能改We Chinese always keep our word. ⑨ 某些从不及物动词转化来的及物动词,直接宾语在表示动作的方式或效果时,这些动词在意思上起状语的作用,没有被动The girl kiss

什么是被动语态
被动语态
谓语动词中有两种语态:一种叫主动语态,一种叫被动语态.
主动就是主语是动作的执行者;被动就是主语是动作的承受者(物)
不及动词只有主动,没有被动;
被动语态构成:be + vt-ed 或 be + vi-ed +prep
其中be动词是用来体现时态的,也就是通过be的变化体现时态.
比如:am/are/is + vt-ed 是一般现在时;was/were + vt-ed 是一般过去时等;
简而言之:
及物动词后面没有宾语时,就考虑用被动式

被动语态的用法及不能使用被动语态的情况
被动语态用法被动语态是怎么用的
被动语态,即不知道动作执行者或强调动作承受者的一种语态。英语的语态是通过动词形式的变化表现出来的。英语中有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的物件。
英语被动语态的构成通常是:“be+done”。但“get+done”也可以构成被动语态,用这种结构的句子侧重于动作的结果而不是动作本身。如: The man got hurt on his way home. 那个男人在回家的路上受伤了。 How did the glass get broken? 杯子怎么破了?
例如:Chinese is spoken by many people. 中文Chinese是动词speak的承受者。被例如中文常说:我被他打,这就是一种被动。但有时由于句子结构上的需要也要用被动,例如It is not unusual for workers in that region to be paid more than a month it 在句中作形式主语。而不定式to be paid more than a month是句子的逻辑主语。结合选项全句的意思是:“那个地方的工人一个多月后才得到工资是常有的事”。
被动语态用法怎么用?
A.主动语态中主语是谓语动词的发出者。宾语是谓语动词的物件。
B.被动语态中主语是谓语动词的承受者(动作的物件)。
(把主动语态改为被动语态也就是把主动句中的宾语改为被动句的主语,这是最关键的着眼点,同时谓语动词作相应的变化。)
被动语态的谓语构成: 助动词be+动词过去分词
(根据句子的主语和时态,助动词be有am, is, are, was, were,
been几个形式变化。)
什么时候要用被动语态呢?
在下列三种情况之一要用被动语态:
①不知道动作的执行者是谁,用被动语态。
②没有必要指出谁是动作的执行者,用被动语态。
③需要强调动作的承受者时,用被动语态。
在上面我们已经初步了解了被动语态的构成和主动变被动的方法。下面
我们接着学习在被动语态中要注意的问题。
①一些使役动词(let, have, make等)或感观动词(see, hear, watch,
notice等)在主动语态中后面接的动词不定式不带to,但改为被动语态时,要
补上to。如:
The boss makes the workers work 18 hours a day.
The workers are made to work 18 hours a day by the boss.
I saw him enter the house.
He was seen to enter the house by me.
The teacher let them leave the classroom after class.
They were let to leave the classroom by the teacher after class.
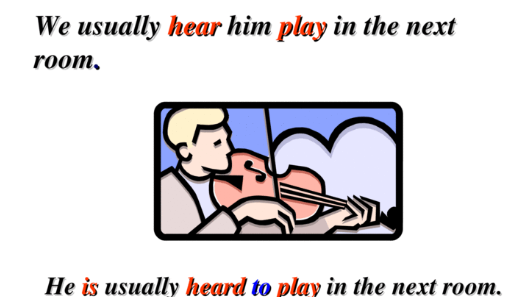
We hear her sing in the room every day.
She is heard to sing in the room every day.
[注意]当使用see/hear/watch *** doing sth时,变为被动语态时,
doing保持不变。如:
I saw him going into the shop.(主动)
He was seen going into the shop.(被动)
②含有短语的被动语态结构。
一般来说,只有及物动词才有被动语态,因为只有及物动词才有承受者。
但许多不及物动词加上副词或介词构成动词短语也相当于及物动词的用法,可以
带宾语,因而也有被动语态。动词短语主要有三种:
A 及物动词+副词 如:
turn off 、 set up 、 carry out 、 put off 、take away 、 turn on 、 hand in 、 move away 、 pass on 、 write down 、put away 、 put on 、 take down 、send away 、 try on 、 put down 、sell out 、 hold on 、 try out 、 send up 、 take off 、 wear out 、wake up 、take out 、dress up 、 give back 、 work out 、 get back 、 find out 、pick up 、give up 、 pull up 、 put up 等
B 不及物动词+介词 如:
look after talk about play with等
C.“动词+名词+介词” 构成的短语。如:
take care of、 pay attention to、make use of等动词短语是不可
分割的整体,在变被动语态时,不可丢掉构成动词短语的副词或介词。
请看下面的例子:
①They set up the factory in 2000.
The factory was set up in 2000.
②Our school will put off the School Sports meeting until December.
The School Sports meeting will be put off until December.
③People have talked about the aident .
The aident has been talked about.
④You should pay more attention to your study this year.
Your study should be paid more attention to this year.
带有介词或副词的动词短语,在改为被动语态时,不能把介词或副词
拆开。
③带有双宾语的被动结构在句中的使用。
有些动词可以带两个宾语,即指人的间宾和指物的直宾。可以将其中一
个宾语提到前面做主语,另一个留在后面。
①Her parents bought her a new puter yesterday.
She was bought a new puter yesterday.
A new puter was bought for her yesterday.
②They have given me some good advice.
I have been given some good advice.
Some good advice has been given to me.
③She will write a long letter to David Smith.
A long letter will be written to David Smith.
David Smith will be written a long letter
被动语态用法
被动语态1:英语中语态有两种:主动语态和被动语态。
语态的作用:语态是动词的一种形式,用来说明主语和谓语之间的关系。
语态的选用:如果主语是动作的执行者,谓语用主动语态。
例如:We clean the room every day.
如果主语是动作的承受者,或者说是动作的物件,谓语则是要用被动语态。
例如:The room is cleaned every day.
2:被动语态的各种形式
1) am/is/are +done
eg:I'm asked to take care of myself.
eg:Football is played all over the world.
2)has /have been done
eg:This book has been translated into many foreign languages.
eg:The prices of many goods have been cut again .
3)am/is /are being done
eg:A road is being built around the mountain.
eg:Many new houses are being built in this city.
4) was/were done
eg1:This house was built in 1958.
eg2:His leg was broken in an aident.
5) had been done
eg1:A new school had been set up by the end of last year.
eg2:When the anthem had been played the conference began.
6) was/were being done
eg1: meeting was being held when I was there.
eg2:We were being trained this time last year.
7) shall/will be done
eg1:More factories will be built in our city.
eg2:He will be taken to hospital tomorrow.
8) shall/will have been done
eg1:The project will have been pleted before July.
eg2:Your clothes shall have been made for you soon.
9) should/would be done
eg1:He told me that his new cloths would be made by his mother.
10) should/would have been done
eg1:He told me that his new clothes would have been made very soon.
3:主动形式表示被动意义
1)及物动词的不及物用法:主语通常是物,且有着某种内在的特点。句子简短,且一定有付词。
eg1:Some silks wash well.
eg2:The pen writes *** oothly.
eg3:The poem reads fluently(流利地).
eg4:The shoes wear well(很耐穿).
eg5:The paper tears easily.
2)否定句
eg1:The plays won`t act.
eg2:His novels don`t sell.
eg3:The door won`t open.
3)某些日常用语,谓语是进行时态
eg1:The dinner is cooking.
eg2:The cakes are baking(烘烤).
eg3:The book is printing.
eg4:He paid all that was owing(欠的钱他都还了).
4)谓语是不及物动词或连系动词。
eg1:The flowers look beautiful.
eg2:what he said sounds reasonable.
eg3:The roses *** ell sweet.
eg4:The medicine tastes bitter.
eg5:The cloth feels soft.
eg6:The door blew open.
eg7:The road measures 50 feet across.
eg8:Sheep feed chiefly on grass.
被动语态的基本用法
一. 何时使用被动语态
1. 不知道谁是动作的执行者或没有必要
如:Paper is made from wood.
The house is quite old. It was built in 1950.
He was wounded in the fight.
2. 需要强调动作的承受者时
如:Calwlator can't be used in the maths exam.
Books and newspapers in the reading room mustn't be taken away.
He was awarded first prize in that contest.
3为了使语气婉转,避扩音及自己或对方而使用被动语态,或由于修饰的需要,使用被动语态,使句子得以更好的安排.
如:The construction of the new lab must be pleted by the end of next
month.
Electricity is used to run machines.
二. 被动语态的构成
1. be+done 可以是被动语态,也可以是系表结构形式.被动语态中,done可以带by短语,而系表结构中done相当于adj. 不带
by短语.
如:The question is settled. (系表结构)
Such questions are settled by us. (被动语态)
The position is well written. (系表结构)
The position is written with great care . (被动语态)
The job was well done. (系表结构)
The job was well done by a skilled worker. (被动语态)
2. 许多verbs(broken, interested, shut, worried),
既可以用做adj.也可以在被动语态结构中做过去分词.句中如果有by,通常是被动语态.
如:I was worried abeutyou all night. (表状态)
I was worried by mosquitoes all night. (表动作)
The glass was broken by Jack. (表动作)
The glass is broken. (表状态)
I was frightened by his ghost story.
She was frightened at the sight of a snake.
三. 不同形式的被动语态
1. 含有直宾和间宾的主动结构,变为被动时,可将其中一个宾语变为主语,另一个不动一般是主语结构的间接宾语变为被动的主语.
如:He showed me his pictures.
I was shown his pictures by him.
His pictures were shown to me by him.
Aunt made me a new dress.
I was made a new dress by aunt.
A new dress was made for me by aunt.
He sent me a birthday present.
I was sent a birthday present by him.
A birthday present was sent to me by him.
2含有复合宾语的主动句,宾补不变.
(1) 将宾语变为主语,宾补不变.
如:They call her XiaoLi. She is called XiaoLi.
He left the door open. The door war left open by him.
(2) make, let, have,hear, watch, see, feel, notice.
help既动词后变做宾补的不定式一般不加to,变为被动,必须加to .
如:My brother often made me do this and that when I was young.
I was often made to do this and that by my brother when I young.
I heard her move about in her room upstairs last night.
She was heard to move about in her room uptairs last night.
Did you see Jack take away the magazine?
Was Jack seen to take away the magazine?
3. 情态动词的被动语态.是由情态V+be+p.p.构成
如:They can not find him.
He can not be found.
You must pay me for this.
I must be paid for this.
He can repair your watch.
Your watch can be repaired.
4. 短语V的被动语态
一般来讲,只有及物V才有被动语态,因为只有vt才能有动作的承受者;
但有许多由不及物动词+介词及其他词类构成的短语动词,相当与及物动词,可以有宾语.因而可以有被动语态,但应注意短语V是一个不可分割的整体.变被动时,不可丢掉构成短语的prep或adv.这样的短语有:look
after, listen to, look at, pay attention to, take care of, look forward to, make
ues of,etc.
如:They had put out the fire before the fire--brigade arrived.
The fire had been put out before the fire-brigade arrived.
They will set up a new public school here.
A new public school will be set up here.
5. 有些动词用主动形式表被动含义..
如:The goods sells well. The door can't open.
6.有些词如want,need,require和 be worth后面,v-ing形式为主动,意义为被动.
如:The room needs/wants/requires cleaning.
The book is worth reading.
7.主动语态中的宾语是从句,变成被动时使用形式替代词it.
如:We know that Britain is an island country.
It's known that Britain is an island country.
The teacher said that this book has been translated into several
languages
It's said that this book has been franslated into several languages
8. 宾语为反身代词,相互代词及虚词it时,不用被动,只用主动.
如:I will do it myself. The man introduced himself as Mr. Wang.
9. 谓语动词是以下时,无被动.
happen, belong to, suit, fit(适合), have, let, join, fall,
last(延长),cost(花费)
break out(爆发)appear, burst out(迸发),hold(容纳),lack(缺乏),agree with(同意).
10. 据说类动词:say,consider, think, report, know, believe, suggest, understand,
hope, etc.
如:It is said that… There is said to be… Sth./Sb. is said to…
11.主动形式表被动
① 感官动词:sound,taste, *** ell,fell,look,seem等主语是物时;
② 一些vi主动形式表被动含义open, close, shut, read, write, translate, wash, clean, lock,
sell, wear, cut, cook, eat, weigh, drink, pay, draw, etc.
③不定式to blame,to let(出租)作表语时,主动形式表被动含义
④表(sth)需要的need ,want,require等后的动名词用主动形式表被动含义
⑤be worth后的动名词主动形式表被动含义
被动语态怎么用?
什么时候用被动语态:
不想让听者知道这个动作的执行者
The book was takne away.
及物动词没有宾语
He was seen last night by me.
被动语态结构:
be+及物动词的过去分词(通过be动词的变化体现时态)
英语被动语态和中文被动语态是怎么形成的?
中文和英文都有主动语态、被动语态的语法。
比如你的题目中三个句子,1、3是被动态,2是主动态。中文中的被动语态不一定需要必须说出“被”字,主要看句子结构,放在句子前面的主语结构是动作的实施物件,就是被动语态。
你的问题补充中,“你吃了吗”是省略了“饭”这个实施物件,改成被动语态的时候,不能省略这个物件,所以要改成“饭吃了吗”。还有一个,“病被治好了吗”实际上也是省略了实施主体的,就是治病的“医生”,所以改成主动语态的时候不能省略这个主体,要改成“医生治好你的病了吗”。
所以,主动、被动语态,最主要的就是要看我们强调的是哪个方面,如果强调的是动作的实施主体,就用主动语态,于是实施的物件就无关紧要了;如果强调的是动作实施的物件,就用被动语态,这时实施的主体就可有可无了。
主动语态指主语是谓语动作的使动方。也就是说谓语的动作源自主语,而施加于宾语。相反,被动语态中,主语是谓语动作的受动方,如果有宾语的,宾语往往是谓语动作的使动方。
在语法机构上,主动语态和被动语态的区别主要在于,主动语态直接使用动词原形作为谓语,然后再在该动词原形的基础上施加时态和其他语法;而被动语态则使用系词+动词的过去分词作为谓语,各种时态和其他语法也施加在系词上。
举例:
主动:Thesnowslidekilledhim.
被动:Hewaskilledbythesnowslide.
意义均为:他死于雪崩。
英语中的被动语态使用得比汉语要多,要普遍,许多课本乃至实际应用中都常常涉及到这个问题。一般说来,当强调动作承受者,不必说出执行者或含糊不清的执行者时,多用被动式。须注意的是,许多地方与汉语不同。注意那些汉语中没有"被……"的意思,英语却用被动态。还要注意,英语的被动态往往由"by"引出,而有用介词"by"的短语往往又不是被动态,而是系表结构。还有些待殊现象,如…knowntoman(人类......所知),onfoot步行(美国人有时用byfoot),incarraige(乘四轮马车)等等。还有假主动,真被动的十几个常用词的用法,以及soheavytocarry而不用soheavytobecarried等习惯用法。有关这类情况,做到心中有数对全面掌握被动态,准确无误地解答习题非常关键,被动态必须涉及的是动词的各种时态变化的问题。英语的时态本来很复杂,怎样记住各自的被动形式呢?首先要明确"将来进行无被动,现在完成进行
同"。这两种时态无被动形式。
另外,不及物动词带有同源宾语的动词,反身代词的动词和系动词都无被动形式。即便如此,还有不定式,动名词,分词,以及它们的复合结构)的被动态,再加上情态动词,助动词以及它们的疑问式和否定式从中掺杂,真是令人头痛,眼花缭乱。下面口诀就以动词do为例,即dodid过去式done过去分词,以口诀形式总结各种时态的被动态,一定对你有所启示。
被动语态(一般现在时)
主动语态变被动语态时,主动语态句中的宾语变成被动语态句中的主语,主动语态句中的主语成为被动语态句中的动作的发出者。
《被动语态的口诀》
一般现、过用bedone,be有人称、时、数变。
完成时态havedone,被动将been加中间。
一般将来shall(will)do,被动变do为bedone。
将来进行无被动,shall(will)bedoing,
现在完成进行同,have(has)beendoing。
现、过进行bedoing,被动be加beingdone。
情、助、有、是妥安排,一律随新主语变。
否定助后加not,疑问一助置主前。
主语恰是疑问词,直陈语序主在前。
一般情助加bedone,双宾多将间宾变。
复合宾语宾变主,宾补、主补相应变。
特别注意:不用被动语态的情况:
1)不及物动词或动词短语无被动语态:
appear,diedisappear,end(vi.结束),fail,happen,last,lie,remain,sit,spread,stand
breakout,etrue,fallasleep,keepsilence,loseheart,takeplace.
Afterthefire,verylittleremainedofmyhouse.
比较:rise,fall,happen是不及物动词;raise,seat是及物动词。
(错)Thepriceha *** eenrisen.
(对)Thepricehasrisen.
(错)Theaidenashappenedlaseek.
(对)Theaidenthappenedlaseek.
(错)Thepricehasraised.
(对)Thepriceha *** eenraised.
(错)Pleaseseat.
(对)Pleasebeseated.
要想正确地使用被动语态,就须注意哪些动词是及物的,哪些是不及物的。特别是一词多义的动词往往有两种用法。解决这一问题唯有在学习过程中多留意积累。
2)不能用于被动语态的及物动词或动词短语:
fit,have,hold,marry,own,wish,cost,notice,watchagreewith,arriveat/in,shakehandswith,sueedin,sufferfrom,happento,takepartin,walkinto,belongto
Thiskeyjustfitsthelock.
Yourstoryagreeswithwhathadalreadybeenheard.
3)系动词无被动语态:
appear,bebee,fall,feel,get,grow,keep,look,remain,seem, *** ell,sound,stay,taste,turn
Itsoundsgood.
4)带同源宾语的及物动词,反身代词,相互代词,不能用于被动语态:
die,death,dream,live,life
Shedreamedabaddreamlastnight.
5)当宾语是不定式时,很少用于被动语态。
(对)Shelikestoswim.
(错)Toswimislikedbyher.PS:
编辑本段有些动词可以带双宾语
在用于被动结构时,主动结构中的间接宾语变为主语时,直接宾语仍然保留在谓语后面;直接宾语变为主语时,直接宾语前通常加上介词for/to
Hewasaskedanumberofquestionsatthepressconference.在记者招待会上人们问了他很多问题
Theyaretaughtalotofthingsinthekindergartens.他们在幼儿园被教给很多东西。
AnewMP4wasgiventohima *** irthdaypresent/gift.作为生日礼物他收到了一个新MP4。
怎样把主动语态改成被动语态?
把主动语态改为被动语态非常简单,可以遵循以下几个步骤:
1.先找出谓语动词;
2.再找出谓语动词后的宾语;
3.把宾语用作被动语态中的主语;
4.注意人称、时态和数的变化。
be lost用法.被动语态是什么?
在这里lost当作丢失的,遗失的 解释,形容词,已经不再具有动词的含义,当lose后面跟有宾语时,可改为被动语态,如:he lost his wallet yesterday his wallet was lost by him yesterdat
英语被动语态用法
一、语态概述
英语的语态是通过动词形式的变化表现出来的。英语中有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。
主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。巧记为:主动、主动、主去动。
例如:Many people speak English.
谓语:speak的动作是由主语many people来执行的。
被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的物件。巧记为:被动、被动、主被动。例如:English is spoken by many people.主语English是动词speak的承受者。
主动态和被动态指的是动词形式,是词法概念;而主动句和被动句则指的是句子结构,从而是句法概念。所谓主动句就是由主动态动词(片语)作谓语动词的句子,而被动句则是由被动态动词(片语)作谓语动词的句子。
例如:He opened the door.他开了门。(主动句)
The door was opened.门被开了。(被动句)
二、被动语态的构成
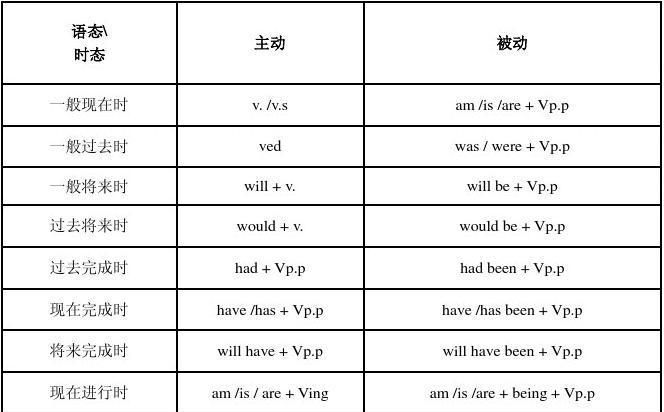
被动语态由“助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。人称、数和时态的变化是通过be的变化表现出来的。现以teach为例说明被动语态在各种时态中的构成。
一般现在时:am/is/are+taught
一般过去时:was/were+taught
一般将来时:will/shall be+taught
现在进行时:am/is/are being+taught
过去进行时:have/has been+taught
现在完成时:have/has been+taught
歌诀是:被动语态be字变,过去分词跟后面。
三、被动语态的用法
(1)不知道或没有必要说明动作的执行者是谁。
例如:
Some new puters were stolen last night.
一些新电脑在昨晚被盗了。(不知道电脑是谁偷的)
This book was published in 1981.这本书出版于1981年。
(2)强调动作的承受者,而不强调动作的执行者。
例如:the window was broken by Mike.窗户是迈克打破的。
This book was written by him.这本书是他写的。
Eight hours per day for sleep must be guaranteed.每天8小时睡眠必须得到保证。
歌诀:谁做的动作不知道,说出谁做的没有必要;
动作承受者需强调,被动语态运用到。
四、主动语态变被动语态的方法
(1)把主动语态的宾语变为被动语态的主语。
(2)把谓语变成被动结构(be+过去分词)
(根据被动语态句子里的主语的人称和数,以及原来主动语态句子中动词的时态来决定be的形式)。
(3)把主动语态中的主语放在介词by之后作宾语,将主格改为宾格。例如:
All the people laughed at him.
He was laughed at by all people.
They make the bikes in the factory.
The bikes are made?by them?in the factory.
歌诀是:宾变主,主变宾,by短语后面跟。
谓语动词变被动,be后“过分”来使用。
五、含有情态动词的被动语态
含有情态动词的主动句变成被动句时,由“情态动词+be+过去分词”构成,原来带to的情态动词变成被动语态后“to”仍要保留。
歌诀是:情态动词变动,情态加be加“过分”,原来带to要保留。例如:
We can repair this watch in o days.
This watch can be repaired in o days.
You ought to take it away.
It ought to be taken away.
They should do it at once.
It should be done at once.
什么是被动语态
主动语态与被动语态的区别:
1、在主动语态中,主语后面接人(be +动词原型),被动语态(be+动词过去分词),。
主动语态:We use electricity to runmachines. 我们用电力来开动机器。
被动语态:Electricity is used to run machines.电力被我们用来开动机器。
2、在主动语态中,主语是谓语动词的使动方。在被动语态中,主语是谓语动词的受动方。
主动语态:Bell invented the telephone in1876.贝尔于1876年发明了电话。
被动语态:The telephone was invented byBell in1876.电话是贝尔于1876年发明的。
3、在语法结构上,主动语态和被动语态的区别主要在于,主动语态直接使用动词原形作为谓语,然后再在该动词原形的基础上施加时态和其他语法;而被动语态则使用系词+动词的过去分词作为谓语,各种时态和其他语法也施加在系词上。
主动语态:The snowslide killed him. 雪崩害死了他。
被动语态:He was killed by the snowslide.他死于雪崩。
以上就是关于被动语态是怎样的,什么是被动语态的全部内容,以及被动语态是怎样的 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
