本文目录
虚拟语气语法总结框图
英语虚拟语气语法总结如下:
1、虚拟语气是说话者用来表示一种假想,或者难以达到的情形,而非客观存在的事实。
2、虚式语气在条件句中的使用:条件句有真实条件句和虚拟条件句。当主句不需要虚拟语气时,真实条件句所表示的假设是可能的,而虚拟条件句则表示与事实相反或不太可能发生的假设,此时使用虚拟语气。
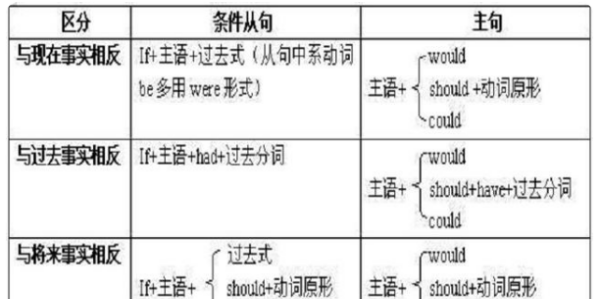
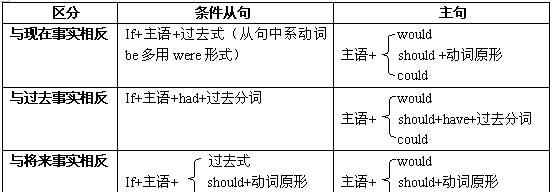
3、与过去事实相反,条件从句的谓语用过去完成时(had+过去分词),主句谓语用 should (would, could, might)+ have+过去分词。
使用虚拟语气的常用结构或句子:
1、 wish和 hope接宾语从句的区别在于: hope表示一般可实现的希望;宾语从句用陈述语气。wish表示难以或不可能实现的希望,宾语从句使用虚拟语气。
2、 if only同 I wish一样,用于表示与事实相反的愿望, wish后的虚拟语气与 wish后所接时态相同。
3、 I wouldrather句用虚拟语气仅分现在和过去。
当 would rather、 would sooner、 would just as soon之后的 that从句中,句子谓语习惯上要使用虚拟语气,表示"想做什么"。
英语虚拟语气语法总结表格
虚拟语气是什么
在英语中,虚拟语气表示说话人的主观愿望、猜疑、建议或与事实不符的假设等,而不表示客观存在的事实。如:
If I were a bird,I would be able to fly in the air.
如果我是一只小鸟,我就能在空中飞行。
虚拟语气英语语法
虚拟语气是由句中的谓语动词的特殊形式表示出来的。
1、主语从句中的虚拟语气主要取决于某些形容词和过去分词,用来表示建议、命令、要求、惊异和失望等。其形式为:(should)+动词原形。
2、表语从句和同位语从句中的虚拟语气在表示建议、命令、主张、目的和愿望等名词后面的表语从句和同位语从句中谓语动词要求使用虚拟语气。其形式为:(should)+动词原形。
3、宾语从句的动词后所接宾语从句中的谓语动词要求用虚拟语气,用来表示建议、命令和要求等。其形式为:(should)+动词原形。
以上就是英语虚拟语气的语法知识点。在表示假想的虚假的、与事实相反的或难以实现的情况时用虚拟语气,表示主观愿望或某种强烈情感时,也可以用虚拟语气。
虚拟语气的全面总结怎么写
虚 拟 语 气 语气 (mood)是一种动词形式,用以表示说话者的意图或态度。英语中的语气有三种:陈述语气、祈使语气和虚拟语气。
直陈语气(indicative mood),表示所说的话是事实。
祈使语气 (imperative mood),表示所说的话是请求或命令。
虚拟语气(subjunctive mood),表示说的话不是事实,或者是不可能发生的情况,而是一种愿望、建议或与事实相反的假设等。
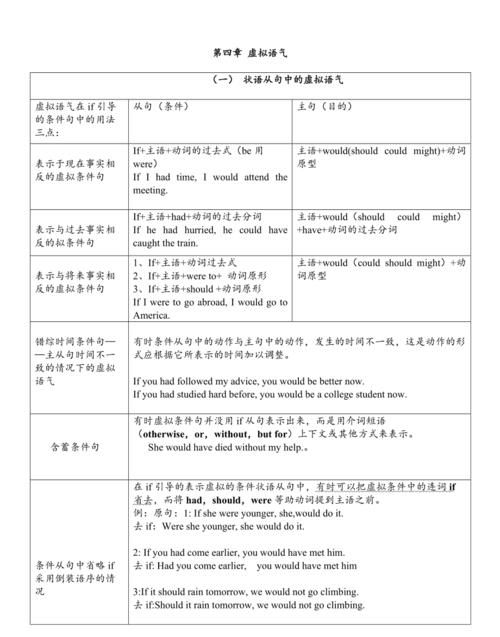
一. 虚拟语气在条件句中的应用
学习虚拟语气在条件句中的用法之前我们必须清楚条件句的种类:条件句有真实条件句与非真实条件句(或称虚拟条件句)两种。真实条件句所表的假设是可能发生或实现的,句中的条件从句与结果主句都用陈述语气。
如:
If it doesn't rain tomorrow, I will go for a picnic. 假若明天不下雨,我就去野餐。
Oil floats if you pour it on water. 你如把油倒在水里,油就浮起来。
虚拟条件句所表的假设则是不可能或不大可能发生或实现的,句中的条件从句与结果主句皆须用虚拟语气。 条件从句主句与现在事实相反 If 主语 +动词过去式(be的过去式用were)should (would, might, could)+动词原形 与过去事实相反 If 主语 +had+过去分词should ( would, might, could)+ have +过去分词 与将来事实可能相反 If 主语 +动词过去式(be的过去式用were); should+动词原形;were to+动词原形should (would, might, could)+动词原形
1. 与现在事实相反的虚拟条件句,条件从句的谓语用动词的过去式 (be的过去式用were), 主句的谓语用should (would, might, could)+动词原形。
如:
If it were not raining, we should go for a picnic.如果现在不下雨的话,我们就出去野餐了。
(事实是:天在下雨,我们不能出去野餐。表示愿望。)
If he came here, he might be able to help you. 如果他来这,他就能够帮助你了。
(事实是:他没来这,他不可能帮助你。表示对他的良好印象。)
2. 与过去事实相反的虚拟条件句,条件从句的谓语用had+过去分词,主句的谓语用should ( would, might, could)+ have +过去分词。
如:
She would have gone to the party if she had been invited.
要是当初她被邀请的话,她就会去参加这次聚会了。
(事实是:当时没有人邀请她,因此,她没有来参加聚会。表示后悔。)
If she hadn't called me, I would have overslept this morning.
今天早上,她要是不叫我的话,我就会睡过头了。
(事实是:她今天早上叫我了,我没有睡过头。表示感激。)
3. 与将来事实可能相反的虚拟条件句,条件从句的谓语用动词的过去式(be的过去式用were); should+动词原形;were to+动词原形,主句用should (would, might, could)+动词原形。
如:
If I were to be twenty years old next year, I would take the course of French.
明年我要是二十岁,我就会学法语。
(事实是:我现在已经老了,明年我学不了法语了。)
If it should fail, I would try again.要是失败了,我会再试一次。
(事实是:有可能失败,可我会再试。表示未知。)
虚拟过去式有时并不表示“不大可能实现的假设”,而是表示一种希望或不希望发生的动作。
如:
If we caught the early train, we'd get there by lunch time.
假如我们赶上早班火车,到午饭时间我们就会到达那里了。(表希望)
If we missed the train, we should have to wait an hour at the station.
假如我们赶不上这班火车,我们就得在车站等一小时。(表不希望)
4. 混合型的条件句
当条件从句与主句所表的时间不一致时,虚拟语气的形式应作相应的调整。主句和从句的谓语动词并不相互呼应,这种条件句叫混合条件句。较多见的混合型条件句是从句用过去完成时(指过去行为),而主句用一般时(指目前状态)。
He would pass the test if he had taken my advice.如果他听了我的劝告,他现在会通过考试。
If I had spoken to him yesterday, I should know what to do now.
假如昨天我对他说了,现在我就知道该怎么办了。
You would be much better now if you had taken my advice.
假如你接受了我的意见,你现在就会好得多。
如条件从句用if I were...,主句则可用表任何时间的虚拟形式。
如:
If I were not busy, I would have come.
假如我不忙,我就会去了。(were表过去)
If I were you, I would go.
假如我是你,我会去的。(were表现在)
二. 连词if的省略
如果虚拟条件句的谓语部分有were,had和should时,可省略if,把were,had和should放到从句主语前面去,多见于书面语。
Had you not helped me, I should have failed.要是没有你的帮助,我就失败了。
Were you in my position, you would do the same. 假如你处在我的地位,你也会这样干的。
Should they attack us, we'll wipe them out completely.
假如他们进攻我们,我们就把他们彻底消灭干净。
三. 含蓄条件句
虚拟条件句中的条件从句有时不表出来,只暗含在上下文中,这种句子叫做含蓄条件句。含蓄条件句大体有三种情况。
1) 条件暗含在短语中。
如:
But for your help we couldn't have succeeded in the experiment.
如果没有你的帮助,我们的实验是不会成功的。(暗含在分词短词but for your help)
What would I have done without you? 如没有你,我会怎么办呢?(条件暗含在介词短语without you 中)
It would be easier to do it this way. 这样做会比较容易。
(条件暗含在不定式短语 to do it this way中)
This same thing, happening in wartime, amount to disaster.
同样的事,如发生在战时,就会酿成大祸。(条件暗含在分词短语happening in wartime 中)
He must have the strength of a hippopotamus, or he never could have vanquished that great beast. 他一定是力大如河马,否则他绝不会击败那只庞大的野兽。(暗含条件是连词or)
Alone, he would have been terrified. 如是单独一人,他是会感到害怕的。(暗含条件是alone)
2) 条件暗含在上下文中。
如:
You might stay here forever. 你可以永远待在这儿。(可能暗含if you wanted to)
We would have succeeded. 我们本来是会成功的。(可能暗含if we had kept trying)
Your reputation would be ruined. 你的名誉会败坏的。(可能暗含 if you should accept it)
3) 在不少情况下,虚拟式已变成习惯说法,很难找出其暗含的条件。
如:
You wouldn't know. 你不会知道。
I would like to come. 我愿意来。
四. 不用if引导的条件从句
虚拟条件句中的条件从句除用if引外,还可用when, unless, lest, suppose, as if, for fear, in case, on condition 等词语来引导。
如:
The peasants prepared to feed the city when it should be freed.
农民已准备在这座城市解放后供给粮食。
Lest you should not have heard all, I shall begin at the beginning.
我怕你没有听全,所以我再从头开始讲一遍。
Unless I were well, I wouldn't be at school. 除非我好了,否则我不会上学。
Suppose you were given a chance to study in America, would you accept?
假如给你一个到美国学习的机会,你会接受吗?(suppose 或 supposing =what if)
Supposing it were so?(=Supposing it were so,what would happen?)
要是这样的话,会怎么样呢?
He can use the bicycle on condition that he should return it tomorrow.
如果明天能还回来,他就可以借用这辆自行车。
In case I forget , please remind me of my promise 如果我忘了,请提醒我的诺言。
Susan is walking slowly ,as if she were tired. 苏珊走得很慢,就像是累了似的。
与if一样,上述词语所引导的条件从句亦可用陈述语气,表可能实现或发生的事。 虚拟语气除主要用于条件句(也就是状语从句)外,还可用于主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、定语从句等。
1. 虚拟语气在主语从句中的应用
“常用在It is (was)+形容词 / 过去分词+that引导的主语从句”的句型中的主语从句要用虚拟语气。主语从句的谓语用should+动词原形(或should+have+过去分词)或只用动词原形(尤其是美国英语)。should在此是助动词,本身并无实义,这种主语从句中的should有时有感情色彩。
It's important that we(should)work out a plan. (带有“要求”的含义)
It's better that he go at once. (带有“建议”的意思)
☆ 用于本句型的形容词并不多,常见形容词有:necessary,important,best, right, impossible,preferable,desirable, imperative, advisable,essential,reserved,urgent, 等。
It is necessary that he(should)be sent there at once.
It's strange that he should say so.
I was glad that he should go.
It is important that we should speak politely.
It is a pity that she should fare so badly.
It's right that you should think that way.
☆ 用于本句型中的过去分词就是表示提议、要求、命令等动词的过去分词,如suggested,settled, required,requested,demanded,urged,decided, proposed,ordered,desired,advised等。
It is requested that Professor Liu(should)give us a lecture.
It is desired that we(should)get everything ready by tonight.
I’m ashamed you should have done such a thing.
It has been suggested that the meeting(should)be put off.有人建议推迟会议。
It is settled that you leave us, then?
注意:这种句型中的主语从句也可用陈述语气,如:It was important that he made an explicit statement on this score last week. 他上个星期对于这一方面做了明确的说明,这是很重要的。
2. 虚拟语气在宾语从句中的应用
1). 宾语从句在表示提议、要求、命令、意志等动词后,其谓语用should+动词原形或只用动词原形的虚拟语气,作为suggest,request,demand,urge,propose,prefer,advise,insist,require,order,command,maintain,ask,object, arrange, desire等动词的宾语。
如:
The doctor suggested that he not go there.医生建议他不要去那里。
He suggested that we should leave early. 他建议我们早点动身。
The judge ordered that the prisoner should be remanded. 法官命令被告还押。
2). wish的宾语的从句,表示愿望,常省去连词that。
☆ 从句的谓语动词可用过去式,表示现在的愿望(与现在事实相反),虽实现的可能性不大,但仍有实现的可能。
I wish it were true.我但愿这是真的。
☆ 从句的谓语动词还可用“could(would,might)+动词原形”用来表示将来的愿望
I wish you would stay a little longer.我希望你再待一会儿。
☆ 表示无能为力的过去愿望(与过去事实相反),可用“had +过去分词”或“could(would,might)+have+过去分词”
I wish you had called yesterday.我希望你昨天来过电话。
We wish you had come to our New Year’s party.我们真希望你来参加了我们的新年联欢会。
3). would rather, would sooner等表示愿望,其宾语从句常用虚拟过去式。
☆ 表示与现在和将来含义事实相反的虚拟语气要用动词的过去式
☆ 用过去完成式(had + 过去分词)表示过去事实相反的含义
I would rather you came tomorrow.我宁愿你明天来。
I'd sooner she left the heavy end of the work to some one else.我宁愿她把重活留给别人。
4). 有些动词,如think, expect, believe,其否定式的宾语从句亦可用should+动词原形。如:
I never thought he should refuse.我万没有想到他会拒绝。
She did not expect that you should come.她没有预料你会来。
3. 虚拟语气在表语从句中的应用
名词suggestion,proposal,order,advice,demand等作主语,其后的表语从句中的谓语动词一般使用虚拟语气,用should +动词原形或省略should。
My suggestion is that we (should) send a few soldiers to help them.
我的建议是我们应派几个战士去增援他们。
My advice is that you (should) treat her well. 我的忠告是你应该善待她。
He makes the demand that she (should) leave the place at once.
他提出一个要求,要求她立刻离开这个地方。
My suggestion is that we should tell him.我的建议是我们应该告诉他。
Our only request is that this should be settled as soon as possible.
我们唯一的请求就是尽快解决这个问题。
注意:虚拟语气也可以用于同位语从句。
如:
There was a suggestion that Brown should be dropped from the team.有一项建议是布朗应该离队。
4. 虚拟语气在定语从句中的应用
常用在It is time (that)…句型中,定语从句常用虚拟过去式
It is time the children went to bed. 孩子们早该上床睡觉了。(表示催促)
It's high time that he began to think how to deal with money.
他早该开始考虑如何与钱打交道。
It is time we left.我们该走了。
It is time we went to bed.我们该去睡觉了。
5. 虚拟式动词原形亦常用在独立句中,表愿望
Long live the Communist Party of China!中国共产党万岁!
God bless you! 上帝保佑你。
God damn it! 该死的!
The devil take you! 见鬼去吧!
So be it then. 就那样吧。
6. 虚拟时态与谓语动词时态的关系:从句中的虚拟时态往往不受全句谓语时态的影响。
1) 用于主语从句。试比较:
It is important that he should know about this.他必须知道此事。
It was important that he should know about this.他必须知道此事。
2) 用于宾语从句。试比较:
I suggest that we should go tomorrow.我建议我们明天走。
I suggested that we should go the next day.我建议我们第二天走。
She said, “If I were a boy I would join the army.”她说,“我如是男孩,就参军。”
She said that if she were a boy, she would join the army.她说她如是男孩就参军。
但强调现在时刻的虚拟式在间接引语中需要遵守时态一致的原则。试比较:
“If I knew how it worked, I could tell you what to do,” he said.
“假如我知道它是如何运行的话,我就会告诉你该怎么办,”他说道。
He said that if he had known how it worked he could have told me what to do.
他说假如他知道它是如何运行的话,他就会告诉我该怎么办。
“If I knew the answer to all your questions I'd be a genius,” he said.
“我如知道你所有问题的答案,我就是天才了。”他说道。
He said that if he knew the answer to all my questions, he’d be a genius.
他说他如知道我所有问题的答案,他就是天才了。
但如果全句谓语是虚拟语气,其后从句的时态则多受其影响,现在时态应随之而变为过去时态。
如:
I would think he was wrong.我看他是错了。(须用was,试比较:I think he is wrong)
It would seem that she was right. 她似乎是对的。(须用was,试比较:It seems that she is right)

if only虚拟语气用法总结
老师叮咛:李辉老师说,语法填空这种题型,考点极其固定,因为百年以来英语语法都没发生过巨大的变化。高考语法考点本来就有限,能用填空这种形式来考的语法考点就更有限了。只要掌握知识点,考试必须妥妥的!下面的虚拟语气“很重要”!经过了全网首席高考英语名师李辉老师团队高度认真的整理校对,无错,可信!可供全国各省高中生打印、学习、背诵!
一、语气概述
时态语态一样,语气也是谓语动词的一种形式,它表明说话者的目的和意图。英语中有三种语气:陈述语气,祈使语气和虚拟语气。(有的语法书说语气有四种,即还包括疑问语气)。
eg:
①He doesn ’ t see very well in his right eye. 他右眼视力不太好。(陈述语气)
②Have they ever been to Australia ? 他们去过澳大利亚没有?(疑问语气)
③Please read through the instruction in advance. 请先通读说明书。(祈使语气)
二、虚拟语气概述
在英语中,由于说话人的意图不同,动词需用不同的形式,称为语气。虚拟语气是指说话人表示一种假设的情况,一种愿望,怀疑,推测,请求等,即认为动词所表示的动作或状态并非事实。虚拟语气可用于状语从句,名词性从句,定语从句及其他结构中。
三、虚拟语气的定义
如果一件事不是真实的,而是虚拟的,就在这个动词身上加一个did。
四、非真实条件句中的虚拟语气
A.由 If 引导的两种条件句:
真实条件句(遵循主将从现原则)
非真实条件句(虚拟语气)
以下为 If 在非真实条件句中虚拟语气的形式和用法:
eg:
① If I were you ,I would reconsider their advice .
如果我是你的话,我会重新考虑他们的意见。(与现在事实相反)
② You would not have caught a cold if you had put on more clothes .
如果你多穿了些衣服,你就不会得感冒了。(与过去事实相反)
③ If I were to / should do i t ,I would do it in different way.
如果我做这件事,我将用不同的方法做。(与将来事实相反)
注意:在非正式文体中,如果 If 条件句中有助动词 were / should / had 可将其提于主语之前(位于句首),再把 If 省掉,即形成部分倒装。
当主从句所表示的时间不一致时,主从句按各自的时间采用相应的谓语形式。
常见的有:
①If I were you ... = Were I you ... 如果我是你/我要是你......
② If it were not for ... = Were it not for ... 如果要不是......
③ If it had not been for ...=Had it not been for ... 如果当时要不是......
(③主句用: should / could / would / might + have done 的形式,ps.在此结构中,had为助动词。若为谓语动词,则不能省略、倒装。)
B.错综时间条件句
主句和从句不是一个时间平台,需要分别在三个时间平台里“选形式”。
从过完用had done,主过将用would do
从用should / were to,主过将完用would have done
eg:
① If the weather had been more favorable ,the crops would be growing still better.
如果天气更好的话,庄稼就会长得跟好些。(从句指过去,主句指现在)
②If I were you ,I would have taken his advice.
我要是你,我就采取了他的建议。(从句指现在,主句指过去)
C.含蓄虚拟条件句(if省略句)
有时假设的情况不以条件句的形式表现出了,而是通过一个介词短语或分词或其他方式表现出来。当虚拟条件句的谓语动词含有were / should / had时,if可以省略,这时条件从句要用倒装语序,即把were, should, had等词置于句首,这种多用于书面语。
(1)省略if
Step1:去掉if。
Step2:助系情提到主语之前。
• Were I you, I would go.
• Had I known about the party, I would have come.
• Should I go abroad, I would buy you a gift.
注意:在虚拟主句中,主语只有是第一人称时,才能用should。
(2)根本没有if
有些句子里,没有if,但是有but for(若不是)/ without / under / otherwise / but / or / but that(若不是)等,此时可把它们看做虚拟条件句,然后根据时间平台,选择主句的动词形式。
• Without your help, I wouldn’t have passed the exam.
= If you didn’t help me, I wouldn’t have passed the exam.
=But for your help, I would not have passed this exam.
• I don’t have your telephone number, otherwise / or I would have called you back.
= If I had your number, I would have called you back.
• What would you do with a million dollars?
=What would you do if you had a million dollars?
D.wish,as if / though和 if only 用法
(1)wish用法如下:
1.表示与现在相反的愿望: 主语 + wish (that)...did (were)...
eg: I wish I were a bird.
2.表示与过去相反的愿望: 主语 + wish (that)...had done...
eg: I wish I had seen the film.
(注意:如果wish在表达对过去情况的虚拟而不是未实现的愿望时,有
时也可用:主语+wish(that)...would / could have done)
3.表示与将来相反的愿望: 主语 + wish (that)... could / would / might do
eg: I wish you would do that again.
(2)由 as if/though引导的表语从句
虚拟:同wish用法;be在第一,三人称可用were / was。
陈述:表示可能发生的几率很大或被假设为真实的。
(3)If only...引导的条件句
(常用感叹的形式)表示强烈的不满,遗憾或愿望,主句常省略,意为:“要是 / 如果......该多好啊 / 就好了!”。(注意:“only if ...”意为:“只要......”,位于句首时采用部分倒装。)
eg:
①If only I could see him once more ! 我要是再见到他就好了!
②If only we had telephoned him in advance ! 要是事先给他打个电话就好了!
E. Suppose / Supposing / providing / provided (that)... / what if...等某些特殊的连词后引导的条件句中(有时无主句),表示与现在或将来事实相反用 did ;表示与过去相反用 had done 。
eg:
①Suppose / Supposing (that) we told her the truth. 假定我们把事情的真相告诉她。
②What if you came tomorrow instead of today. 如果我是你明天来而不是今天来呢?
F.would rather后的宾语从句:表示愿望或尚未发生的动作。
had / would sooner / rather + that...从句中意为“宁愿”,用did(be动词用were)表示对现在或将来的虚拟;用had done表示对过去的虚拟。
eg:
①She will get home at dinner time, but I would rather she got home a little earlier.
②He got drunk last night. I ’ d rather he hadn ’ t drunk so much.
五、名词性从句中的虚拟语气 (should 类虚拟语气 )
即主句含有:建议、命令、请求、要求、愿望、主张等意思时,后面的从句用 (should)+V 原/ should have done的形式。但注意,若从句中含有“竟然,惊讶,诧异 ” 之意时, “ should ” 则不可以省。
(常见简记:一坚持,二命令,三建议,四要求) 其他同下述用法:urge / propose
insist
order / command
advise / suggest / recommend +(that) sb. (should) do
ask / require / request / demand
eg:
①The teacher suggested that we (should) make good use of every minute.
②He ordered that all the book (should) be sent at once.
③She insisted that she (should) go to the south for her holiday.
注意:
六、 副词性从句中的虚拟语气
A.as if / though用法
虽同wish,但也有一些区别,如下:
as if / though从句时态不受主句限制 。
①在谈论现在情形时用一般过去时。
②在谈论过去情形时用:
Ⅰ.一般过去时:表示过去当时存在的某种状态,但若状态动词后带有持续的时间状语,则要用过去完成时。
eg:
①They talked as if they had been friends for years. 他们谈起话来,好像是多年的朋友。
②He looked at me as if I were mad. 他看着我,好像我疯了似的。
Ⅱ.过去完成时: 表过去的动作先于主句而发生,即使主句是现在时,as if 从句中的谓语动词也要用 had done。
eg: It seems as if it had gone bad.它闻起来好像坏了。
③在谈论将来情形时用: would (could/might)+do
B.in case / lest / for fear that表“以防,以免”等引导的目的状语中的虚拟语气,其后的形为:(should)+
V原 (但注意in case 句中的should通常不省)。若不用虚拟也可用陈述,即用: 一般现在时或过去时。
C.even if / though “ 即使/纵然/虽然 ”
虚拟:同 if 用法相同。(方法:主句含有情态动词的过去式)
陈述:表示真实情况。
七、形容词性从句中的虚拟语气
八、 虚拟语气固定句型
1. Would you mind+主语 + 谓语虚拟? 您是否介意 …?
2. would rather (that) 主语 + 谓语虚拟 宁愿 …
3. It is high time that sb. d id / (should) do sth. 到某人做某事的时间
4. It is necessary / important / essential / strange / natural /
advisable / surprising that sb. (should) do sth .
5. It is a pity / duty / shame / regret that sb. (should) do sth.
6 But for / Without + sth. +主语+谓语虚拟 要不是…
7. If only+主语 + 谓语虚拟 要是…就好了!
8.主句+ as if / as though +主语+谓语虚拟 就好像…
九、情态动词+have done
could / mig ht have done 本来能做却没做
s hould / ought to have done 本该做而实际上没做(抱怨和责备)
should not / ought not to have done 本不该做而做了
needn ’ t have done 本不必做而做了
十、虚拟语气的其他用法
(1)表示过去本打算做而实际上没有做。
句型:had done (be / intend / think / mean / plan / hope etc) to do
= V-ed + to have done ,would love / like to have done
(2)had hoped表过去未实现的愿望,译为“要想,希望 … ”,从句谓语常用“would +V原”。
eg: He had hoped that the family would come before his granny came.———2013年湖北高考
(3)may(might) as well + V原 ,译为“不妨,倒不如”,表示劝说、建议、劝告。
若其后带有某种消极情绪时,常用:might.
[if !supportLists](4) [endif] 表示祝愿、命令的简单句中。常用“may +主语+动词原形”。
eg:
①Long may you live.
②May you have a good journey!
(5)表示对过去事情的懊悔时,谓语用“should + have + 过去分词”。
eg: You should have returned the money to Mary.
十一、 虚拟语气解题常用技巧
1.找固定句型 。
2.主过将从过 ; 主过将完从过完 。
十二、虚拟用法形式总结
含三种:
①所有含if的从句(除what if … 外)。
②wish从句。
含两种:
①某些特殊连词后的条件句。
②what if … 从句。
③would rather从句。
④定从中的虚拟。
含一种:
①含蓄虚拟语气(情+have done / do)。
②名词性从句(除 wish 外)与表“ 以防 ”意义的条件句中的虚拟一样(should+V原)。
以上就是关于虚拟语气笔记总结,虚拟语气语法总结框图的全部内容,以及虚拟语气笔记总结 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
