本文目录
六种时态的被动语态造句
1. 一般现在时
Rice is grown in the south of the states.
大米长在南方的州上.
We are not allowed to enter the chemistry lab without a teacher.
我们不允许在没有老师陪同的情况下进入实验室.
2. 一般过去时
The building of a new car factory was agreed on last month.
一家新汽车工厂的建筑上个月已经被同意了.
He had a strange way of making his classes lively and his lessons were not easily forgotten.
他有一种特殊的使课堂活跃的方法,他的课总是不容易被遗忘.
3. 一般将来时
Cars will be sent abroad by sea.
汽车将经由水路运往国外.
Plenty of jobs will be given to school-leavers.
学校毕业生将有大量工作机会.
4. 过去将来时
The manager said the project would be completed by the end of the year.
经理说这项计划将在今年年底完成.
The workers told me that the car would be mended as soon as possible.
工人们告诉我这辆汽车将尽快被修好.
5. 现在进行时
English lessons are being broadcasted on the radio.
广播正在播放英语课程.
The rooms are being painted.
这些房间正在被粉刷.
6. 过去进行时
——Why didn't they drive there on time?
----Because the road was being mended.
---为什么他们没有准时开车到那儿?
---因为那条路正在修理当中.
Trees were being planted here this time last year.
去年的这个时候这里正在种许多树.
7. 现在完成时
I have been told the sports meet might be put off.
我已经说过运动会可能会推迟举行.
The price has been brought down.
价格已经下降.
8. 过去完成时
When I got to the theatre, I found the tickets had already been sold out.
当我到达剧院的时候,我发现票已经卖完了.
He had been considered to be a great leader.
他曾经被认为是最好的领导.
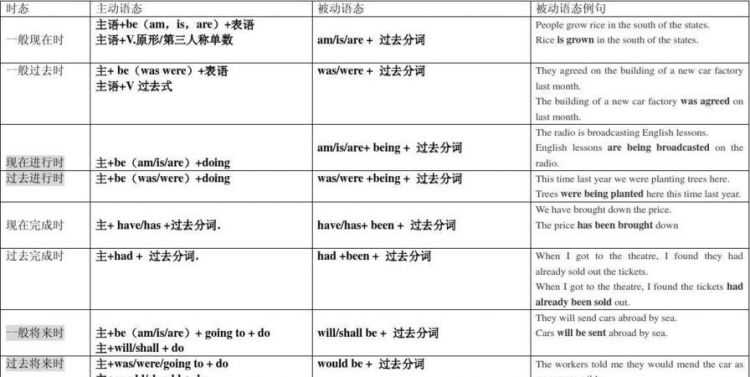
英语中8种时态的主动语态和被动语态
1、一般现在时
(1)一般现在时表示没有时限的持久存在的动作或状态或现阶段反复发生的动作或状态,常和副词usually,often,always sometimes, regularly,near,occasionally,every year, every week等连用.例如: 1)The moon moves round the earth..
(2)在由after,until,before,once,when,even if,in case,as long as,as soon as,the moment以及if,unless等引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,通常用一般现在时代替将来时.例如:
1)I will tell him the news as soon as I see him.
(3)某些表示起始的动词,可用一般现在时表示按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,这类动词有:be,go,come,start,depart,arrive,begin,leave等.例如:
1)The plane leaves at three sharp.
(4)在由why,what,where,whoever,who,that,as等引导的从句中,也常用一般现在时代替将来时.例如:
1)Free tickets will be given to whoever comes first.
2.一般过去时
(1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用.例如:
We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film.
(2)表示过去习惯性动作.例如:
1)He always went to class last.
2)I used to do my homework in the library.
(注意与be used to doing短语的区别)
3.一般将来时
1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态.例如:
I shall graduate next year.
2)几种替代形式:
1)be going to +v在口语中广泛使用,表示准备做或将发生的事情.例如:
I’m going to buy a house when we’ve saved enough money.
2)be to +v表示计划安排要做的事,具有“必要”的强制性意义.例如:
I am to play tennis this afternoon.
3)be about to +v表示即将发生的事情.例如:
He was about to start.
4)be due to +v表示预先确定了的事,必定发生的事.例如:
The train is due to depart in ten minutes.
5)be on the point/verge of +v – ing强调即将发生的某种事态.例如:
The baby was on the point of crying when her mother finally came home.
二、进行时态
1.现在进行时
(1)表示现在正在进行的动作,常与now,right now,at the mother,for the time being,for the present等连用.例如:
Don’t disturb her. She is reading a newspaper now.
(2)表示现阶段经常发生的动作,常与always,continually,forever,constantly等连用.例如:
My father is forever criticizing me.
(3)表示根据计划或安排在最近要进行的事情.具有这种语法功能的动词仅限于过渡性动词.即表示从一个状态或位置转移到另一个状态或位置上去的动词.常用的有:go,come,leave,start,arrive,return等.例如:
They are leaving for Hong Kong next month.
(4)有些动词不能用进行时,这是一类表示“感觉,感情,存在,从属”等的动词.如:see,hear,smell,taste,feel,notice,look,appear,(表示感觉的词);hate,love,fear,like,want,wish,prefer,refuse,forgive(表示感情的动词);be,exist,remain,stay,obtain(表示存在状态的动词);have,possess,own,contain,belong,consist of,form(表示占有与从属的动词);understand,know,believe,think,doubt,forget,remember(表示思考理解的动词).但是如果它们词义改变,便也可用进行时态.例如:
1)Tom looks pale. What’s wrong with him?
(look在此为联系动词,意为“显得,看上去”)
2)Tom is looking for his books.
(look在此为实义动词,意为“寻找”)
2.过去进行时
过去进行时表示一个过去的动作发生时或发生后,另一个过去的动作正在进行,或表示过去反复的习惯,常与always,continually,constantly等动词连用.例如:
1)We were discussing the matter when the headmaster entered.
2)Whenever I visited him, he was always writing at the desk.
3.将来进行时
将来进行时主要表示将来某一时刻正在进行的动作,或表示要在将来某一时刻开始,并继续下去的动作.常用来表示礼貌的询问、请求等.例如:
1)This time next day they will be sitting in the cinema.
2)What will you be doing at six tomorrow evening?
4.完成进行时
(现在、过去、将来)完成进行时是(现在、过去、将来)完成时的强调形式,将放在完成时态部分讲述.
三、完成时态
完成时态通常表示已完成或从事的动作.它可分为:
1.现在完成时
(1)现在完成时用来表示对目前状况仍有影响的,刚刚完成的动作(常与yet,already,just连用),或者过去某一时刻发生的,持续到现在的情况(常与for,since连用).例如:
1)I have just finished my homework.
2)Mary has been ill for three days.
(2)常与现在完成时连用的时间状语有:since, for, during, over等引导出的短语;副词already, yet, just, ever, now, before, often, lately, recently等;状语词组this week (morning, month, year), so far, up to now, many times, up to the present等.例如:
1)I haven’t been there for five years.
2)So far, she hasn’t enjoyed the summer vacation.
3)There have been a lot of changes since 1978.
(3)完成时态可用在下列结构中:
This (That, It) is (was) the first (second…) time +定语从句;This (That, It) is (was) the only (last) + n +定语从句;This (That, It) is (was) +形容词最高级+ n +定语从句.如果主句的谓语动词是一般现在时,从句的谓语动词通常用现在完成时;如果主句谓语动词是一般过去时,从句谓语动词通常用过去完成时.例如:
(1)This is one of the rarest questions that have ever been raised at such a meeting.
(2)There was a knock at the door. It was the second time someone had interrupted me that evening.
2.过去完成时
(1)表示过去某时间前已经发生的动作或情况,这个过去的时间可以用by,before等介词短语或一个时间状语从句来表示;或者表示一个动作在另一个过去动作之前已经完成.例如:
1)We had just had our breakfast when Tom came in.
2)By the end of last year they had turned out 5, 000 bicycles.
(2)动词expect, hope, mean, intend, plan, suppose, wish, want, desire等用过去完成时,表示过去的希望、预期、意图或愿望等没有实现.例如:
I had meant to take a good holiday this year, but I wasn’t able to get away.
另外两种表示“过去想做而未做的事”的表达方式是:
1)was / were + to have done sth,例如:
We were to have come yesterday, but we couldn’t.
2)intended (expected, hope, meant, planned, supposed, wished, wanted, desired) + to have done sth,例如:
I meant to have told you about it, but I forgot to do so.
(3)过去完成时常用于以下固定句型:
1)hardly, scarcely, barely + 过去完成时+ when + 过去时.例如:
Hardly had I got on the bus when it started to move.
2)no sooner +过去完成时+ than +过去时.例如:
No sooner had I gone out than he came to see me.
3)by (the end of ) +过去时间,主句中谓语动词用过去完成时.例如:
The experiment had been finished by 4 o’clock yesterday afternoon.
3.将来完成时
将来完成时表示在将来某一时刻将完成或在另一个未来的动作发生之前已经完成的动作;也可以用来表示一种猜测.常与将来完成时连用的时间状语有:by (the time / the end of ) +表示将来时间的短语和句子;before (the end of ) +表示将来时间的词语或句子;when, after等加上表示将来动作的句子等.例如:
1)By this time tomorrow you will have arrived in Shanghai.
2)I shall have finished this composition before 9 o’clock.
3)When we get on the railway station, the train will probably have left.
4.完成进行时
完成进行时是完成时的强调形式,有现在完成进行时,过去完成进行时,将来完成进行时.
(1)现在完成进行时表示过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直延续到过去某一时刻.例如:
I have been looking for my lost book for three days, but I still haven’t found it.
(2)过去完成进行时表示过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直延续到过去某一时刻.例如:
It had been raining cats and dogs for over a week and the downpour had caused landslides in many places.
(3)将来完成进行时表示在将来某一时刻之前开始的一个动作或状态一直延续到将来某一时刻.例如:
By the time you arrive tonight, she will have been typing for hours.
四:时态一致
时态一致是英语四、六级考试的一个重要内容.通常应由主句谓语的时态决定从句的谓语时态.一般原则是:
1、当主句谓语使用现在时或将来时,从句的谓语根据具体情况使用任何时态
He says that he lives in Wuhan.
We hope that there will be many people at your party today.
“Did you hear that Bill finally sold the house?” “Yes, but I don’t know who bought it.”
“There’s a lot of excitement on the street.”
“There certainly is. Do you suppose the astronauts have returned?”
2、当主句谓语使用过去时的时候,从句的谓语必须使用过去范围的时态
He said he was writing a novel.
The teacher wanted to know when we would finish the experiment.
He said his father had been an engineer.
3、当从句是表示没有时间概念的真理时,从句的谓语应使用一般现在时.例如:
The teacher told them since light travels faster than sound, lightning appears to go before thunder.
注:在此种情况下,即使主句谓语用了过去式的各种时态,从句谓语也应用一般现在时.
4、从句谓语只能用虚拟语气的情况
利用时态一致原则确定从句动词时态时,还应注意,若主语动词是表示命令、请求、要求、建议、劝告等的动词,从句谓语只能用虚拟语气,不能遵循时态一致原则.例如:
We insisted that we do it ourselves.
动词的语态
语态也是动词的一种形式,英语有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态.主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,而被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者.
1)We use electricity to run machines. (主动语态)
2)Electricity is used to run machines. (被动语态)
1.不能用于被动语态的动词和短语
(1)在英语中,不及物动词不能用于被动语态,但有些不及物动词(包括短语)容易引起误用.如:appear, belong, belong, die, escape, fall, happen, last, remain, succeed, occur, come true, take place, consist of.
(2)某些表示状态或特征的及物动词,如:become, contain, cost, fit, have, resemble, suit也没有被动语态.
2.被动语态的时态形式
常用的被动语态有表1所列的几种时态形式.
表1
时?SPAN lang=EN-US> 一般时 进行时 完成时
现在 am asked am being asked
is asked is being asked
are asked are being asked
过去
was be asked was being asked
were be asked were being asked
将来 shall be asked shall have been asked
will be asked will have been asked
过去 should be asked should have been asked
将来 would be asked would have been asked
3.短语动词的被动语态
短语动词转换为被动语态时,通常被看作是一个动词,后面的介词或副词不能拆开或省略.例如:
1)So far no correct conclusion has arrived at.
2)All the rubbish should be got rid of.
4.“get + -ed分词”的被动语态
“get + -ed分词”结构强调动作的结果,而非动作本身,常用来表示突发性的,出乎意料的偶然事件.例如:
The boy got hurt on his way home from work.
另外,“get + -ed分词”还可用于谈论为自己做的事,是主动的行为而不是被动的行为.例如:
get dressed(穿衣服) get divorced(离婚)
get engaged(订婚) get confused(迷惑不解)
get lost(迷路) get washed(洗脸)
get married(结婚)
5.能带两个宾语和复合宾语的动词改为被动语态
(1)能带两个宾语的动词改为被动语态时,一次只能由一个宾语作主语,另一个宾语被保留下来.例如:
1)We showed the visitors our new products.(主动语态)
2)The visitors were shown our new products.(被动语态)
3)Our new products were shown to the visitors.(被动语态)
(2)能带复合宾语的动词改为被动语态时,原来的宾语补足语变为主语补足语.例如:
1)The teacher appointed him League secretary.(主动语态)
2)He was appointed League secretary.(被动语态)
6.被动语态与系表结构的区别
(1)The novel was well written.(系表结构)
(2)The novel was written by Diskens.(被动语态)
7.少数动词的主动语态有时有被动的意思
例1:The book is selling remarkably well.
例2:The song sounds very beautiful.
能这样用的动词还有read(读起来),clean(擦起来),wash(洗起来),write(写起来).
例3:My watch needs cleaning. (= My watch needs to be cleaned).
能像need这样用的动词还有:want, require, deserve, do, owe, bind等.
例4:The meat is cooking.
例5:The book written by the professor is printing.
在英语中被动语态分时态,我给你举些例子:
(1)一般现在时:This song is often sung by children.孩子们常唱这首歌.
(2)一般过去时:This house was built in 1958.这房子建于1958年.
(3)一般将来时:Many buildings will be built in my home town.在我的家乡,许多大楼将要建成.
(4)过去将来时:The old scientist said that he would be invited to vist their country before long.那位老科学家说不久他将应邀访问他们的国家.
(5)现在进行时:The proposal is being considered now.正在考虑这个提案.
(6)过去进行时:Mr Wu was in hospital .When we went to see him,he was being operated on.吴先生住院了.我们去看他时,他正在动手术.
(7)现在完成时:Have the letters been posted ?信已经寄出去了吗?
(8)过去完成时:He came and told us that the work had been finished.他来告诉我们,工作已经完成.
(9)将来完成时:By the end of this year,the tall building will have been built.到今年年底,这幢高楼将建成.
(10)过去将来时:The boy told mother that his homework have been finished by ten o'clock.男孩告诉妈妈到10:00他将做完作业.
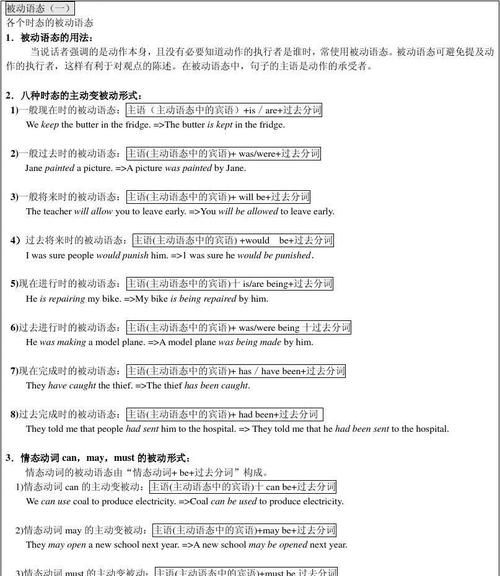
用英语八大被动时态各写一个句子废话就不要进来了
一) 一般现在时
被动语态:
主语+be+动词过去分词+by(加宾格)
eg: He waters the flowers every day.
The flowers are watered by him every day.
二)一般过去时
被动语态:主语+was\were+动词过去分词
eg: He took care of his little brother yesterday.
His little brother was taken care of by him yesterday
三)现在进行时
被动语态:主语加am\is\are加being加动词过去分词
例句:Helen is writing a letter.
A letter is being written by helen.
四)过去进行时
被动语态:主语+was\were+being+动词过去分词
eg:He was making a model plane.
A model plane was being made by him.
五)现在将来时
主语+be going to be+动词过去分词
eg:They will clean the windows tomorrow.
The windows will be cleaned by them.
六)过去将来时
主语+was/were going to be +动词过去分词
eg:He said he would finish the project by the time we reached there.
He said the project would be finished by the time we reached there.
七)现在完成时
主语+have/has + been+动词过去分词
eg:he has sung a nice song.
A nice song has been sung by him.
八) 过去完成时
主语+had +been +动词过去分词
eg:He had posted the letter .
The letter had been posted by him.
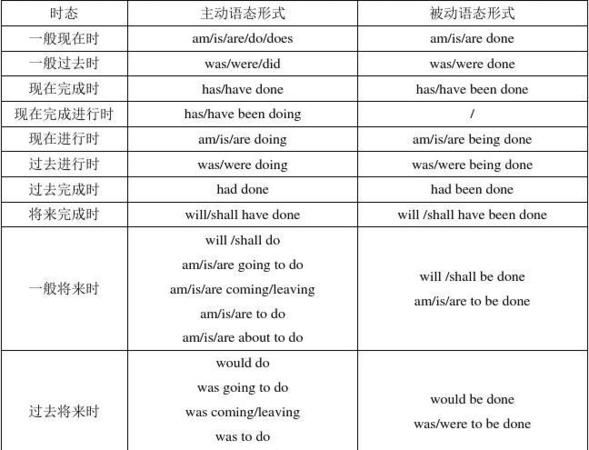
八大语态的主动语态和被动语态
一般现在时现在进行时现在完成时一般将来时am/is/aretaken am/is/arebeing taken have/has been taken will/shall be taken一般过去时过去进行时过去完成时过去将来时was /weretaken was/werebeing taken had been taken would/shouldbe taken 从上表中可以看出,被动语态的各种时态变化都是通过助动词“be”的各种时态来表示的,因此只要知道“be”的时态形式,也就掌握了被动语态构成。下面是被动语态各种时态的例句:e.g. You are wanted on the phone . 有你的电话。(一般现在时) The railway was built in 1998. 这条铁路建于1998 年。(一般过去时) A new railway is being built in this city. 这个城市正在修建一条新的铁路。(现在进行时) The railway was being built this time last year.去年这个时候这条铁路正在修建。(过去进行时) The new railway has already been built.新铁路已经建成了。(现在完成时) The new railway had been built by the end of last year.这条铁路在去年年底前已经建成了。(过去完成时) A new railway will be built in this city next year.这个城市明年将建一条新的铁路。(一般将来时) He told us that the new railway would be built the next year.他告诉我们新铁路将于第二年建成。(过去将来时)第二节 被动语态的各种句型1.单宾语结构。 e.g. Our English teacher often uses a tape-recorder in teaching English.我们英语老师经常用录音机教英语。(主动语态) A tape-recorder is often used (by our English teacher) in teaching English.录音机经常用来教英语。2.双宾语结构 这种结构可有两种被动语态句型,即分别用间接宾语和直接宾语作主语。e.g. The villagers gave the foreign guests warm welcome.(主动语态)The foreign guests were given a warm welcome by the villagers.(被动1)A warm welcome was given to the foreign guests by the villagers.(被动2)3。复合宾语结构 这种结构只能将主动语态的宾语改作被动语态的主语。 e.g. They heard someone singing in the next room.(主动) Someone was heard singing in the next room. (被动)4. 含情态动词的被动结构 含情态动词的句子其被动语态形式是“情态动词+ be+过去分词”。 e.g. The trees should be watered every day. 这些树应每天浇水。 This word can be pronounced in two ways. 这个单词可以有两种发音。5.短语动词结构 相当于及物动词的短语动词也可以有被动语态,如 look after, give up , take care of , pay attention to , make use of , put off, wake up , put out 等。e.g. The children must be taken good care of .这些孩子必须得到好的照顾。The big fire has been put out . 大火已被扑灭。特别提醒A. 只有及物动词和及物短语动词才可以有被动语态不及物动词,不及物短语动词或系动词都不可以有被动语态,如happen, go on , take place , belong to , sound, feel等。e.g. This room belongs to me. .这房子属于我。不可以说:This room is belonged to me .e.g. This music sounds sweet.这音乐听起来很悦耳。不可以说:This music is sounded sweet.B.被动语态只有在强调动作的承受者或不知道动作的执行者时才使用。e.g. This sock is made of silk.这袜子是丝的。(不知道动作的执行者是谁。)English is required in many schools of our country.在我们国家许多学校要求开设英语课。(强调动作的承受者English.)C. 千万不能按中文意思死搬硬套,如句子“你的信我已经收到了。”不能说:Your letter has been received by me .只能说:I have received your letter.D. 主动语态变为被动语态的步骤 1。找出主动语态的宾语,作为被动语态的主语;2。将谓语动词有主动形式变为被动形式;3。有无必要用 by 短语。4。注意被动语态的句式,时态必须主动语态一致。e.g. Have you found your lost book? 你找到你丢的书了吗?(一般问句,现在完成时) Has your lost book been found?你丢的书找到没有?(一般问句,现在完成时)E. 有些动词常用主动形式表示被动意义,如动词act, cook, keep , look , open , write, read, sell , wash 等,这时句子的主语通常是没有生命的。e.g. This hall measures 100 metres long and 60 meters wide. 这个大厅长100米,宽60 米。 This pen sells well in that country. 这种笔在那个国家很好销。F. 在一些固句型中常用被动语态结构,如:It is said that … 据说……,人们说…… It is reported that … 据报道…… It is hoped that … 人们希望…… It is well known that… 众所周知…… It is believed that…人们相信…… It must be admitted that…必须承认…… It must be pointed that…必须指出的是……
以上就是关于英语八大被动语态的例句,六种时态的被动语态造句的全部内容,以及英语八大被动语态的例句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

