本文目录
名词的主要语法特征包括
名词的语法特征是:
1)经常作主语和宾语;多数能作定语和带定语.不能作补语.
2)名词前一般能够加上表示物量的数量短语,一般不能加副词.
3)名词不能用重叠式表示某种共同的语法意义.
4)表人的名词后面能够加“们”表示群体.
英语名词的分类及用法
初中英语中,名词部分的知识有名词的分类、名词所有格、名词的用法、名词的单、复数形式等等,要掌握这些知识就要从中发现规律,下面来和大家分享一下初中英语名词分类用法大全。
英语名词分类用法大全,名词复数变化规则
名词的定义
名词是表示人、事物、地方、现象或抽象概念的名称的词。
名词的分类
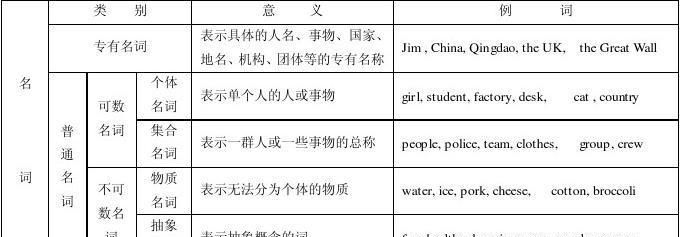
英语名词(Noun)可以从形式上进行分类,英语名词可以划分成专有名词和普通名词两大类。
从意义上划分,英语名词可分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词四类。
一般来说,个体名词可以用数目来计算,称为可数名词(Countable Nouns)。
物质名词、抽象名词和专有名词无法用数目来计算,称为不可数名词(Uncountable Nouns)。
集合名词有的可数,有的不可数。
一、普通名词
普通名词指一类人或事物的名称。英语中普通名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词一般有单、复数两种形式。如a/one child, ten children。而不可数名词一般只有一种形式。如cash(现金)。不可数名词之前不可直接用泛指限定词和数词。不可数名词可与some一起用。如:some money,some water。也可与the一起用:the information(这信息)。
(一)可数名词及其复数形式
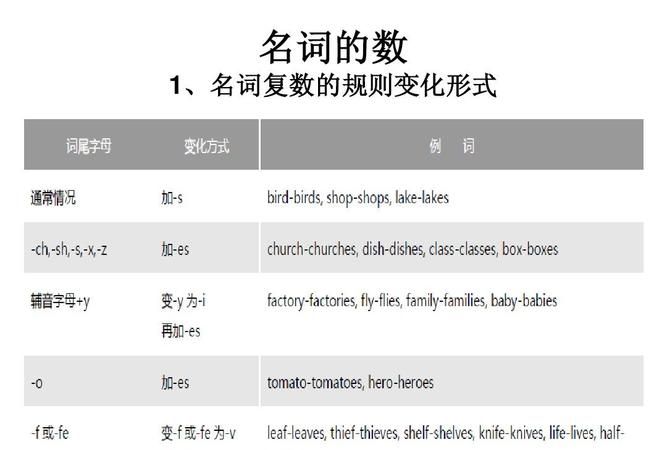
(1)可数名词的复数形式一般由词尾加-s或-es构成,其规则见下:
一般情况 加-s,在清辅音后读/s/ maps, books;在浊辅音及元音后读/z/ cars, photos;在/t/后读/ts/ cats, students;在/d/后读/dz/ beds, guards在/dZ/后读/iz/ bridges, ages
以字母s, x, ch, sh 结尾的词 加-es 在/s/, /z/, /S/,/tS/后读/iz/ classes, brushes
以辅音字母+y结尾的词 将y改成i,加-es /z/ factories, stories
以字母o结尾的词 一般加-es /z/ potatoes, tomatoes;少数外来词或缩略词加-s /z/ radios, pianos简称为有生命的+es 无生命的+s 有生命的有黑人英雄爱吃土豆西红柿
以字母f或fe结尾的词:一般加-s /s/ roofs, chiefs;少数将f, fe, 改为-ves /z/ shelves, knives;有些加-s或改为-ves均可 /s/或/z/ scarfs/scarves
(2)可数名词复数形式的不规则构成法
英语中有一部分名词由于历史或词源原因其复数形式的构成法是不规则的。这种情况主要有:
①元音字母变化。例如:
foot-feet man-men woman-women
tooth-teeth goose-geese mouse-mice
②结尾为-en。例如: child-children
③单复数同形。
单复数同形的名词主要有:sheep, fish, Chinese, Japanese, deer等。
④只有复数形式。例如:trousers, goods 等。
(二)可数名词和不可数名词
英语中的绝大多数名词既可以用作可数名词也可以用作不可数名词。
英语名词分类用法大全,名词复数变化规则
1.可数名词
可数名词一般可以分成以下三类:
第一类:如bike,desk, factory等,这类名词占可数名词的多数。以bike为例:
There are fifty bikes at this shop.这家商店有50辆自行车。
第二类:如clothes等,本身表示复数形式。以clothes为例:
She cares for nice clothes.她 爱好 穿着。
2.不可数名词
不可数名词的用法特征主要有以下几种:
(1)不带冠词的单数形式需用动词单数作谓语。例如:
Knowledge is power.知识就是力量。
(2)由much,little等词修饰。例如:
They have saved much money for future use.他们存了很多钱以备未来使用。
(3)与表示单位的量词如a piece of等连用。例如:
Go and fetch me a piece of chalk.给我去拿一支粉笔。
要十分注意的是:不可数名词不能与不定冠词或数词直接用在一起。如不能说a good news, an advice, a hard work等。
不可数名词可以与量词使用构成不同的词组:
如: a piece of paper 一张纸 a drop of water 一滴水
a 1oaf of bread 一条面包 a bag of money 一袋钱
a bottle of milk 一瓶牛奶 a pair of shoes 一双鞋
二、专有名词
专有名词用来指具体的人、地点、日子或物体的专有名称。其特点是:第一个字母大写,通常不与冠词连用,无复数形式。
(一)人名
英美人的姓名与中国人的恰恰相反,姓在后面,名在前面,姓名前通常不用冠词。例如:
Mary Smith;George Washington。
(1)一般熟人间通常用名称呼。例如:
How’s John getting on? 约翰近来好吗?
(2)在不熟悉人之间或表示礼貌时,常把姓和称谓连用。例如:
Would you please tell John Smith to come to the office? 请你告诉约翰?史密斯到办公室来一次好吗?
(3)姓氏复数前加定冠词可表示全家人。例如:
The Turners have gone to America.特纳一家人去美国了。
(二)地名
(1)大部分单数形式的地名不用定冠词。例如:
Asia;America;China; London;Shanghai
(2)大部分单数形式的湖、岛、山名前不加定冠词。例如:.
Silver Lake;Mount Tai
(3)山脉、群岛、海洋、河流、运河、海湾、海峡、半岛、沙漠名前一般加定冠词。
例如:
the Pacific;the English Channel;the Sahara
(三)日期名
(1)节日名前通常不用冠词。例如: Christmas;National Day
(2)星期名前通常不用冠词。例如: Sunday;Tuesday
(3)月份名前通常不用冠词。例如: April;December
三、名词所有格
名词所有格是指一个名词与另一个名词之间存在所有关系时所用的形式。其构成有两种:一种是由名词末尾加’s构成;另一种由介词of加名词构成。前者多用来表示有生命的东西;后者多用来表示无生命的东西。例如:
Children’s Palace 少年宫
Tom’s bike 汤姆的自行车
the title of the book 书名
the legs of the table 桌子的腿
(一)所有格形式的构成
(1)单数名词后加’s,其读音与名词复数结尾的读音相同。例如:
the girl’s father 女孩的父亲
(2)以s结尾的复数名词后加’。例如:
two hours’ walk 两个小时的步行
(3)不以s结尾的复数名词后加’s。例如:
the children’s holiday 孩子们的节日
(4)以s结尾的人名,可以加’s,也可加’号。例如:
Thomas’s brother 托马斯的兄弟
Charles’s job 查尔斯的工作
(5)表示各自的所有关系,不是共有的,则要分别在名词末尾加’s,如:
John’s and Mary’s rooms 约翰和玛丽各人的房间
若表示共有的,则在最后一个名词的末尾加’s,如:
John and Mary’s room 约翰和玛丽合住的房间
(二)’s所有格的用法
’s所有格常表示有生命的东西,但也可表示无生命的东西。例如:
(1)表示时间:
today’s newspaper 今天的报纸
(2)表示自然现象:
the moon’s rays 月光
(3)表示国家、城市机构:
Shanghai’s industry 上海的工业
(4)表示度量衡及价值:
twenty dollars’ value 20美元的价值
five miles’ distance 5英里的距离
(三)’s所有格所表示的关系
1.表示所有关系
可分为可分割的所有关系和不可分割的所有关系。可分割的所有关系通常指身外之物,一般不可用of表示。例如:
John’s pen(John has a pen)约翰的钢笔
不可说:a pen of John
但不可分割的所有关系,指自身拥有的不可分割的东西可用’s也可用of表示。例如:
Mary’s hands(Mary has two hands)玛丽的手
可以说:the hands of Mary
2.表示主谓关系
the doctor’s advice(The doctor advised)医生的建议
his mother’s request(His mother requested)他母亲的请求
3.表示动宾关系
Tom’s failure 汤姆的失败
children’s education 年轻一代的 教育
4.表示同位语关系(通常用of表示)
the city of Rome罗马城
the city of Pairs巴黎城
四、复习时需要注意的要点
(1)有些名词形式像复数,但含义是单数,而有些名词是没有单数形式的,应注意谓语动词的选用。例如:
a.Maths is the language of science.
b.No news is good news.
c.The Chinese people are a great people.
(2)在“there be”的 句子 中,谓语动词的数应和它最近的主语的数相一致.例如:
a.There are two pictures on the wall.
b.There is a cat and two dogs in the garden.
(3) 不规则名词的复数形式
①改变单数名词中的元音字母或其他形式。如:man men,woman women,tooth teeth,foot feet,mouse mice,child children等。
②单复数形式相同。如:sheep,deer,fish等,以及由汉语音译表示度量、币制等单位的名词。如:yuan.另外以-ese或-ss结尾的表示民族的名词也一样同形。如:Chinese,Japanese,Swiss等。
③以-an结尾或其他形式结尾的表示民族、国家的人的名词变复数时在词尾加-s.如:Americans,Asians,Russians,Australians,Italians,Germans等。
注意:Englishman Englishmen,Frenchman Frenchmen.
④复合名词的复数形式:在词末加-(e)s,如:afternoons,housewives等。
把主体名词变成复数形式。如:lookers-on(旁观者),passers-by(过路人)等。
⑤由man或woman作为第一部分的复数名词,两个组成部分皆变为复数形式。如:man driver men drivers,woman doctor women doctors等。5
注意:banana tree banana trees
(4)几种特殊的复数形式的名词
① 有些表示由两部分构成的东西和部分学科的名词总以复数的形式出现。如:glasses(眼镜),shorts(短裤),mathematics(数学),physics(物理学),politics(政治学)等。
②.有些复数形式的名词表示特别的意义。如:papers(文件),manners(礼貌),goods(货物),times(时代),conditions(环境;情况)等。
③有些名词在习惯用语中一定要用复数形式。如:make friends with(与……交朋友),shake hands with(与……握手)等。
五、例题选讲
例1 There are in this river.
A. a great deal of fish B. a great number of fish
C. a great amount of fish D. huge amounts of fish
答案: B
提示: 根据题意应填入许多鱼,而fish是单复数同形的可数名词,如果要表示各种各样的鱼可以用fishes表示。Fish解释为鱼肉是不可数名词。本句表示河里有许多鱼,只有a great number of修饰可数名词。
例2 He has done many
A. work B. job
C. works D. jobs
答案: D
提示: job是可数名词,在many后应填复数名词。work作为“工作”是一个不可数名词。
例3 father is a doctor.
A. The twin’s B. The twins’
C. The twin D. Twin’s
答案: B
提示: 名词复数的所有格形式只需在词尾加“’”,不能再加“-s’”。
例4 I take violin from Mr. Wang at school everyday.
A. lesson B. lessons
C. class D. course
答案: B
提示: 在英语中有些名词常以复数形式出现,Lessons表示课程。
例5 There on the wall, they are very nice.
A. are photos B. are photoes
C. is a photo D. is photo
答案: A
提示: photo的复数形式是加-s。
例6 The police searching for a tall man with long hair.
A. is B. has been
C. had been D. are
答案: D
附加练习
1. We went to Dr. Brown's yesterday. He gave us_____.
A.some advice B.advices C.an advice D.some advices
2. What _____ they've got! No wonder they are very happy.
A.a good news B.quite a few news C.good news D.little news
3. Much _____ to fight against pollution.
A.have been done B.has been done C.had been done D.has done
4. What _____! Let's go swimming.
A.a fine weather B.fine day C.a fine day D.bad weather
5. You have made ______. You should be more careful.
A.a lot of mistake B.a great deal of mistakes C.a large number of mistakes D.few mistakes
6. Before we moved into the new house, we bought many _____
A. furnitures B. furniture C. pieces of furniture D. pieces of furnitures
7. The bookshelf over there is_________.
A.Mary’s and Jane’s B.Mary’s and Jane C.Mary and Jane’s D. Mary and Jane
8. We saw the guest off at ______ yesterday..
A. The Shanghai’s Railway Station. B. The Shanghai Railway Station.
C. Shanghai Railway Station. D. The Railway Station of Beijing Railway
9. They had a good time at the _____ Palace.
A.children B.Children’s C.Children D.Childrens’
10. Xiao Li was ____ in my boyhood.
A. my close friend B. mine a close friend C. a close friend of mine D. a close friend of me
11. These are ____ from other presses. They are having a meeting in one of the ___ office.
A. editor- in-chiefs, editor’s-in-chief B.editors –in –chief , editors-in-chief’s
C. editors –in-chief’s, editor’s –in-chief’s D.editor-in-chief’s , editors –in-chief
12. There are five ____ in our class.
A. Zhang’s B. Zhangs’ C. Zhangs D. The Zhangs
13. How far is your school ?
A. twenty - five minutes walk B. the walk of twenty-five minutes
C. twenty-five minutes walks D. twenty-five minutes’ walk
14. ---What’s the distance from here to the station? - ---It’s __________from here.
A. two kilometre distance B. two kilometres’ distance
C. distance of two kilometers D. distance of two kilometres’
15. We’re going to have __________next month.
A. two day’ holiday B. two day holiday C. two days holiday D. two days’ holiday
16. Who’s a cousin?
A. Uncle or aunt’s son B. Uncle or aunt’s daughter
C. Uncle or aunt’s child D. Uncle or aunt’s brother or sister
17. She always wears beautiful _____.
A.clothes B.cloth C.dress D.clothings
18.Will you have a little ______?
A.more fishes B.more fish C.much fishes D.fishes
19. There _____ in my class. Which of them do you want to see?
A.is John B.are three Johns C.are the John's D.is the John
20. Twenty dollors ____ what he needs
A.was B.were C.is D.has been
21.The United Nations ____ a resolution
A. has past B. has passed C. have passed D. has through
22. The Arabian Nights ____ a very interesting storybook
A. is B. are C. has been D. had been
23. The New York Times ____ a wide circulation
A. is B. has C. are D. have
24. Mathematics_____ a very important subject.
A. are B. is C. were D. was
25. His mathematics ____ weak
A. is B. seems C. was D. are
26. An iron works _____ now.
A. is being built B. are being built C. has built D. had been built
27. Every means _____ tried to improve teaching and learning
A. has B. has been C. have D. were
28. The police _____ searching for a tall dark man with long hair.
A. is B. has been C. are D. had been
29. One of his fingers was wounded. What about _____.
A. the other B. another C. others D. the others
30. There’s an English book in _____ of his hands, and he also has a dictionary in his _____ hand.
A. one, other B. one, another C. one, the other D. another, second
附加练习参考答案
1.A 2.C 3.B 4.C 5.C 6.C 7.C 8.C 9.B 10.C11.B 12.C 13.D 14.B 15.D 16.A 17.D 18.C 19.A 20.B
英语名词分类用法大全相关 文章 :
1. 名词语法讲解及练习题分类及用法
2. 英语学习:按意义分类的名词
3. 英语动词的分类以及用法
4. 英语数词的分类和用法
5. 英语术语的分类及语言特点
6. 初中英语名词知识点:名词所有格用法
7. 小学英语不可数名词的归类与用法
8. 英语中名词所有格的用法讲解
9. 关于名词的英语语法
10. 小学英语单词分类大全
英语名词动词形容词副词怎么区别
1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。
如:boy,morning,bag,ball,class,orange.
2、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good,right,white,orange.
3、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am,is,are,have,see.
4、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now,very,here,often,quietly,slowly.
副词(Adverb)是指在句子中表示行为或状态特征的词,用以修饰动词、形容词、其他副词或全句,表示时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。副词可分为:时间副词、频率副词、地点副词、方式副词、程度副词、疑问副词、连接副词、关系副词、表顺序的副词。
动词(Verb),简称v。一般就是用来表示动作或状态的词汇。在英语中,动词按作用和功能主要分为两大类,一类是谓语动词,另一类是非谓语动词。基本上每个完整的句子都至少有一个动词。比如
突跃,突击,突袭等描述动作过程均属动词。
语法是语言的组织规律,任何人在使用语言时,不管他是否学过语法,但都必须合乎语法。另外,总结语法本身的规律也能加深我们对语言的理解,让我们能够真正熟练地运用语言。想要掌握规范标准的英语,语法是不可忽略的部分。就形容词而言,也是英语语法中一个不可或缺的部分。

英语名词动词形容词副词怎么区别
英语名词、动词、形容词、副词可以从以下几点辨别:
一、词性不动,位置不同。
名词一般处于句子中主语或宾语的位置,动词处于句子中谓语的位置,而形容词用来修饰名词,一般是紧挨着名词的,副词用来修饰动词,一般处于状语的位置。
1、名词(Noun,简称n.),是词类的一种,属于实词,名词表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称,名词同时也分为专有名词和普通名词。
2、动词(Verb),一般就是用来表示动作或状态的词汇。在英语中,动词按作用和功能主要分为两大类,一类是谓语动词,另一类是非谓语动词。
3、形容词(Adjective),主要用来描写或修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、 状态、特征或属性,常用作定语,也可作表语、补语或状语。
4、副词(Adverb 简称adv.)是指在句子中表示行为或状态特征的词,用以修饰动词、形容词、其他副词或全句,表示时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。副词可分为:时间副词、频率副词、地点副词、方式副词、程度副词、疑问副词、连接副词、关系副词、表顺序的副词。
二、重在积累。
在掌握了基本定义后,就需要在平时学习中多积累固定用法。

扩展资料
一、注意:
1、大多数方式副词位于句尾,但宾语过长,副词可以提前,以使句子平衡.。
We could see very clearly a strange light ahead of us.
2、方式副词well,badly,hard等只放在句尾.
He speaks English well.
二、副词的排列顺序:
1、 时间,地点副词,小单位的在前,大单位在后
2、 方式副词,短的在前,长的在后,并用and或but等连词连接
Please write slowly and carefully.
3、 多个不同副词排列:程度+地点+方式+时间副词
注意:副词very 可以修饰形容词,但不能修饰动词
参考资料:百度百科-形容词
以上就是关于英语名词的四大特征,名词的主要语法特征包括的全部内容,以及英语名词的四大特征 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
