本文目录
英语八种时态基本句型主被动
1.一般现在时 现在的事或者既成事实
1) He goes to school at seven o’clock everyday.
2) I am a teacher.
2.一般过去时 过去的事
1) I used to play football when I was young.
2) he was born in 1989.
3.一般将来时 表示打算啊,现在的推测之类的
1) We will visit the science museum next week.
2) We are going to discuss the problem tomorrow.
4.现在进行时 现在正在发生的事或动作
1) The boy is playing video games.
2) His father is writing a novel these days.
5.现在完成时 过去发生并持续到现在或对现在有影响
1) Great changes have taken place in China since 1980.
2) I have finished my task.
6.过去进行时 过去正在发生的事,一般有一个明确的过去的时间点
1). When I came in, they were having supper.
2) He was reading an interesting book this time yesterday
7.过去完成时 过去的过去发生的事对过去有影响
1) He was reading an interesting book this time yesterday.
2) When I came in, they were having supper.
8.过去将来时 过去的推测,打算之类的
1)She had had dinner before she went out.
2)He left the office after he had called Davy.
英语八大时态造句加翻译
1、一般现在时:
一般疑问句:Dose she go to school by bike?
肯定句:She goes to school by bike.
否定句:She does not go to school by bike.
2、一般过去时:
一般疑问句:Did you finish your homework yesterday?
肯定句:I finished my homework yesterday.
否定句:I did not finish my homework yesterday.
3、一般将来时:
一般疑问句:Will/Are you going to go fishing tomorrow?
肯定句:I will/am going to go fishing tomorrow.
否定句:I won't/am not going to fishing tomorrow.
4、现在进行时:
一般疑问句:Is he playing computer game?
肯定句:He is playing computer game.
否定句:He isn't playing computer game.
5、现在完成时:
一般疑问句:Have you been to Beijing?
肯定句:I have been to Beijing three times.
否定句:I haven't been to Beijing.
6、过去进行时:
一般疑问句:Were you watching TV at 7:00a.m. yesterday?
肯定句:I was watching TV at 7:00a.m. yesterday.
否定句:I wasn't watching TV at 7:00a.m. yesterday.
7、过去完成时:
一般疑问句:Had you finished your homework when you watched the TV.
肯定句:I had already finished my homework when I watched the TV.
否定句:I hadn't finished my homework yet when I watched the TV.
8、过去将来时:
一般疑问句:I didn't know whether he would help me.
肯定句:He said he would help me.
否定句:He said he wouldn't help me.
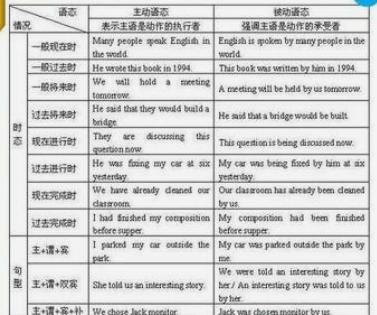
英语八大时态被动语态例句
一)一般现在时
被动语态:
主语+be+动词过去分词+by(加宾格)
eg:He waters the flowers every day.
The flowers are watered by him every day.
二)一般过去时
被动语态:主语+was\were+动词过去分词
eg:He took care of his little brother yesterday.
His little brother was taken care of by him yesterday
三)现在进行时
被动语态:主语加am\is\are加being加动词过去分词
例句:Helen is writing a letter.
A letter is being written by helen.
四)过去进行时
被动语态:主语+was\were+being+动词过去分词
eg:He was making a model plane.
A model plane was being made by him.
五)现在将来时
主语+be going to be+动词过去分词
eg:They will clean the windows tomorrow.
The windows will be cleaned by them.
六)过去将来时
主语+was/were going to be +动词过去分词
eg:He said he would finish the project by the time we reached there.
He said the project would be finished by the time we reached there.
七)现在完成时
主语+have/has + been+动词过去分词
eg:he has sung a nice song.
A nice song has been sung by him.
八) 过去完成时
主语+had +been +动词过去分词
eg:He had posted the letter .
The letter had been posted by him.
英语八大时态例句各五个例句
时态三、 现在进行时
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2.时间状语:now, at this time, days, etc. look . listen
3.基本结构:be+doing
4.否定形式:be+not+doing.
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6.例句: How are you feeling today? He is doing well in his lessons.
时态四、 过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3.基本结构 s+was/were+doing
4.否定形式:s+was/were + not + doing.
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。(第一个字母大写)
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit. When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
时态五、 现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:yet,already,just,never,ever,so far,by now,since+时间点,for+时间段,recently, lately, in the past few years, etc.
3.基本结构:have/has + done
4.否定形式:have/has + not +done.
5.一般疑问句:have或has。
6.例句:I've written an article. The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years.
时态六、 过去完成时
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc.
3.基本结构:had + done.
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left. By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books
基本结构:主语+had+过去分词(done)
①肯定句:主语+had+过去分词+其他
②否定句:主语+had+not+过去分词+其他
③一般疑问句:Had+主语+过去分词+其他
④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
时态七、 一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
3.基本结构:主语+am/is/are+going to + do;will/shall + do.
4.否定形式:am/is/are not going to do ;will/shall not do。
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies. It is going to rain.
时态八、 过去将来时
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:was/were+going to + do;would/should + do.
4.否定形式:was/were/not + going to + do;would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6.例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day. I asked who was going there.
时态九、将来完成时
1.概念:在将来某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态
2.时间状语:by the time of;by the end of+时间短语(将来);by the time+从句(将来)
3.基本结构:be going to/will/shall + have done
4.例句:By the time you get back,great changes will have taken place in this area.
时态十、现在完成进行时
1.概念:表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到现在的动作。这一动作可能刚刚开始,也可能仍在继续,并可能延续到将来。
2.基本结构:have/has +been+doing
3.时间状语:since+时间点,for+时间段等。
4.例子:I have been sitting here for an hour. The chirdren have been watching TV since six o'clock.
时态十一、 一般过去时与现在完成时的转换
在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能。
但是,可用别的表达方式:
①瞬间动词用于“一段时间 + ago”的一般过去时的句型中;
②瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用;
③瞬间动词用于“It is + 一段时间 + since + 一般过去时”的句型中,表示“自从……以来有……时间”的意思,主句一般用it is来代替It has been;
④瞬间动词用于“Some time has passed since + 一般过去时”的句型中。
请看:
A. He joined the League two years ago.
B. He has been in the League for two years.
C. It is two years since he joined the League.
D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
时态十二、 一般现在时与现在进行时的转换
在一般现在时中,at加上名词表示“处于某种状态”,如atwork(在工作),atschool(上学、上课)等。此短语可与进行时态转换。
请看: Peter is at work, but Mike is at play. Peter is working, but Mike is playing.
时态十三、 现在进行时与一般将来时的转换
在现在进行时态中go, come, leave, start, arrive等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作。如:I am coming, Mum! 意为“我就来,妈妈!”请看: The train is leaving soon. The train will leave soon.
时态 互相转换英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
十六种时态所谓“时”就是行为发生的时段或状态存在的时段,即:现在、过去、将来和过去将来四种;所谓“态”就是行为或状态发生时说呈现的状态,有一般状态、进行状态、完成状态或完成进行状态四种。由时和态结合,便形成下列十六种时态: 一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,一般过去将来时; 现在进行时,过去进行时,将来进行时,过去将来进行时; 现在完成时,过去完成时,将来完成时,过去将来完成时; 现在完成进行时,过去完成进行时,将来完成进行时,过去将来完成进行时。

时态三、 现在进行时
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2.时间状语:now, at this time, days, etc. look . listen
3.基本结构:be+doing
4.否定形式:be+not+doing.
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6.例句: How are you feeling today? He is doing well in his lessons.
时态四、 过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3.基本结构 s+was/were+doing
4.否定形式:s+was/were + not + doing.
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。(第一个字母大写)
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit. When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
时态五、 现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:yet,already,just,never,ever,so far,by now,since+时间点,for+时间段,recently, lately, in the past few years, etc.
3.基本结构:have/has + done
4.否定形式:have/has + not +done.
5.一般疑问句:have或has。
6.例句:I've written an article. The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years.
时态六、 过去完成时
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc.
3.基本结构:had + done.
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left. By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books
基本结构:主语+had+过去分词(done)
①肯定句:主语+had+过去分词+其他
②否定句:主语+had+not+过去分词+其他
③一般疑问句:Had+主语+过去分词+其他
④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
时态七、 一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
3.基本结构:主语+am/is/are+going to + do;will/shall + do.
4.否定形式:am/is/are not going to do ;will/shall not do。
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies. It is going to rain.
时态八、 过去将来时
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:was/were+going to + do;would/should + do.
4.否定形式:was/were/not + going to + do;would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6.例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day. I asked who was going there.
时态九、将来完成时
1.概念:在将来某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态
2.时间状语:by the time of;by the end of+时间短语(将来);by the time+从句(将来)
3.基本结构:be going to/will/shall + have done
4.例句:By the time you get back,great changes will have taken place in this area.
时态十、现在完成进行时
1.概念:表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到现在的动作。这一动作可能刚刚开始,也可能仍在继续,并可能延续到将来。
2.基本结构:have/has +been+doing
3.时间状语:since+时间点,for+时间段等。
4.例子:I have been sitting here for an hour. The chirdren have been watching TV since six o'clock.
时态十一、 一般过去时与现在完成时的转换
在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能。
但是,可用别的表达方式:
①瞬间动词用于“一段时间 + ago”的一般过去时的句型中;
②瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用;
③瞬间动词用于“It is + 一段时间 + since + 一般过去时”的句型中,表示“自从……以来有……时间”的意思,主句一般用it is来代替It has been;
④瞬间动词用于“Some time has passed since + 一般过去时”的句型中。
请看:
A. He joined the League two years ago.
B. He has been in the League for two years.
C. It is two years since he joined the League.
D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
时态十二、 一般现在时与现在进行时的转换
在一般现在时中,at加上名词表示“处于某种状态”,如atwork(在工作),atschool(上学、上课)等。此短语可与进行时态转换。
请看: Peter is at work, but Mike is at play. Peter is working, but Mike is playing.
时态十三、 现在进行时与一般将来时的转换
在现在进行时态中go, come, leave, start, arrive等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作。如:I am coming, Mum! 意为“我就来,妈妈!”请看: The train is leaving soon. The train will leave soon.
时态 互相转换英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
十六种时态所谓“时”就是行为发生的时段或状态存在的时段,即:现在、过去、将来和过去将来四种;所谓“态”就是行为或状态发生时说呈现的状态,有一般状态、进行状态、完成状态或完成进行状态四种。由时和态结合,便形成下列十六种时态: 一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,一般过去将来时; 现在进行时,过去进行时,将来进行时,过去将来进行时; 现在完成时,过去完成时,将来完成时,过去将来完成时; 现在完成进行时,过去完成进行时,将来完成进行时,过去将来完成进行时。
以上就是关于英语八大时态各造八个句子,英语八种时态基本句型主被动的全部内容,以及英语八大时态各造八个句子 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
