本文目录
英语六大时态的思维导图
英语不是只有六个时态,而是十六种时态,而德语中则有八种时态。
英语的时间可以分为现在时、过去时、将来时和过去将来时(也就是从过去某一点看将要发生的事情),而发生的方式可以分为一般、进行、完成和完成进行四种,这样就组合成了英语的十六种时态,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、过去将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时、过去将来完成时、现在完成进行时、过去完成进行时、将来完成进行时和过去将来完成进行时。
而德语中没有进行时,所以德语只有八种时态,也就是一般现在时、一般过去时、第一将来时、第一过去将来时、现在完成时、过去完成时、第二将来时、第二过去将来时。第一过去将来时和第二过去将来时很少使用。
希望我能帮助你解疑释惑。
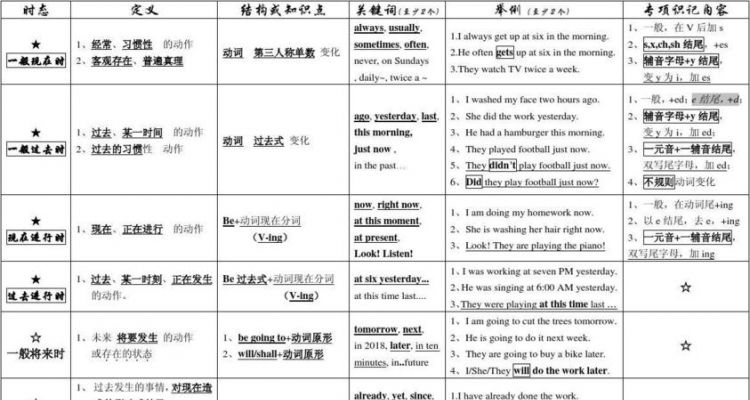
英语六大时态的思维导图
一 、一般现在时
1、概念:一般现在时可用来表示经常性或习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态;表示事实和客观真理等。
2.时间状语:
Always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week (day, year, month…), on Sundays (on Mondays…), 等
3.基本结构:
主语+be(am,is,are)
主语+行为动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式)
4.否定形式:
主语+am / is / are+not+其他;
主语+don't/doesn't+行为动词原形+其他;
5.一般疑问句:
把 be 动词放于句首;
用助动词 do、does(主语为第三人称单数用),同时,还原行为动词。
eg:
①It seldom snows here. 这里很少下雪。
②He is always ready to help others. 他总是乐于帮助别人。
③Action speaks louder than words.事实胜雄辩。
二 一般过去时
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.时间状语:
ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week, last (year,night,month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time,etc.
3.基本结构:
主语+动词的过去式或 be 的过去式+名词
4.否定形式:
主语+was / were+not+其他;
主语+didn't+行为动词原形+其他;
5.一般疑问句:
was 或 were 放于句首;
Did+主语+行为动词原形+其他;
eg:
①She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。
②I didn't know you were so busy.我不知道你这么忙。
三 、一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.时间状语:
tomorrow, next day (week,month, year…),
soon, in a few minutes, the day after tomorrow,etc.
3.基本结构:
主语+am/is / are+going to+do+其它;
主语+will / shall+do+其它
4.否定形式:
主语+am /is/ are not going to+do;
主语+will / shall not do+其它
5.一般疑问句:
be 放于句首;will / shall 提到句首。(首字母大写)
eg:
①They are going to have a competition with us in studies.他们将在学习中与我们竞争。
②It is going to rain.天要下雨了。
四、 现在进行时
1.概念:
表示现在或现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的事。
2.时间状语:
now, at this time,, at the moment,these days, look, listen, etc.
3.基本结构:
主语+be+doing+其它
4.否定形式:
主语+be+not+doing+其它
5.一般疑问句:
把be动词放于句首。
eg:
①Are you feeling good today?
你今天感觉如何?
②He is doing well in his lessons.
在课上他表现得很好。
五 过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:
at this time yesterday, at that time ;
at 7 am yesterday, at that time,
when / while引导的时间状语从句等,以 when 引导的谓语动词是一般过去时,while加过去进行时。
3.基本结构:
主语+was / were+doing+其它
4.否定形式:
主语+was/were+not+doing+其它
5.一般疑问句:
把 was 或 were 放于句首。(第一个字母大写)
eg:
①At that time she was working in a company.
那段时间她在一家公司工作。
②When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
他进来时,我正在读报纸。
六现在完成时
1.概念:
表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,也可表示过去发生的动作一直持续到现在。
2.时间状语:
yet, already, just, never, ever,
so far,
since+时间点,for+时间段,
recently, lately, in the past few years,etc.
3.基本结构:
主语+have / has+过去分词+其它
4.否定形式:
主语+have / has+not+过去分词+其它
5.一般疑问句:have 或 has 放句首。
eg:
①I've written an article.
我已经写了一篇论文。
②The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years.
在过去的几年,农村发生了巨大的变化。
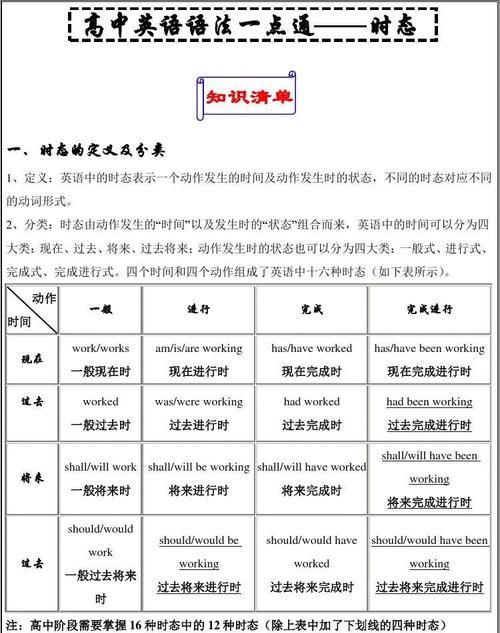
英语六大时态结构和标志词
在英语语法中,“时”指动作发生的时间,“态”指动作的样子和状态。六大时态结构以及各自的标志词分别如下:
1、一般现在时
表示习惯性、通常性、规律性、事实性的动作或状态,或者动作有时间规律发生的事件的一种时间状态。又或者是描述主语的状态、性质、特征、能力。
标志词包括every day 、often、on Sundays等。例句:I often eat oranges.我经常吃桔子。
2、一般过去时
表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。标志词包括ago 、yesterday、last night、once upon a time(过去曾经)。
例句:I ate oranges last night.我昨晚吃了桔子。
3、一般将来时
表示将来某一时段的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。它的构成形式是will + 动词原形。
标志词包括will、in an hour(一小时后)。例句: I will eat an orange in an hour. 我一个小时后将会吃一个桔子。

4、现在进行时
表示现在进行的动作或存在的状态。现在进行时表示动作发生的时间是“现在”,动作目前的状态是“正在进行中”。在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
它的构成形式是be+动词的ing形式。标志词为look、now、 listen。例句:I am eating oranges.我正在吃桔子。
5、过去进行时
表示过去在某一时间段或某一段时间内正在发生或进行的动作。它的构成形式是was/ were+动词的ing形式。标志词为at ten yesterday、at that time等。
6、现在完成时
表示过去的动作或状态持续到现在,对现在造成的影响,可能持续发生下去。它的结构形式是have /has + 过去分词。标志词为already(肯定)、yet(否定/ 疑问)、jus等。
英语六种时态
最简单的记法是:
一般过去时 S+V(pt)+O
过去进行时 S+was/were+Ving
过去完成时 S+had+V(pp)+O
一般现在时 S+V+O
现在进行时 S+am/is/are+Ving
现在完成时 I+have/has+V(pp)+O
一、 一般现在时:
用动词原型表示,但单数第三人称后要加-s,在词尾加-s时要注意:
1. 一般情况:加-s 例:reads,writes,says2. 以s,x,ch,sh收尾的词加-es 例:teaches,washes,guesses3. 以辅音字母+y结尾的词变y为i再加-es 例:try—tries,carry—carries。这个时态的疑问句一般以句首加助动词do,does构成。句中动词要用原型动词be提前:do you know it?are you students?does she have a pen?1.一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作:we always care for each other and help each other。they cycle to work every day。
2.现在的特征或状态:he loves sports。do you sing?a little。i major in english。
3. 遍真理:light travels faster than sound。two and four makes six。the moon moves round the earth。有些表示状态和感觉的动词常常可用于一般现在时:be,love,like,hate,want,hope,need,prefer,wish,know,understand,remember,believe,recognize,guess,suppose,mean,belong,think(以为),feel,envy,doubt,remain,consist,contain,seem,look(看起来),see,fit,suit,owe,own,hear,find,suggest,propose,allow,show(说明),prove,mind(在意),have(有),sound(听起来),taste(尝起来),matter,require,possess,desire等等。i feel a sharp pain in my chest。the soup contains too much salt。 you see what i mean?the coat fits you very well。how do you find the book?有些表示动作的动词间或可用于这一时态,表示现刻的动作,由于动作持续时间机短,用于进行时不自然:i send you my best wishes。i salute your courage。now i extend my heartfelt thanks to you。在口语中这个时态用来表示一个按规定、计划或安排发生的情况(这是都有一个表示未来时间的状语):when do the train leave(stop at jinan)?the plane take off at 11 am。tomorrow is saturday。is there a firm on tonight?但这只限少数动词,如begin,come,go,leave,sail,start,arrive,return,dine,end,stop,depart,open,close,be等。另外,在时间或条件从句中,将来动作或状态多用这一时态表示:tell her about that when she come。turn off the light before you leave。we‘ll start as soon as you are ready。在口语中,这个时态间或可以用来表示一个已经发生的动作(这个动作发生的时间在说话人脑中处于很不重要的地位):they say xiao wu is back。is that true?xiao yu tells me you‘re going abroad。oh,i forget where he lives。yes,you answer quite well。此外一般现在时还多用于报刊、电影、电视解说等其他几种情况。
二、 现在进行时
现在进行时用助动词be的人称形式加现在分词构成,它的肯定、否定、疑问形式如下:i am working。i am not working。am i working?现在进行时主要表示现在或现在这一阶段正在进行的动作。where are they having the basket-ball match?they are putting up the scaffolding。he‘s showing a foreign guest round the city。在不少情况下,表示正在进行的动作的汉语句子,并没有“正在”这样的字,在译为英语时却必须用进行时态:how are you getting on with the work?the work is going fairly smoothly。you are making rapid progress。it is blowing hard。who are you waiting for?whenever i see her,she is working in the garden。我每次看到她时,她总是在花园里干活。在一般现在时所列的表示状态和感觉的动词,一般不能用于进行时态,因为他们不能表示正在进行的动作。但如果词义转变,能表示一个正在进行的动作,就能够用于进行时态,试比较下面的句子:do you see anyone over there?你看到那里有什么人吗?are you seeing someone off?你在给谁送行吗?i hear someone singing。我听见有人唱歌。they are hearing an english talk?他们在听一个英语报告。what do you think of it?你觉得这怎么样?what are you thinking about?你在想什么?另外,表示无法持续动作的动词,一般不宜用于进行时态,但有些可以用于这个时态表示重复、即将等:he is jumping up and down。她一上一下地跳着。the train is arriving。火车就要进站了。the old man is dying。老头病危了。
现在进行时有时可用来表示一个在最近按计划或安安排要进行的动作(这是多有一个表示未来时间的状语):we are leaving on friday。are you going anywhere tomorrow?a foreign guest is giving a lecture in english this afternoon。xiao hong!coming。who is interpreting for you?we are having a holiday next monday。但这仅限于少量动词,如go,come,leave,start,arrive,lunch,return,dine,work,sleep,stay,play,do,have,wear等。
另外,“be going+不定式”这个结构经常用来表示即将发生的事或打算(准备)做的事:i am afraid it is going to rain。it is going to be rather cold tomorrow。she is not going to speak at the meeting。在这个结构中过去有许多人不赞成用go和come这两个动词,感到很别扭,主张不说are you going to go anywhere tomorrow?而说are you going anywhere tomorrow?不说is she going to come?而说is she coming?但现在在这种结构中用两个动词的人越来越多,这种用法基本上被大家接受了。此外,在时间和条件状语从句中,间或也可用现在进行时表示将来的情况或一般情况:do not mention this when you are talking with him。remember that when you are taking a rest,some else is always working。if she is still sleeping,do not wake her up。
现在进行时有时用来代替一般现在时,表示一个经常性动作或状态,这是或是为了表示一种感情(a)如赞叹、厌烦等,或是为了强调情况的暂时性
(b)a. how are you feeling today?(比how do you feel today?更显亲切)xiao hua is doing fine work at school。(比xiao hua does fine work at school。更富赞美)he is always thinking of his work。表赞许he is constantly leaving his thing about。她老是乱扔东西。(表不满)he is always boasting。他老爱说大话。(表厌烦)
b.he is sleeping in the next room now。他现在现在是在隔壁房间睡了(不再原来房间睡了)。the professor is typing his own letters while his secretary is ill。where is he working?他现在在那里工作?(可能刚换工作)for this week we are starting work at 7:30。he is walking to work because his bicycle is being repaired。be间或可用于进行时态,表示一时的表现:you are not being modest。he is being silly。she is being friendly。xiao hong is being a good girl today。do not talk rot。i am being serious。注: 在there和here引起的句子中,常可用一般现在时代替现在进行时:here comes the bus。(=the bus is coming.)there goes the bell. (=the bell is ringing.)在某些情况下两种情况都可以用,没有多少差别:i wonder (am wondering) how i should answer then.does your leg hurt? (is your leg hurting?)it itches (is itching) terribly.my back aches (is aching).i write (am writing ) to inform you.
三、 一般将来时
一般将来时由助动词shall或will加动词原型构成,shall用于第一人称,will用于第二、三人称。这个时态的肯定、否定及疑问机构可表示如下:i shall go.i shall not go.shall i go?除英国以外的说英语的国家,在陈述句中,即使在第一人称一般也用will,在英国也有这种趋势,在口语中常紧缩为i’ll.
一般将来时表示将要发生的动作和情况:i will (shall) arrive tomorrow.will you be busy tonight?the agreement will come into force next spring.we won’t (shan’t) be free tonight.有时表示将来的时间状语,有时没有时间状语,这时要从意思上判断是否指未来的动作或情况:i will think it over.who will take the chair?will she come?they won’t object it.在以i 或 we 作主语的问句中,一般用shall,这时或是征求对方的意见(a),或是询问一个情况(b):a. shall i make a fair copy of it?which book shall i read first?where shall we meet?b. shall we have any classes tomorrow?when shall we have the rehearsal?shall i be able to find them there?在这类问句中,近年来也有不少人用will,特别是美国。what will we do?how will get there?which will i take?注意在时间或条件状语从句中,一般不能用将来时态,而用现在时态代替:i’ll let you have the book when i’m through.they’ll fight till they win complete victory.i’ll be round to see you if i have time tomorrow.
注:在两种情况下条件从句可以用一般将来时:1. 表示愿望:if they won’t cooperate, our plan will fall flat.2.主句的谓语表时现在的情况:if he won’t arrive this morning, why should we wait here。表示将要发生的动作或情况,除了一般将来时外,还有一些其他结构和时态:1. be going +不定式(表打算、准备作的事或即将发生或肯定要发生的事):we ‘re going to put up a building here.how are you going to spend your holiday?who is going to speak first?2. be +不定式(表示按计划安排要发生的事或用来征求对方的意见):when is the factory to go into production?the line is (going) to be opened to traffic next week.am i to (=shall i ) go on with the work?3.一般现在时(限于某些动词,表示按计划或时刻要发生的事):school finishes on january 18th.we get off at the next stop.when does the winter vacation begin?
4.现在进行时(限于某些动词,表示按计划安排要发生的事):we are having an english evening tonight.they are playing some folk music next.i am talking the children to the zoo (on sunday ).在单纯表示将来情况,特别是谈一连串的事情或在带时间或条件状语从句的句子中,谓语多用将来时:next term i will try to do better. i’ll speak more english and do more reading-aloud.he’ll come to see you when he has time.he’ll tell you if you ask him.在表示打算或准备时,如不提时间、条件等,多用be going to这个结构,用一般将来时时很少的,特别是在口语中:he is going to buy a dictionary.(很少说he will buy a dictionary.)在谈即将发生的情况时,用be going to 这个结构也多一些。在表示按计划安排要做得事时,用be to 的时候也不少。另外还有将来进行时等时态也可表示将来的动作。注:be about to 可表示即将作某事we are about to leave.he is about to retire.一般将来时有时还可用来表示一种倾向或习惯性动作:a drowning man will catch at a straw.crops will die without water.oil will float on water.注:这一时态有时用来表示揣测(a)或容量(b):a. that man in the middle will be the visiting minister.b. the hall will seat 500people.
以上就是关于英语六大时态基本结构,英语六大时态的思维导图的全部内容,以及英语六大时态基本结构 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
