本文目录
不定代词的作用用法
不定代词的定义
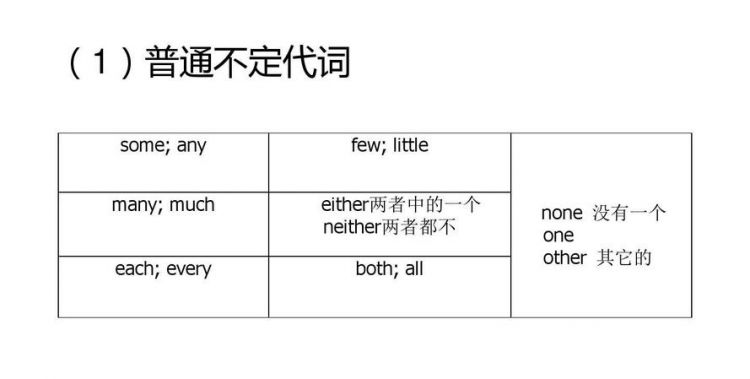
常用不定代词有: some,any,all ,none,both,either,neither,each, every,other,another,much, many,few,little,one,nothing,nobody和where。 一般来讲,修饰不定代词的词要置于其后。
一、不定代词的用法
不定代词大都可以代替名词和形容词,在句中作主语、宾语、表语和定语。
1.作主语
Both of them are teachers.他们两人都是教师。
2.作宾语
I know nothing about this person.我对这个人一无所知。
3.作表语
This book is too difficult for a child.这本书对一个小孩来说太难了。
4.作定语
There is a little water in the glass.玻璃杯里有一些水。 修饰不定代词的词,一般情况下要后置
二、常用不定代词用法举例
一般不定代词用法例子
1.some 一些,某些,某个 不定代词some可以代替名词和形容词,常用在肯定句中作主语、宾语、定语等。作定语时,它可以修饰可数名词(单、复数皆可)和不可数名词。例如: some are doctors,some are nurses.有些人是医生,有些人是护士。(作主语)
2.any一些,任何 不定代词any可以代替名词和形容词,常用在否定句或疑问句中作主语、宾语、定语等。作定语时,它可以修饰可数名词(多为复数)和不可数名词。例如: there isn’t any ink in my pen.我的钢笔没有墨水。(作定语) 不定代词any有时也可以用在肯定句中,表示"任何的"。例如: you may come at any time;i’ll be home the whole day.你任何时候来都行,我整天都将呆在家里 。 不定代词any也可以用作副词,做状语,表示程度。例如: is he any better today?他今天好一点了吗?
3.all 全体,所有(指三者以上) 不定代词all在句中可以作主语、宾语、表语、定语或同位语。它可以代表或修饰可数名词和不可数名词。代表或修饰可数名词时,指两个以上的人或物。作先行词时,引导词用that。例如: all were present at the meeting.全都到会了。(作主语,代表可数名词) 4.both 全部,都 不定代词both指两个人或事物。和all一样,可以用作主语、宾语、定语或同位语。例如: we invited both to come to our farm.我们邀请两个人都来我们的农场�(作宾语)
5.none 无人或无 不定代词none的含义和all物相反,和no one,not any同义,但其用法相当于名词,在句子中一般作主语或宾语。它代替不可数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式;代替可数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单、复数皆可。例如: none of the problems is /are easy to solve.这些问题没有一个是容易解决的。(作主语, 代替可数名词)
6.either 两者之中的任何一个,这个或那个。 不定代词 either 可以作主语、宾语和定语。例如: either of them will agree to this arrangent.他们两人中会有人同意这样的安排的。(作主语)
7.neither 两个之中一个也不是 不定代词 neither 是 either 的否定形式,可以作主语、宾语和定语。例如: neither is interesting.两个都没有趣。(作主语)
8.each 每个,各自的 不定代词each指每一个人或事物的个别情况,甚至指这些个别情况各不相同。它在句中可以作主语、宾语、定语和同位语。例如: she gave the children two apples each.她给了每个小孩两个苹果。(作the children的同位语。)
9.every 每个,每一的,一切的 不定代词every有"全体"的意思,和all的意义相近,但只能作定语。
复合不定代词使用例子
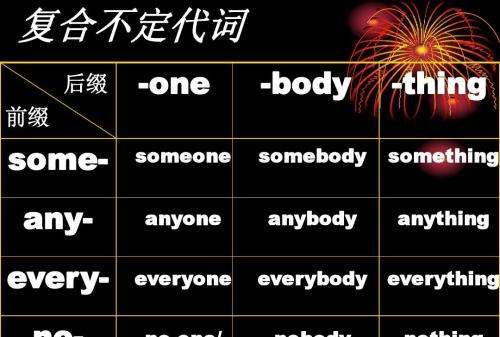
1. some, any, every, no都能和one, body, thing一起构成代词,这些代词叫复合不定代词。它们基本含义为: 指 人 somebody someone 某人 anybody anyone 任何人 everybody everyone每人 nobody no one 没人 指物 Something某物某事 anything任何事物 everything一切 nothing没东西
2. 一般情况下,some构成的复合不定代词,其作用和some相同,用于肯定句;any构成的复合不定代词用于否定句或疑问句;no构成的复合不定代词表示否定含义,用于否定句。如: ① I have something to tell you. 我有事要告诉你。 ② He didn’t say anything at the meeting yesterday. 昨天在会上他没发言。 ③ Everybody likes swimming. 每个人都喜欢游泳。 ④ There is nothing wrong with your ears. 你耳朵没毛病。
3. something可用于提建议或请求的问句中,以及希望说话对方作出肯定回答的问句中。如: Would you like something to eat? 你要吃点东西吗?
4. 复合不定代词在句子中作主语时,谓语动词一般用单数形式。如: Nobody knows his name. 没有人知道他的名字。
5. 不定代词的定语要后置。如: Is there anything important in today’s newspaper? 今天的报纸上有什么重要新闻吗?
常用单三形式
一般的,不定代词(包括复合不定代词)在句子中,通常用单三形式
1.不定式是英语动词的一种形式。它在许多情况下可省略"to",它不同于汉语动词,汉语动词只有一种形式。如:我看书。她看书。但英语要说“看”必须根据主语的人称,动作发生的时间等确定其形式。如:1)I read a book. 2)She reads a book.1)句中的“read” 是一般现在时第一人称的动词定式。2)句中的“reads”是一般现在时第三人称单数的动词定式。 I want to read a book./She wants to read a book. 我想要看书。她想要看书。其中的“看”不易确定其形式。因为动作还未发生,因此称不定式。通俗的说,就是“不一定是什么形式”
2.不定代词是不指明代替任何特定名词或形容词的代词,英语中不定代词有:some(something,somebody,someone),any(anything,anybody,anyone), no(nothing,nobody,no one), every(everything,everybody,everyone),all,each,both,much,many,(a)little,(a)few,other(s),another,none,one,either, neither等。
1) 陈述部分的主语是I,疑问部分要用 aren't I. I'm as tall as your sister,aren't I?
2) 陈述部分的谓语是wish,疑问部分要用may +主语。 I wish to have a word with you, may I?
3) 陈述部分用 no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词时,疑问部分用肯定含义。 The Swede made no answer, did he / she? Some plants never blown (开花), do they ?
4) 含有ought to 的反意疑问句,陈述部分是肯定的,疑问部分用shouldn't / oughtn't +主语。 He ought to know what to do, oughtn't he? / shouldn't he?
5) 陈述部分有have to +v. (had to + v.),疑问部分常用don't +主语(didn't +主语)。 We have to get there at eight tomorrow, don't we?
6) 陈述部分的谓语是used to 时,疑问部分用didn't +主语或 usedn't +主语。 He used to take pictures there, didn't he? / usedn't he?
7) 陈述部分有had better + v. 疑问句部分用hadn't you? You'd better read it by yourself, hadn't you?
8) 陈述部分有would rather +v.,疑问部分多用 wouldn't +主语。 He would rather read it ten times than recite it, wouldn't he?
9) 陈述部分有You'd like to +v. 疑问部分用wouldn't +主语。 You'd like to go with me, wouldn't you?
10) 陈述部分有must 的疑问句,疑问部分根据实际情况而定。 He must be a doctor, isn't he? You must have studied English for three years, haven't you? / didn't you? He must have finished it yesterday, didn't he?
11) 感叹句中,疑问部分用be +主语。 What colours, aren't they? What a smell, isn't it?
12) 陈述部分由neither… nor, either… or 连接的并列主语时,疑问部分根据其实际逻辑意义而定。 Neither you nor I am engineer, are we?
13) 陈述部分主语是指示代词或不定代词everything, that, nothing, this, 疑问部分主语用it。 Everything is ready, isn't it?
14) 陈述部分为主语从句或并列复合句,疑问部分有三种情况:
a. 并列复合句疑问部分,谓语动词根据邻近从句的谓语而定。 Mr. Smith had been to Beijing for several times, he should have been in China now, shouldn't he?
b. 带有定语从句,宾语从句的主从复合句,疑问部分谓语根据主句的谓语而定: He is not the man who gave us a talk, is he? He said he wanted to visit Japan, didn't he?
c. 上述部分主句谓语是think, believe, expect, suppose, imagine等引导的定语从句,疑问部分与宾语从句相对应构成反意疑问句。 I don't think he is bright, is he? We believe she can do it better, can't she?
15) 陈述部分主语是不定代词everybody, anyone, somebody, nobody, no one等,疑问部分常用复数they,有时也用单数he。
This is our new headmaster, isn’t it?
Those are Japanese, aren’t they?
One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?
One can’t be too careful, can you?
Each of the students has a dictionary, hasn’t he?
Each of the students passed the examination, didn’t they?
None of his money is left, is it?
None of his friends are interested, are they?
None of his friends has come, has he?
Something will have to be done about the price, won’t it? Everybody is kind to you, aren’t they?
No one left here yesterday, did they?
Someone turned that radio down, don’t they?
Neither side could win, could they?
Everything that he says is false, isn’t it?
I am older than you, aren’t I / ain’t I?
I am working now, ain’t I / am I not?
I wish to see the movie now, may I?
I wish I were you, may I?
16) 带情态动词dare或need的反意疑问句,疑问部分常用 need (dare ) +主语。 We need not do it again, need we ? He dare not say so, dare you? 当dare, need 为实义动词时,疑问部分用助动词do + 主语。 She doesn't dare to go home alone, does she?
17) 省去主语的祈使句的反意疑问句,疑问部分用will you。
Don't do that again, will you? Go with me, will you / won't you ? 注意: Let's 开头的祈使句,后用shall we?
Let us 开头的祈使句,后用will you? Let's go and listen to the music, shall we? Let us wait for you in the reading-room, will you ?
18) 陈述部分是"there be"结构的,疑问部分用there省略主语代词。 There is something wrong with your watch, isn't there? There will not be any trouble, will there?
19) 否定前缀不能视为否定词,其反意疑问句仍用否定形式。
It is impossible, isn't it?
He is not unkind to his classmates, is he?
20) must在表"推测"时,根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句。
He must be there now, isn't he?
It must be going to rain tomorrow, won't it?
快速记忆表 陈述部分的谓语 疑问部分 I aren't I Wish may +主语 no,nothing,nobody,never, few, seldom, hardly, 肯定含义 rarely, little等否定 含义的词 ought to(肯定的) shouldn't/ oughtn't +主语 have to+v.(had to+v.) don't +主语(didn't +主语) used to didn't +主语或 usedn't +主语 had better + v. hadn't you would rather + v. wouldn't +主语 you'd like to + v. wouldn't +主语 must 根据实际情况而定 感叹句中 be +主语 Neither…nor, either…or 连接的根 据其实际逻辑意义而定 并列主语 指示代词或不定代词 everything,that, 主语用it nothing,this 并列复合句 谓语根据邻近从句的谓语而定 定语从句,宾语从句的 主从复合句 根据主句的谓语而定 think,believe,expect, suppose,imagine等引导 与宾语从句相对应的从句 everybody,anyone, somebody,nobody,no one 复数they, 单数he 情态动词dare或need need (dare ) +主语 dare, need 为实义动词 do +主语 省去主语的祈使句 will you? Let's 开头的祈使句 Shall we? Let us 开头的祈使句 Will you? there be 相应的谓语动词+there(省略主语代词) 否定前缀不能视为否定词 仍用否定形式 must表"推测" 根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句
不定代词each和every的用法区别
不定代词是不指明代替任何特定名词或形容词的代词,英语中不定代词有:some(something,somebody,someone),any(anything,anybody,anyone),no(nothing,nobody,no one),every(everything,everybody,everyone),all,each,both,much,many,(a)little,(a)few,other(s),another,none,one,either,neither等.
不定代词的用法比较
1)all,every和each的比较
all在表示抽象的整体概念时,作单数,相当于everything(一切东西),例:
All was destroyed in the big fire.
大火中一切都毁了.
Grasp all,lose all.
什么都抓,什么都抓不住.(谚)
Is that all you Want to know?
你想知道的就这些吗?
all指人时用作复数,意为指三者以上的“全部”、“全体”,相当于everyone(每个),例:
All are present.
大家都出席了.
There is room for all of us.
我们所有的人全坐得下.
She knows us all.
她认识我们所有的人.
all在人称代词前面,只能用all of,而且要与人称代词的宾格us,you,them等连用,如:all of us,而不能说成all us.
every用于三个或三个以上的人或物,是“每一个”的意思,只能作定语,强调整体概念,例:
Every player is present.
每个运动员都出场了.
They helped us in every way.
他们从各方面帮助我们.
在表示“每个”、“全体”意思时,every的意思与all很接近.但一般情况下every和单数名词搭配,all和复数名词搭配,例:
Every child enjoys Christmas.
每个孩子都喜欢过圣诞节.
All children enjoy Christmas.
所有的孩子都喜欢过圣诞节.
Each也是“每一个”的意思,但与every不同,each用于指两个或两个以上的人或物,着重于个别概念,例:
Two men came into the room. Each carried an umbrella.
两个人走进房间,每人拿着一把伞.
Each book on this desk is worth reading.
这桌子上每一本书都值得读.
He gave three to each(of them).
他给(他们)每人三个.

不定代词的用法
不定代词有:something、somebody、someone、somewhere、anything、anybody、anyone、anywhere、nothing、nobody、no one。
everything、everybody、everyone、everywhere、all、each、both、much、many、a little、a ew、others、another、none、one、either、 neither。
不定代词可以分为很多种类,它的功能与用法也非常丰富,不定代词大都可以代替名词和形容词,在句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语和状语。
不定代词的句法功能
1、作主语
例: Both(of us) are right.
(我们)两人都对。
2、作宾语
例: There is room for all of us.
我们所有的人全坐得下。
3、作表语
例: That’s nothing.
没什么。
4、作定语
例: You may take either road.
两条路你走哪条都行。
扩展资料
1、除every 和no外,不定代词既可用作名词,也可用作形容词。every和no在句中只能作定语.
例如:I have no idea about it.
我没有任何主意。
2、all指三者以上,是“都”的意思。all的单复数由它所修饰或指代的名词的单复数决定。
例如:All goes well.
一切进展得很好。
all 通常不与可数名词单数连用,如:不说 all the book,而说 the whole book.
但all可与表时间的可数名词单数连用,如 all day,all night,all the year;但习惯上不说all hour,all century.
all还可以与一些特殊的单数名词连用,如 all China,all the city,all my life,all the way.
3、both都,指两者。both 与复数动词连用,但 both… and…可与单数名词连用。both,all 都可作同位语,其位置在行为动词前,be 动词之后。如果助动词或情态动词后面的实义动词省去,则位于助动词或情态动词之前。
Who can speak Japanese? We both (all) can.
4、neither两者都不,neither作主语时,谓语动词用单数。
作定语与单数名词连用,但neither… nor 用作并列连词,可与复数名词连用。其谓语采用就近原则。
5、如前句是否定式从句,则主句用neither,而不用 nor。
If you don't do it,neither should I.
如果你不干,我也不干。
6、如后连续有几个否定句式,则用nor,不用neither。
He can't sing,nor dance,nor skate.
7、some 某些,一些,某个
不定代词some可以代替名词和形容词,常用在肯定句中作主语、宾语、定语等。作定语时,它可以修饰可数名词(单、复数皆可)和不可数名词。
例如:some are doctors,some are nurses.
有些人是医生,有些人是护士。
8、any一些,任何
不定代词any可以代替名词和形容词,常用在否定句或疑问句中作主语、宾语、定语等。作定语时,它可以修饰可数名词(多为复数)和不可数名词。
例如:there isn’t any ink in my pen.
我的钢笔没有墨水。(作定语)
9、不定代词any有时也可以用在肯定句中,表示"任何的"。
例如:you may come at any time;I’ll be home the whole day.
你任何时候来都行,我整天都将呆在家里。
10、不定代词any也可以用作副词,做状语,表示程度。
例如:is he any better today?
他今天好一点了吗?
11、none 无人或无
不定代词none的含义和all物相反,和no one,not any同义,但其用法相当于名词,在句子中一般作主语或宾语。它代替不可数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式;代替可数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单、复数皆可。
例如:one of the problems is /are easy to solve.
这些问题没有一个是容易解决的。(作主语, 代替可数名词)
12、each 每个,各自的
不定代词each指每一个人或事物的个别情况,甚至指这些个别情况各不相同。它在句中可以作主语、宾语、定语和同位语。
例如:he gave the children two apples each.
她给了每个小孩两个苹果。(作the children的同位语)
13、every 每个,每一的,一切的
不定代词every有"全体"的意思,和all的意义相近,但只能作定语。
初中英语语法不定代词的用法有哪些
很多同学都英语的不定代词都不甚了解,但是在我们常见的英语学习当中,不定代词又是很常见的学习。下面就和我一起了解一下,供大家参考。
(一)some的用法
(1)some通常指不定数量“一些”修饰代替可数名词复数或不可数名词,即可以指人,又可以指物。常用在肯定句中。eg.He has some Chinese paintings.
(2)some也可以用在表示“请求,建议,反问”的句子中,期待得到对方的肯定回答。eg. Would you like some coffee?
(3)some有时可以修饰单数可数名词,表示“某个”eg.This morning, some boy asked for you.
(4)some也可以修饰数词,表示“大约”eg.It took me some twenty days to get there.
(二)any的用法
(1)不定代词any和some一样表示不定数量“一些”,修饰和代替可数名词复数和不可数名词,既可指人又可指物。但一般用在否定句、疑问句,条件从句中。eg.Ask me if you have any questions?
(2)用于肯定句中,表示“任何—个”,修饰单数可数名词和不可数名词。eg.I don't know any of you.
(三)no的用法
(1)不定代词no只有形容词性质.—般作定浯来构成否定句,表示“不是”、“没有"’。
(2)用于警告、命令等。eg. No Parking!
(3)修饰表语时,有特殊的意思。试比较:eg.I am no teacher.I am not a teacher.
(四)none的用法
none只具有名词性质,可以代替人和事物,表示“三者(以上)都不”,“没有一个人(一件事物)。做主语时,如果谈到的是所有人的情况,动词多用复数形式;如果谈每个人的状况,则多用单数形式。它在句中还可充当同位语。eg.None of us are / is afraid of difficulties.
none和neither的区别:none表示“在三个或三个以上当中,没有人或物...";而neither指“在两个当中,没有人或物”。eg.None of the students has ever read the book.
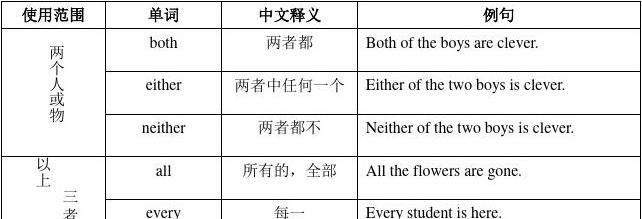
(五)both的用法
both的意思是“两个都”, 具有名词和形容词的性质,可做主语、宾语、同位语和定语。做主语时谓语动词用复数
eg:Both would like to have a try.
a.both后常跟of短语,of+名词,代词(复数),接复数名词时of常省略,接复数代词时of则不省略。
b.both在句中还用做同位语,其位置取决于谓语动词的形式。
(1)做主语同位语时,如谓语为实义动词(包括用做实义动词的have),both位于主语之后、谓语动词之前。如:We both had a haircut.我俩都理了发。
(2)如谓语部分为系动词,both则位于系动词之后和表语之前。如:The children were both too young.
(3)如谓语是含有助动词或情态动词的短语,both则位于助动词或情态动词之后。如:My parents have both been invited.
(六)all的用法
(1)当all做主语时,常代表三个以上的人,谓语动词用复数形式;指事物或情况时。往往表示“—切”、“所有的”意思,常被看作单数意义,谓语动词用单数形式。当all做定语时,既可修饰可数名词,也可修饰不可数名词。all具有名词和形容词性质,常表示“全体”、“所有的”、“一切”的意思;在句中可用做主语、宾语、表语、定语、同位语或状语。eg.All are here.
(2)当all用做主语时,如果后面跟有人称代词。须在它们之间加上of;如果后面跟的是名词,它们之间可of,也可不加。eg. All of them are from Beijing.
(3)当all做同位语时.它在句中的位置随谓语动词而定。当谓语动词是实义动词时,all放在动词前面;谓语动词是be时.all放在be后面;谓语是由情态动词或助动词加实义动词组成时,all放在它们之间。eg. They all know the answer.
(4)当all用做人称代词宾语的同位语时,all放在宾语后面。如 you all, them all, us all。eg. I’ll have to think about them all again.
(七)each的用法
each具有名词和形容词的性质,在句中可用做主语、定语、宾语和同位语。指每个人或事物的个别情况,相当于汉语的“各个”eg.Each of the boys has a bike.
以上就是关于英语不定代词妙用,不定代词的作用用法的全部内容,以及英语不定代词妙用 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

