本文目录
英语八大时态的构成
英语时态总结 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。在这里,我们重点讲解一下最常见的11种时态的用法和注意事项。 1. 一般现在时:小学就开始学这个,大家都会吧,有几点强调一下我们就走。 A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。If it is not too much trouble, I would like a cup of tea. B) 习惯用语:这个要在平时自己积累,因为习语太多,我不做过多解释。 Ie: Believe it or not, his discovery had created a stir in scientific circles. 口语中常说believe it or not,意思是:“信不信由你”,“我说的是真的”。believe it or not是一个固定说法,相当一个插入语,短语中的believe没有词形变化。这点要注意,以后会教你们动名词的用法,到时候会牵涉到主语的问题。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 Ie:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致.ex: He said that the sun rises in the east.这个句子要注意,到了以后的定语从句经常会有这样的问题,具体细节到 时候在说,不过你们要先有这样的概念:客观事实无论谓语的时态是什么都用一般现在时。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词 )可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 ex: When does the plan leave?这个句子注意一下,就是这么用的,有人会注意到这样的问题: The plane leaves at 3 o’clock this afternoon.为什么不用将来时,对了,很奇怪,但就是这么用的。 F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 Ie: When you finish the report, I will have waited for 3 hours.(完成时,往下看会出现) 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 的用法:上了初一就教这个吧,比一般现在还简单。表示现在正在做的动作,但要注意有的动词不能用于进行时,这类词称为短暂性动词,如,open, borrow等等,在完成时态常常会碰到,平时要注意积累。 3. 现在完成时(have done):重要考点,初二以后几乎都是完成时态。 A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 ex: I have just finished my homework. B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for 加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。这里联系进行时,他们都一样,不能用短暂性动词,★★★☆☆考点。 C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose等。 例:John has broken his left leg.(约翰摔断了左腿。) 注意: A) 现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带。现在完成时和过去时的区别在于:现在完成时强调动作的动态,或受动态的影响,是动态的结果,对现在有影响;过去时只表示过去的某个具体时间里发生的动作,与现在没有联系。 例:He worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他曾经在那家医院工作了8年。这只是讲述一个过去的事实,他现在已经不在那家医院了。) He has worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他已经在那家医院里工作了8年。表示他从过去开始工作,一直工作到现在,现在仍在那家医院工作。) B) 因为含有for加一段时间或since加一个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以不能使用终端动词或瞬间动词。 例:My sister has been married for 5 years.(过去分词做表语表示状态,可以延续) My sister has married. Don't disturb her.(终端动词) C) 在"this is the first/ second/ third…… time that……"句型里要求用完成时。 例: This is the second time that the products of our company have been shown in the International Exhibition. (这是我公司产品第二次参加国际展览会。) D) 句型"It is/ has been……since"所使用的两种时态都正确。 例:It is/ has been 10 years since I last saw him.(从我上次见到他以来已经10年了。) E) 在"no sooner than"、"hardly/ scarcely ……when"、"before"、"prior to"等句型中,主句要求完成时。 例:I haven't met that professor prior to today.(以前我从未见过那位教授。) 4. 现在完成进行时(have been doing):和现在进行时很像 1) 用法:表示某一动作开始于过去某一时间,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。 例:We have been working on this project for over a month now.(到目前为止,我们一直在处理那个项目,已经花了一个多月时间了。) 2) 注意事项:与现在完成时相比,现在完成进行时更强调:在从过去到现在的时间里,动作或状态一直持续或一直反复出现。 5. 一般过去时 A) 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。 ex:I went to Beijing last year. B) 表示过去习惯性动作。特别是由would/ used to do表达的句型,本身表示的就是过去时。 ex: I used to live here.(注意used to 和be used to 的区别,used to表过去常常,be used to 表示习惯于,前者to是不定式符号,后者则是介词,后接名词、动名词、代词) C) 有时可代替一般现在时,表达一种婉转、客气、礼貌、商量的语气。 ex: Would you mind my sitting here?(您介意我坐在这里吗?) Could you pass me the pen? 注意: A) 注意时间状语的搭配。一般过去时的时间状语应该是表示过去某个时间的词或词组,如:yesterday, last month, in 1999, two days ago等,绝对不可与recently, in the past 10 years, this month等连用,因为这样的时 间状语都与现在有关系,应该用现在完成时或一般现在时。注意,到了初二将会是★★★★☆考点,不会不行,逃不了的,几乎每次都考。 B) used to do的否定形式和疑问形式很特别:你怎么写都正确。以否定形式为例:used not to do, didn't used to do, didn't use to do都对。 6. 过去完成时(had done) 用法:表示在过去的某个时间或动作以前已经发生的动作或已经存在的状态。就是我们常说的:表示"过去的过去的动作或状态"。 画一条时间轴过去完成__●_一般过去_◇_一般现在___○______ 2) 注意事项:“过去的过去”这种逻辑关系常通过上下文体现出来,而不一定受某个时间状语的限制。 ex: There had been some one in our room just now, because I noticed a burning cigarette end on the floor when we opened the front door. 7. 过去将来时(would/ should do) 表示从过去的某个时间看将要发生的事。其实和将来时没什么区别啦。 ex: I said on Thursday I should see my friend the next day.宾从、直引经常碰到这样的例子,注意。 8. 过去进行时(was/ were doing) A) 表示在过去一个比较具体的时间正在发生的动作。 ex: I was doing my homework at this time yesterday. B) 如果when, while这样的时间状语引导词所引导的主从句之一是一般过去时,则另一个句子常用过去进行时。 ex: I was washing my hair when you knocked at the front door. 9. 一般将来时 A) 基本结构是will / shall do。古英语认为will用于第二、三人称,shall用于第一人称,但后来没做硬性规定,will比较常用。I will be home at 10. B) 有些动词,如:arrive, be close, come, do, done, go, have, leave, open, play, return, sleep, start, stay等,用于一般进行时,并且通常与一个表示将来时间的时间状语连用,可以表示将来时。初一接触比较 多的是be going to,后面的包括will/shall到了后来才出现,其他如sleep很少见,初中阶段我几乎没见过sleep这么用的, leave, come, arrive也常见 ex: My mother is coming to visit me next week and is staying here until May. C) 表示“即将、正要”时,可用be about to do。强调近期内或马上要做的事,后常与when连用。ex: I was about to speak when you interrupted me. D)"be to do"的5种用法: a) 表示“按计划、安排即将发生某事或打算做某事”。 例:She is to be seen in the lab on Monday.(星期一你准会在实验室见到她。) b) 该做或不该做的事情(语气上接近于should, must, ought to, have to),表示一种命令、规劝性语气。 例:You are to go to bed and keep quiet, kids. Our guests are arriving in less than 5 minutes.(孩子们,你们必须 上床睡觉,不准吵闹。我们的客人5分钟之内就要到了。) c) 能或不能发生的事情(接近can, may) 例:How am I to pay such a debt?(我怎么可能还得起这么大的一笔债呢?) d) 不可避免将要发生的事情,后来将要发生的事情。 例:I assure you that the matter _______ as quickly as possible. Have a little patience. A. will be attended B. will be attended to C. is attended D. is attended to will be attended to关键的一点是:attend表示“处理,解决”时是不及物动词,必须与to连用。另外,从上下文看,事情显然尚未解决,所以应该用将来时的被动语态。答案是B。 A) is to be B) can be C) will be D) has been 答案是A) is to be。全句的意思是:“如果要避免食品短缺,就必须作出更大努力来增加农业产量。” E) 同样可以表示“正要、将要”的意思的句型是be on the point of doing。 The coach is on the point of giving up the game because our team has been scored 7 points. 注意: 在以if, when, as long as, as soon as, after, before, in case, until, unless 等连词以及具有连词作用的副词(immediately, the moment, directly)等引导的状语从句,一般用现在时代替将来时。强调 延续性或动态时,可用完成时。 例:I hope his health will have improved by the time you come back next year.(我希望到明年你回来的时候,他的身体已经好多了。) 10. 将来进行时(will be doing) 调在将来的某个具体时间正在发生的动作或事情。 ex: Don't worry, you won't miss her. She will be wearing a red T-shirt and a white skirt at that time. 11. 将来完成时(will have done) 表示从将来的某一时间开始、延续到另一个将来时间的动作或状态,或是发生在某个将来时间,但对其后的另一个 将来时间有影响的动作或状态。就好象把现在完成时平移到时间轴的将来时时段一样。其用法从和过去及现在有关,变成了和将来及将来的将来有关。 ex: It is reported that by the end of this century the people of Chinese will have increased by 2 billion. 一般现在时: 主语+ be(is, am , are)/do/does + 其它 一般过去时: 主语 + be(was, were) + 其它 一般将来时: 主语 + will be / will do + 其它 一般过去将来时: 主语 + would be/ would do+ 其它 现在进行时: 主语+ be(is, am, are) doing + 其它 过去进行时: be(was, were) doing 将来进行时: will be doing 过去将来进行时: would be doing 现在完成时: have/has done 过去完成时: had done 将来完成时: will have done 过去将来完成时: would have done 现在完成进行时: have/ has been doing 过去完成进行时: had been doing 将来完成进行时: will have been doing 过去将来完成进行时: would have been doing
采纳哦
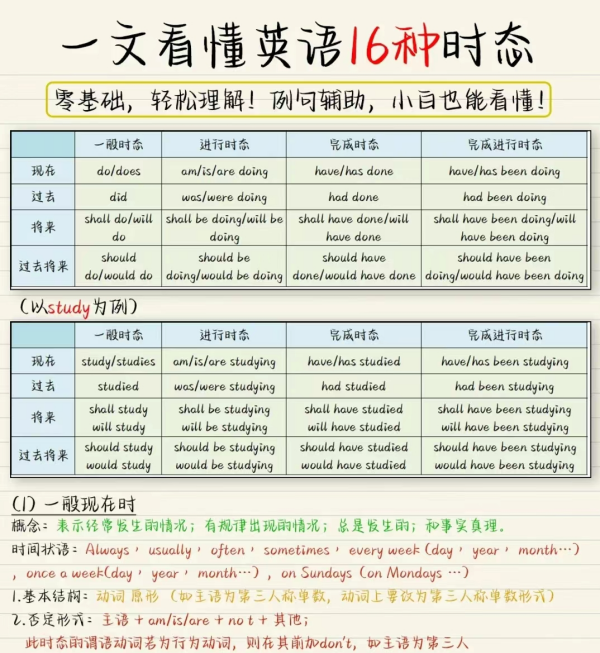
英语的16种时态的结构图
以Study为例:
一般时:1、现在 study 2、过去 studied 3、将来 will study 4、过去将来 would study
进行时:1、现在 studing 2、过去 was/were studing 3、将来 will be studing 4、过去将来 would be studing
完成时:1、现在 have studied 2、过去 had studied 3、将来 will have studied 4、过去将来 would have studied
完成进行时:1、现在 have been studying 2、过去 had been studying 3、将来 will have been studying 4、过去将来 would have been studying
一般时态 进行时态 完成时态 完成进行时态
现在 do/does am/is/are doing have/has done have/has been doing
过去 did was/were doing had done had been doing
将来 shall/will do shall/will be doing shall/will have done shall/will have been doing
过去将来 should/would do should/would be doing should/would have done should/would have been doing
英语时态
英语共有16种时态,主要有:完成时态——现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时;进行时态——现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、完成进行时;一般时态。
一般现在时
(1)一般现在时表示没有时限的持久存在的动作或状态或现阶段反复发生的动作或状态,常和副词 usually,often,always sometimes, regularly,near,occasionally,every year, every week 等连用。例如: The moon moves round the earth..
Mr. Smith travels to work by bus every day.
(2)在由after,until,before,once,when,even if,in case,as long as,as soon as,the moment 以及 if,unless 等引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,通常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如: I will tell him the news as soon as I see him.
I will not go to countryside if it rains tomorrow.
I will have arrived by the time the meeting begins.
(3)某些表示起始的动词,可用一般现在时表示按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,这类动词有:be,go,come,start,depart,arrive,begin,leave 等。例如:
The plane leaves at three sharp. The new teachers arrive tomorrow.
(4)在由why,what,where,whoever,who,that,as 等引导的从句中,也常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如:
Free tickets will be given to whoever comes first.
You’ll probably be in the same train as I am tomorrow.
一般过去时
(1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。如 yesterday, last year, in 1949, a minute ago, just now
例如: We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film.
(2)表示过去习惯性动作。例如:
He always went to class last.
I used to do my homework in the library.
(注意与be used to doing短语的区别)
(3) 在since 引导的状语从句多用一般过去时.主句中一般用完成时
He has changed much since I saw him last.
一般将来时
(1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。例如:
I shall graduate next year.
(2)几种替代形式:
1)be going to +v在口语中广泛使用,表示准备做或将发生的事情。例如:
I’m going to buy a house when we’ve saved enough money.
2)be to +v表示计划安排要做的事,具有“必要”的强制性意义。例如:
I am to play tennis this afternoon.
3)be about to +v表示即将发生的事情。例如: He was about to start.
4)be due to +v表示预先确定了的事, 必定发生的事。例如:
The train is due to depart in ten minutes.
5)be on the point/verge of +v – ing 强调即将发生的某种事态。例如:
The baby was on the point of crying when her mother finally came home.
6) 有些动词用现在进行时,表示在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作,多和表示未来时间的状语连用 We are leaving on Friday.
现在进行时
(1)表示现在正在进行的动作,常与now,right now,at the moment,for the time being,for the present等连用。例如:
Don’t disturb her. She is reading a newspaper now.
(2)表示现阶段经常发生的动作, 常与always,continually,forever,constantly等连用。例如: My father is forever criticizing me.
(3)表示根据计划或安排在最近要进行的事情。具有这种语法功能的动词仅限于过渡性动词。即表示从一个状态或位置转移到另一个状态或位置上去的动词。常用的有:go,come,leave,start,arrive,return等。例如:
They are leaving for Hong Kong next month.
(4)有些动词不能用进行时,这是一类表示“感觉,感情,存在,从属”等的动词。如:see,hear,smell,taste,feel,notice,look,appear,(表示感觉的词);hate,love,fear,like,want,wish,prefer,refuse,forgive(表示感情的动词);be,exist,remain,stay,obtain(表示存在状态的动词);have,possess,own,contain,belong,consist of,form(表示占有与从属的动词);understand,know,believe,doubt,forget,remember(表示思考理解的动词)。但是如果它们词义改变,便也可用进行时态。例如: Tom looks pale. What’s wrong with him?
(look 在此为联系动词,意为“显得,看上去”)
Tom is looking for his books. (look 在此为实义动词,意为“寻找”)
过去进行时
过去进行时表示一个过去的动作发生时或发生后,另一个过去的动作正在进行,或表示过去反复的习惯,常与always,continually,constantly等动词连用。例如:
We were discussing the matter when the headmaster entered.
Whenever I visited him, he was always writing at the desk.
将来进行时
将来进行时主要表示将来某一时刻正在进行的动作,或表示要在将来某一时刻开始,并继续下去的动作。常用来表示礼貌的询问、请求等。例如:
This time next day they will be sitting in the cinema.
What will you be doing at six tomorrow evening?
完成进行时
(现在、过去、将来)完成进行时是(现在、过去、将来)完成时的强调形式,将放在完成时态部分讲述。
现在完成时
(1)现在完成时用来表示对目前状况仍有影响的,刚刚完成的动作(常与yet,already,just连用),或者过去某一时刻发生的,持续到现在的情况(常与for,since连用)。例如:
I have just finished my homework. Mary has been ill for three days.
(2)常与现在完成时连用的时间状语有:since, for, during, over等引导出的短语;副词already, yet, just, ever, now, before, often, lately, recently等;状语词组this week (morning, month, year), so far, up to now, many times, up to the present等。例如:
I haven’t been there for five years.
So far, she hasn’t enjoyed the summer vacation.
There have been a lot of changes since 1978.
(3)完成时态可用在下列结构中:
This (That) is (was) the first (second…) time +定语从句;This (That, It) is (was) the only (last) + n +定语从句;This (That, It) is (was) +形容词最高级+ n +定语从句。如果主句的谓语动词是一般现在时,从句的谓语动词通常用现在完成时;如果主句谓语动词是一般过去时,从句谓语动词通常用过去完成时。例如:
This is one of the rarest questions that have ever been raised at such a meeting.
There was a knock at the door. That was the second time someone had interrupted me that evening.
过去完成时
(1)表示过去某时间前已经发生的动作或情况,这个过去的时间可以用by,before等介词短语或一个时间状语从句来表示;或者表示一个动作在另一个过去动作之前已经完成。例如:
We had just had our breakfast when Tom came in.
By the end of last year they had turned out 5, 000 bicycles.
(2)动词expect, hope, mean, intend, plan, suppose, wish, want, desire等用过去完成时,表示过去的希望、预期、意图或愿望等没有实现。例如:
I had meant to take a good holiday this year, but I wasn’t able to get away.
另外两种表示“过去想做而未做的事”的表达方式是:
1)was / were + to have done sth, 例如:
We were to have come yesterday, but we couldn’t.
2)intended (expected, hope, meant, planned, supposed, wished, wanted, desired) + to have done sth, 例如:
I meant to have told you about it, but I forgot to do so.
(3)过去完成时常用于以下固定句型:
1)hardly, scarcely, barely + 过去完成时+ when + 过去时。例如:
Hardly had I got on the bus when it started to move.
2)no sooner +过去完成时+ than +过去时。例如:
No sooner had I gone out than he came to see me.
3)by (the end of ) +过去时间,主句中谓语动词用过去完成时。例如:
The experiment had been finished by 4 o’clock yesterday afternoon.
将来完成时
将来完成时表示在将来某一时刻将完成或在另一个未来的动作发生之前已经完成的动作;也可以用来表示一种猜测。常与将来完成时连用的时间状语有:by (the time / the end of ) + 表示将来时间的短语和句子;before (the end of ) + 表示将来时间的词语或句子;when, after等加上表示将来动作的句子等。例如:
By this time tomorrow you will have arrived in Shanghai.
I shall have finished this composition before 9 o’clock.
When we get on the railway station, the train will probably have left.
完成进行时
完成进行时是完成时的强调形式,有现在完成进行时,过去完成进行时,将来完成进行时。
(1)现在完成进行时表示过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直延续到过去某一时刻。例如:
I have been looking for my lost b here?
但就大多数动词而言,在不用表示一段时间地状语的情况下,现在完成时表示动作的完成,而现在完成进行时表示动作的继续. ook for three days, but I still haven’t found it.
有少数动词如work, study, live, teach 等, 用现在完成时和现在完成进行时意思相差无几.
How long have you studied here?
How long have you been studying
They have widened the road.
They have been widening the road.
(2)过去完成进行时表示过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直延续到过去某一时刻。例如:
It had been raining cats and dogs for over a week and the downpour had caused landslides in many places.
(3)将来完成进行时表示在将来某一时刻之前开始的一个动作或状态一直延续到将来某一时刻。例如:
By the time you arrive tonight, she will have been typing for hours.
英语的几种时态结构表格
英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时,最常用的5个时态是一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去式、一般将来时和现在完成时.
动词的时态
细分有16种时态.
时态按时间分可以分四种:过去时,现在时,将来时,过去将来时;
按动作来分也可以分四种:一般时,进行时,完成时,完成进行时.
故组合起来共16种,可依据具体的语言环境判断时间是哪种,动作属哪种来使用(以下以第一人称为例说明):
1.一般过去时(I did);
一般现在时(I do);
一般将来时(I will do);
一般过去将来时(I would do).
2.过去进行时(I was doing);
现在进行时(I am doing);
将来进行时(I will be doing);
过去将来进行时(I would be doing).
3.过去完成时(I had done);
现在完成时(I have done);
将来完成时(I will have done);
过去将来完成时(I would have done).
4.过去完成进行时(I had been doing);
现在完成进行时(I have been doing);
将来完成进行时(I will have been doing);
过去将来完成进行时(I would have been doing).
可粗列为下表:
动作\时间 过去 现在 将来 过去将来
一般 (I did) (I do) (I will do) (I would do)
进行 (I was doing) (I am doing) (I will be doing) (I would be doing)
完成(I had done) (I have done)(I will have done) (I would have done)
完成进行(I had been doing)(I have been doing)(I will have been doing) (I would have been doing)
英语时态8种基本时态结构
1 一般现在时 用动词原形

2 一般过去时 用动词过去时
3 现在进行时 be + ving
4 过去进行时 was/were + ving
5 一般将来时 will + 动词原形 或 be going to +动词原形
6 过去将来时 would + 动词原形 或 was/were going to +动词原形
7 现在完成时 have/has + v过去分词
8 过去完成时 had + v过去分词
9 现在完成进行时 have/has been + ving
10 过去完成进行时 had been + ving
11 一般将来进行时 will be + ving
12 过去将来进行时 would be + ving
13 将来完成时 will have + v过去分词
14 过去将来完成时 would have + v过去分词
15 将来完成进行时 will have been + ving
16 过去将来完成进行时 would have been + ving英语动词时态用法
一般现在时: 经常反复的动作或状态
现在进行时:正在进行的动作或状态
现在完成时:强调动作的结果和影响
一般过去时:过去的动作或状态
一般将来时:将来的动作或状态
现在完成时:现在完成时是英语时态中最不好掌握的时态,
现在完成时的定义:
1.动作发生在过去,对现在的影响和结果。
2.强调过去的动作和状态对现在产生的影响和结果。
3.刚刚和最近发生的动作和状态。
4.从过去一直延续到现在的动作和状态。
5.从过去到现在一段时间的动作和状态。
6.对过去的体验和经历。
以上就是关于英语6种时态的基本结构,英语八大时态的构成的全部内容,以及英语16种时态的基本结构 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

