本文目录
英语中的被动语态解释和形式,用法
1-1 当句子的主语为动作的承受者即受动者,动词用被动语态.
Eg. John helped Peter. (John是动作的施行者,而Peter是动作的承受者即承受者.)
Peter was helped by John. (Peter是句子的主语,而且是动作的承受者,所以用被动语态.)
1-2 被动语态的构成:be + 动词的过去分词
2. 特别提醒:被动语态的时态和人称的变动都是由动词be作改变的,不论发生什么改变,动词的过去分词(v+ed或不规则的分词) 都不改变.时态用的助动词和人称代词由被动语态句子中的主语,即动作的承受者,所决定.
2-1 Eg. He cleans the room everyday.
The room is cleaned (by him) everyday.
(一般现在时的被动语态构成: is / am / are + 动词的过去分词)
2-2 Eg. They have brought many toys since last week.
Many toys have been brought (by them) since last week.
(现在完成时的被动语态构成:has/have + been + 动词过去分词.)
2-3 Eg. They are meeting the foreigners at the gate.
The foreigners are being met (by them) at the gate.
(现在进行时的被动语态构成:is/ are/ am + being + 动词过去分词)
2-4 Eg. They will build some new buildings next year.
Some new buildings will be built (by them) next year.
They are going to draw a new picture tomorrow.
A new picture is going to be drawn tomorrow.
(一般将来时被动语态构成:will + be +动词过去分词, 或is/am/are going to +be + 动词过去分词)
2-5 Eg. Father has been painting the room all morning.
The room has been being painted (by father) all morning.
(仅作了现在完成进行时的被动语态:has/ have + been+ being + 动词过去分词)
2-6 Eg. They wrote the book last year.
The book was written (by them) last year.
(一般过去时的被动语态构成:was/ were+动词过去分词)
2-7 Eg. The children had broken the window when the teacher arrived.
The windows had been broken (by the children) when the teacher arrived.
(过去完成时被动语态构成had + been + 动词过去分词.)
2-8 Eg. She was reading the book at 8:00 last night.
The book was being read at 8:00 last night.
(过去进行时被动语态构成:was/ were being + 动词过去分词)
2-9 Eg. They said they would cook some food.
They said some food would be cooked.
They said he was going to buy a new house.
They said a new house was going to be bought.
(过去将来时被动语态构成:would +动词过去分词,或:was/were going to be + 动词分词)
2-10 Eg. He must finish the work in two days.
The work must be finished in two days.
(情态动词被动语态:must/have to/had better/ should/can/could/may/might/need to + be +动词分词)
3. 间接引语中的被动语态:
3-1 引述动词是一般现在时的时候,引语的人称根据引述动词前面的主语而作调整,但时态不变.
Eg. He often says, “ I was chosen to take part in the exam when I was twelve.”
He often says he was chosen to take part in the exam when he was twelve. (人称由引述动词says前面的主语he 决定,但引语的时态不变.)
3-2 引述动词为过去时态,引语部分的时态和人陈都按照引述部分进行改变.
Eg. He said, “ My father has been hit by a car.”
He said his father had been hit by a car. (引语部分的时态和人称都发生了改变.)
3-3 从上文可看出:引述动词是过去时态时,被动语态形式的引语改动规则与主动语态形式的引语的改动规则一样,但无论如何,只要是被动语态,它的动词的过去分词总是不改的.)
4.几种特殊的情况需要特别注意:
4-1. 带介词的双宾语可以有两种改法:
eg. They gave him an apple.
He was given an apple.
An apple was given to him. (双宾语中当直接宾语apple 作被动语态句子的主语时,要记得写上介词to.)
4-1-1这样的动词有:buy/make/cook sth for sb
或:show/bring/give/take/ send/write/… to sb.
4-2. 多词动词的被动语态:
eg. She looked after his children.
His children were looked after (by her).
4-2-1这样的动词有:look after, look into, talk about, set up, put off, bring about, do away with, look forward to, take good care of 等等词.
4-3 It is/was/has been said/reported/known + that + 从句
4-4 有些动词在主动语态里不带to,但改为被动语态时要还原to
make/see/have/hear/let sb do sth sb be made/seen/heard/let to do sth
eg. The boss made the workers work for a long time.
The workers were made to work for a long time (by the boss).
4-5 有些动词在主动语态中带sb doing sth, 改为被动语态时仍用doing sth
eg. I heard him singing in his room. He was heard singing in his room.
4-6 特别区分:当句子中出现suddenly, 具体的时间时,用see/hear sb doing sth的形式
当句中出现often, always, sometimes, 或不具体的时间时,用see/hear sb do sth的形式.
Eg. 1) I often hear him sing in his room.
2) Yesterday I saw him cross the road.
3) Suddenly they heard someone crying in the forest.
4-7 不及物动词没有被动语态:happen, take place, begin, become, go, come
eg. Great changes have taken place in the last two years.
4-8 表静态的动词没有被动语态:cost, last, agree with, own
4-9 主动形式表示被动意义,通常用于表示sth的功能或效用: write/wash/cut/use/sell/cook
eg. The cooker cooks well.
The washing machine washes well.
注意:动词的搭配:
1.带sb to do sth的动词:allow/encourage/help/want/wish/ask/tell sb to do sth,
2.带 to do sth 的动词:hope/agree/decide/want/wish/prefer to do sth
3.带 doing sth 的动词:enjoy/practise/think about/doing sth
4.几对特殊的例子:remember to do sth (记得要做,但还没做)
remember doing sth (记得要做,而且做了)
forget to do sth ( 忘记要做,没有做)
forget doing sth ( 做了,但忘记已经做了)
5.prefer doing sth to doing sth
6.look forward to doing sth
7.介词后面用doing sth
8.动词做句子的主语时用ing形式:Collecting stamps is interesting

初中语法被动语态
英语的语态分为主动语态和被动语态两种,而在英语中习惯使用被动语态,汉语中以主动语态为主。中主动语态表示主语是动作的发出者或执行者,而被动语态则表示主语是动作的承受者。那么主动语态如何转化成被动语态呢?
一、被动语态的构成
被动语态由“be动词+过去分词”构成:如
Everybody likes the cute girl. 大家都喜欢这个可爱的女孩。(主动语态)
The cute girl is liked by everybody. 这个可爱的女孩受到大家的喜欢。(被动语态)
二、主动语态变被动语态的基本方法
将主动语态的宾语变为被动语态的主语,将主动谓语变为被动谓语(be+过去分词),将主动语态的主语变为by短语(在被动句中用作状语),如:
He finished the task. → The task was finished by him.
注:如果不强调动词发出者,被动语态中的by短语通常可以省略。
三、 特殊用法
主动句可以转换成两种被动句型,它们通常是一些表示客观说明的句子,如:
People believed that the old man is innocent. 大家相信那个老人是无辜的。
→ It’s believed that the old man is innocent.. 大家相信那个老人是无辜的。
→ The old man is believed to be innocent. 大家相信那个老人是无辜的。
比较上面两类被动句型可以发现,一类是“it+be+过去分词+that从句”,另一类则是“主语+be+过去分词+不定式”,通常可用于这两类被动句型的动词有suppose, think, understand, assume, believe, expect, presume, report, say, fear, feel, know,等,如:
It’s known that she is a kind girl. =She is known to be a kind girl. 大家知道她是个善良的女孩。
It’s expected that he will be better soon. = He is expected to be better soon. 他应该很快就会好起来。
以上就是主动句变被动句的方法。其实,主被动在我们写作或翻译过程中还是非常重要的,英语多被动,汉语多主动,所以学会这两种语态的转变对我们今后的学习至关重要。所以,希望大家能多思考对比,反复练习运用,尽快掌握该知识点。

什么是被动语态和主动语态
一、被动语态的基本用法 当谓语表示一个动作时,主语和它可以有两种不同 关系;主动关系或被动关系。 在表示主动关系时(即主语为动作的执行者时),谓语的形式称为主动语态(the Active Voice)。在表示被动 关系时(即主语为动作的承受者时),谓语要用另一种形 式,称为被动语态(the Passive Voice)。在被动结构的句 子中,动作执行者可以由介词by引起的短语表示。 1.被动语态的构成 被动语态由助动词be加过去分词构成,时态通过 be表现出来。 1)一般现在时 You're wanted on the phone.有人给你打电话。 2)一般过去时 The book was finished last week. 这书是上周写完 的。 3)一般将来时 You'll be allowed to go out tomorrow. 明天让你出去。 4)现在进行时和过去进行时 ① The building is being built. 这幢楼正在建设之中。 ②The bikes were being repaired. 那时正在修自行车。 5)现在完成时和过去完成时 ①This book has been translated into English. 这本 书已被译成英语。 ②The car had been repaired. 这时汽车已修完了。 2.被动语态主要的用法 1)我们不知道或没有必要说明动作的执行者是谁(这时 都不带由by引起的短语)。 The book is written for teachers. 这种书是为教师写的。 2)动作的承受者是谈话的中心(这时可带有by引起的短语)。 The shop is run by a young man.这家商店是由一个年轻人经营的。 3)出于礼貌措辞等方面的考虑不愿说出动作的执行者 是谁。 It is generally considered not advisable to smoke here.一般认为在这儿吸烟是不妥当的。 4)被动结构能使句子得到更好的安排。 Liu Dehua appeared on the stage and was warmly applauded by the audience.刘德华在台上出现,观众给予了热烈的掌声。 5)在汉语中被动结构的句子是很多的,有些带有“被”、 “受”、“由”等词,译成英语时较易想到用被动结构。 ①他被选为我班班长。He was elected monitor of our class. 但在更多情况下却不带这类标记,这种情况值得特别注意。 ②运动会什么时候开? When will the sports meet be held? 二、被动语态的特殊结构 1.带情态动词的被动结构 Water can be turned into vapour.水可转化成蒸汽。 2.带不定式的被动结构 The plan has to be revised. 必须修改计划。 除了单一的及物动词可用于被动结构外,一些相当于及物动词的成语动词也可用于被动结构。常可这样用 的成语动词有: 1)动词+介词 No conclusion has been arrived at so far.到目前为止还没得出结论。 2)动词+副词 The boy was brought up by his aunt. 这个小男孩是由他姑姑带大的。 3)其他成语动词 She was often made fun of. 人们常取笑她。 4)有些动词可以有两个宾语,在用于被动结构时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一个宾语仍然 保留在谓语后面。 The manager was asked a number of questions at the press conference. 在记者招待会上,人们问了经理很多问题。 被动语态的用法: 1. 一般现在时的被动语态构成:is / am / are + 及物动词的过去分词 Our classroom is cleaned everyday. I am asked to study hard. Knives are used for cutting things. 2. 一般过去时的被动语态构成:was / were + 及物动词的过去分词 A new shop was built last year. Dinosaur eggs were laid long long ago. 3. 现在完成时的被动语态构成:has / have + been + 及物动词的过去分词 This book has been translated into many languages. Many man-made satellites have been sent up into space by many countries. 4. 一般将来时的被动语态构成:will+ be + 及物动词的过去分词 A new hospital will be built in our city. Many more trees will be planted next year. 5. 含有情态动词的被动语态构成:情态动词+ be + 及物动词的过去分词 Young trees must be watered often. Your mistakes should be corrected right now. The door may be locked inside. Your homework can be handed in tomorrow. 6. 现在进行时的被动语态构成:am / is / are + being + 及物动词的过去分词 Uncle Wang is mending my bike now.→ My bike is being repaired by Tom now. They are planting trees over there. → Trees are being planted over there by them. 7. 不定式的被动语态:to + be + 及物动词的过去分词 There are two books to be read. → There are twenty more trees to be planted. 二、 怎样把主动语态改成被动语态? 把主动语态改为被动语态非常简单,可以遵循以下几个步骤: 1. 先找出谓语动词; 2. 再找出谓语动词后的宾语; 3. 把宾语用作被动语态中的主语; 4. 注意人称、时态和数的变化。 例:1. Bruce writes a letter every week. →A letter is written by Bruce every week. 2. Li Lei mended the broken bike this morning.→The broken bike was mended by Li Lei this morning. 3. He has written two novels so far.→Two novels have been written by him so far. 4. They will plant ten trees tomorrow.→Ten trees will be planted by them tomorrow. 5. Lucy is writing a letter now.→A letter is being written by Lucy now. 6. You must lock the door when you leave.→the door must be locked when you leave. 三、 使用被动语态应注意的几个问题: 1. 不及物动词无被动语态。 What will happen in 100 years. The dinosaurs disappeared about 65 million years ago. 2. 有些动词用主动形式表示被动意义。
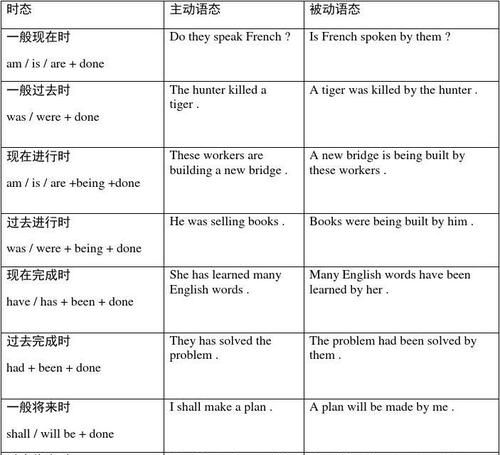
英语中什么是被动语态
1. 被动语态的构成与用法
英语的语态有主动语态和被动语态两种。决定动词用主动语态还是被动语态主要看动词和主语的关系。如果主语是动作的执行者,也就是说它们是主动关系,此时动词用主动语态;如果主语是动作的承受者,也就是说它们是被动关系,此时动词则用被动语态。英语的被动语态由“助动词be+过去分词”构成,其中be有时态、人称和数的变化。如:
English is taught in most schools. 大多数学校都教英语。
The children are not allowed (permitted) to play on the grass. 孩子们不允许在草地上玩耍。
After the accident, the injured were taken to hospital. 事故发生之后受伤的人被送往医院急救。
2. 九种时态的被动语态
各种时态的被动语态
请看以下用例:
We are given a lot of homework to do. 我们有很多作业要做。
They were given a warm send-off. 他们受到热烈的欢送。
I think we are being followed. 我想有人在跟踪我们。
They told me that the case was being investigated. 他们告诉我案子正在调查。
The documents for which they were searching have been recovered. 他们找寻的文件已找到了。
He asked if Mary had been sent to hospital. 他问玛丽是否已被送进医院。
Check carefully, so any mistakes will be caught. 仔细检查一遍,把所有错误都找出来。
He knew he would be punished for it. 他知道他会为此受到惩罚。
3. 含有情态动词的被动语态
含有情态动词的被动语态由“情态动词+be+过去分词”构成。如:
You might be asked to speak at the meeting. 可能请你在会上发言。
Whenever (they are) known, such facts should be reported. 这类情况一旦发现就要报告。
All the above items can be obtained from our office. 所有上述资料可向我们办公室索取。
Something must be done to stop these accidents. 必须采取某种措施以防止这些事故。
These books may be appreciated better by older children. 年龄稍大的孩子可能更会欣赏这些书。
4. 短语动词的被动语态
“动词+介词或副词”构成的短语动词,以及“动词+名词+介词”构成的短语动词,在被动语态中不要漏掉后面的介词或副词。如:
Good use is made of the library. 这图书馆的利用率很高。
A man who is much talked about is always very attractive. 被人谈论多的人经常是很有吸引力的人。
Many interesting experiments are carried out in our laboratory. 我们实验室做了许多有趣的实验。
5. 关于“get+过去分词”
在英语口语中,有时可用“get+过去分词”构成被动语态。如:
I got dressed as quickly as l could. 我尽快穿上衣服。
I wasn’t surprised she get elected after all the efforts she made. 她尽了一切力量之后,当选了,这不使我感到奇怪。
We got delayed because of the holiday traffic. 因为节日交通阻塞,所以我们被耽误了。
I tried to find my way round London without a map and got lost. 我试图不带地图在伦敦寻路,结果迷路了。
注:这样结构比较常见的搭配有get arrested, get caught, get confused, get delayed, get divorced, get dressed, get drowned, get drunk, get elected, get engaged, get hit, get killed, get lost, get married, get stuck等。
引用地址:***/Article/201204/2854.html

以上就是关于英语中被动语态的含义和构成,英语中的被动语态解释和形式,用法的全部内容,以及英语中被动语态的含义和构成 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
