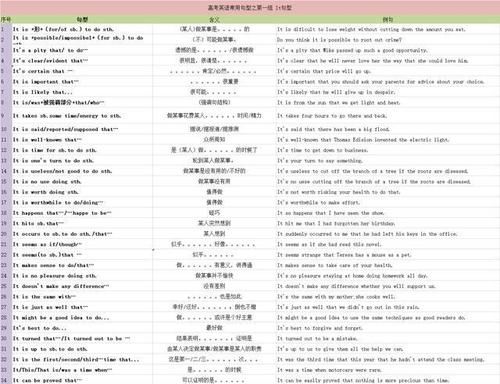
本文目录
英文中虚拟语气的用法
英语语法讲解:虚拟语气的几点特殊用法
1、在错综条件句子中,虚拟条件从句和主句动作发生的时间不一致,因此,主句和从句的谓语动词应根据所指的时间选用适当的虚拟语气形式。例如:
1)If I were you,I wouldn't have missed the film last night.如果我是你,我就不会错过昨天晚上的那部电影。(从句与现在事实相反,主句与过去事实相反。)
2)If he had followed the doctor's advice,he would recover already.如果他遵照医生的劝告,现在病就好了。(从句与过去事实相反,主句与现在事实相反。)
2、在if虚拟条件句中,有时可把连词省去,采用倒装语序把谓语动词were或助动词did,had,should移到句首构成非真实条件从句的另一种句型,其意思不变。例如:
1)Had we time to spare,we would be glad to go to the park.如果能抽出时间,我们很乐意逛公园。
2)Were it not for the discovery of electricity,the modern world would experience great inconveniece.假如没有发现电,现代世界将很不方便。
3、有时假设的情况不用if引导虚拟条件从句来表述,而用介词(如without, but for等)引出的短语、分词(如supposing等)引出的短语、并列连词(如or,otherwise,but,though等)、由动词suppose引出的祈使句或通过上下文的意思来表达。此时句中谓语动词仍采用虚拟语气的相应形式。例如:
1)But for your advice,I would not be able to do this work.要不是你的劝告,我是不会做这份工作的。
2)Victor obviously doesn't know what's happened,otherwise he wouldn't have made such a stupid remark.显然维克多不知道发生了什么事情。不然的话,他就不会说这样愚蠢的话了。
4、在一些表示愿望、建议、请求、命令等含义的动词后面的宾语从句中,谓语动词用动词原形或"should+动词原形"表示虚拟语气。这类动词有ask,demand, insist,order,propose,move,desire,require等。例如:
1)They demanded that the aggressor troops(should)be withdrawn immediately.他们要求立即撤出侵略军。
2)I moved that he(should)be discharged for his serious mistake.我建议,由于他犯有严重错误,应解除他的职务。
5、在"would(had)rather(would sooner,would as soon)+宾语从句"句型中,要求后面的宾语从句用虚拟语气。但这种虚拟语气表示的不是与事实相反的假设,而是一种尚未实现的愿望,其从句谓语动词用一般过去时。例如:
1)I would rather you came next Friday.我希望你下周五来。
2)I'd just as soon you didn't speak rudely to her.我真希望你别对她那么粗鲁地讲话。
6、在和idea,necessity,plan, motion,order,proposal,recommendation,suggestion,under- standing等词有关的同位语或表语从句中,谓语动词用动词原形或"should+动词原形"表示虚拟语气。例如:
1)M y idea is that the group(should)hold another session to discuss the problem.我的意见是小组召开另一次会议来讨论这个问题。
2)Emphasis is laid on the necessity that all the objectives to be attained be taken into account before starting a new project.我们强调在开始制定一个新的计划之前,必须把要达到的所有目标都考虑进去。
7、在某些"It is+形容词+that..."句型中,如"It is important(necessary,essential, natural,desirable,unusual,pity,strange)that...",that所引导的主语从句中谓语动词均用动词原形或"should+动词原形"来表示虚拟语气。例如:
1)It is highly desirable that a new president be appointed for this college.人们迫切地希望能给这个学院派一个新院长。
2)It is strange that the girl(should)be so arrogant.真奇怪,这个女孩竟会如此傲慢。
8、在"It is ordered(suggested,demanded,moved,planned等)+that..."这个句型中,that引导的主语从句要用虚拟语气形式,谓语动词用动词原形或"should+动词原形"。例如:
1)It is moved that Lucy give a performance at the party.有人提议露茜在晚会上表演一个节目。
2)It was suggested that more teachers
(should)be sent there to help them.有人建议派更多的老师去那儿帮助他们。
9、as if /though可以引出一个状语从句也可以引出一个表语从句。当as if/though跟在be,feel,look,seem,sound等系动词之后时,引导的是表语从句;如果主句的谓语动词不是联系动词be等,as if/though引导的则是方式状语从句。无论是哪种类型的从句,只要从句的内容是不真实的,都必须用虚拟语气。当从句表示与现在的事实相反,谓语动词用一般过去时;表示与过去事实相反要用"had+过去分词";表示与将来可能相反的则用"would(could,might)+动词原形"。例如:
1)I feel as if I were going to faint.我感到我像要昏过去似的。(与现在事实相反的表语从句)
2)She cried as if her heart could be broken.她哭的好像心都要碎了。(与将来可能相反的主语从句)
10、在It is(about /high)time引导的定语从句中,也可以根据需要使用虚拟语气,用以表示"(此刻)该做……而没有做"的意思,其谓语动词用过去时或"should+动词原形(用should时,不能将其省略)"。例如:
1)It is time I should leave.我该走了。
2)It is about time that you got(should get) dressed.你该穿衣服了。
11、if only引导的是省略了表示结果的主句的虚拟结构,现在已成为惯用法,表达愿望。从句用过去时表示现在没有实现的愿望;对过去没有实现或不能实现的愿望,从句就用过去完成时。这类句型表示一种不真实的条件,常译成"要是……就好了!"例如:
1)If only I had taken mother's advice.我要是听取妈妈的建议就好了。
2)If only I could speak several foreign languages.我要是能讲几种外语就好了。
12、在以in order that,so that,lest引导的目的状语从句中,谓语动词一般用虚拟语气。从句中的谓语动词用"may(might)+动词原形"或"should+动词原形"。在以lest引导的从句中,谓语动词用"should+动词原形"。例如:
1)She stayed at home for a few days so that she might take care of her sick mother.她在家里呆了好几天,以便能照顾生病的母亲。
2)The teacher explained the sentences again and again in order that the students could understand them clearly.老师一再解释这些句子以便学生能够清楚地理解。

英语当中虚拟语气的用法
虚拟语气的用法
一、虚拟语气条件从句
(一)与现在事实不相符合,主句动词would / should+动词原形,从句动词一般过去时(be可采用were形式),如:
1. If I were you, I would phone the police. 如果我是你,我会打电话给警察的。
2. Would he pay all of us if he had the money? 他有钱了会给我们吗?
3. If it weren’t snowing, we wouldn’t stay in the house. 要是现在不下雪的话,我们就不会待在屋里。
(二)与过去事实不相符合,主句动词would / should have+过去分词,从句动词为过去完成时,如:
1. I would have died if they had given up searching. 如果他们放弃搜索,我会没命的。
2. If we had left a little later, we should have missed the train. 我们再晚点儿就赶不上火车了。
3. The shot would have killed me if I hadn’t had my mobile phone. 若不是有了移动电话,那颗子弹可能就击中了我。
4. If a better material had been used, the strength of the part would have been increased. 如果用了更好的材料,这个部分的力量就增加了。
5. Had the weather been good, the children could have gone out for a walk. 假如天气很好,孩子们都会出去散步。 (省略连接词if,从句使用部分倒装语序。)
(三)与将来事实不相符合,主句动词would / should + 动词原形,从句动词should + v,或者动词过去式,或者were to + v,如:
1. If it were fine tomorrow, I should go to see my sister. 明天天好我就去看姐姐。
2. If he should go there tomorrow, she would meet him. 假如他明天去那里,她就会见到他。
3. If it were to snow tomorrow, I would go skiing. 如果明天下雪,我就去滑雪。
4. If I should have a chance to try it, I would do it in another way. 要是我有机会试一试,我会用另一种方法做的。
(四)主句与现在事实相反,从句与过去事实相反,主句谓语would / should + v, 从句谓语had + 过去分词;主句与将来事实相反,从句与过去事实相反,主句谓语would / should / were to do, 从句谓语had + 过去分词。如:
1. If you had taken the medicine last night, you would be much better now. 假如你昨晚吃药,现在就会好得多。
2. I wouldn’t have missed the flight last night if I were you. 如果我是你,就不会错过那航班。
3. If you had had the car repaired yesterday, we were to go there this afternoon. 如果你昨天修理一下车,我们今天下午就会到达那里。
4. They would be back home tomorrow evening if they had booked the tickets in advance. 如果他们提前订了车票,明晚就回到家。
(五)As if,as though,even if虚拟语气:
1. He looked as if he were an artist. 他看起来像一个艺术家。
2. He speaks English as if he had studied it in England. 他说起英语来就好像在英国学过一样。
3. Even if he were there,he could not solve the problem. 即使他在那里,也不能解决这个问题。
4. He talks as though he knew who she was. 他说气话来好像认识她一样。
(六)用于if only引导的感叹句中。例如:
1. If only I had taken his advice! 要是我听他的话就好了!
2. If only I were ten years younger now. 要是我现在年轻10岁就好了。
3. If only we had passed all the final exams! 要是我们期末考试都考过了就好了!
(七)一些介词词组或连词构成的句子或其他形式的句子也可以表达虚拟语气。常用的介词或连词有but(除外), but for(除外,若不是), but that(若不是), in that case(若那样的话), or(不然),without(没有), otherwise(否则)等,是不是表达虚拟语气则要看句子的内容。如:
1. Without water there would not be life on the earth. 没有水,地球上就不会有生命。
2. But for electricity, there would be no modern industry. 要是没有电,就不会有现代工业。
3. We could have done the work better in that case. 要是那样的话,我们本可以把工作干得更好一些的。
4. But that you helped me a lot, I would have failed in getting good marks in English. 若不是你帮我很大的忙,我不会在英语上取得好成绩。
5. The teacher was lecturing then, otherwise, he would have played basketball with us. 老师当时在讲课,要不然他会更我们一起打篮球的。
6. He went away without a word. 他没说一句话就走掉了。(非虚拟语气)
二、虚拟语气宾语从句
虚拟语气有时也用在一些特殊动词所带的宾语从句中,表示希望、建议、命令、要求等。主句中常用的动词谓语有:insist, order, command, suggest, propose, advise, ask, demand, require, request, recommend等等,由于表达的建议、命令、要求等事情说话时还没有发生,这时宾语从句中从句的动词往往采用should/would+动词原形的方式,实际运用中往往省略should/would,只用动词原形。wish表达的愿望从句,表现为现在不能实现的愿望、过去不能实现的愿望和将来不能实现的愿望等。would rather(宁愿、但愿)是一种特殊用法。如:
1.The judge insisted that the accused man appear in person. 法官坚持让被告出席。
2. The doctor ordered that Ben stay in bed. 医生命令本卧床休息。
3. He suggested that his son be sent to the countryside. 他建议把儿子送到农村。
4. Our teacher asked that we hand in our homework today. 老师要求我们今天交作业。
5. I wish I knew the professor’s address. 我希望知道那个教授的地址。 (表示现在不能实现的愿望,从句动词用一般过去时态。)
6. I wish I hadn’t spent so much money on lottery. 我真希望自己没在彩票上花那么多钱。 (表示过去没有实现的愿望,从句动词用过去完成时。)
7. Peter wishes that he had studied law instead of literature when he was in college. 彼得希望上大学时学的是法律而不是文学。 (表示过去没有实现的愿望,从句动词用过去完成时。)
8. She wishes she would learn all the English songs within a week. 她希望一周之内学会所有英文歌曲。 (表示将来没有实现的愿望,从句动词用过去将来时。)
9. The board deemed it urgent that these files should be printed right away. 董事会认为,迫在眉睫的是马上把这些档案印出来。
10. I would rather
三、虚拟语气主语从句
在It is (was)important (necessary, desirable, imperative, advisable, incredible, urgent, possible, essential, natural, preferable, insistent, crucial, better, best, ridiculous, vital) that…能及It is (was) a pity (shame, wonder, must, suggestion, proposal, requirement, request, desire, order, recommendation) that….,It is (was)desired (arranged, decided, ordered, proposed, requested, recommended, suggested, settled) that…等句型的主语从句中,其谓语用“should+动词原形(其中should可以省略)”来构成虚拟语气。
1. It is important that we (should) speak politely. 我们说话要有礼貌,这是很重要的。
2. It is essential that these application forms be sent back as early as possible. 将这些申请表格尽快地反馈回来是很必要的。
3. It was a pity that you(should)be so careless. 你这么粗心大意真遗憾。
4. It’s desired that she come to teach us at least twice a week. 希望她每周至少来教我们两次。
5. It was my proposal that he be sent to further his study abroad. 我建议派他到国外进一步学习。
四、虚拟语气表语从句
作advise,order,suggestion,demand,plan,proposal,request等名词的表语从句和同位语从句,其谓语动词要用虚拟语气的结构“(should)+动词原形”。例如:
1. The plan is that another power station(should)be built in our city. 这个计划是在我们城市里再建造另一座发电站。
2. The general’s command was that the soldiers leave their fort and carry out more important task. 将军的命令是,战士撤离堡垒去执行更重要的任务。
3. Her demand is that all of us be present at the meeting. 她要求我们大家都要出席会议。
4. His proposal is that we have our lunch at the canteen. 他提议我们在食堂吃午饭。
五、虚拟语气定语从句
这种从句常用在“It is time that...”句型中,表示“该……”“是……时候了”。从句的谓语动词一般用“过去式或should/ought to+动词原形”的虚拟结构。例如:
1. It is (high) time we should go to bed. 该上床睡觉了。
2. It is time that we left for our hometown. 是我们离开家乡的时候了。
3. Do you think it is time you gave up smoking? 你认为是戒烟的时候了吗?
4. It is high time we had begun to prepare the experiement. 正是我们开始准备试验的时候。
六、虚拟语气同位语从句
使用名词表达愿望、建议、命令、要求等,而其后有从句补充说明愿望、建议、命令、要求等内容,构成虚拟语气同位语从句。如:
1.We all agreed to his suggestion that we(should)leave here at once. 我们都同意他的建议,立马离开这里。
2. We are all for the recommendation that John Strong be promoted to headmaster. 我们都赞同推荐约翰斯特朗为校长。
3. The workers raised the demand that their pay be increased to cope with the inflation. 工人们提出要求,上调工资以应付通货膨胀。
4. I offered the advice that we hike to the ancient castle the next day. 我建议我们第二天徒步去古城堡。
判断是真实条件句还是非真实条件句。只有在非真实条件句中才使用虚拟语气。通过句子意思,看假设的条件是否能够实现,能够实现是真实条件句,不能使用虚拟语气;假设的条件不能实现则是非真实条件句,要用虚拟语气。
判断这个假设是与哪个事实相反。通常有三种情况:①与过去事实相反。②与现在事实相反。③与将来事实可能相反。
在准确地判断了该句与哪一事实相反后,按虚拟语气的后退一步法处理从句谓语动词的时态。即:在非真实条件状语从句中,谓语动词按正常情况“后退一步”。也就是:
①与过去事实相反,在从句中用过去完成时形式表示。
②与现在事实相反,在从句中用过去一般时形式表示。
③与将来事实可能相反,在从句中用过去将来时形式表示。
主句中则用情态动词would, should, could 等加一个与从句一致的动词形式。
例:If I had come her yesterday, I would have seen him.
If I were a teacher, I would be strict with my students.
If it should snow tomorrow, they couldn’t go out.

英语虚拟语气
虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,而不表示客观存在的事实,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。虚拟语气通过谓语动词的特殊形式来表示。英语中的语气分为陈述语气、祈使语气、虚拟语气三类。
真实条件状语从句与非真实条件状语从句
条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。非真实条件句表示的是假设或实际可能性不大的情况,故采用虚拟语气。 eg: If he doesn’t hurry up, he will miss the bus. 如果他不快点,他将错过巴士。( 真实) If he is free, he will ask me to tell stories. 如果他是空闲的,他会要求我讲故事。(真实) If I were you, I would go at once.如果我是你,我马上就会去。 (非真实,虚拟语气) If there were no air, people would die. 如果没有空气,人就会死亡。(非真实,虚拟语气)
用法及动词形式
1、表示与现在事实相反的情况: 从句:主语+过去时 主句:主语+should/would/could/might+do 例: 1.If I were you, I would take an umbrella. 如果我是你,我会带把伞。(事实:我不可能是你) 2.If I knew his telephone number, I would tell you. 如果我知道他的电话号码,我就会告诉你。(事实:不知道) 3.If there were no air or water, there would be no living things on the earth. 如果没有水和空气,地球上就不会有生物。(事实:地球上既有空气也有水) 4.If I had any money with me, I could lend you some. 如果我带钱了,我就会借给你些。(事实:没带钱) 5.If he studied harder, he might pass the exam. 如果他再努力些,就能通过考试了。(事实:没有努力) 2、表示与过去事实相反的情况 从句:主语+had done 主句:主语+should/would/could/might+have done 例: 1. If I had gotten there earlier, I should/could have met her. 如果我早到那儿,我就会见到她。 (事实:去晚了) 2.If he had taken my advice, he would not have made such a mistake. 如果他听我的劝告的话,就不会犯这样的错误了。 (事实:没有听我的话) 3、表示对将来情况的主观推测 从句:①if+主语+were to do 主句:①主语+should/would/could/might+do ②if+主语+did/were ②主语+should/would/could/might+do ③if+主语+should+do ③主语+should/would/could/might+do 例: 1.If he should come here tomorrow, I should/would talk to him. 如果他哪天来这儿的话,我就跟他谈谈。 (事实:来的可能性很小) 2.If there were a heavy snow next Sunday, we would not go skating. 如果下周日下大雪,我们就不能去滑冰了。(事实:不知能否下雪) 3.If she were to be there next Monday, I would tell her about the matter. 如果她下周一来这儿的话,我就会告诉她这件事的始末。 4、 有时,虚拟条件句中,结果主句和条件从句的谓语动作若不是同时发生时,虚拟语气的形式应作相应的调整。 ①从句的动作与过去事实相反,而主句的动作与现在或现在正在发生的事实不符。 如: If I had worked hard at school, I would be an engineer, too. 如果我在学校学习刻苦的话,我现在也会成为一个工程师了 If they had informed us, we would not come here now. 如果他们通知过我们的话,我们现在就不会来这里了。 ②从句的动作与现在事实相反,而主句的动作与过去事实不符。 如: If he were free today, we would have sent him to Beijing. 如果他今天有空的话,我们会已经派他去北京了。 If he knew her, he would have greeted her. 要是他认识她的话,他肯定会去问候她了。 5、 当虚拟条件句的谓语动词含有were, should, had时,if可以省略,这时条件从句要用倒装语序,即将were, should, had等词置于句首,这种多用于书面语。 如: Should he agree to go there, we would send him there. 要是他答应去的话,我们就派他去。 Were she here, she would agree with us. 如果她在这儿的话,她会同意我们的。 Had he learnt about computers, we would have hired him to work here. 如果他懂一些电脑知识的话,我们已经聘用他来这里工作了。 6、非真实条件句中的条件从句有时不表达出来,只暗含在副词、介词短语、上下文或其他方式表示出来,这种句子叫做含蓄条件句,在多数情况下,条件会暗含在短语中,如without…., but for….等 如: But for his help, we would be working now. 要不是他的帮助,我们还会在工作呢。 Without your instruction, I would not have made such great progress. 要是没有你的指导,我不会取得如此大的进步。 We didn’t know his telephone number; otherwise we would have telephoned him. 我们不知道他的电话号码,否则我们就会给他打电话。 7、 有时,虚拟条件句中,主、从句可以省略其中的一个,来表示说话人的一种强烈的感情。 ①省略从句 He would have finished it. 他本该完成了。 You could have passed this exam. 你应该能通过这次考试了。 ②省略主句 If I were at home now. 要是我现在在家里该多好啊。 If only I had got it. 要是我得到它了该多好啊。、
编辑本段虚拟语气(Subjunctive Mood)的其他用法
用在wish 后的宾语从句
a、表示与现在事实相反的愿望,谓语动词用过去式 eg. I wish I had your brains. 我希望我有你那样的头脑。(事实:我根本比不上你) b、表示与过去事实相反的愿望,谓语动词:had+done eg:.I wish I had known the truth of the matter. 我希望我原来知道这件事的真相。(事实:原来不知道) c、表示将来难以实现的愿望 谓语动词:should/would + 动词原形 eg. I wish I should have a chance again. 我希望我还能有一次这样的机会。(事实:很难再有这样的机会了) (注:if only和as if/as though也有相同用法)
用在目的状语从句中
1.在for fear that, in case, lest引导的从句中,若用虚拟语气时,从句谓语为:should + 动词原形。并且 should不能省略 She examined the door again for fear that a thief should come in. 她又把门检查了一遍,以防盗贼的进入。 He started out earlier lest he should be late. 他很早就出发了以防迟到。 2、在so that, in order that所引导的目的状语从句中,从句中的谓语为:can / may / could / might / will / would / should + 动词原形。 He goes closer to the speaker so that he can hear him clearer. 他走近说话的人以便能听得更清楚。 He read the letter carefully in order that he should not miss a word. 他把信读得很仔细以便不漏掉一个单词。
其他用法
1、一想要(desire)二宁愿(prefer)三命令(order. command)四建议(advice. suggest. propose)五要求(demand. require. request. desire.insist)中,无论主句谓语动词为何种时态,从句的谓语动词都用:“should + 动词原形”或只用“动词原形”。 如: He suggested that we (should) takethe teacher’s advice. He insisted that we (should) takethe teacher’s advice. He demand that we (should) takethe teacher’s advice. He ordered that we (should) takethe teacher’s advice. insist如果翻译成坚持某种动作才用虚拟语气;翻译成坚持某种观点就不用虚拟语气。 如:He insists he is a student. 他坚持说他是个学生。 这个语句表示的是事实,因此在这个语句中不能使用虚拟语气。 suggest意为“建议”才用虚拟语气,意为“暗示”则不用虚拟语气。 如: His face suggests that he looks worried . 他的表情暗含着他很担心。 这个句子本身是事实,因此它就没有用到虚拟语气。 2、表情绪.观点的形容词或名词也要用虚拟语气.如:necessary、important、impossible、natural、strange、surprising、funny、right、wrong、better、a pity等。 句型:It is.......that +主语从句,从句的谓语动词都要用should+原型 或只用动词原型。 3、 在even if, even though 所引导的让步状语从句中,可用虚拟语气,主句、从句的结构与if所引导的条件从句结构相同。如: Even if he were here himself, he should not know what to do. 即使他亲自来也不知该怎么办。(事实:他没来) Nobody could save him even though Hua Tuo should come here. 即使华佗在世也救不了他。(事实:华佗不在世) 4、 在whatever,whichever,whenever,whoever, wherever,however, no matter wh-word 等引导的让步状语从句中,从句虚拟语气结构为: 指现在或将来: may +动词原形。 如: We will finish it on time no matter what may happen. 不管发生什么事,我们都要按时完成。 We will find him wherever he may be. 无论他在哪里,我们都要找到他。 I will wait for him no matter how late he may come. 不管他来的多么晚,我都会等他。 指过去: may +完成式 。 如: You mustn’t be proud whatever great progress you may have made. 不管你取得了多么大的进步,你也不能骄傲。 We must respect him no matter what mistakes he may have made. 不管他犯过什么错误,我们必须尊敬他。 5、一般would rather, had rather, would sooner等之后的宾语从句常表示与客观事实不相符的一种愿望,故使用虚拟语气。其虚拟语气的结构为:
过去 had + 过去分词 现在 过去时(be 用were ) 将来 过去时(be 用were ) 如: I’d rather you had seen the film yesterday. 我倒想你昨天看过了这场电影。 I’d rather you were here now. 我倒想你现在在这儿。 We’d rather you went here tomorrow. 我们倒想你明天去那儿 6、虚拟语气还可用在定语从句中,表示:“早该做某事了”时,定语从句中的谓语动词须用虚拟语气,其虚拟语气的结构为:It is (high / about) time that + 主语+ 动词的过去式/ should + 动词原形,即从句用虚拟过去式。 如 It is time that I went to pick up my daughter at school. 我该去学校接我的女儿了。 It is high time you should go to work. 你早该上班了。 7、 简单句中的虚拟语气 (1) 说话时,为了表示客气、谦虚、委婉而有礼貌,言语常使用虚拟语气。其虚拟语气的结构形式常为:would / could / might / should + 动词原形。 如: Would you mind my shutting the door? 我把门关起来你介意吗? You should always learn this lesson by heart. 你要把这个教训牢记于心。 I should agree with you. 我应该同意你的观点。 (2) 表示“祝愿”时,常用may + 主语+ 动词原形。 如: May you have a good journey! 祝你一路顺风。 May your youth last for ever! 祝你青春永驻。 (3)表示强烈的“愿望”、“祝愿”时,常用动词原形。 如: Long live the Communist Party of China. 中国共产党万岁。 God bless us. 上帝保佑。 (4) 习惯表达中常用的虚拟语气。 ① 提出请求或邀请。如: Would you like to have a talk with us this evening? 今天晚上来跟我们聊天好吗? Could I use your bike now? 我可以用一下你的单车吗? ② 陈述自己的观点或看法。如: I should glad to meet you. 见到你我会很高兴。 I would try my best to help you. 我会尽力帮助你。 ③提出劝告或建议。如: You’d better ask your father first. 你最好先问一问你的父亲。 You should make a full investigation of it first. 你应该先全面调查一番。 ④ 提出问题。如: Do you think he could get here on time? 你认为他能按时来吗? Do you expect he would tell us the truth? 你期望他会告诉我们真相吗? ⑤ 表示对过去情况的责备时,常用虚拟语气。其虚拟语气的结构为:情态动词 + have + 过去分词。 如: You should have got here earlier. 你应该早就到这里了。 You should have returned it to him. 你应该把它还给他了。 8、虚拟语气在方式状语从句的应用。详见百度百科之方式状语从句词条。
编辑本段四、省略的虚拟条件句型
省略连词if
有时可将条件从句的连词if省略,但此时应用倒装句型,即将从句中的were, should, had 等提到句首: Were I Tom, I would refuse. 如果我是汤姆,我会拒绝。 I will go, should it be necessary. 假若有必要,我会去的。 Had it not been for the bad weather we would have arrived in time. 若不是天气坏,我们就准时到达了。 【注】 ① 若条件从句为否定句,否定词not应置于主语之后,而不能与were, should, had 等缩略成Weren’t, Shouldn’t, Hadn’t而置于句首。 ② 有时省略if后提前的had不是助动词: Had I time, I would come. 假若我有时间,我会来的。(=If I had time…)
省略条件句的主语和其后的动词be
若主从句主语一致,且谓语部分包含有动词be,通常可将主语和动词be省略: If repaired earlier, the tractor would not have broken down. 要是早点儿修一下,拖拉机就不会抛锚了。(=If it had been repaired earlier…)
省略“it+be”
If necessary, I would send more farm-hands to help you. 如果需要的话我会派更多的民工去帮你。(=If it was necessary, I would…)
省略整个条件从句
这样的省略通常需要借助一定的上下文,即省略条件从句后,所剩下的主句的意思在一定的上下文中意思是清楚的: I might see her personally. It would be better. 我可以亲自去看她,这样好一些。(=…If I saw her personally, it would be better.)
编辑本段在含蓄条件句中的用法
(1) 条件暗含在短语中。如: We didn’t know his telephone number; otherwise we would have telephoned him. 我们不知道他的电话号码,否则我们就会给他打电话。(暗含条件是otherwise) Without your help, we wouldn’t have achieved so much. 没有你的帮助,我们不可能取得这么大的成绩。 (暗含条件是介词短语without your help) But for your help, I would not have succeeded in the experiment. 如果没有你的帮助,我的实验就不会成功。(暗含条件是but for your help) It would cause great trouble not to lubricate the bearing immediately. 不立即润滑轴承就会引起很大的故障。 (暗含条件是not to lubricate the bearing immediately) (2) 条件暗含在上下文中。如: I would not have done it that way. 我是不会那么做的。(可能暗含if I were you) I was busy that day. Otherwise I would have come to help you. 我那天很忙。否则我会来帮你的。(可能暗含if I hadn’t been so busy.) You might come to join us in the discussion. 你可以参加我们的讨论。(可能暗含if you wanted to) I would have bought the DVD player. 我是会买下那台影碟机的。(可能暗含if I had the money) But for the storm, we should have arrived earlier. 要不是碰到暴雨,我们还会早些到。(可能暗含if it had not been for the storm)。

虚拟语气英语诗歌
When I poured Mocha lively vitality of all the
Fangfei are nothing but to maintain their moment, and
The stage of the universe only to show off some tricks
The constellation was God in somewhere traction;
When I found the same people and vegetation Fan Yan,
Either the same day he was encouraged and obstruction
When young and vigorous thriving Boom again anti-China,
Prosperous and splendid have been erased from memory;
Then suddenly it all castrate symptomatic of Floating Life
Bianba in my youthful eyes of your presentation,
Saw the brutal and corrupt complicity time,
Make your day into a night of youth;
For your love I will argue, and time:
He Cuizhe you, I want you to re-grafting.
以上就是关于英文清单诗虚拟语气,英文中虚拟语气的用法的全部内容,以及英文清单诗虚拟语气 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
