本文目录
状语分哪三种
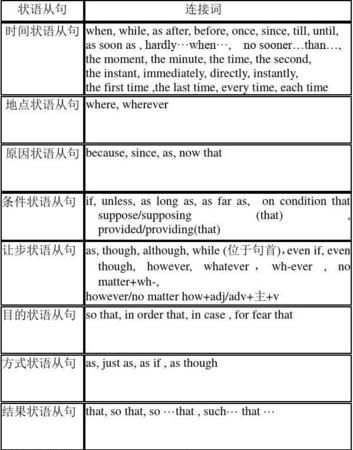
状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。一般可分为九大类,分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。尽管种类较多,但由于状语从句与汉语结构和用法相似,所以理解和掌握它并不难。状语从句的关键是要掌握引导不同状语从句的常用连接词和特殊的连接词即考点。现分别列举如下:
1. 时间状语从句
常用引导词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until
特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
I didn’t realize how special my mother was until I became an adult.
While John was watching TV, his wife was cooking.
The children ran away from the orchard(果园) the moment they saw the guard.
No sooner had I arrived home than it began to rain.
Every time I listen to your advice, I get into trouble.
2. 地点状语从句
常用引导词:where
特殊引导词:wherever, anywhere, everywhere
Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
Wherever you go, you should work hard.
3. 原因状语从句
常用引导词:because, since, as, since
特殊引导词:seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that, considering that, inasmuch as, insomuch as
My friends dislike me because I’m handsome and successful.
Now that everybody has come, let’s begin our conference.
The higher income tax is harmful in that it may discourage people from trying to earn more.
Considering that he is no more than 12 years old, his height of 1.80 m is quite remarkable.
4. 目的状语从句
常用引导词:so that, in order that
特殊引导词:lest, in case, for fear that,in the hope that, for the purpose that, to the end that
The boss asked the secretary to hurry up with the letters so that he could sign them.
The teacher raised his voice on purpose that the students in the back could hear more clearly.
5. 结果状语从句
常用引导词:so … that, so… that, such … that,
特殊引导词:such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that,
He got up so early that he caught the first bus.
It’s such a good chance that we must not miss it.
To such an degree was he excited that he couldn’t sleep last night.
6. 条件状语从句
常用引导词:if, unless,
特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, suppose that, in case that, on condition that
We’ll start our project if the president agrees.
You will certainly succeed so long as you keep on trying.
Provided that there is no opposition, we shall hold the meeting here.
7. 让步状语从句
常用引导词:though, although, even if, even though
特殊引导词: as(用在让步状语从句中必须要倒装),while ( 一般用在句首 ),no matter …, in spite of the fact that, while, whatever, whoever, wherever, whenever, however, whichever
Much as I respect him, I can’t agree to his proposal.
尽管我很尊敬他, 我却不同意他的建议。
The old man always enjoys swimming even though the weather is rough.
No matter how hard he tried, she could not change her mind.
He won’t listen whatever you may say.
8. 比较状语从句
常用引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较)
特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than; not A so much as B
She is as bad-tempered as her mother.
The house is three times as big as ours.
The more you exercise, the healthier you will be.
Food is to men what oil is to machine. 食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。
9. 方式状语从句
常用引导词:as, as if, how
特殊引导词:the way
When in Rome, do as the Roman do.
She behaved as if she were the boss.
Sometimes we teach our children the way our parents have taught us.

状语共有几种类型
一、时间状语从句
主要连词:when、while、as、as soon as(一......就......)、before、after、since等。时间状语从句要符合“主将从现”的原则:即主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时。
二、条件状语从句
主要连词:if, unless(除非=if...not...), as long as(只要)等。条件状语从句要符合“主将从现”的原则:即主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时。
三、原因状语从句
主要连词:because, as(由于), since(因为,既然)等。because 引导的原因是未知的原因,as和since引导的原因是已知的原因。
1、副词:
What you said is only partly true.
你的话只部分地对。
2、介词短语:
Thank you for bringing it.
谢谢你帮我带来了。
3、不定式(短语):
I've come to say goodbye to you.
我是来和你道别的。
4、分词(短语):
They were busy earning a living.
他们都为生活奔忙。
5、形容词:
Now she was back,eager to see her friends.
现在她回来了,非常期待见到她的朋友们。
6、词组:
She jumped ten feet.她跳了十英尺远。
7、复合结构(独立结构):
That being the case,we'11 have to reconsider the whole thing.
情况既然如此,我们就得重新考虑整个这件事。
8、从句:
Strong as he was,he couldn't lift it.
尽管他很健壮,却把它提不起来。
作状语的是什么词
可以分为时间状语、地点状语、方面状语。
在不同的语言中“状语”有不同的作用,中文状语是动词或形容词前面的连带成分,用来修饰、限制动词或形容词,表示动作的状态、方式、时间、处所或程度等;英语状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子;德语状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。

现代汉文中,状语分一般状语和句首状语,一般状语位于主语、谓语之间,起修饰、限制谓语中心词的作用;句首状语则比较少见,但在表示时间、处所、目的的名词、介词结构做状语时,可以把状语放在主语的前边,如“一九四九年,我们国家举行了开国大典”、“在北京,我们游览了故宫”其中“一九四九年、在北京”就是分别表时间、地点的句首状语。
状语的书面标志是“地”,如“小明愉快地回了家”,当然有时候状语也不带“地”,如“他们在上海见了面”,其中愉快地、在上海就是状语
状语有哪几种类型
一、用to do sth表目的
用不定式表目的是最简单也是最常用的方法,它既可以用于句末,也可用于句首,但比较而言,用于句首时,其强调意味较浓。如:
After missing a term through illness he had to work hard to catch up with the others.
他因病一学期未上课,得努力赶上其他同学。
To avoid any delay please phone your order direct.
为免延误,请直接打电话预订。
To keep themselves awake they sat on the floor and told each other stories.
为了不至于睡着,他们坐在地板上轮流着讲故事。
To avoid back problems, always bend your knees when you lift heavy objects.
为了不使背部受伤,你在扛重东西时,一定要将膝盖弯曲着。
不定式的否定式为not to do sth,而不是 to not do sth。如:
She had to struggle not to give in to a desire to laugh.
她极力控制自己不要笑出来。
Then there was the mad rush not to be late for school.
然后就是匆忙往学校赶,以免迟到。
I went to France not to study French, but to study architecture.
我去法国不是为了学法语,而是为了学建筑。
He claimed he had bought the cigarettes for home consumption, not to sell them.
他声称他买烟是为了自家享用,不是为了出售。

二、用so as to do sth表目的
so as to do sth是to do sth的变体,意思是“以便”“为了”“为的是”等。用so as to do sth表示目的时,它通常用于句末。如:
I left a message so as to be sure of contacting her.
我留下了张条子以便与她取得联系
The two lovers dropped back so as to be alone.
那对情人落在后面,为的是两人好单独在一起。
I always keep fruit in the fridge so as to keep insects off it.
我总是把水果放在冰箱里,以防虫子叮咬。
表示目的的so as to do sth有时也可放在句首(但是若so as to do sth是表示结果,则不可放在句首)。如:
So as to show his boss what a careful worker he was, he took extra trouble over the figures.
为了向老板显示他是个工作非常细心的人,他在这些数字上费了比平常更多的力气。
so as to do sth的否定式是so as not to do sth,意思是“为了不……”“以免”。如:
They tiptoed upstairs so as not to wake the baby.
他们踮着脚上楼,以免吵醒孩子。
We left in the daytime so as not to arouse suspicion.
我们在白天离开以免引起怀疑。
I shut the door quietly, so as not to wake the baby.
为了不惊醒宝宝,我轻轻地关上门。
三、用in order to do sth表目的
in order to do sth也是to do sth的变体。用in order to do sth表示目的时,它既可以用于句末,也可用于句首,但比较而言,用于句首时,其强调意味较浓。如:
She lied about her age in order to get the job.
她为了谋得那份工作隐瞒了年龄。
She arrived early in order to get a good seat.
她到得很早,图的是得个好座位。
Teamwork is required in order to achieve these aims.
完成这些目标需要团队合作。
In order to get the job, you must be able to drive.
要做这项工作你得会开车。
In order to get into a good school,, I must study even harder.
为了考入一个好的学校,我必须更加用功。
in order to do sth的否定式是in order not to do sth,意思是“为了不……”“以免”。如:
She slept in a separate room in order not to disturb him.
她在另一房间睡觉,为了不至打扰他。
Please reply at once in order not to lose this opportunity at a lower price.
请立即回复,以免失去这次低价的机会。
They must have worn gloves in order not to leave any fingerprints.
他们一定戴上了手套,以防留下指纹。
注意,in order to do sth 还有另外一个否定形式,那就是 not in order to do sth,其意为“不是为了……”。如:
Big farmers are moving in, not in order to farm, but in order to speculate with rising land prices.
大农场主正在不断涌进来,不是为了耕作,而是要利用不断上涨的地价进行投机。
This expression refers to encounters between ships of hostile nations. One ship might fire a shot at another,
not in order to hit it, but to warn it to move.
这个表达源于敌对国船只在海上相遇时,一方可能向另一方鸣炮,不是为了击中目标,而是警告其快速离开。
四、用so that表目的
so as to和so that均可表示目的,两者的区别是,前者引出不定式,后者用以引导目的状语从句。与用so as to do sth表示目的的情形相似,so that引导的目的状语从句通常位于主句之后。如:
I will give him a key so that he can get into the house whenever he likes.
我会给他一把钥匙,好让他能随时进来。
I got here early so that we could have a few minutes alone together.
我到这儿早些是为了我们能单独在一起待几分钟。
They wrote the notices in several languages so that foreign tourists could understand them.
他们把通知用几国文字写出来,以便让各国游客都能看得懂。
有时可省略其中的that。如:
Leave the keys out so (that) I remember to take them with me.
把钥匙放在外面,好让我记得带。
I deliberately didn’t have lunch so (that) I would be hungry tonight.
我有意没吃午饭,为的就是让自己今晚能感到饿。
so that 引导的目的状语从句有时还可置于主句之前(但是,若so that引导的从句是表示结果,则不可放在句首)。如:
So that I shouldn’t worry, he phoned me on arrival.
为了不让我担心,他一到就给我打了电话。
So that I shouldn’t forget it, I made a knot in my handkerchief.
为了免得忘记,我将手帕打了一个结。
So that the coming generation can learn the martial arts, he has recently devoted much time to writing books on the subject.
为了下一代能够学会这些武术,他近来花了许多时间著书立说。
五、用in order that表目的
in order to和in order that均可表示目的,两者的区别是,前者引出不定式,后者用以引导目的状语从句。与用in order to do sth表示目的的情形相似,in order that引导的目的状语从句可以位于主句之前或之后。如:
We arrived early in order that we could get good seats.
我们到得早,以便找到好座位。
These men risk their lives in order that we may live more safely.
这些人甘冒生命危险,为的是让我们生活更安全。
I bought a new car in order that my wife might learn to drive.
我买了一辆新车,以便我妻子学习驾驶。
In order that you may create such a picture, you have to possess certain artistic weapons.
创作这样的画,你得具有某些艺术手段。
以上就是关于状语有多少种类型,状语分哪三种的全部内容,以及状语有多少种类型 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
