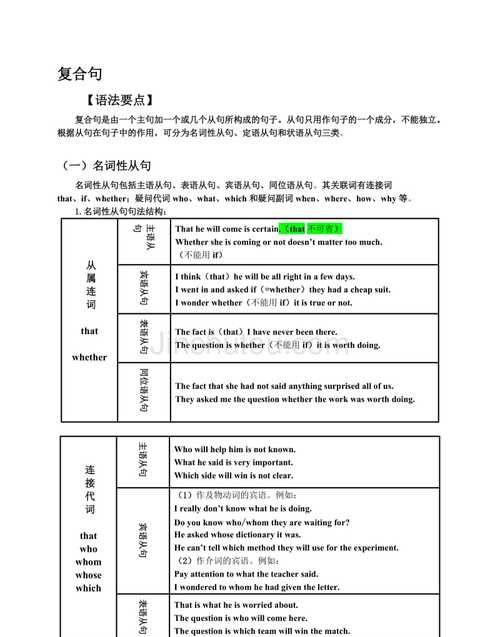
本文目录
方式状语从句怎么理解
引导方式状语从句的连词:as(如同);as if(或as though)(好象)。
(1)as和like都有“就像”的意思,as是连词,后加句子;like是介词,后加名词、代词或名词性短语:
Iworkasothersdo(或like others)。
我像别人那样工作。
(2)as if,as though两者意义相同,从句谓语动词常用虚拟语气,as if比as though更常用:
Theyaretalkingasif(或as though)theyhadseenaghost.
他们谈着话,就像是见了鬼。
▲as if和as though有时可引导表语从句。

英语语法状语从句
一. 状语从句的概念
状语:状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或全句,说明方式、因果、条件、时间、地点、让步、方向、程度、目的等。
状语在句子中的位置很灵活,常见情况为:通常在句子基本结构之后,强调时放在句首;修饰形容词或副词时,通常位于被修饰的词之前;表示时间、地点、目的的状语一般位于句子两头,强调时放在句首,地点状语一般须在时间状语之前;一些表示不确定时间(如:often)或程度(如:almost)的副词状语通常位于be动词、助动词、情态动词之后,动词之前。
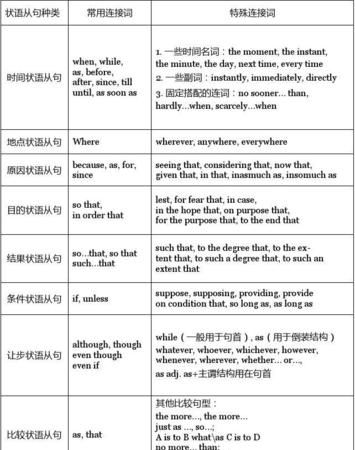
二. 状语从句的类型
1. 地点状语从句
地点状语从句通常由where, wherever引导。
例如:
Where I live there are plenty of trees.
在我住的地方有很多树。
Wherever I am I will be thinking of you.
不管我在哪里,我都会想到你。
2. 方式状语从句
方式状语从句通常由as, as if, as though引导。
(1)as的用法
Will you please do the experiment as I am doing?
请按我的方法做这个实验好吗?
(2)as if, as though的用法
①引导的方式状语从句所表示的情况是事实或具有很大的可能性时,通常用陈述语气,常与look/seem/taste/smell/sound等词连用。
It looks as if it is going to rain.
看来要下雨。
②从句所表示的情况不是事实,而是主观的想象或夸大性的比喻,通常用虚拟语气。
The injured man acted as if nothing had happened to him.
这个受伤的男子行动起来似乎什么也没有发生似的。
说明:
as if/as though也可以引导一个分词短语、不定式短语。
例如:
He stared at me as if seeing me for first time.
他目不转睛地看着我,就像第一次看见我似的。
He cleared his throat as if to say something.
他清了清嗓子,像要说什么似的。
3 原因状语从句
because,as,since与for的不同用法:
相同之处:
中文都表示“因为”,均为连词。
区别:
(1) 如果表示原因的状语从句语气较强,在整个句子中占重要位置,是句子的主要部分,一般用“because”。即回答why问句的提问,应用because。
— Why did they come to China? 他们为什么要去中国?
— Because their father wanted to work in China. 因为他们的父母想到中国工作。
(2) 如果原因不重要,或为人所知,一般用as或since。它所引导的从句常常放在句首。
As you ask, I will tell you.
你既然问我,我就告诉你。
(3) for引导的句子表示原因,语气较because弱,类似一种补充说明,一般不用它来回答why提出的问题。它引导的从句不能放在句首,而且前面一般用逗号与主句分开。
We can’t go, for it’s raining.
由于天下雨,我们不能走了。
说明:
for是并列连词。
4 目的状语从句
表示目的状语从句可以由that, so that, in order that, lest, for fear that, in case等词引导。
例如:
You must speak louder so that/in order that you can be heard by all.
你必须大点声,别人就能听见了。
Better take more clothes in case the weather is cold.
最好多穿点衣服,以防天冷。
5 结果状语从句
结果状语从句常由so…that或such…that引导。so...that与such…that之间可以转换。
例如:
The boy is so young that he can’t go to school.
(= He is such a young boy that he can’t go to school.)
这男孩年龄太小,不能上学。
6 条件状语从句
连接词主要有if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that等。if引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。非真实条件句已在虚拟语气中阐述。
unless = if not.
例如:
Let’s go out for a walk unless you are too tired.
(= If you are not too tied, let’s go out for a walk.)
如果不太累,我们去散散步。
典型例题
You will be late ______ you leave immediately.
A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or
答案A。句意:除非你立即走,否则你就会迟到的。可转化为 If you don’t leave immediately, you will be late。B、D句意不对,or表转折。
7 让步状语从句
(1)though, although引导的让步状语从句,后面的从句不能有but,但是though和yet可连用。
例如:
Although it’s raining, they are still working in the field.
虽然在下雨,但他们仍在地里干活。
(2)as, though引导的让步从句必须表语或状语提前(形容词、副词、分词、实义动词提前)。
例如:
Child as though he was, he knew what was the right thing to do.
虽然他是个孩子,但是他知道该做什么,不该做什么。
(3)ever if, even though即使。
例如:
We’ll make a trip even though the weather is bad.
即使天气不好,我们也要去远足。
(4)whether…or… 不管……都。
例如:
Whether you believe it or not, it is true.
信不信由你,这确实是真的。
(5)“no matter +疑问词”或“疑问词+后缀ever”。
例如:
No matter what happened, he would not mind. (= Whatever happened, he would not mind.)
不管发生什么,他不在意。
替换:
no matter what = whatever
no matter who = whoever
no matter when = whenever
no matter where = wherever
no matter which = whichever
no matter how = however
注意 :no matter 不能引导主语从句和宾语从句。
(错)No matter what you say is of no use now.
(对)Whatever you say is of no use now.
你现在说什么也没用了。
(错)Prisoners have to eat no matter what they’re given,
(对)Prisoners have to eat whatever they’re given.
囚犯们只能给什么吃什么。
英语语法 | 状语从句【 春喜外语 】供稿!春喜外语,学英语告别复读模式,与 真人外教一对一 面对面交谈,不管帅哥还是美女都任你选择。 在线英语培训 ,只要有网络就可以轻松进入学习状态,老师、上课时间、地点你说了算。5年时间12000名学员的共同选择,欲了解更多详情,欢迎咨询在线客服!

状语从句的具体知识及用法了解
状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。它可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语或整个句子。根据其作用可分为时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、让步、方式和比较等从句。状语从句一般由连词(从属连词)引导,也可以由词组引起。从句位于句首或句中时通常用逗号与主句隔开,位于句尾时可以不用逗号隔开。 状语从句的种类 用来修饰谓语动词、其它动词、定语、状语或整个句子的从句叫做状语从句。状语从句可分为: 1.时间状语从句;(adverbial clause of time) 2.地点状语从句;(adverbial clause of place) 3.原因状语从句;(adverbial clause of cause) 4.条件状语从句;(adverbial clause of condition) 5.目的状语从句;(adverbial clause of purpose) 6.让步状语从句;(adverbial clause of concession) 7.比较状语从句;(adverbial clause of comparison) 8.方式状语从句;(adverbial clause of manner) 9.结果状语从句。(adverbial clause of result) [编辑本段]状语从句的时态特点 一般情况下,时间和条件状语从句的谓语动词一般用“一般现在时”表示“一般将来时”,用“现在完成时”表示“将来完成时”。例如: I will call you as soon as I arrive in Beijing. 我一到北京就给你打电话。(这是由as soon as引导的时间状语从句,从句中的谓语动词arrive是一般现在时,表示一般将来时,决不可用will arrive) As soon as I have finished this work, I will go home. 我一完成此工作,就回家。(从句中的谓语动词用现在完成时have finished,表示将来完成时,决不可用will have finished) If he comes back, please let me know.如果他回来了,请通知我。(从句中的谓语动词用comes back,表示一般将来时,决不可用will come back) 状语从句讲解和练习 状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。通常由副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词和从句等担当。例如: 1. Naturally , our grandparents were pleased to get our phone call . (副词) 2. We worked hard , from sunrise to sunset . (介词状短语) 3. To help my disabled aunt , I spend an hour working in her house every day . (不定式) 4. Seen from a distance , the farmhouse looked deserted . (过去分词) 5. I know how to light a camp fire because I had done it before .(原因状语从句) 状语的位置比较灵活,可以位于句首、句末或句中。enough用作状语修饰形容词和副词时必须后置。 状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。一般可分为九大类,分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。尽管种类较多,但由于状语从句与汉语结构和用法相似,所以理解和掌握它并不难。状语从句的关键是要掌握引导不同状语从句的常用连接词 和特殊的连接词即考点。现分别列举如下: 1. 时间状语从句 常用引导词:when, as, while, as soon as, before, after, since , till, until 特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when I didn’t realize how special my mother was until I became an adult. While John was watching TV, his wife was cooking. The children ran away from the orchard(果园) the moment they saw the guard. No sooner had I arrived home than it began to rain. Every time I listen to your advice, I get into trouble. 2. 地点状语从句 常用引导词:where 特殊引导词:wherever, anywhere, everywhere Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories. Wherever you go, you should work hard. 3. 原因状语从句 常用引导词:because, since, as, for 特殊引导词:seeing that, now that, in that, considering that, given that. My friends dislike me because I’m handsome and successful. Now that everybody has come, let’s begin our conference. The higher income tax is harmful in that it may discourage people from trying to earn more. Considering that he is no more than 12 years old, his height of 1.80 m is quite remarkable. 4. 目的状语从句 常用引导词:so that, in order that 特殊引导词:lest, in case, for fear that,in the hope that, for the purpose that, to the end that The boss asked the secretary to hurry up with the letters so that he could sign them. The teacher raised his voice on purpose that the students in the back could hear more clearly. 5. 结果状语从句 常用引导词:so … that, so… that, such … that, 特殊引导词:such that, to the degree that, to the extent that, to such a degree that, He got up so early that he caught the first bus. It’s such a good chance that we must not miss it. To such an degree was he excited that he couldn’t sleep last night. 6. 条件状语从句 常用引导词:if, unless, 特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, supposing that, in case that, on condition that We’ll start our project if the president agrees. You will certainly succeed so long as you keep on trying. Provided that there is no opposition, we shall hold the meeting here. 7. 让步状语从句 常用引导词:though, although, even if, even though 特殊引导词: as(用在让步状语从句中必须要倒装),while ( 一般用在句首 ),no matter …, in spite of the fact that, while, whatever, whoever, wherever, whenever, however, whichever Much as I respect him, I can’t agree to his proposal. 尽管我很尊敬他, 我却不同意他的建议。 The old man always enjoys swimming even though the weather is rough. No matter how hard he tried, she could not change her mind. He won’t listen whatever you may say. 8. 比较状语从句 常用引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较) 特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than; not A so much as B She is as bad-tempered as her mother. The house is three times as big as ours. The more you exercise, the healthier you will be. Food is to men what oil is to machine. 食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。 9. 方式状语从句 常用引导词:as, as if, how 特殊引导词:the way When in Rome, do as the Roman do. She behaved as if she were the boss. Sometimes we teach our children the way our parents have taught us. 看在我辛苦的份上 给我吧 嘻嘻
状语从句的讲解和用法
状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。其实状语从句也是有一定的使用 方法 的。下面我就给大家介绍状语从句的用法讲解。
状语从句的概说状语从句即指在主从复合句用作状语的从句。按照其意义,状语从句可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句等。状语从句是 英语学习 中的一个语法重点,也是历年重点考查的内容之一。学习状语从句主要应注意引导状语从句的从属连词的用法与区别,以及从属连词在一定的语言环境中的意义与用法。
时间状语从句的介绍1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词很多,常见的有before, after, when, while, as, since, till, until, as soon as 等。
2. 表示“当…时候”的 while, when, as 的用法区别是:while从句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词;表示带有规律性的“每当”或当主、从句谓语动词的动作发生有先后时,只能用when;当表示“一边…一边…”或“随着”时,只能用as。另外,用于此义的 as 所引导的时间状语从句谓语只能是动作动词,不能是状态动词。如下面一道高考题的答案是B 而不能是A:
“I’m going to the post office.” “_____ you’re there, can you get me some stamps?”
A. As B. While C. Because D. If
3. until 在肯定句中通常只连用延续性动词,表示相应动作结束的时间;在否定句中通常连用非延续性动词,表示相应动作开始的时间,意为“直到…才”。如:
He waited until she was about to leave. 他等着一直到她准备离开。
I did not begin to work till he had gone. 他走了后我才开始工作。
4. 表示“一…就”除用as soon as 外,还可用 the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, no sooner…than, hardly…when 等。如:
I came immediately you called. 你一来电话我就来了。
Hardly had she arrived when it began to snow. 她刚到就下起雪来了。
The moment I have finished I'll give you a call. 我一干完就给你打电话。
5. every time, each time, (the) next time, (the) last time, by the time, the first time, any time 等以time 结尾的词语也可用作连词,引导时间状语从句。如:
Next time you come in, please close the door. 下次你进来,请关门。
He didn’t tell me anything the last time I saw him. 上次我见到他时他什么也没告诉我。
By the time I got home, she had already gone to bed. 我到家时她已睡觉了。
条件状语从句的介绍1. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词主要有 if, unless, as [so] long as等。如:
Don’t come unless I telephone. 除非我打电话,否则你别来。
If you watch carefully you will see how to do it. 如果你仔细瞧你会看出该怎样做。
As long as you do your best, we’ll be happy. 只要你尽力,我们就满意了。
2. in case 也可引导条件状语从句,其意为“如果”、“万一”。如:
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 如果我忘了,请提醒我。
让步状语从句的介绍1. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词主要有 although, though, however (=no matter how), even if (即使), whether…or (不论…还是)等连词。如:
The speech is good, though it could be better. 这次演讲不错,虽然还可以再好一点。
He went out even though it was raining. 尽管下雨,他还是出去了。
2. as 也可引导让步状语从句,但要将名词、形容词或副词等提到as 前,若提前的是单数可数名词,要省略a / an。如:
Teacher as he is, he can’t know everything. 虽然是老师,他也不可能什么都懂。
3. 连词while 有时也可表示“尽管”、“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。如:
While we don’t agree we continue to be friends. 尽管我们意见不同,我们还是朋友。
4. whatever, whoever, however, whenever, wherever 等引导让步状语从句。如:
Don’t lose heart whatever you do. 不管你做什么,都不要灰心。
Whoever you are, you can’t pass this way. 不管你是谁,你都不能从这里通过。
注:表示“虽然”的 though, although 不可与 but 连用,但可与 yet, still 连用。
点击下页还有更多 >>>原因状语从句的介绍
以上就是关于方式状语从句的讲解和用法 ,方式状语从句怎么理解的全部内容,以及方式状语从句的讲解和用法 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

