本文目录
怎样判断定语从句和宾语从句
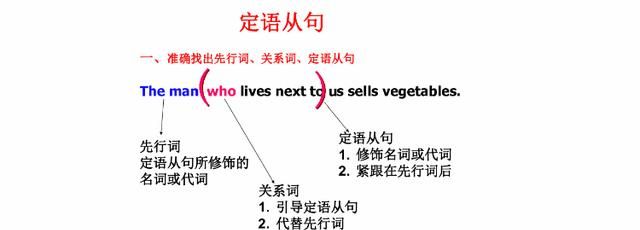
定语从句在句中作定语,修饰名词或代词,被修饰的名词词组或代词即先行词。定语从句通常出现在先行词之后,由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引出。 那么怎样判断定语从句?下面我们去了解一下吧!
怎样判断定语从句
一、定语从句的识别:
名词(句子)+连接词+句子
其中识别度最高的关键之处,就是连接词,它有三种:
① 关系代词:who, whom, that, which, as, whose
② 关系副词:when, where, why, how
③ 介词+关系代词:介词+whom, 介词+which, 介词+whose
但注意,有时你会看到 in that,但in that=because,算是一种固定搭配,这和定语从句没关系。
这里单独说一下as引导的定语从句吧,因为其它都还比较常见,as相对来说比较生疏。
主要是在same和such之后,定语从句用as引导,但偶尔the same后面也用that.
如:I've never heard such stories as he tells.
我从来没听到过他讲的这种故事。
He is wearing the same suit as(或that) he wore at Mary's wedding.
他穿着与他在玛丽的婚礼上穿的一样的衣服。
二、定语从句的处理
原则:将定语从句完整地切分出来,独立成句。
两个关键点:
① 完整地切分;
② 独立成句
第一步,切分:切分点在连接词前,如果连接词前有介词那就在介词前。
如:I love this girl / who is beautiful.
I went to Changchun / where I met my wife for the first time.
I have three books / of which the red is my favorite.
第二步,找指代(也就是关系代词的指代对象):
如:This is the expert / to whom we are turning.
注:turn to = resort to = 求助于……
这句话里的关系代词是 whom , 它的指代对象是the expert.
所以这句话翻译过来是:这就是我们正在求助的那个专家。
第三步,调语序
需要调整语序的也就是关系代词和(介词+关系代词)
还是上面那句话:This is the expert to whom we are turning.
先切分,① this is the expert /
② to whom we are turning
再找到第②句中whom的指代对象,whom=the expert
也就是 to the expert we are turning
这时落实到我们要讲的调语序了,因为我们发现to the expert we are turning,它由于受到定语从句规则的限制,所以不是正常语序,现在我们把它变成正常语序就是:we are turning to the expert
这时,你再翻译成中文时就没有障碍了。
至此,我们总结一下,定语从句的处理就是分三步,1.切分;2.找指代;3.调语序
这样就可以完成了将一个定语从句从英文到中文的转换,所以下次遇到定语从句时,你只管先“咔嚓”来一刀,给它切开,两个句子安安静静地出现在你面前,你就别么费劲地去前置了,那么定语从句就不能前置了吗?也不是不能,语义如果挺顺畅的你就前置呗,只是能前置的定语从句基本上都退化成后置定语了,比如,an apple which is on the table也可以写成an apple on the table(桌子上的苹果)
a way which is to solve the problem也可以写成 a way to solve the problem(解决这个问题的方法)
定语从句的几个难点
难点一:定语从句与并列句的区别
观察下面三个句子:
1.Wang Hong failed in the College Entrance Examination, ________ disappointed his mother.
2.Wang Hong failed in the College Entrance Examination and ________ disappointed his mother.
3.Wang Hong failed in the College Entrance Examination; ________ disappointed his mother.
(提示:判断是定语从句还是并列句,要注意句中的标点符号和句中的连接词。)
例1:Tom’s mother kept telling him that he should work harder, but _____ didn’t help.
A.he B.which
C.she D.it
例2:The weather turned out to be very good, _____ was more than we expected.
A.that B.which
C.where D.it
例3:The mother told her lazy son to work instead of staying at home; ____ didn’t help.
A.it B.she
C.which D.as
难点二:介词+关系代词引导定语从句中介词的选择
“介词+关系代词”可引导限制性定语从句也可引导非限制性定语从句,可从以下几点定位关系代词前的介词。
1.介词与先行词搭配是一种固定搭配
I still remember the day ____________ I first came to school.
The company ______________ I once worked has changed much.
2.介词与从句中动词的搭配
He is a man of great knowledge, _____________ much can be learned.
In the dark street, there wasn’t a single person _____________ she could turn for help.
3.介词与从句中形容词的搭配
China is a beautiful country, _____________we are greatly proud.
The teacher talked about some subjects _________________ the students were interested.
4.与名词之间的搭配
He may be late, ________________ we ought to wait for him.(如果是这样)
Call me at six o’clock, __________________ I should get up.(到那个时候)
Ex:
(1)There is a room, _______________________ faces the river.
那儿有一间房子,窗户面对这条河。
(2)They are the very people _______________________ for help.
他们就是那些你可以向其求助的人。
(3)China has many islands, _______________________ Taiwan is the largest.
中国有很多岛屿,台湾是其中最大的一个。
(4)They arrived at a house, _______________________.
他们到达一所房子,前面坐着一个小男孩。
(5)Gun control is a subject ________ Americans have argued for a long time.
A.of which B.with which
C.about which D.into which
(6)By nine o’clock, all the Olympic torch bearers had reached the top of Mount Qomolangma, ________ appeared a rare rainbow soon.
A.of which B.on which
C.from which D.above which
(7)For many cities in the world, there is no room to spread out further, _____ New York is an example.
A.for which B.in which
C.of which D.form which
注意:The way ________ he explained to us was quite simple.
The way ________ he explained the sentence was simple.
难点三:引导词as , which
1.引导非限制性定语从句,指代整个主句内容时的区别:
(1)表达“正如”之意时,用as, 如果仅指代整个主句内容而没有“正如”之意,则用which。
He went abroad, ______ was unexpected.
She is a good mother, _____ her mother used to be.
(2)当从句位于主句前面时,用as。
______ is known to everybody, the moon travels round the earth.
2.限制性定语从句中有such, the same 时,其后常用as 引导定语从句。
He is such a good teacher _______ we all love and respect.
This is the same pen _______ I lost.
3.which既可指代整个主句内容,又可以指代先行词。
The river, _______ flows through London, is called the Thames.
4.as常与从句中的know, see, hear, expect等动词连用,也常用于as often happens, as is often the case等句子中。
He was absent from school, _______ is often the case.
难点四关系代词与关系副词(补全法或还原法)
1.Do you still remember the chicken farm ________ we visited three months ago?
2.In an hour, we can travel to places ________ would have taken our ancestors days to reach.
3.Some pre-school children go to a day care centre, ________ they learn simple games and songs.
练习:
1.By 16:30, ________ was almost closing time, nearly all the paintings had been sold.
A.which B.when
C.what D.that
2.A woman with a bleeding hand hurried in and asked, “Is there a hospital around ________ I can get some medicine for my wounded hand?”
A.that B.which
C.where D.what
3.—How do you like the film Examination 1997, Mr. Li?
—It brings the hours back to me _____ I was forced to raise pigs in a faraway village.
A.who B.that
C.when D.where
难点五先行词为point, case, situation等时所构成的定语从句
1.—Do you have anything to say for yourself?
—Yes, there’s one point ______ we must insist on.
A.why B.where
C.how D./
2.I have reached a point in my life ______ I am supposed to make decisions of my own.
A.which B.where
C.how D.Why
3.Our new partnership with France Telecom is really a win-win situation _____ both sides benefit a great deal.
A.which B.that
C.where D.what
4.Today, we’ll discuss a number of cases _____ beginners of learning English fail to use the language properly.
A.which B.as
C.why D.where
5.It’s helpful to put children in a situation ___________________________________.
把孩子们放在一个能使他们从另外一个角度认识自己的环境中对他们有益。
6.Now there is just one point _____________________________________.
现在只有一点你能弄清楚。
定语从句语法总结
一.几个基本概念1.定语从句的定义:用作定语的从句叫定语从句。
2.先行词:被定语从句所修饰的'名词或代词。
3.定语从句的位置:紧跟先行词(名词或代词)之后。
4.引导词:引导定语从句的词(包括关系代词和关系副词)。
(1)关系代词:that/who/whom/which/as
(2)关系副词:when/where/why
5.引导词的位置:位于定语从句之前(先行词之后)。【as除外】
6.引导词的功能(作用):
(1)连接先行词和定语从句。
(2)在定语从句中充当一定的成分(关系代词充当主语或宾语,关系副词充当状语)。
7.定语从句的类型:
(1)限定性定语从句(主句和定语从句之间无逗号)。
① 直接由引导词引导定语从句
The man who you’re talking to is my friend.
② 由介词+关系代词(whom/which)引导
The man to whom you’re talking is my friend.
I need a pen with which I can write a letter.
=I need a piece of paper on which I can write a letter.
介词的选用可根据从句中的相关词组确定,该介词通常可以放在关系代词之前,也可放在从句之尾。例如:
The man (who/whom/that) I talked about at the meeting is from Beijing University.
=The man about whom I talked at the meeting is from Beijing University.
The palace (which/that) I often pay a visit to was built in the 17th century.
=The palace to which I often pay a visit was built in the 17th century.
(2)非限定性定语从句(主句和定语从句之间用逗号隔开)。
① 直接由引导词引导定语从句。
② 由介词+关系代词(whom/which)引导。
I live in a house far away from the city, in front of which is a big tree.
There is an apple tree standing at the gate, on which are many apples.
This is the man to whom I gave the book.
③ 由“代词/名词+of+whom/which”或“of which/ whom +名词/代词”(先行词指
人用whom,指物用which)引导。One, some, any, none, all, both, several, many, most, neither, either等词、数词、分数或百分比与of whom或of which连用。
He has five children, two of whom are abroad.
(比较:He has five children, and two of them are abroad.)
We have three books, none of which is/are interesting.
(比较:We have three books, but none of them is/are interesting.)
除why和that不能引导非限定性定语从句外,其余引导词都可以,用法同限定性定语从句一样。但要注意以下区别。
1.在形式上非限定性定语从句与主句有逗号隔开。
2.非限定性定语从句的作用:它只是补充说明先行词的情况,翻译时可译成两个句子。
The engineer, whose leg was badly hurt, was quickly sent to hospital.
(那位工程师被很快送往医院,其腿部受了重伤)
The engineer whose leg was badly hurt was quickly sent to hospital.
(那位腿部受了重伤的工程师被很快送往医院)
3.在非限定性定语从句中,任何引导词都不能省略(包括引导词在此定语从句中充当宾语在内)。指人做主语时只能用who, 做宾语时用whom; [要学习网-中学生最喜欢的学习论坛;
指物做主语,宾语都用which; 关系副词用when或where,也不能省略。
The man, ______ is sitting on the chair, is my father.
The woman, _______ I met yesterday, is my English teacher.
The city, _______ is far away, is very beautiful.
He went to America, ______ his parents live.
He joined the Army yesterday, ______ I left, too.
4.whose引导非限定性定语从句:
The house, whose window faces south, is mine.
=The house, the window of which faces south, is mine.
=The house, of which the window faces south, is mine.
二.定语从句中关系代词和关系副词的`基本用法
1.who/that指人是主格在定语从句中代替先行词,又作定语从句的主语,不能省略。
Do you know the gentleman who/that is sitting there?
2.whom/who/that指人是宾格,在定语从句中代替先行词,又作定语从句的宾语(动宾或介宾)。
① 当作动宾(动词后接宾语)时,关系代词可省略。
Do you know the gentleman (whom/who/that) we met just now?
② 当作介宾(介词后接宾语)时:
介词不提前时,关系代词可省略;
介词提前时,关系代词不可省,即介词+whom(指人时介词后的关系代词只能用whom)。
The man (whom/who/that) I spoke with is my teacher.
The man with whom I spoke is my teacher.
注:固定的动词短语(动词+介词)如look for, take care of等不能把动词与介词拆开,既介词不能提至引导词前。
She is the right girl (who/whom/that) we are looking for.
3.whose: 指人或物,是所有格“…的”形式。Whose+n.一起在定语从句中充当主语、宾语(动宾或介宾)即先行词的什么东西怎样了,whose不能省略。。Whose+n. = the +n. + of which/whom= of which/ whom+ the =n.
I didn’t find the desk whose leg was broken. (主语)
He is the student whose pencil I broke yesterday. (动宾)
The boss in whose company I work is very kind. (介宾)
4.which/that 指物,指代先行词且在定语从句中作主语或宾语(动宾或介宾)。
① 当作动宾时,关系代词可省略。
② 当作介宾时:
介词不提前时,关系代词可省略;
介词提前时,关系代词不可省,即介词+which(指物时介词后的关系代词只能用which)。
The house which/that was destroyed in the earthquake is weak.
The pen (which/that) you found yesterday is mine.
The games (that/which) the young men competed in were difficult.
The games in which the young men competed were difficult.
注:介词+关系代词即介词+whom/which(先行词指人用whom,指物用which)。
5.as指人或物,在定语从句中可作主语,宾语,表语或状语,不能省略。主要用于 “the same …as…;such …as…;so …as…;as … as…;as follows”固定结构中,形式固定此时的引导限定性定语从句。要用as代替who(m), which, 或that引导定语从句:
Such people as knew Hill thought he was honest.
Such people as Hill knew thought he was honest.
My hometown is no longer the same as it was.
Here is so big a stone as no one can lift.
The child knows as much as grow-ups (know).
I’d like to have the same books as are used in your school.
He is not such a person as I expected.
He will marry as pretty a girl as he can find.
如何判断定语从句和宾语从句
首先定语从句是形容词性从句,在限定性定语从句中,被修饰词叫做“先行词”,而用来引导定语从句的引导词是代替先行词在从句中作相应的成分,这些成分一般包括:主、宾、表、定、状语几种。判断其成分要先看从句,不要先受主句的影响,一个英语句子必有动词作谓语,动作的发出者就是主语了这是不可缺少的!!关键的一步就是看动词是及物动词(必须有宾语)还是不及物动词(不能直接加宾语),及物动词后无宾语,则引导词代替先行词在句中充当宾语,若是不及物动词则引导词不做宾语。
如主宾表都不缺,在看先行词雨引导词后的名词是否存在所属关系,若有则做的是定语(通常用whose)以上都不是就只剩状语了,至于是时间状语还是地点状语就自己判断好啦。再加上对引导词用法的了解,就没什么大问题了。
如何判断是定语从句还是宾语从句
位置:先行词之后 例:Those who are willing to attend the party , sign your name please. 定语从句是由关系代词或关系副词引导的从句,其作用是作定语修饰主句的某个名词性成分,相当于形容词,所以又称为形容词性从句,一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词后面. 引导定语从句的关联词称为关系词,关系词有关系代词和关系副词.关系代词有that, which, who, whom, whose, as等,绝对没有“what”;关系副词有where, when, why等.关系词常有3个作用: ①连接作用,引导定语从句. ②代替先行词. ③在定语从句中担当一个成分. 注:关系代词有主语、宾语之分.一般whom作为宾语.关系代词在从句中作主语,宾语,表语,定语等,关系副词在从句中作地点状语(where)时间状语(when),原因状语(why).
定语
定语用来限定、修饰名词或代词,是对名词或代词起修饰、限定作用的词、短语(动词不定式短语、动名词表示的)汉语中常用“……的”表示.主要由形容词担任,此外,名词、代词、数词、分词、副词、不定式以及介词短语也可以来担任,也可以由一个句子来担任.单词作定语时通常放在它所修饰的词之前,作前置定语.短语、从句作定语时则放在所修饰的词之后,作后置定语. 被定语从句修饰的名词、代词称为先行词.如“The man”、“The book”.
编辑本段关系代词引导的定语从句举例
关系代词所代替的先行词是人或物的名词或代词,并在从句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分.关系代词在定语从句中作主词保持一致.
1,who, whom, that
这些词代替指人,“whom”作宾语指人,“that”既可作主语又可作宾语(作宾语可以省略),可以指人也可以指物.在从句中所起作用如下: (1)Is he the man who/that wants to see you? 他是那个想见你的男人吗?(who/that在从句中作主语) (2)He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday. 他就是我昨天见的那个人.(whom/that在从句中作宾语) (3)The man whom you spoke to just now is our English teacher. 你刚刚说话的那个男人是我们的英语老师.
2,Whose 用来指人或物
(只用作定语, 等,作宾语时可以省略),例如: (1)Prosperitywhich / that had neppearsin te. 农村出现了前所未有的繁荣.(which / that在从句中作主语) (2)The package (which / that) you are carryingis about to come unwrapped.你拿那个包裹快要散开了.(which / that在从句中作宾语)
whose
“whose”表示谁(可以为人也可以为物)的(东西) 例:A child whose parents are dead is called an arphan.双亲都死了的孩子叫做孤儿.(“whose”表示那个孩子的双亲) He lives in a room whose window faces south.他住的那个房子的窗户是朝南的.(“whose”表示那个房子的窗户) 关系代词:在句中作主语、宾语或定语. 1. that既可代表事物也可代表人,“which”代表事物;它们在从句中作主语或宾语,“that”在从句中作宾语时常可省略关系词,“which”在从省略.[eg:This is the book (which)you want.] 2. 不及物动词+介词”的介词的宾语代词“wh”放在它原来的位置. 3. 代表物时多这时的that常被省略; c)被形容词最高级修饰时;既有人又有物时; e)整个句中前面已有“which”,“wh”行 关系副词:在句中作状语 关系副词=介词+关系代词 why=for which where=in/ at/ on which(介词同先行词搭配) when=during/ on/ in/…… which(介词同先行词搭配) 1. “where”是关系代词,当然也不用“that”引导. By the time when you arrived in London, we had stayed there for two weeks. 到你到达伦敦的时候,我们在那里已经待了两个星期. I still remember the her. 我仍然记得我第一次见到她. Each time when he goes to business trip, he brings a lot of living necessities, such as towels, soap, toothbrush etc. 他每次出差都带来了生活必需品,如毛巾,肥皂,牙刷等其他东西. 3. 当从句的逻辑主语是some, any, no, somebody, anybody, nobody, something, anything, everything或nothing时,常用“there is”开头. There is somebody here who wants to talk to you. 这里有人要和你说话. 分作进一步说明,通常是引导词和先行词之间用逗号隔开,将从句拿掉后其他部分仍可成立.
编辑本段非限制性定语从句
意义: 非限制性定语从句起补充说明作用,缺少也不会影响全句的理解.在非限制性定语从句的前面往往有逗号隔开,如若将非a lovely garden. 我去年买的的房子带着个漂亮的花园. This novel, which I have read three times, is very touching. 这本我已经读过三遍的小说很感人. 3. 非限定性定语从句可将整个主句作为先行词, 对其进行修饰, 这时从句谓语动词要用第三人称单数,例如: He seems not to have grasped what I meant, which greatly upsets me.他似乎没抓住我的意思,这使我心烦. Liquid water changes to vapor, which is called evaporation. 液态水变为蒸汽,这就叫做蒸发. 4. 有时as也可用作关系 5. 在非限定性定语从句中,不能用关在从句中做主语 (1)The boys who are playing football are from Class One. 在踢足球的男孩们是一班的. (2)Yesterday I helped an old man who lost his way. 昨天,我帮助了一个迷路的老人.
whom指人
注意:关系代词“whom”在口语和非正式语体中常用“who”代替,可省略. 如果在从句中做宾语,就用“whom”或“who”. He is the man whom has an English book. 他就是那个有英语书的男人. You just meet the person whom is my friend. 你刚刚见到的那个人就是我的朋友.
whose通常指人也可指物
在定语从句中做定语,表所有. (1)He has a friend whose father is a doctor. 他有一个朋友的父亲是医生. (2)I once lived in a house whose roof has fallen in.我曾经住在一座现在已经倒塌的房子中. “whose”指物时通常以以下结构来代替: (3)What is the color.Football isa game which is liked by most 颜色是什么.足球是大多数男孩都喜欢的游戏. (4)This is the pen(which)he bought yesterday. 这是他昨天刚买的钢笔.
that指人时
相当于“who”或者“whom”;指物时,相当于“which”当前头有最高级序数词“all”不定代词时必须用“that”. 在定语从句中做主语、表语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略. (5)The number of the people that/who come to visit the city each year rises one million. 每年来这座城市观光的游客数目上升了100万. (6)Where is the man this morning? 今天早上这个男人在哪?
when指时间
在定语从句中做时间状语也可做连接词用. (1)(1) I still remember the day when I first came to the school. (2) The time when we got together finally came.
why指原因
在定语从句中做原因状语. (1)Please tell me the reason why you missed the plane. (2)I don't know the reason why he lookswhen/in which he was going to school he began to know what he wanted when he grew up.
编辑本段介词和关系代词
1)介词后面的关系代词不能省略. 2)“that”前“Do you”作介词的宾语,且可以省略.例如: (1)The school(that/which)he once studied in is very famous.“that/which”可以省略. = The school i which hied is very famous.“which”不可省略. (2)Tomorrow I will bring here 用,如:look for, look after, take care of等. T This is the watch which/that I am looking for.(T=正确) F This is the watch for which I am looking.(F=错误) 2. 若介词放在关系代词前,关系代词指人时用“whom”,不可用“who”或者“that”;指物时用“which”,不能用“that”;关系代词是所有格时用“whose” (1)The man with whom you talked is my friend.(T) The man famous. (2)I bought many books yesterday, three of which are written by Lu Xun.
关系代词
关系代词(一般情况下)“that”可用在从句做主语,谓动词的宾语,但是不能做介词的宾语. “which”指物,在从句句中作主语; “whom”在从句中作宾语; “why”在从句中修语,先行词通常是“the reason”; 有时“why”也可用“for+which”代替. 例:A doctor who looks after people's health. 主语 谓语 先行词 定语从句修饰先行词
判断介词和关系代词
方法一: 用关系代词,还是关系副词完全取决于从句中的谓语动词.不及物动词后面无宾语,就必须要求用关系副词或者是介词加关系代词;而及物动词后接宾语,则要求用关系代词.例如: This is the mountain village where I stayed last year. 判断改错: (错) This is the mountain village where I visited last year. (错) I will never forget the days when I spent in the countryside. (对) This is the mountain village (which) I visited last year. (对) I'll never forget the days (which) I spent in the countryside. 例. Is this the museum ____ the exhibition was held? A. where B. that C. on which D. the one ,解析: 主、谓、宾俱全,从句部分为句子的状语表地点,既可用副词where,又因 in the museum词组,可用介词in + which 引导地点状语.而此题中,介词on 用的不对,所以选A. 关系词的选择依据在从句中所做的成分,先行词在从句中做主、宾语时,选择关系代词(who, whom, that, which, whose); 先行词在从句中做状语时,应选择关系副词(“where”地点状语,“when”时间状语,“why”原因状语).
编辑本段先行词和关系词
1)Whoever spits in public will be punished here.(“Whoever”可以用“anyone who”代替) 2)The parents will use what they have to send their son to technical school. (“what”可以用“all that”代替) 但这两句句子已经不是定语从句了,是名词性从句.因为定语从句一定要有先行词,而名词性从句没有.将“Whoever”、“what”分别用“Anyone who”、“all that”代替后,才是定语从句,先行词分别是“Anyone”、“all”.an invitation from her boss, ___came as a surprise. A. it B. that C. which D. he 答案C. 此为非限定性从句,不能用“that”修饰,而用“which”、“it”和“he”都使后句成为句子,两个独立的句子不能单以逗号连接.况且选“he”句意不通. 2)The weather turned out to be very good, ___ was more than we could expect. A. what B. which C. that D. it 答案B 英语语法上行不通. 3)It rained hard yesterday, ____ prevented me from going to the park. A. that B. which C. as D. it 答案B “as”和“which”在引导非限宾语.但不同之处主要有两点: (1)importance to me, as my own is. 在一定的语言环境里,有些名词可以具有形容词的性质.这些名词主要是那些表示人的身份、职业、状态的名词.值得一提的是,在这些具有形容词性质的名词之后,引导定语从句的关系代词不能用“who / whom”. (2)动词短语先行成分. 这种动词短语既可是限定形式也可是非限定形式.如果是动态动词短语,它们在从句中就一般有限定或非限定形式的替代动词“do”和“as / which”一起代替.“do”可以出现,也可以不出现,但不能用其它动词代替. (3)句子作先行成分. 这句子可以是整个主句也可以只是主句中的一个从句.有时是连续几个句子,有时甚至可以是一个完整的故事. 二、“as/which”特殊定语从句在句中的位置. 由于先行成分的构成成分”特殊定语从句在句中的位置有以下几种情况: 1. 形容词做先行成分时:形容质的which”特殊定语从句置于先行成分之后. 2. 动词词短语作先行成分时,“as / which”特殊定语从句置于先行成分之后.但是,当从句中含有表示主观意志的插入成分时,“as”特殊. 3. 句子作先行成分时:“as”特殊定语从句的位置较灵活,可以置于先行成分之前、之中或之后.但如果先行成分是直接引语,“as”特殊定“s”特殊定语从句与否定词的相对中则常用一些表示“合乎自然规律”、“众所周知”或“经常发生”等意义的词语,如natural, known to all, usual等. 3. 有无状语意要是方式状语意义,而“which”特殊定语从句则无状语意义.“as”特殊定四、关系代词“as”与“which”一词.如: Freddie, as might be expected, was attending the conference. 1. “Which”作主语时,谓语动词不限,主动被动皆可,只是谓语动词为被动语态时助动词“be”省略. 2. “as”和“which”都可以在特殊定语从句中宾语. 3. “as”和“which”在特殊从句中作补语.如: We thought him a gentleman, as/which he could never be. “as”特殊定语从句中可以主谓倒装,“which”从句中则不能主谓倒装. 如果先行成分不是主语补语或宾语补语,关系代词用“which”而不用“as”.如: He talked like a native, which/as he hardly was. 4. “which”在特殊从定法 (1)不用that的情况 (a)在引导非限定性定语从句时. (错)The tree, which is four hundred years old, Is very famous here. (b)介词后不能用. We depend on the land from which we get our food. We depend on the land that/which we get our food from. (2)只能用“that”作为定语如“last,just”修饰时,只用“that”. (d)先行词为序数词、数容词,又有物时. (f)先行词指物,在主句中作是“the way”或“the reason”时,“that”可作关系副词,也可省略 (h)主句的主语是疑问词“who /which”时,避免重复要用“that”. 举例: Is this the book that you borrowed in the library? 这是你在图书馆借的书吗? Who that break the window should be punished. 谁打碎了窗户. All that is needed is a supply of oil. 所需的everything that he had stolen to the police. 那贼最终把偷的全部东西交给了警察. “that”必用 1、先行词是最高级或被最高级修饰. 2、是序数词或被序数词修饰. 3、不定代词指物. 5、被“only”、“the every”、“no”、“one of”等修饰 6、主句有“which”、“who”、“whom” 7、“there be”句型中 8、如果有两个从句,其中一个关系代词已用了“which”,另一个关系代词宜用“that” 9、先行词在主句中作表语,或者关系代词本身作从句的表语是宜用“that” “that”在作宾语时可省略. 10、不是任何时刻关系词作主语宾语是能用“that”难点分析“you”注意1:the only,the same,the last ,any,little等修饰时(1) This is the very good dictionary that I want to buy,(2) After the fire in his house, the old car is the only thing that he owned.当先行词指人时,偶尔也可以用who(3) Wang Hua is the only person in our school who will attend the meeting?5、当先行词前面有who, which等疑问代词时(1) Who is the man that is standing there?(2) Which is the T-shirt that fits me most?6、当先行词既有人,也有动物或者物体时Can you remember the scientist and his theory that we have learned?7.当关系代词在定语从句中做表语The village is no longer the one that it used to be 10 years ago.8.当在which引导的定语从句as和which引导非限制性定语从句,有相同之处也有不同之处.具 a developing country.(2) He is from the south, as we can see from his accent.(3) John, as you know, is a famous writer.(4) He has been to Paris more than several times, which I don’t believe.注意:当主句和从句存在逻辑上的因果关系时,常用which.(5) Tom was always late for school, which made his teacher angry.3、当先行词受such, the same修饰时,常用as(1) I have never heard such a story as he tells.(2) He is not such a fool as he looks.(3) This is the same book as I lost last week.注意:当先行词由the same修饰时,偶尔也用that引导定语从句,但是和由as所引导的定语从句意思不同(4) She wore the same dress that she wore at Mary’s wedding. 她穿着她注意:定语从句such…as …与结果状语从句such… that…的区别:as在所引导的定语从句中作主语,宾语;that在结果状语从句中不做成分 (6)He has such a good laptop as I want to buy. (7)He idea.(but= who don’t) (五)区分定语从句和同位语从句 1、定语从句修饰先行词,它和先行词是修饰关系; 同位语从句说明先行词的具体内容,是补充说明的关系 (1)The planeis clear. 同位语从句 2、定语从句由关系代for advice. (3)The fact that the moon moves around the earth is known to all. (4)The fact is that the moon moves around the earth. [定语从句]介词+关系词 1)介词后面的关系副词不能省略. 2)“that”前不能有介词. 3)某些在从句中充当时间,地点或原因状语的"介词+关系词"结构可以同关系副词“when”和“where”互换.例如: This is the house in which I lived two years ago. 这是我两年前住过的房子. This is the house where I lived two years ago. Do you remember the day on which you joined our club? 还记得你加入我们俱乐部的那一天吗? Do you remember the day when you joined our club?

定语从句怎么判断是主语还是宾语
判断定语从句
第一步判断先行词
先来看个句子:The tall boy published a lot of books. (那个高个子男孩出版了许多书。)我们都知道这句话中的tall是定语,用来修饰boy。
再比如:The girl who works as a waitress here is a college student. (那个在这里当服务员的女孩是一名大学生。)这句话中的who works as a waitress here用来修饰girl,其功能相当于前面例句中的tall,只不过这里的定语是个句子,用来解释说明前面的名词girl,此时who works as a waitress here就叫做定语从句,被这个定语从句修饰的词girl即为先行词。

第二步判断定语从句是否完整
一般来说,有关定语从句的试题通常考查的都是关系词的选择。因此在判断先行词、确定句子为定语从句后,接下来需要判定从句是否完整。
然后才能决定使用哪个关系词来连接。既然确定是定语从句,那么关系词在从句中要充当句子成分,所以判断从句是否完整至关重要。那么如何判断从句是否完整呢?大家可通过以下步骤来进行判定。
首先判断从句的谓语动词是be动词、及物动词还是不及物动词。接下来,从句谓语动词如果是及物动词或be动词,则要看其前面是否有主语,后面是否有宾语或表语;如果是不及物动词,则只需看前面是否有主语即可。我们按照这个步骤接着看前面讲的这道题:
第三步判断关系词
通过第二步,我们已经判断出从句是否完整,接下来就是选择关系词了。在选用关系词时大家应从以下三个方面考虑。
以上就是关于怎么判断从句为定语从句 ,怎样判断定语从句和宾语从句的全部内容,以及怎么判断从句为定语从句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

