本文目录
定语从句属于句子结构吗
长难句当中最最常见的一定是定语从句,因为在英语里如果要对一个概念修饰,并且修饰的部分偏多的话往往很难用一个或二个形容词解决,所以定语从句的使用一定是非常广泛了,如下是我给大家整理的定语从句句子结构分析,希望对大家有所作用。
一、理论常识
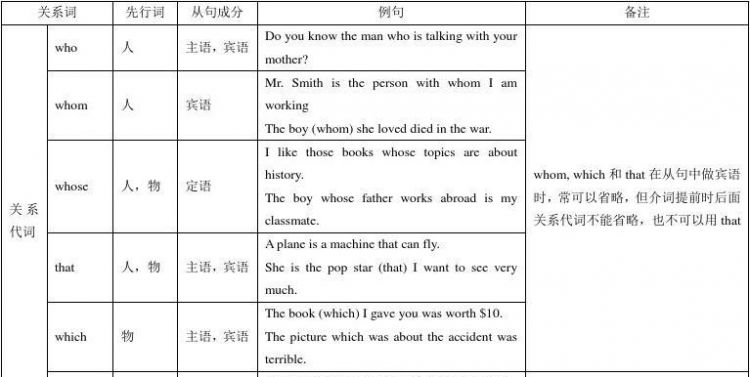
在复合句中作定语,修饰主句中某一名词或代词的从句。
结构:先行词+关系词(分为关系副词和关系代词)+从句
关系代词(that , who , which , whose , as)
关系副词(when , where , why , how)
定语从句分为限制性定语从句及非限制定语从句,限定从直接放在先行词后,非限定从与先行词之间要加逗号。
二、真题举例
例句1:The Aswan Dam , for example , stopped the Nile flooding but deprived Egypt of the fertile silt that floods left-all in return for a giant reservoir of disease which is now so full of silt that it barely generates electricity .
【重点词汇解析】deprive sb. of sth. 剥夺某人某物;silt,n. 淤泥 v. (使)淤塞
【参考翻译】例如,阿斯旺大坝阻止了尼罗河的洪水侵袭,但是也夺去了埃及的洪水留下的肥沃淤泥---这一切换来的却是一个巨大的病态的水库,这个水库积满了淤泥,以至于几乎不能发电了。
例句2:The second , by Joshua Greenberge , takes a more empirical approach to universality , identifying traits (particularly in word order) shared by many languages , which are considered to represent biases that result from cognitive constraints . (2012,49)
【重点词汇解析】empirical,adj. 经验主义的;result from 由……造成;cognitive,adj. 认知的
【参考翻译】第二个为此做出努力的.人是约书亚·格林伯格,他采用经验主义的方法来研究普遍性,确认多种语言(尤其是语序方面的)共同特征,这些特征被认为是体现了由于认知局限性而带来的偏见。
例句3:His function is analogous to that of a judge , who must accept the obligation of revealing in as obvious a matter as possible the course of reasoning which led him to his decision . (2006,47)
【重点词汇解析】analogous,adj. 类似的;reveal,vt. 揭露;reason,n. 理由 v. 推论
【参考翻译】他的职责类似于法官的职责,后者必须承担起这样的责任:用尽可能明显的方式来揭示让他做出决定的推理过程。

英语定语从句语法讲解
英语定语从句语法解析 篇1
1.先行词为all, anything, something, nothing, everything, much, little, none等不定代词时,关系代词一般只用that,不用which。在大多数情况下that可以省略.
Please tell me everything you know about the matter.
Thats all we can do at the moment.
2.as引出的限制性定语从句
在such as的结构中as可作关系代词,引出限制性定语从句。有时和same连用,在从句中可作主语、宾语或表语等。
Such people as were recommended by him were reliable.
Ive never seen such a talented young man as he is.
I have the same trouble as you .
3.as引出的非限制性定语从句
as可作关系代词引出非限制性定语从句,代替整个主句,通常译为(正)如一样,(正)象一样等。as引导的从句一般用逗号与主句隔开,可以位于主句的前面、中间或后面.
I live a long way from work, as you know.
She did not, as her friend had feared, break down.
As is generally accepted, economic growth is determined by the smooth development of production.
4.分隔式定语从句
定语从句一般紧跟在先行词之后,但有时会被其他句子成分与先行词隔开,从而构成分隔式定语从句。
英语定语从句语法解析 篇2
1)介词后面的关系词不能省略。
2)that前不能有介词。
3)某些在从句中充当时间,地点或原因状语的介词+关系词结构可以同关系副词when 和where 互换。例如:
This is the house in which I lived two years ago. 这是我两年前住过的房子。
This is the house where I lived two years ago.
Do you remember the day on which you joined our club? 还记得你加入我们俱乐部的那一天吗?
Do you remember the day when you joined our club?
18.6 as, which 非限定性定语从句
由as, which 引导的非限定性定语从句,as和which可代整个主句,相当于and this或and that。As一般放在句首,which在句中。例如:
As we know, smoking is harmful to ones health. 如我们所知,吸烟有害健康。
The sun heats the earth, which is very important to us. 太阳使地球暖起来,这对我们人类很重要。
典型例题
1)Alice received an invitation from her boss, ___came as a surprise.
A. it B. that C. which D. he
答案C. 此为非限定性从句,不能用 that修饰,而用which.,it 和he 都使后句成为句子,两个独立的句子不能单以逗号连接。况且选he句意不通。
英语定语从句语法解析 篇3
1、限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句
定语从句就其与先行词的关系而言,可分为限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句。限定性定语从句和先行词之间没有逗号,表示对先行词起修饰限制作用;而非限定性定语从句和先行词之间有逗号分开,是对先行词进行补充说明,相当于并列句。
如:He is the man who has a strong personality. 他是个个性很强的人。(限定性定语从句)
My brother, who works abroad, is coming next week. 我哥哥在国外工作,他下周将回来。(非限定性定语从句)
注:
1) 非限定性定语从句不能用that来引导,一般用which,as或who(指人)。用which或as引导时,既可以修饰主句的部分内容,也可修饰主句的全部内容。如:
He spoke confidently, which impressed me most. (which指代整个主句,在从句中作主语)
2) as引导的非限定性定语从句既可以放在主句之前,也可以放在主句之后,但which或who引导的非限定性定语从句不能放在主句之前。如:As we all know, the moon is a satellite of the earth.The large area is covered with thick snow, which affects people‘s life greatly.
3) 在限定性定语从句中,关系代词作宾语时可以省略;但在 非限定性定语从句中,关系代词作宾语时不能省略。如:
The film (which) I saw last night is about a young teacher. (which可以省去)
She introduced me to her husband, whom I hadn’t met before. (whom不能省去)
2、只用关系代词that,不用 which,who或whom的几种情况
1)当先行词是all, everything, nothing, something, anything, little, much, none, few等时。如:All that you want are here.
2) 当先行词被all, no, some, any, every, a few, a little, much, only, very等修饰时。如:There is no person that doesn’t make mistakes.
3)当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。如:This is the best film that I have ever seen.
4)当出现两个或两个以上的先行词,并同时兼指人和物时。如: We are talking about the people and countries that we have
visited.
5) 当主句是以which 或 who 开头的特殊疑问句时。如: Who is the person that is standing over there?
6) 当定语从句为there be 句型时,关系代词只用that,
但经常可以省略。如: I know the difference (that) there is between you.
7)当关系代词在从句中作表语时,常用that。如:He does not seem to be the man that he was
他似乎和过去不一样了。
3、 as 与其他词连用引导的定语从句
as 引导定语从句时,可指人也可指物,通常与the same,such,so等连用,形式为:the same… as,such… as,as …as,so… as。As在定语从句中可作主语、宾语、表语等。如:
She knew he felt just the same as she did. 她知道他的感觉与她自己的一样。(as代替事,作宾语)
I lend you such books as will interest you. 我借给你使你感兴趣的书。(as代替物,作主语)
注:the same… as 和the same… that的用法不同。as引导的定语从句表示其内容与主句所讲的事物“相似”,指同类事物;that引导的定语从句表示其内容与主句所讲的事物是“同一个”,指同一事物。如:
This is the same pen as I lost yesterday. 这和我昨天丢的笔一样。(类似的笔)
This is the same pen that I lost yesterday. 这支笔就是我昨天丢的'那支。(同一支笔)
4、“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
在“介词+which/whom”结构中,介词的选择取决于3种情况:
1)定语从句中谓语动词或表语的搭配。如: This is the college in which I am studying. He is the man about whom we are talking.
2)先行词与介词的习惯搭配。如: The speed at which the machine operates is shown on the meter.
仪表上显示出这台机器运转的速度。
3)当定语从句为最高级时只能用of which; 否则用其他介词。如: I have five dictionaries of which Longman Dictionary is the best. I have five dictionaries among which Longman Dictionary is published in UK.
注:不可拆分的动词短语介词不能提前,如put up with;有的短语可能有不同的介词搭配,此时需要根据上下文来确定。如:be familiar with/to,compare with/to等。
有时为表意清楚,还可以在关系副词where/ when前加介词from, to等。如:
China is the birthplace of kites, from
where kite flying spreads to Japan, Korea, Thailand and India.
中国是风筝的故乡,从这里,放风筝的运动传到了日本、韩国、泰国和印度。
注 定语从句和同位语从句的区别
定语从句在复合句中的功能相当于形容词,它对先行词起修饰、描述或限制作用。而同位语从句则属于名词性从句,对与它有同位关系得名词作进一步解释,使其内容具体化。例如:
She felt very sad because of the news that her husband was killed in an aircraft crash. (同位语从句)
The fact that she told me made me very angry. (定语从句)
英语定语从句语法解析 篇4
关系代词as与which引导的非限制性定语从句,其先行词都可以是整个主句,指代主句的整个意 思。但as和which具有不同的词义、句法和用法。
1. as引导的从句表示说话人的看法、态度、解释或评论
引导定语从句时,as仍具有正如,像,由……可知等意思,翻译时 有时可不必译出。as定语从句常含有这些动词:see, know, hear, watch, remember, say, tell, show, expect, guess等,这类动词与as连用几乎成了一种固定搭配。as引导的此类从句可以置于句首、句中或 句尾。如:
The famous magician Liu Qian, as we all know, is from Taiwan. 众所周知,著名魔术师刘 谦是台湾人。
There is a net bar around here, as I remember. 我记得这儿附近有一家网吧。
As is often the case, girls like dolls while boys like guns. 女孩子喜欢玩具而男孩子 喜欢枪,这是常见的情况。
2. which引导的从句对主句所叙述的事情进行补充说明,表明事物的状态或结果
which此时指前面主句所提到的这件事,常译为这一点,这件事等。这时它所引 导的从句与主句之间常含有并列、因果关系。注意,它引导的从句不像as那样位置灵活,它只能位于主句 的后面。如:
He changed his mind again, which made us all angry. 他又改变了主意,这使我们大家都生 气了。
She tore up my photos, which (=and that) upset me.她撕碎了我的照片,这使我很不安。
3. 在从句中作定语或介词的宾语时,要用which,不用as
Jenny might come, in which case I‘ll ask her. 詹妮可能会来,要是那样的话我就去问 她。
She graduated from a local middle school, after which she went to Beijing University. 她毕业于当地的一所中学,之后她去了北京大学。
4. 当从句的谓语动词是否定形式或含着一个复合宾语时,一般用which而不用as
He pretended not to know me, which I didn’t understand. 他假装不认识我,这是我搞 不明白的。
He admires everyone in his class, which I find quite strange. 他羡慕班里的每个学生, 我认为太奇怪了。
【特别说明】
as引导非限制性定语从句的最大特点是位置灵活;其次,as有以下常见的,而which不具备的 固定表达:
as we all know 众所周知
as I can remember 正如我所记得的
as often happens 正如经常发生的那样
as we expect 正如我们预料的那样
as you see 这一点你明白
as was expected 正如预料的那样
as can be seen 看得出来
as may be imagined 正如可以想象的那样
as has been said above 如上所述
as we all can see 正如我们都能看到的那样
as is often the case 像常规那样
as everybody can do 正如人人都能做到的那样
英语定语从句语法解析 篇5
1. 分隔定语从句。
先行词与定语从句之间有时也会插入别的成分,构成先行词与定语从句的隔离,这种从句叫分隔定语从句。例如:
This is the article written by him that I spoke to you about.
He was the only person in this country that was invited.
①因定语从句过长,为使句子保持平衡,常将定语从句和其所修饰的名词或代词分开。
The film brought the hours back to me when I was taken good care of in that faraway village.
②在定语从句中使用“插入语”以增加语言的灵活性。
The pen I thought I had lost is on my desk,right under my nose.
2. as 和 which 引导的定语从句。
① as 有“正如,就像”之意,在非限制性定语从句中充当主语、宾语或表语,从句可位于主句的前面、中间或后面,一般用逗号与主句隔开。
As we had expected,her performance was wonderful.
A panda, as we know,is a lovely animal.
Tom is the tallest in our class,as you know.
但 which 引导的非限制性定语从句一般只能放在主句之后。例如:
The result of the experiment was very good,which we hadn’t expected.
②在主谓宾结构的非限制性定语从句中,which 和 as 作宾语时可互换使用。
He was an Englishman,which / as I knew from his accent.
作主语时通常用 which ,而不用 as .但在“主语 +be+done ”结构中,as 作主语。例如:
He passed the examination,as was known.
③ as 引导非限制性定语从句时,通常用在表示肯定意义的从句中,而不能用在表示否定意义的从句中; which 则不受此限制。例如:
Mummy treats me just as a baby,which (不用 as ) I can’t bear.
She married again,which (不用 as )was unexpected.
④在宾补结构的非限制性定语从句中,作主语或宾语时,宜用 which ,而不用 as .例如:
He believed in God,which (不用 as ) I find strange.
He changed his mind,which (不用 as ) made me very angry.
⑤定语从句中动词若为表示知觉的词,如 see ,expect ,say ,know 等时,用 as 而不用 which .
As we expected / know, Xiao Ming took the first place in the game.
⑥ as 引导的定语从句与 it 作形式主语的主语从句和以 what 引导的主语从句的区别。试比较:
As is known to everybody,the moon travels round the earth once every month.
It is known to everybody that the moon travels round the earth once every month.
What is known to everybody is that the moon travels round the earth once every month.
3. 定语从句与并列句的识别。
定语从句与主句之间要用“逗号”分隔,并且不能加入 and , but , so 等连接词。并列句一般由 and , but , so 等词连接,或中间用“分号”隔开。例如:
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows,most of which hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. (定语从句)
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows,and most of them hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. (并列句)
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows;most of them hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. (并列句)
Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase,the price of which was reasonable. (定语从句)
Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase;the price of it was reasonable. (并列句)
John’s parents kept telling him that he should work hard,but it didn’t help. (并列句)
4. that 引导的定语从句与结果状语从句的区别。
This is so interesting a book that all of us want to read it. ( so …… that 引导的结果状语从句)
This is so interesting a book as all of us want to read. ( as 引导的定语从句)
通过以上两个例句不难看出, so …… that 引导结果状语从句,而定语从句中先行词前有 so , such , the same 修饰时,常用“ as ”来引导定语从句。
5. 定语从句与同位语从句的区别。
同位语从句是位于名词 answer , belief , doubt , decision , explanation , fact , hope , idea , information , news , order , problem , promise , truth 等后的句子,并对这些句词进行补充说明或解释;从句一般是一个完整的句子,引导词 that 只起引导作用,不作句子成分,且 that 不可省略;同位语从句不可用 which 引导。而定语从句通常是一不完整的句子,缺少主语或宾语等。作宾语时, that 可省略。
The fact that she hasn’t known the result of the examination is clear. (同位语从句)
The fact (that / which) she told me yesterday is very important. (定语从句)
「巩固性练习」
1. _________ is mentioned above, the number of the students in senior high school is increasing.
A. As B. It C. That D. What
2. Now Children like to go to the fast food restaurant, _________ as the name says, eating doesn’t take much time.
A. which B. that C. what D. where
3. Sometimes the earthquake is so violent that it can destroy the whole city, _________ happened in Tang Shan in 1976.
A. as B. that C. where D. like
4. Recently my father bought a Chinese painting, _________ was very reasonable.
A. the price of it B. which price
C. the price of which D. its price
5. We will be shown around the city: schools, museums, and some other places, _________ other visitors seldom go.
A. what B. which C. where D. when
6. We were next-door neighbors for three years, during ________ time we met only twice.
A. which B. this C. in which D. same
7. Living in the central Australia desert has its problems, _________ getting water is not the least.
A. as B. for what C. of which D. for what
8. We should do more such exercises in the future, I think, ________ those we did yesterday.
A. as B. which C. that D. it
9. Gone are the days _________ we spent together in the village.
A. that B. when C. in which D. on which
10. He failed his exam, _________ proves that he wasn’t working hard enough.
A. as B. which C. that D. A and B
11. He must be from Africa, _________ can be seen from his skin.
A. that B. as C. who D. what
「参考答案」
1. A 2. D 3. A 4. C 5. C 6. A
7. C 8. A 9. A 10. D 11. B
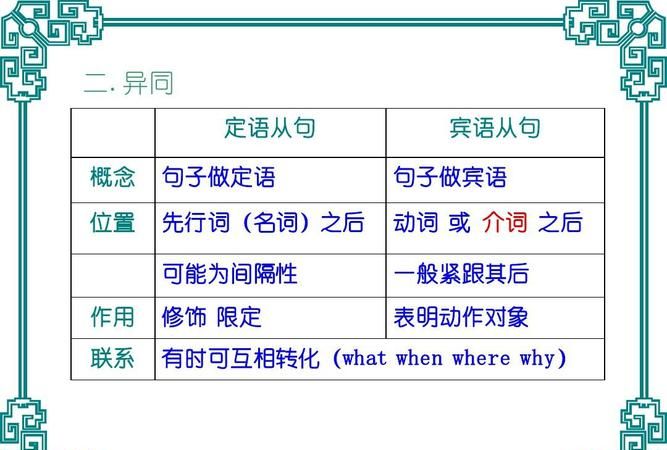
英语定语从句怎么找
定语从句
定语从句就是修饰名词的从句,被修饰的名词称为先行词(Antecedent)。定语从句由关系代词(Relative Pronoun)和关系副词(Relative Adverb)引导,前者在从句中作主语、宾语或表语,后者在从句中作状语。
1.关系代词的选择
先行词为事物时,关系代词用which或that;先行词指一个模糊的、一般的人时,who和that都适宜。如:
I need someone who can do the work quickly.
我需要能够迅速完成这项工作的人。
当先行词指一个具体的、特定的人时,多用who。如:
The aunt who came to see us last week is my father’s sister.
上星期来看我们的姑姑是我父亲的姐姐。
先行词指物,前面又有一个不定代词、最高级形容词或序数词修饰时,关系代词多用that。如:
He has got all the tools that we need.他有我们需要的所有工具。
This is the funnest film that has come from the studio.
这是那个制片厂制作的最滑稽的电影。
The first statement that was issued gave very few details.
最先发布的声明没有公布什么细节。
先行词本身为不定代词时,关系代词多用that。如:
The government has promised to do all that lies in its power to alleviate the hardships of the people.
政府承诺尽其一切力量减轻人民的苦难。
关系代词在从句中作表语时,只能用that或which,不能用who或whom,但可以省略。如:
John is not the man (that/which) he was years ago.
约翰已不再是多年前的他了。
当先行词和定语从句被其他句子成分隔开时,用who或which较为恰当,用that容易造成句子结构不清楚。如:
A war broke out which lasted for forty years.
一场延续了四十年的战争爆发了。
Anybody can explain this who knows English grammar.
任何懂得英语语法的人都能解释这一点。
先行词为集合名词时,如果该词指一个整体,则关系代词用which;如果指组成整体的所有成员,则关系代词用who。如:
Our team, who are all in good form, will do well in the coming matches.
我们组织良好的队伍在未来赛事中一定会表现出色。
Our team, which placed second last year, played even better this year.
去年排名第二的我们队今年打得更为出色。
2.介词十关系代词
有时关系代词之前要用介词。“介词+关系代词”在从句中作状语。如:
The world is stage, on which every role will find a player.—Middleton
世界是个舞台,各种角色都是人扮演。(英)米德尔顿
This is a question in which people are interested.这是人们感兴趣的问题。
A bottle opener is a tool with which bottles are opened.
开瓶器是用来打开瓶盖的工具。
当介词+关系代词作地点状语、时间状语时,它们常常可以被where,when或why代替。如:
The malls of the future will be small cities where/in which you can shop.
eat, and see a film and even dance.
未来的购物街会像一个个小商城,你可以在那里购物、就餐、看电影甚至跳舞。
He was born on the day/when his father died.他在父亲去世的那一天出生。
This is another reason which/why food gram has to be imported.
这是必须进口谷物的另一原因。
重点提示
对于定语从句,基于意义上的需要,可以在some, any, few, several, many, most, all, both, noce, neither, either, each, enough, half, one, two等词和形容语最高级之后接of whom或of which。如:
The North Island is famous for an area of an anrea of hot springs.some of which throw hot water hight into the air.
北岛是著名的温泉胜地,有些温泉的热水能高高地喷向半空。
New Zealand has a population of about 3.8 million people, of which about fourteen percent are Maori.
新西兰大约有380万人口,其中大约14%是毛利人。
The tomatoes, half of which have gone bad, are in a basket.
放在篮子里西红柿有一半已经烂掉了。
The car ran into a crowd of people, several of whom were sent to hospital immediate.汽车撞进了人群,其中好几个人立即被送望医院。
I met the table tennis players, two of whom were studying in university.
我见到了那些乒乓球选手,其中有两人正在大学就读。
3.限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句
限定性定语从句(Restrictive Attributive Clause)表示一种区别意义,它帮助读者或听者把先行词所指的人或物与其他的人或物区别开来。没有它,先行词所指的人或物就会模糊不清。非限定性定语从句(Non-Restrictive Attributive Clause)表示一种附加意义,它对先行词作附带说明。省了它,先行词所指的人或物仍然明确清楚。如:
My uncle is a man who believes in discipline.我叔叔是个十分守纪的人。
My uncle, who believes in discipline, is very strict with his children.
我那十分守纪的叔叔对他的孩子们很严格。
Beijing, which is the capital of China, will hold 2008 Olympic Games.
北京是中国的首都,将主办2008年奥林匹克运动会。
Animals and plants must have a habitat or home, which is comfortable and clean.
动植物必须拥有一个栖息地或家园,而这个栖息地应舒适、清洁。
重点提示
修饰整个主句的定语从句为非限定性定语从句。这种定语从句由which或as引导。如果用which引导,定语从句位于主句之后;如果用as引导,定语从句可以位于主句之后,也可以位于主句之前。which或as指整个主句。如:
We can’t do without rules, which/as you know.
=As you know, we can’t do without rules.你知道的,没有规矩不行。
He failed the exam, which/as was natural.
=As was natural, he failed the exam.他没有考及格,这很自然。
All the schools will reopen on 1st September, which/as announced in today’s papers.
=As is announced in today’s newspapers, all the schools will reopen on? lst September.正如报上的通告,所有学校都将在九月一日重新开学。
在这类定语从句中,关系代词as作主语时,其后面必须有动词be;否则只能用which引导的定语从句。如:
He admires Mr Brown very much, which surprises me.
他很崇拜布朗先生,这使我觉得很奇怪。
He arrived half an hour late, which annoyed us all.
他迟到了半小时,我们都生气了。
所有定语从句的试题都可分成两种基本题型,它们有各自的解题钥匙。
一、基本题型一及解题钥匙
基本题型一:先行词+关系词直接引导定语从句
解题钥匙:唯成份论
说明:用什么关系词直接引导定语从句,唯一取决于先行词在从句中的作用,即取决于先行词在从句中作什么成份,若先行词在从句中相当于代词作用,则应使关系代词who/whom/which/whose/as引导定语从句,而先行词在从句中相当于副词作用,则应使用关系副词when/where/why引导定语从句。
例1:Dorothy was always speaking highly of her role in the play, ______, of course, made the others unhappy.(NMET 2000)
A、who B、which C、this D、what
析:选B,先行词为整个主句,在从句中作主语,所以应使用关系代词,但that不能引导非限制性定语从句,所以只能使用which。
例2:After living in Paris for fifty years he returned to the small town ______ he grew up as a a child.(NMET 96)
A、which B、where C、that D、when
析:选B,因为先行词the small town表地点,在定语从句中作地点状语,所以应使用关系副词where。
区别于:This is the small town ______ is often praised.
A、which B、where C、when D、who
析:选A,先行词the small town仍表地点,但在从句中作主语应属关系代词范畴。
二、基本题型二及解题钥匙
基本题型二:先行词+特定词汇+关系代词which/whom引导定语从句。
说明:特定词词汇通常为:
1、介词(包括复杂介词)
2、数词(包括不定量数词)+of
3、其它词汇(表所属关系)+of
解题钥匙:定语从句与先行词联系论
说明:要找出用什么特定词汇引导定语从句,方法是将定语从句和先行词联系成一个完整的句子,此时缺什么词,特定词汇就由什么词担任。
例1:In the dark street, there wasn't a single person ______ she could turn for help.(NMET 92)
A、that B、who C、from whom D、to whom
析:选D,根据定语从句与先行词联系论,可得到这样一个句子:She could turn ______ the single person for help,显然该句缺介词to,因此应用to whom(其先行词指入)引导定语从句。
例2:He paid the boy for washing ten windows, most of ______ hadn't been cleaned for at least a year.(NMET 90)
A、these B、those C、that D、which
析:选D,因为根据定语从句与先行词联系论,可得到这样一个句子:most of the ten windows hadn't been cleaned for at least a year most of which正体现了不定量数词+of which引导定语从句的特点。
注意上述特定词汇前不能加and、but等连词,否则就不能使用定语从句,而应将whom、which改成them,如:
I have many friends and the tallest of ______ is LiPing.
A、who B、whom C、them D、which
析:选C,因为特定词汇the tallest前面有连词and,所以不能使用定语从句。

复杂定语从句例句分析
初中定语从句例句分析 篇1
一、 定义:
在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫做定语从句。
如:1)The man who lives next to us is a policeman.
2)You must do everything that I do.
上面两句中的man和everything是定语从句所修饰的词,叫先行词,定语从句放在先行词的后面。
引导定语从句的词有关系代词that,which,who(宾格who,所有格whose)和关系副词where,when、why关系词常有三个作用:
1、引导定语从句
2、代替先行词
3、在定语从句中担当一个成分
二、关系代词引导的定语从句
1.who指人,在从句中做主语
The boys who are playing football are from Class One.
Yesterday I helped an old man who lost his way.
2.whom指人,在定语从句中充当宾语,常可省略。
Mr.Liu is the person (whom) you talked about.
注意:关系代词whom在口语和非正式语体中常用who代替,可省略。
The man who/whom you met just now is my friend.
3.which指物,在定语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略
Football is a game which is liked by most boys.
( which 在句子中做主语)
This is the pen (which) he bought yesterday.
( which 在句子中做宾语)
4.that指人时,相当于who或者whom;指物时,相当于which。
在宾语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略。
The people that/who come to visit the city are all here.(在句子中做主语)
Where is the man that/whom I saw this morning? (在句子中做宾语)
5.whose通常指人,也可指物,在定语从句中做定语
He has a friend whose father is a doctor.
I lived in a house whose roof has fallen in.
whose指物时,常用以下结构来代替
The classroom whose door is broken will soon be repaired.
=The classroom the door of which is broken will soon be repaired.
Do you like the book whose color is yellow?
=Do you like the book the color of which is yellow?
初中定语从句例句分析 篇2
要了解定语从句,我们先得明白定语是啥,如果我给介绍一个人或者描述一样东西,以介绍一个人为例,如果我说是个女孩,那么你头脑中的对我介绍的人印象清晰么,应该就一女孩轮廓,但如果我说一个漂亮的,穿着红色衣服的,站在站台上的,那么你对这个人印象是不是逐渐清晰了,这里漂亮的,红色的,站在站台上的便是定语。
我们看看例子
a pretty girl
a girl in red
a girl standing in the platform
a girl who is standing in the platform is lucy
上例中打彩色部分便都是定语,定语通常是修饰名词,如果定语是一个词并且能完整表达一个意思,定语便放在被修饰词前面,否则就放后面,请观察pretty是一个词,便是放前面的,这是你也许会说,a pretty little girl,pretty 和little不是两个词,怎么就放被修饰词前面了呢,一定要注意,pretty和little都是一个并且是各自能表达完整的意思滴。
上例中彩色部分都是定语,定语可以是一个形容词(pretty),可以是介词短语(in red),也可以是分词短语(standing in the platform),也可以是一个句子(who is standing in the platform),而当定语从句是一个句子时,这个句子呢,就是定语从句。
由于定语从句是一个句子,毫无疑问滴,必定不可能是一个词,所以都是放在被修饰词的后面,我们还给这个被修饰的词起了个名字,先行词,因为修饰她的句子还在后面,她先出现的。
然后我们在说说这定语从句,在英语中呢有个规定就是一个句子中有且只能有一个谓语,就好比我们人呢只能有一个心脏。(事物是普遍联系的定语从句经典例句),那我们人啥时候可能会有两个心脏呢?对了,有宝宝的时候,男同胞貌似目前不可能哈,那么句子有个子句的时候便可以有两个谓语了,这时候我们便需要一个东西来标志其子句特征,人类呢是以大肚子,从句便以她的关系代词。我们例子中的who便是关系代词,这个关系我们也可以理解成人类的脐带,将子句和母句联系到一起。所以这关系代词也是紧挨着先行词的。
所以偶们先要搞清楚啥是定语从句,啥是先行词,啥是关系代词。咱再琢磨这定语从句如何用。
1.He is a famous star.
2.Who’s that girl in red?
3.A suitcase that doesn’t have handles is useless.
4.The blue suitcase ,which doesn’t have handles,is useless.
注意上面画线部分有什么相同的。
都是修饰名词,对一个名词进行修饰,补充,让我们对这个名词在我们头脑中都有更清晰的认识。
这类成分就是定语。
观察最后两句,充当定语时一个完整句子,我们叫这类叫定语从句。
注意定语从句,that doesn’t have handles,that作代词+连词,在从句充当主语,并且连接两个句子。
我们叫that为关系代词。和普通代词的区别是它还可以连接两个句子。
被修饰的词叫先行词。如最后两句的suitcase。
Restrictive: A suitcase that doesn't have handles is useless.
Non-Restrictive: The blue suitcase,which doesn't have handles,is useless.
注意这两个句子。
限定性定语从句和非限定定语从句的区别在哪里。
前面那句是限制性定语从句,定语从句对先行词进行修饰,紧挨先行词,去掉从句句子不完整。
后面那句是非限定定语从句,定语从句对先行词进行补充说明,先行词和从句用逗号隔开,去掉句子仍然完整。
对定语从句有大概了解后,我们看看关系词,我们得搞清楚这什么时候用什么关系词,关系词分关系代词和关系副词,关系词通常在定语从句中充当成分的`,当关系词在句子中作状语的时候便用关系副词
引导定语从句的关系词有关系代词who,whom,whose,that,which,as和关系副词when,where,why等。
初中定语从句例句分析 篇3
定语从句由关系词(关系代词、关系副词)引导,关系代词、关系副词位于定语从句句首。
定语从句例句成分分析
一,主语:
是一个句子的主体,一般放在谓语之前,是动作的实施者。
主语由名词,代词,数词,不定式,动词-ing形式或从句充当。
1.is a good students.(名词)
2.is strength.( 名词)
3.enjoys walking in the fields.(代词)
4.is ten.(数词)
5.is important.(不定式短语)
6.is my job t(不定式短语是真正的主语,it 为形式主语)
7.is bad for health.(动词-ing形式作主语)
8.has not been decided yet.(从句作主语,即主语从句)
二,谓语:
用来说明主语的动作或状态,表明主语是什么,做什么,或怎么样。
谓语由动词担当,可由各种时态的动词表示
1.Great hopes great men.(动词)
2.Shehim two years ago.(动词词组)
3.I your question after class.(助动词+动词)
4.She English very well.(情态动词+动词)
5.The dictionary(连系动词+表语)
6.She(连系动词+表语)
三,宾语:
表示动作的对象,是动作的承受者,由名词,代词,不定式,相当于名词的词或从句充当充当,一般放在及物动词或介词的后面。
(一)单宾语
1.Paper catches easily.(名词)
2.He will do for her.(代词)
3.She is listening .(不定式短语)
4.He doesn?t like .(动词-ing形式)
5.He said .(从句,即宾语从句)
(二)双宾语 (直接宾语sth+间接宾语sb)
常见的带双宾语的动词有:give bring buy get lend make offer pass teach tell write read show send leave return
1.Mother bought yesterday.
2.She taught then.
3.I send m last month.
(三)复合宾语(宾语+宾语补足语)
有些及物动词带了宾语后,还需要有一个补足成分,才能使句意完整,即补充说明宾语,能都充当宾补的词有名词,形容词,副词,介词短语,不定式,分词(现在分词和过去分词)
常跟宾补的动词有 allow,ask,advise,call,elect,keep,consider,make,see,name,have,get,help,wish,let,feel,hear,find smell
1.We elected him .(名词)
2.I want him.(副词)
3.Cell phones make it for us to anyone from anywhere.(形容词)
4.The doctor advised me .(不定式短语)
5.I heard Mary singing in her room.(动词-ing形式)
6.He had his watch yesterday.(过去分词)
7.Please make yourself.(介词短语)你请自便。
四,表语:
放在连系动词be ,become,seem,feel turn(当“变得”讲时)等之后,用来说明主语的特征,状态,身份等,可以充当表语的词有名词,动词-ed形式或句子
1.He became when he was only a child.(名词)
2.The book is (代词)
3.He is today.(形容词)
4.Her mother will be soon.(副词)
5.Im 数词)
6.He seemed(动词过去分词)
7.It is to hear the news.(动词现在分词)
8.The problem is ahead of time.(不定式短语)
9.This is .(从句,即表语从句)
五,定语:
用来修饰名词或代词,可作定于的词有名词,代词,数词,介词短语,不定式,动词-ing形式,动词-ed形式以及从句,定于分为前置定语和后置定语
1.Yao Ming is anbasketball player.(形容词,前置)
2.Ronaldo is a player.(名词,前置)
3.hair needs cutting.(代词,前置)
4.students attended the party.(数词,前置)
5.He is in the room.(现在分词,前置)
6.You can see leaves everywhere in fall.(过去分词,前置)
7.Who is the girl (现在分词短语,后置)
8.The hotel is the best in the city.(过去分词短语,后置)
9.This the house (从句,即定语从句,后置)
六,状语:
用来修饰形容词,副词,动词或整个句子,用来表示时间,地点,原因,方式,程度,目的,结果,条件,让步,频度等情况。
通常用作状语的词有副词,介词短语,不定式,动词-ing形式,动词-ed形式,名词词组,从句等,状语一般放在词尾,但有的也放在句首或句中
1.The plane will take off .(介词短语作地点状语)
2.He came late .(介词短语作原因状语)
3.She cut the apple .(介词短语作方式状语)
4.There are plenty of fish .(介词短语作地点状语)
5.The river is long.(副词作程度状语)
6.He ran fast .(不定式作目的状语)
7.She woke suddenly .(不定式作结果状语)
以上就是关于定语从句句子及成分分析 ,定语从句属于句子结构吗的全部内容,以及定语从句句子及成分分析 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

