本文目录
英语定语从句用法详解
定语从句用法详解
想要学好英语怎么能不知道定语从句的用法呢?下面就让我为大家详解一下吧。
在英文中,有两种定语从句:限定性定语从句与非限定性定语从句。这两种定语从句在其功能和形式方面都有明显的区别:
限定性定语从句限定性定语从句与主句的关系很紧奏,对其先行词起限定、修饰的作用。如果将其去掉,会影响句子意思的.完整性;有时甚至于引起费解、误解。例如:
Rainforests are being cleared for valuable timber and other resources to speed up the economic growth of the nationsin which they are located .
为了加速他们各自所在国家的经济发展,热带雨林作为有价值的原木和其他资源正为人们所砍伐。
Ocean currents affect the climates of the lands near which they flow.
洋流影响其流经的附近地区的气候。
They explained the reason to us why they had hated us before.
他们向我们解释为什么他们不喜欢我们的原因。
非限定性定语从句非限定性定语从句在形式上就与主句很松散,它与主句之间有一个逗点","隔开;它对其先行词没有限定、修饰的作用,只起补充、说明的作用。有时也用它来对全句进行补充、说明。即使将其去掉,也不会影响句子意思。由于上述原因,非限定性定语从句在表达意思方面也有别于限定性定语从句。另外,非限定性定语从句在中文译文里,我们往往将其作为一个分句处理,而不把它作定语翻译。 例如:Earlier , the Babylonians had attempted to map the world , but they presented it in the form of a flattened disc rather than a sphere , which was the form adopted by Ptolemy .
(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对先行词a sphere进行补充、说明。)
更早之前,巴比伦人曾试图绘制世界地图,但是他们把它绘制成平盘状而不是托勒密所采用的球体状。
The combination of satellites, which transmit information , computers , which store information , and television , which displays information , will change every home into an education and entertainment center .
(此句中,三个非限定性定语从句分别对三个先行词:satellites ,computers和television进行补充、说明。如果去掉这三个非限定性定语从句,那么句子可简化为:
The combination of satellites , computers and television will change every home into an education and entertainment center .)卫星能传输信息,计算机能储存信息,电视能显示信息,把这些手段结合起来可以使每个家庭都成为教育娱乐的中心。
The sun heats the earth , which makes it possible for plants to grow .(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对全句进行补充、说明,将全句表达的意思看成"一件事情)。太阳给予大地热,这就使植物的生长成为可能。
The old man has a son , who is in the army .(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对先行词son进行补充、说明。但本句所传达的信息是:"这位老人只有一个儿子" .如果将此句改写成限定性定语从句:
The old man has a son who is in the army . 那位老人有一个在部队工作的儿子。那么,限定性定语从句就要对先行词son进行限定、修饰。这样一来,句子所传达的信息就变成了:"这位老人有一个儿子在部队工作,还有其他的儿子在干别的工作".)那位老人有一个儿子,他在部队工作。
限定性定语从句与非限定性定语从句的区别
a) 非限定性定语从句和主句的关系不十分密切,朗读时先行词部分一般用降调并稍做
停顿,书写的时候多半用逗号分开。
b) 非限定性定语从句能够修饰整个句子,限定性定语从句则不能。
c) 非限定性定语从句与限定性定语从句的含义不一样,限定性定语从句是确指,而非
限定性定语从句是泛指。
d) 先行词为专有名词或者具有特指对象的名词时,一般要用到非限制性定语从句。
e) 在非限定性定语从句中,现行词指人的时候,关系代词只能是who,whom,不能用
that;先行词指物的时候,关系代词只能用which, 不能用that.
;
高中定语从句详解PPT绝对经典课件
定语从句是高中阶段的重点,大家要记住相关的语法规则,并且需要通过以后的练习来逐渐透彻掌握。学习中肯定会遇到一些困难,不好弄懂的知识点一定要结合例句细心多看几遍。下面为大家带来高中定语从句详解,希望能帮到你!
Ⅰ.概念:
(1) 定语从句:在主从复合句中用作定语的从句叫定语从句。定语从句一般紧接在先行词后面。
(2) 先行词:被定语从句修饰的成份。先行词可以为一个词,短语,或整个主句。
(3) 引导定语从句的词叫关系词,分为关系代词和关系副词。
关系词的作用:
1) 引导定语从句,连接主句和从句,相当于一个连词;
2) 必在从句中作某个句子成份(可以做主语,宾语,表语,定语,状语)
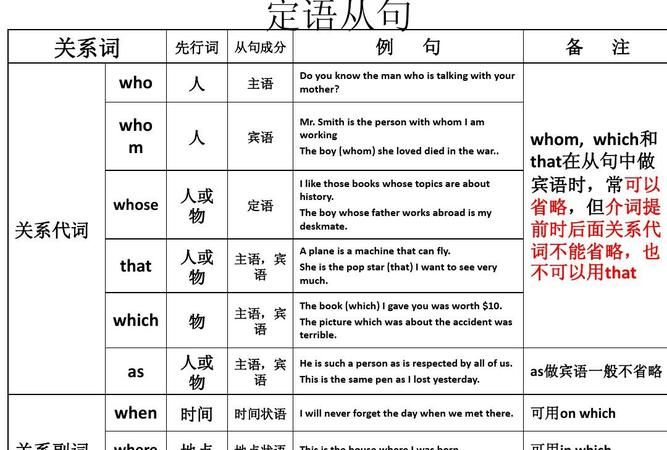
常用的关系代词: that、 which、 who、whom、as , 在从句中作主语,宾语,whose在从句中作定语)
常用的关系副词(在从句中只作状语): when、why、 where
The student who answered the question was John.
I know the reason why he was so angry.
The boy (whom) you are talking to is my brother.
I'd like a room whose window looks out over the sea.
定语从句三步:
第一找出先行词;
第二看先行词在定语从句中的语法的功能(做主语、宾语或状语);
第三选择合适的'关系词。
Ⅱ. 几个关系代词的基本用法:
●that: 可指人或物;在定语从句中作主语,宾语,表语。(指人时,相当于who或 whom;指物时,相当于which)(不用于非限制性定语从句; 不可置于介词后作宾语) 如:
1. Do you know the gentleman that/who spoke just now?
2. You can take anything ( that) you like.
3. What is the question (that/which) they are talking about?
4. Here is the man ( who/whom/that ) you want to see.
5. She's no longer the girl ( that) she used to be before.
●which: 指物;在定语从句中作主语,宾语,表语,定语。如:
1. The bookwhich/that was on the desk was bought by my father.
2. The book (which/that) I bought yesterday is very interesting.
3. The factory in which his father works is far from here.
●who, whom, whose:
who: 主格, 在从句中作主语,在口语或非正式用法中作宾语; 只可指人
whom: 宾格,在从句中作宾语; 只可指人
whose: 属格,在从句中作定语,可指人也可指物。
1. I like the students who/that work hard.
2. All who heard the story were amazed.
(代词如he, they, any, those, all, one等后多用who.)
3. He's a man from whom we should learn.
= He's a man (whom/who/that) we should learn from.
4. A child whose parents are dead is called an orphan.
5. I'd like a room whose window faces south.
=I'd like a room of which the window faces south.
=I'd like a room the window of which faces south.
关系代词作介词宾语: (介词+ whom / which)
关系代词在定语从句中用作介词宾语时, 介词可放于从句之首, 也可放于从句之末. 但以放于句首较为正式.(介词前置,必须注意不影响动词词组的含义。)
1. This is the book for which you asked. =This is the book (that/which) you asked for.
2. Do you know the person with whom I shook hands?
= Do you know the person (whom/who/that) I shook hands with?
3. Is this the factory to which you paid a visit last week?
4. Is this factory the one to which you paid a visit last week?
5. This is the girl whom they are looking after. (介词after与look构成固定词组,不可前置。look at, look for, look after, take care of等)
●as 的用法:(as 引导定语从句, 在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语)
①如为限制性的,多用于the same …as ; the same as;such …as …; as many/much as;so …as等结构中。
1. I have the same book as you (have). 我有一本和你的一样的书。
2. .---Why didn't you mention that in face of the police just now?
--- I thought it was such a minor detail as was hardly worth mentioning.
3. Don't do such things as you are not sure about.
比较:I live in the same house that he used to live in.
I'm wearing the same shirt as you wore yesterday.
比较:Here is so big a stone as no one can lift. (定语从句)
Here is so big a stone that no one can lift it.(结果状语从句)
②如为非限制性的,多单独引导一个定语从句,这种定语从句可置于句首,句中或句尾,译为"正如,这一点"。(动词常为know, see, expect, point out, etc.)
As we all know, smoking is harmful to one's health . (as 作宾语)
=As is known to all, smoking is harmful to one's health . (as 作主语)
=It's known to all that smoking is harmful to one's health .
=Smoking is harmful to one's health, as we all know .(as 作宾语)
=Smoking, as we all know, is harmful to one' health.
He was a foreigner, as I knew from his accent. (宾语, 先行词是前面整个句子)
Ⅲ. 关系副词引导的定语从句:
●When 指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语。其先行词是表时间的名词(如:time, day, week, tear, month, etc.)
He came last night when I was out.
We will put off the picnic until next week, when the weather would be better.
注意:先行词为"时间名词",可用when引导定语从句,when在定语从句中作状语;还可以用which或that 引导,which或that在从句中作主语或宾语。
比较:1. I still remember the day when /on which my brother joined the army.(作状语)
2. I still remember the days which/that we spent together. (作宾语)
3. I shall never forget the day when Shen Zhou Ⅴ was launched, which has a great effect on my life.
●Where 指地点,在定语从句中作地点状语。其先行词是表示地点的名词,如:place, school, factory, room, etc.
This is the place where I was born.
I live in the room where /in which he used to live.
注意:先行词是"地点名词",定语从句可用where引导,还可用which或that引导,which/that 在从句中作主语或宾语。
比较: ※1. This is the factory where /in which he worked last year. (作状语)
2. I think you have got to the point where a change is needed, or you would fail.
3. He's got himself into a dangerous situation where he's likely to lose control of the plane.
4. This is the park which/that they visited last year. (作宾语)
●Why 指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语。先行词为reason 时,可用for which指代;当关系词在从句中作主语或宾语时,则用which或that 引导。如:
1. The reason why / for which / (that) he didn't attend the meeting was that he was ill.
2. I don't believe the reason (that/which) he gave me. (作宾语)
3. Have you asked him the reason that may explain his success? (作主语)
当先行词为way时,the way在从句中作状语时,定语从句常用that, in which,或how引导,that常可以省略。
the way在从句中作主语或宾语时,则用which或that 引导。如:
This is the way (that) /in which I do such things.
比较: Please do the experiment in the way (that/which)I have shown you.
Ⅳ. 限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别:
1. 形式上,非限制性定语从句往往用逗号隔开。
2. 语法上,非限制性定语从句一般不用that.
3. 语义上,限制性定语从句与先行词关系紧密,起限定作用,如果去掉了这个定语从句,整个句子就不完整或者会改变意思;而非限制性定语从句与先行词关系不是很紧密,对先行词起补充说明或描述的作用。
This is the book I like best. 这就是我最喜欢的那本书。
Beijing, which has been China's capital for more than 800 years, is rich in cultural and historic relics. 北京是中国八百年之久的古都,它有着丰富的文化和历史遗产。
4. 翻译时,限制性定语从句可译为一句(较短的一般译为"的"字结构);而非限制性定语从句可译为两句。(见上句翻译)
比较: He has a sister, who is a musician.
He has a sister who is a musician.
引导非限制性定语从句的关系代词,指人时用who, whom, whose , 指物时用which , whose; 关系副词when,where, why, etc.
1. He studied hard at school when he was young, which leads to his success in his later life.
2. Tom's father, who arrived just now, is a famous scientist.
Ⅴ. 几个易混淆的关系代词的比较:
●that & which:
在定语从句中,which 和that 在指代事物时,一般可以互换使用,但并非在任何情况下都是这样,这里介绍宜用that, 而不宜用which 的情况.
①先行词为不定代词,all, much, something, everything, anything, nothing, none, the one等,
1.We should do all that is useful to the people .
2.There's nothing that can be said about it .
3.Do you mean the one that was bought yesterday?
②先行词被only, any, few, little, no, just, very, one of等词修饰时。
1.The only thing that we could do was to wait.
2.That's the very word that is wrongly used.
3. The last place (that) we visited was the chemical works.
比较 *This is one of the best novels that were published last year.
This is the only one of the best novels that was published last year.
③先行词是序数词时或被序数词修饰时。
1.When we talk about Wuxi, the first that comes into mind is Tai Lake.
2.This is the third film that has been shown in our school this term.
④先行词是最高级或被最高级修饰时。
1.This is the best that can be done now.
2.The most important thing that should be done right now is how to stop him from going on.
⑤先行词既有人又有物,用which和who都不适合,这时宜用that.
1.The writer and his novel that you have just talked about is really well known .
2.The rider and his bike that had run over an old woman were held up by the police.
⑥被修饰词为数词时.
1.Yesterday I caught two fish and put them in a basin of water .Now you can see the two that are still alive .
⑦如果有两个从句,其中一个关系代词已用which ,另一个关系代词宜用that,以避免语言的单调或重复。
Edison built up a factory which produced things that had never been seen before.
⑧疑问词是who或which,关系代词宜用that,以避免重复。
1. Which is the book that you like best?
2. Who is the man that is standing at the gate?
⑨主句是There be 结构,修饰其主句的定语从句宜用that 作关系代词. 如:
1. There is still a seat in the corner that is still free.
⑩被修饰成分为表语时,或者关系代词本身是定语从句的表语时,该关系代词宜用that .
1. That's a good book that will help you a lot.
2. My home village is no longer the place ( that ) it used to be .
定语从句中宜用which而不宜用that 的情况:
①当关系代词的前面有介词时.
1.A zoo is a park in which many kinds of animals are kept for exhibition.
2.Is this the room in which Mr. White lives?
②在非限制性定语从句中.
1.Crusoe's dog, which was are now very old, became ill and died .
2.More and more people are beginning to learn English, which is becoming popular in our country. (which指代主句)
③在一个句子中有两个定语从句,其中一个定语从句的关系代词用了that, 另一个宜用which .
1. Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the library which was newly open to us.
④当关系代词后面带有插入语时.
1. Here's the English grammar which, as I have told you, will help improve your English.
⑤先行词本身是that, 宜用which .
What's that which she is looking at?
⑥先行词是those+复数名词.
A shop should keep a stock of those goods which sell best.
●who & that:
who 和 that 指代人时,有些情况宜用who, 而不宜用that
①先行词为anyone, anybody, those, all, one, ones, they, he, people时. 如:
1.The person I want to learn from is the one who studies hard and works well.
2.Anyone who (=Whoever) failed to come to the meeting yesterday must give his reason .
3.Those who are not fit for their work should leave office at once.
②在There be 结构中,修饰主语的定语从句宜用关系代词who 指代人. 如:
1.There is a gentleman who wants to see you .
2.There are several students in our class who are still not sure about the use of attributive clauses.
③当先行词有较长的后置定语时. 如:
1. I met a foreigner in the park yesterday afternoon who could speak Chinese very well.
●as & which:
as & which 引导非限制性定语从句的区别:
①位置的不同:
which 引导的定语从句只置于所限制的句子后;as 位置较灵活,也就是说as可置于所限制的句子前面;插在句子中或放在句子后。如:
1. He was late again, which made his teacher very angry.
2. Jack, as you know, is an honest man. 或Jack is an honest man , as you know.
或As you know, Jack is an honest man.
②先行词的不同:
as引导非限制性定语从句时,其先行词多为一个句子;
which引导非限制性定语从句时,其先行词可以是一个词,一个短语或一个句子。
1. She was very patient towards the children, which her husband seldom was.
2. He was proud, which I dislike very much.(先行词是一个句子)
3. He is an honest man, as is known to all.
③as 一般译为"正如""就像","这一点"
as we all know;as you know; as is known to all; as you see; as we can see; as has been expected; as we have imagined.
定语从句的用法
定语从句的用法
详解
定语从句用来充当句中定语的主谓结构;它主要用于修饰句子中的名词、代词。而定语从句的位置常常是紧跟在被修饰的名词、代词的后面。在被修饰的名词、代词与定语从句之间往往有一个关系词将其前后两部分联系成一个整体,或是构成一个名词短语;或是构成一个代词短语。但从结构上说,关系词与从句是一个整体。排除句子的其他各部分,这种带有定语从句的名词短语或是代词短语的构成可演示如下:
1)three signs that indicate a person is suffering from a panic attack rather than a heart attack
三种意味着一个人是患有惊恐症而不是心脏病的迹象在这个带有定语从句的名词短语中:
signs是:被修饰的名词;
that是:关系词;
that indicate a person is suffering from a panic attack rather than a heart attack是定语从句
2)those who drink a lot 那些大量饮酒的人在这个带有定语从句的代词短语中:
those是:被修饰的名词;
who是:关系词;
who drink a lot是:定语从句通过上面的演示,我们可以归纳出定语从句在句子中的位置、结构如下:
被修饰的名词 / 代词 + 关系词 + 句子 (其中,"被修饰的名词/代词"在语法叫作"先行词".)
要点提示:
1)"先行词"与"关系词"的内在联系"先行词"与"关系词"之间实质上是互等、互换的关系。也就是说,关系词的作用就是将先行词所表达意义"代到"从句中来起作用。例如:
They often become easily frightened or feel uneasy in situations (先行词)where (关系词)people normally would not be afraid .
他们常在人们一般不会感到害怕的情况下却很容易感到恐惧或是感到不自在。
(本句中的关系词where = 先行词(in)situations 。如果把这个复合句拆成两个分句,那就是:
They often become easily frightened or feel uneasy in situations
people normally would not be afraid in situations 由此可以看出,"先行词"与"关系词"之间实质上是互等、互换的关系)。 又例如:
Rude people are those (先行词) whose (关系词)behavior shows little respect
for the rules(先行词) that(关系词) the majority follows .
不讲礼貌的人是指那些,他们的行为对大多数人所遵从的规则并不表示尊敬的人。
由此我们还可以看出,"先行词"往往是分别重复出现在两个分句中的名词或代词。这也就是我们做定语从句的条件之必需。否则,"关系词"就无法去替代"先行词"而构筑定语从句了。这个道理就如同我们在计算机上"做剪贴以前要先做复制"一样。)
2)"先行词"的意义决定"关系词"的选择"关系词"的选择往往是由"先行词"自身表达的意义,以及它在从句中的语法功能而决定的。
这个意思就是说,假如"先行词"自身表达的意义是表示"人的意义"或是"物的意义",那么我们就相应地选择表示"人的意义"或是"物的意义"的"先行词"。"先行词" 在从句中的语法功能也是决定"关系词"选择的重要条件。比如说,同样都是表示"人的意义"的"先行词",如果它在从句中作主语,"关系词"就得用表示"人的意义"的主格形式,如果它在从句中作定语,"关系词"就得用表示"人的意义"的所有格形式。另外,有时"先行词"本身是表示事物的名词,而它在从句中却与介词构成了短语,在从句中充当状语,在这种情况下,我们就应该用"关系副词"而不能用"关系代词"了。例如:
Some people who are successful language learners often fail in other fields .
有些在语言学习上很有成就的人,在其他领域常常一无所成。
In our class , we have some students whose families are not in Wuhan.
我们班上有些家不在武汉市的同学。
There are many sounds which have a meaning and yet are not words .
有许多声音有意义但不是词。
Tell him to go to the classroom where we often have our English class .
如果把这个复合句拆成两个分句,那就是:
tell him to go to the classroom .We often have our English class in the classroom )
告诉他去我们常上英语课的那间教室。
(一) 关系词
从前面的讨论中我们可以清楚地看出,关系词在定语从句的构成里是至关重要的。我们甚至可以说,掌握不好关系词就无法做成定语从句,也无法理解文中带有定语从句部分的意思。因此,我们首先讨论一下关系词的有关问题。
定语从句中的关系词只有两类:关系代词和关系副词;没有连词。也就是说,定语从句中的所有关系词不但都有具体的意义而且都在从句中担任一定的成分。
1)关系代词:who , whom , whose , which , that 等。
who用于代替"表示人的意义"的先行词,并且在从句中作主语;在现代英语里,也可取代whom在从句中作动词的宾语。例如:
I have no idea about the man who wrote the article .
我不认识写这篇文章的那个人。
The little boy who is singing there can recite quiet a number of Chinese poems .
whom 用于代替"表示人的意义"的先行词,并且在从句中作动词或介词的宾语。在现代英语里,如果whom在从句中作动词的宾语,它与who可以通用;但是如果whom在从句中作介词的宾语,那么就只能用whom而不能与who通用了。当然,如果在口语或非正式文体中,介词没有提前,也就没有这点要求了。例如:
Who is the girl whom ( who ) you talked to just now ?
刚才和你说话的那个女孩子是谁?
Yesterday, I happened to meet , in the shopping center , the professor who ( whom ) I got to know at a party .
昨天在购物中心,我碰巧遇见了那位我在一次聚会上认识的教授。
They are looking for the patient on whom doctors just performed an operation . 他们正在寻找那位医生刚刚给他做过手术的病人。
(句中的关系代词whom代替the patient ,在从句中作介词on的宾语,而且介词on提到关系代词的前面,所以who 和whom就绝不可以通用了,此处只能用whom 。)
Who is the girl to who (whom) you talked just now ? (错误)
(句中的关系代词whom(who)代替the girl ,在从句中作介词to的宾语,但是由于介词to已提到了关系代词的前面,who 和whom就绝不可以通用了,所以如果还继续使用who句子就错了。此处只能用whom 。)
whose 用于代替"表示人或物意义"的先行词,在从句中作定语,往往与它所修饰的名词一起构成一个名词短语在从句中担当成分。Whose常表达"某人的、某物的"之意。例如:
Do you know the name of that girl whose brother is your roommate ?
你知道她的哥哥与你同寝室的那位女孩的名字吗?
Water whose boiling point is at 100 degree Centigrade has no color, no flavor.
沸点在摄氏100度的水无色、无味。
which 用于代替"表示事物意义"的先行词,在从句中作主语、宾语。例如:
Views which are entirely new or foreign may also be hard to accept .
那些全新的或是来自国外的观点或许也很难被接受。
I've got a novel which you may like to read .
我弄到一本你或许想看的小说。
That was a fault which could not be forgiven . 那是不能饶恕的错误。
that 既用于代替"表示人的意义"的先行词,也用于代替"表示事物意义"的先行词;在从句中既可以作主语,也可以作谓语动词的宾语,但是不能作介词的宾语。在一定范围内,that = who / whom / which 。例如:
Views that (which ) are entirely new or foreign may also be hard to accept .
那些全新的或是来自国外的观点或许也很难被接受。
Salaried people that ( who) earn more than a few thousand dollars must pay a certain percentage of their salaries to the federal government .工薪在几千美元以上的人必须将工资中的一定百分比交付给联邦政府。
Who is the girl to that you talked just now ? (错误)
要点提示:
定语从句中作宾语的关系代词可以省略;如果关系代词在定语从句中作宾语可以省略。例如:
This is the book ( which ) you were looking for yesterday .
这就是你昨天找的那本书。
I don't like the novel ( that ) you are reading .
我不喜欢你看的这本小说。
Who is the man ( whom ) you're talking about ?
你们谈论的那个人是谁?
定语从句中,关系代词的单复数取决于先行词的单复数。例如:
Those who are in their forties are required to have a physical examination this afternoon .
(先行词Those是复数,关系代词who也就看作是复数,所以从句的谓语动词就用了复数形式are了。)请那些年龄在四十几岁的人于今天下午去进行体检。
This is the magazine which was sent to me by post .
(先行词the magazine是单数,关系代词which也就看作是单数,所以从句的谓语动词就用了单数形式was sent) 这是通过邮局寄给我的杂志。
关系代词that 和which的区别
that 和which在一般情况都可以用于代替"表示事物意义"的先行词,在从句中作主语、宾语。但在下列情况下一般只用that而不用which :
-- 先行词本身是all , everything , something , nothing , anything等不定代词时,例如:
Anything that can burn is a source of heat energy .
任何能够燃烧的东西都是热能源。
There must be something that happened to you .你一定出了什么事。
They had nothing that could cure of his disease .他们没有一点能治愈他疾病的东西了。
-- 先行词已有序数词或形容词的最高级或the last, the only等作定语时,例如:
This is the most impressive TV theater that has never been put on show before . 这是以前从未上演过的最有感染力的电视剧。
That is the only way that leads to your success .那是通向你成功的唯一之路。
We have to consider the first thing that starts our work .
我们必须要考虑启动我们工作的第一件事。
然而,在下列情况下却只用which而不用that:
-- 当先行词表示事物意义,并且在从句中作介词的宾语,那么就只能用which 。当然,如果在口语或非正式文体中,介词没有提前,也就没有这点要求了。例如:
The world in which we live is made of matter .
我们生活于其中的世界是由物质组成的。
Ocean currents affect the climates of the lands near which they flow .
洋流影响其流经的附近地区的气候。
The world that we live in is made of matter.
(正确。因为关系代词虽然在从句中作介词的宾语,但是介词没有提前,所以没有这点要求。)
我们生活于其中的世界是由物质组成的。
The world in that we live is made of matter.
(错误。因为关系代词在从句中作介词的宾语,而且介词已经提前,所以必须遵从这点要求。)
-- 在非限定性定语从句(关于这一点随后就要讲解)中,当关系词表示事物意义时, 只能用which 。这是语法所规定的,没有任何解释。例如:
The sun heats the earth , which makes it possible for plants to grow .
太阳给予大地热,这就使植物的生长成为可能。
The most important form of energy is electrical energy , which is widely used in our daily life .最重要的能源形式是电能,它广泛地运用于我们的日常生活之中。
-- as可以作为关系代词引导限定性定语从句、非限定性定语从句。例如:限定性定语从句 (常用于such … as和the same … as 等句式中)
Such points as you've mentioned are really important in solving the problem .
你提到的这些方面在解决这个问题上的确很重要。
People such as you describe are rarely seen nowadays .
你描述的这种人现在很少见了。
This computer has the same functions as that one has .
这台计算机有着和那台计算机一样的功能。
非限定性定语从句 (as可以作为关系代词引导非限定性定语从句时,as是指全句:也就是说,将整个主句看成一件事或是一个事实;并对其进行补充、说明。这种非限定性定语从句既可以放在主句之前,也可以放在主句之后。)
As I know , she hasn't got married . 如我所知,她还未结婚。
They won the first place in the game, as could be expected.
可以预料,他们在比赛中得了第一。
Professor Li is extremely popular among students , as is known to all of us . 如我们大家所知,李教授极受学生们的欢迎。
2)关系副词:when , where , why 等。在定语从句,关系副词 = 介词 + which 。也就是说,每个关系副词里本身就已经含有了一个介词:when = 在什么时候,where = 在什么地方,why = 为什么原因,等。至于在英文中用哪个具体的介词,就得依具体情况而定了。
when 代替表示时间的名词,而这个名词在从句中又与介词构成了短语,在从句中充当状语,例如:
People will always remember the time when Hong Kong and Macao returned to our motherland .
人们会永远记住香港和澳门回归祖国的那一时刻。
He came at a time when we needed help . 他在我们需要人帮忙的时候来了。
We don't know the exact time when the English Evening will be held . 我们不知道英语晚会举行的确切时间。
where 代替表示地点的名词,而这个名词在从句中又与介词构成了短语,在从句中充当状语。例如:
The place where we're to have the Speech Contest has not been decided yet.我们举行演讲比赛的地点还未定下来。
He is living in a newly-built house where there used to be a pond . 他现在居住的新房是原先一个池塘的旧址。
That is a beautiful campus where I made a lot dreams .
那是一座我曾经在那儿有过许多梦想的美丽的校园。
why 代替表示原因的名词,而这个名词在从句中又与介词构成了短语,在从句中充当状语。例如:
He didn't tell her the reason why he was so happy .
他没有告诉她为什么他那么高兴的原因。
The reason why she was late is not so acceptable .
她迟到的原因不那么令人接受。
They explained the reason to us why they had misunderstood us before .
他们向我们解释为什么他们以前误解了我们的原因。
介词+关系代词
在这种结构中,关系代词若是表示人的意义,就只能用whom ;关系代词若是表示事物的意义,就只能用which 。而这种结构中较难解决的问题是介词的选择问题,因为这个问题的解决取决于多种因素:
A)动词与介词的搭配B)名词与介词的搭配C)形容词与介词的搭配,等等。总之,要依从句的具体需要而定。例如:
A)动词与介词的搭配
He has found a good job for which he is qualified .( qualify + 名词+ for "使…具有…资格" )他找到了一份他能胜任的工作。
The man to whom you talked just now will chair the meeting tomorrow . ( talk to + 名词 "与某人谈话" ) 你刚才与他谈话的那个人明天主持那个会议。
He is bargaining with the landlord over the monthly price at which the apartment rents .名词+ rent at + 表示价格的词 "某物以某价格出租" )
他在与房东就那套公寓出租的月租金进行磋商。
B)名词与介词的搭配
They are still living in the little house in which they've been lived for 15 years . ( in the house "在屋子里" )
他们现在还住在他们已住了15年的那个小房子里。
We've worked out a method by which our production can be raised on a large scale.( by a method通过某种方法) 我们已研制出了一个能大规模提高生产的方法。
She didn't realize the extent to which she had been distracted .( to extend "到某种程度" ) 她没有意识到她心烦意乱的程度。
C)形容词与介词的搭配
The secretary with whom the boss is not happy will be fired for her inefficiency . (happy with "对…表示满意")
老板对其不满意的那个秘书将由于她没有工作效率而被解雇。
I've found the job for which I've been eager for a long time.( eager for "渴望得到…" ) 我已找到了我渴望已久的那份工作。
He is a learned man with whom we are familiar .
(familiar with 熟悉…)他是一位我们熟悉的有学识的人。
2)定语从句的种类
在英文中,有两种定语从句:限定性定语从句与非限定性定语从句。这两种定语从句在其功能和形式方面都有明显的区别:
限定性定语从句
限定性定语从句与主句的关系很紧奏,对其先行词起限定、修饰的作用。如果将其去掉,会影响句子意思的完整性;有时甚至于引起费解、误解。例如:
Rainforests are being cleared for valuable timber and other resources to speed up the economic growth of the nationsin which they are located .
为了加速他们各自所在国家的经济发展,热带雨林作为有价值的原木和其他资源正为人们所砍伐。
Ocean currents affect the climates of the lands near which they flow.
洋流影响其流经的附近地区的气候。
They explained the reason to us why they had hated us before.
他们向我们解释为什么他们不喜欢我们的原因。
非限定性定语从句
非限定性定语从句在形式上就与主句很松散,它与主句之间有一个逗点","隔开;它对其先行词没有限定、修饰的作用,只起补充、说明的作用。有时也用它来对全句进行补充、说明。即使将其去掉,也不会影响句子意思。由于上述原因,非限定性定语从句在表达意思方面也有别于限定性定语从句。另外,非限定性定语从句在中文译文里,我们往往将其作为一个分句处理,而不把它作定语翻译。
例如:Earlier , the Babylonians had attempted to map the world , but they presented it in the form of a flattened disc rather than a sphere , which was the form adopted by Ptolemy .
(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对先行词a sphere进行补充、说明。)
更早之前,巴比伦人曾试图绘制世界地图,但是他们把它绘制成平盘状而不是托勒密所采用的球体状。
The combination of satellites, which transmit information , computers , which store information , and television , which displays information , will change every home into an education and entertainment center .
(此句中,三个非限定性定语从句分别对三个先行词:satellites ,computers和television进行补充、说明。如果去掉这三个非限定性定语从句,那么句子可简化为:
The combination of satellites , computers and television will change every home into an education and entertainment center .)卫星能传输信息,计算机能储存信息,电视能显示信息,把这些手段结合起来可以使每个家庭都成为教育娱乐的中心。
The sun heats the earth , which makes it possible for plants to grow .(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对全句进行补充、说明,将全句表达的意思看成"一件事情)。太阳给予大地热,这就使植物的生长成为可能。
The old man has a son , who is in the army .(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对先行词son进行补充、说明。但本句所传达的信息是:"这位老人只有一个儿子" 。如果将此句改写成限定性定语从句:
The old man has a son who is in the army . 那位老人有一个在部队工作的儿子。那么,限定性定语从句就要对先行词son进行限定、修饰。这样一来,句子所传达的信息就变成了:"这位老人有一个儿子在部队工作,还有其他的儿子在干别的工作"。)那位老人有一个儿子,他在部队工作。
知识过关


以上就是关于定语从句用法详解 ,英语定语从句用法详解的全部内容,以及定语从句用法详解 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

