本文目录
英语初中的从句有哪几种 用法是什么意思
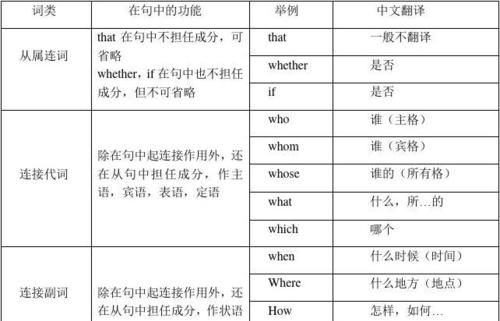
名词性从句(在句中充当名词的作用),它分为主语从句,表语从句,宾语从句,和同位语从句。
引导词:
词性/词形/词义/作从句中的成分
连接词/if/是否/-
连接词/that/-/-
连接代词/who(ever)/(无论)谁[主格]/-
连接代词/whom(ever)/(无论)是谁[宾格]/主,表
连接代词/whose(ever)/(无论)谁的[所有格]/主,宾
连接代词/which(ever)/(无论)哪一个(些)/主,宾,表,定
连接代词/what(ever)/(无论)什么,……东西/主,宾,表,定
连接副词/when/什么时间/状
连接副词/where/什么地点/状
连接副词/how/怎么,如何/状
连接副词/why/为什么/状
★定语从句(在句中修饰名词,也叫先行词作用),它分为限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。
引导词:
词性/词形/先行词/充当从句成分
关系代词/who/人/主,宾表
关系代词/whose/人/宾
关系代词/which/物/主,宾,表
关系代词/that/人或物/主,宾,表
关系代词/as/人或物/主,宾,表
关系代词/whose(of
whom
或
of
which)/人或物/定
关系副词/when(=
in
等
+
which)/时间词/状
关系副词/where(=
in
等
+
which)/地点词/状
关系副词/how/方式词/状
关系副词/why(=
for
which)/reason/状
关系副词/that在口语中可代替关系副词/-/状
★状语从句(在句中起状语的作用),它分为时间状语从句,地点状语从句,原因状语从句,结果状语从句,目的状语从句,让步状语从句,方式状语从句,比较状语从句,条件状语从句,共九种。

初中英语语法三大从句总结
主要是宾语从句和状语从句,如果说考的稍微难一些的话就是定语从句以及名词性从句,一般考的话后两者的难度不会很大.
宾语从句在句中作及物动词或介词的宾语,从句放在主句之后,前后不用逗号分开.
宾语从句:
引导宾语从句的词有:
连词that(在口语中that常可省略),if,whether,如:
He knows that Jim will work hard.
连接代词who,whom,which等,如:
Do you know who (whom) they are waiting for?
连接副词when,where,how,why等,如:Could you tell me how we can get to the station?
3.whether和if都有“是否”的意思,一般情况下两者可以换用,但在介词之后,
不定式之前,与or not连用,在句首或在引导表语从句,同位语从句时,只能用whether,如:I want to know if/whether the news is true.He doesn't know whether to stay or not?
4.宾语从句要用陈述句语序.
5.宾语从句一定要注意时态呼应,即:当主句谓语动词是过去式时,从句中谓语动
词也要用过去范畴的时态,但若从句陈述的是真理或客观规律,其谓语的时态仍用一般现在时,如:
He asked who could answer the question.
My father told me that the earth goes around the sun.

初中英语需要掌握哪些从句
从句我用*表明
宾语从句,例子:I think *(that) I am a good student*.
主语从句,例子:*What he said* is very strange.
定语从句:例子:The child *who wears a red hat* is my friend's little sister.
表语从句,例子:The problem is *that he is too fat to wear the trousers*.
状语从句,分为时间和地点,以及原因,让步状语从句等:*If it rains tommorrow*,I won't go to travel. *When he was a child*,he didn't like to play with friends. *Where he lives*,the sun is shining.
同位语从句也有,但是到高中才是重点,我还是给你个例子:The truth *that the gentleman had been a criminal* surprised every person.
初中英语各种从句的详细讲解
一.主语从句
主语从句是在复合句中充当主语的从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾。
1. It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
It 作形式主语代替主语从句,主要是为了平衡句子结构,主语从句的连接词没有变化。而it引导的强调句则是对句子某一部分进行强调,无论强调的是什么成分,都可用连词that。被强调部分指人是也可用who/whom。例如:
It is a pity that you didn’t go to see the film.
It doesn’t interest me whether you succeed or not.
It is in the morning that the murder took place.
It is John that broke the window.
2. 用it 作形式主语的结构
(1) It is +名词+从句
It is a fact that … 事实是…
It is an honor that …非常荣幸
It is common knowledge that …是常识
(2) it is +形容词+从句
It is natural that… 很自然…
It is strange that… 奇怪的是…
(3) it is +不及物动词+从句
It seems that… 似乎…
It happened that… 碰巧…
(4) it +过去分词+从句
It is reported that… 据报道…
It has been proved that… 已证实…
3. 主语从句不可位于句首的五种情况
(1) if 引导的主语从句不可居于复合句句首。
(2) It is said , (reported) …结构中的主语从句不可提前。例如:
It is said that President Jingo will visit our school next week. (right)
That President Jiang will visit our school next week is said. (wrong)
(3) It happens…, It occurs… 结构中的主语从句不可提前。例如:
It occurred to him that he failed in the examination. (right)
That he failed in the examination occurred to him. (wrong)
(4) It doesn’t matter how/whether …结构中的主语从句不可提前。例如:
It doesn’t matter whether he is wrong or not. (right)
Whether he is wrong or not doesn’t matter. (wrong)
(5) 含主语从句的复合句是疑问句时,主语从句不可提前。例如:
Is it likely that it will rain in the evening? (right)
Is that will rain in the evening likely? (wrong)
4. What 与that 在引导主语从句时的区别
What 引导主语从句时在句时在从句中充当句子成分,如主语.宾语.表语,而that 则不然。例如:
1) What you said yesterday is right.
2) That she is still alive is a consolation.
二.宾语从句
宾语从句就是在复合句中作宾语的名词性从句,通常放在主句谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。
1. 作动词的宾语
(1) 由that引导的宾语从句(that 通常可以省略),例如:
I heard that be joined the army.
(2) 由what, whether (if) 引导的宾语从句,例如:
1) She did not know what had happened.
2) I wonder whether you can change this note for me.
(3) 动词+间接宾语+宾语从句。例如:
She told me that she would accept my invitation.
2. 作介词的宾语
例如:Our success depends upon how well we can cooperate with one another.
3. 作形容词的宾语
例如:I am afraid (that) I’ve made a mistake.
That 引导的从句常跟在下列形容词后作宾语:
nxious, aware, certain, confident, convinced, determined, glad, proud, surprised, worried, sorry, thankful, ashamed, disappointed, annoyed, pleased, hurt, satisfied, content 等。也可以将此类词后的that 从句的看作原因状语从句。
4. It 可以作为形式宾语
It 不仅可以作为形式主语,还可以作为形式宾语而真正的宾语that 从句则放在句尾,特别是在带复合宾语的句子中。 例如:
We heard it that she would get married next month..
5. 后边不能直接跟that 从句的动词
这类动词有Allow, refuse, let, like, cause, force, admire, condemn, celebrate, dislike, love, help, take, forgive等。这类词后可以用不定式或动名词作宾语,但不可以用that引导的宾语从句。例如:
I admire their winning the match. (right)
I admire that they won the match. (wrong)
6. 不可用that从句作直接宾语的动词
有些动词不可用于“动词+间接宾语+that从句“结构中,常见的有Envy, order, accuse, refuse, impress, forgive, blame, denounce, advise, congratulate等。例如:
He impressed the manager as an honest man. (right)
He impressed the manager that he was an honest man. (wrong)
7. 否定的转移
若主句谓语动词为Think, consider, wuppose, believe, expect, fancy, guess, imagine等,其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,一般要把否定词转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。例如:
I don’t think this dress fits you well.(我认为这件衣服不适合你穿。)
三.表语从句
表语从句在复合句中作表语的名词性从句,放在系动词之后,一般结构是“主语+连系动词+表语从句”。可以接表语从句的连系动词有be, look, remain, seem等。引导表语从句的that常可省略。另外,常用的还有the reason is that… 和It is because 等结构。例如:
1) The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.
2) This is why we can’t get the support of the people
3) But the fact remains that we are behind the other classes.
4) The reason he is late for school is that he missed the early bus.
四.同位语从句
同位语从句就是在复合句中作名词的同位语的名词性从句。
1. 同位语从句的功能
同位语从句对于名词进一步解释,说明名词的具体内容,一般由that引导,例如:
1) The king’s decision that the prisoner would be set free surprised all the people.
2) The order that all the soldiers should stay still is given by the general.
2. 同位语在句子中的位置
同位语从句有时可以不紧跟在它所说明的名词后面,而是被别的词隔开。例如:
He got the news from Mary that the sports meeting was put off.
五定语从句
定语从句是由关系代词和关系副词引导的从句,其作用是作定语修饰主句的某个名词性成分,定语从句分为限定性和非限定性从句两种。
一、 限定性定语从句
1. that即可代表事物也可代表人,which代表事物;它们在从句中作主语或宾语,that在从句中作宾语时常可省略关系词,which在从句中作宾语则不能省略。而且,如果which在从句中作“不及物动词+介词”的介词的宾语,注意介词不要丢掉,而且介词总是放在关系代词which的前边,但有的则放在它原来的位置
2. which作宾语时,根据先行词与定语从句之间的语义关系,先行词与which之间的介词不能丢
3. 代表物时多用which,但在带有下列词的句子中用that而不用which,这些词包括all, anything, much等,这时的that常被省略
4. who和whom引导的从句用来修饰人,分别作从句中的主语和宾语,whom作宾语时,要注意它可以作动词的宾语也可以作介词的宾语
5. where是关系副词,用来表示地点的定语从句
6. when引导定语从句表示时间
〔注〕值得一提的是,表示时间“time"一词的定语从句只用when引导,有时不用任何关系代词,当然也不用that引导
By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed there for two weeks.
I still remember the first time I met her.
Each time he goes to business trip, he brings a lot of living necessities, such as towers, soap, toothbrush etc.
7. whose是关系代词,修饰名词作定语,相当于所修饰成分的前置所有格
8. 当从句的逻辑主语是some, any, no, somebody, anybody, nobody, something, anything, everything或nothing时,常用there is来引导
二、非限定性定语从句:非限定性定语从句的作用是对所修饰的成分作进一步说明,通常和主句间用逗号隔开,将从句拿掉后其他部分仍可成立
1. which引导的非限定性定语从句来说明前面整个句子的情况或主句的某一部分
2. 在引导限定性定语从句时,that有时相当于in which, at which, for which或at which
Attitudes towards daydreaming are changing in much the same way that(in which) attitudes towards night dreaming have changed. 人们对白日做梦的态度正在改变,这与人们对夜间做梦的看法的变化有非常相似之处。
I like the music for the very reason that(for which) he dislike it. 我出于某种原因喜欢这种音乐,而他恰恰与我相反。
We arrived the day that(on which) they left. 刚好我们到的那天他们走了。
3. 有时as也可用作关系代词
4. 在非限定性定语从句中,不能用that,而用who, whom代表人,用which代表事物.
一.定语从句及相关术语
1.定语从句:修饰一个名词或代词的从句称为定语从句,一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词后面。
2.关系词:引导定语从句的关联词成为关系词
关系词有关系代词和关系副词。关系代词有that, which, who, whom, whose, as等;关系副词有where, when, why等。
关系词常有3个作用:1,引导定语从句。2,代替先行词。3,在定语从句中担当一个成分。
二.关系代词引导的定语从句
1.who指人,在从句中做主语
(1) The boys who are playing football are from Class One.
2. whom指人,在定语从句中充当宾语,常可省略。
(1) Mr. Liu is the person (whom) you talked about on the bus.
注意:关系代词whom在口语和非正式语体中常用who代替,可省略。
(3) The man who/whom you met just now is my friend.
3. which指物,在定语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略
(1) Football is a game which is liked by most boys.
(2) This is the pen (which) he bought yesterday.
4. that指人时,相当于who或者whom;指物时,相当于which。在宾语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略。
(5) The number of the people that/who come to visit the city each year rises one million.
(6) Where is the man that/whom I saw this morning?
5. whose通常指人,也可指物,在定语从句中做定语
(1) He has a friend whose father is a doctor.
(2) I once lived in a house whose roof has fallen in.
whose指物时,常用以下结构来代替
(3) The classroom whose door is broken will soon be repaired.
(4) The classroom the door of which is broken will soon be repaired.
(5) Do you like the book whose cover is yellow?
(6) Do you like the book the color of which is yellow?
三.介词+关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词在定语从句中做介词宾语时,从句常由介词+关系代词引导
(1) The school (that/which) he once studied in is very famous.
(2) The school in which he once studied is very famous.
(3) Tomorrow I will bring here a magazine (that/which) you asked for.
注意:1. 含有介词的动词短语一般不拆开使用,如:look for, look after, take care of等
(1) This is the watch which/that I am looking for. (T)
(2) This is the watch for which I am looking. (F)
2. 若介词放在关系代词前,关系代词指人时用whom,不可用who或者that;指物时用which,不能用that;关系代词是所有格时用whose
(1) The man with whom you talked is my friend. (T)
(2) The man who/that you talked with is my friend. (F)
(3) The plane in which we flew to Canada is very comfortable. (T)
(4) The plane in that we flew in to Canada is very comfortable. (F)
3. “介词+关系代词”前可有some, any, none, both, all, neither, most, each, few等代词或者数词
(1) He loved his parents deeply, both of whom are very kind to him.
(2) In the basket there are quite many apples, some of which have gone bad.
(3) There are forty students in our class in all, most of whom are from big cities.
四.关系副词引导的定语从句
1. when指时间,在定语从句中做时间状语
(1) I still remember the day when I first came to the school.
2. where指地点,在定语从句中做地点状语
(1) Shanghai is the city where I was born.
3. why指原因,在定语从句中做原因状语
(1) Please tell me the reason why you missed the plane.
注意:关系副词引导的从句可以由“介词+关系代词”引导的从句替换
(1) The reason why/ for which he refused the invitation is not clear,
(2) From the year when/in which he was going to school he began to know what he wanted when he grew up.
五.限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
形式上 不用逗号和主句隔开 用逗号和主句隔开
意义上 是先行词不可缺少的定语,不能删除 是对先行词的补充说明,删除后意思仍完整
译法上 翻译成先行词的定语,“…的…” 通常翻译成主句的并列句
关系词的使用上 A.做宾语时可省略 B。可用that
C.可用who代替whom A.不可省 B。不用that
C。不用who代替whom
限制性定语从句举例:
(1) The teacher told me that Tom was the only person that I could depend on.
非限制性定语从句举例:
(1) His mother, who loves him very much, is strict with him.
要注意区分以下几个句子的不同
(1) His brother who is now a doctor always encourages him to go to college.
他那当医生的哥哥常鼓励他要考上大学。(他还有其他的哥哥)
以上就是关于初中英语几大从句 ,英语初中的从句有哪几种 用法是什么意思的全部内容,以及初中英语几大从句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
