本文目录
什么叫从句
从句(Subordinate Clause)是复合句中不能独立成句,但具有主语部分和谓语部分,由that、who、whom,when,why,where。how,which等引导词(Connective)引导的非主句部分。从句的分类 从句不能单独成句,但它也有主语部分和谓语部分,就像一个句子一样。所不同在于,从句须由一个关联词(connective)引导。根据引导从句为主不同大概可分为:主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句、定语从句和状语从句6类。前四类由于主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句及同位语从句在句子的功用相当于名词,所以通称名词性从句;定语从句功能相当于形容词,称为形容词性从句;而状语从句功能相当于副词,称为副词性从句。状语从句还可以分为条件状语从句、原因状语从句、地点状语从句和时间状语从句。 1.主语从句(Subject Clause):用作主语的从句叫主语从句。引导主语从句的关联词有从属连词、疑问代词、疑问副词、缩合连接代词、缩合连接副词等。 2.表语从句(Predicative Clause):用作表语的从句叫表语从句。引导表语从句的关联词与引导主语从句的关联词大都一样。 3.宾语从句(Object Clause):在句子中起宾语作用的从句叫做宾语从句.宾语从句分为三类:动词的宾语从句,介词的宾语从句和形容词的宾语从句。 4. 同位语从句是名词性从句(主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句)中的主要从句之一,从句作同位语表示与之同位的名词(短语)的实际内容,它的作用相当于名词,对前面的名词(短语)加以补充说明或进一步解释,相当于一个表语从句,它们之间的关系是同位关系,即主表关系。 5.定语从句是由关系代词或关系副词引导的从句,其作用是作定语修饰主句的某个名词性成分,相当于形容词,所以又称为形容词性从句,一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词后面。 6.状语从句可分为: (1)时间状语从句:(adverbial clause of time) (2)地点状语从句:(adverbial clause of place) (3)原因状语从句:(adverbial clause of cause) (4)条件状语从句:(adverbial clause of condition) (5)目的状语从句:(adverbial clause of purpose) (6)让步状语从句:(adverbial clause of concession) (7)比较状语从句:(adverbial clause of comparison) (8)方式状语从句:(adverbial clause of manner) (9)结果状语从句:(adverbial clause of result) 7.德语中的从句:状语从句和宾语从句均用 Dass 来引导编辑本段宾语从句定义 宾语从句就是一个句子作动词或介词的宾语。三要素 连接词、语序和时态。 连接词一般都是that(指事物或人),which(指事),who(指人) 1.从句为陈述句,常选择连接词that或将that省略,直接与主句相连。 2.从句为一般疑问句,常选择连接词if或whether。在whether…or not结构中不能用if替换。 3.从句为特殊疑问句,常选择what,when,where,which,who,how等的疑问代、副词作连接词。 ★当who为主语时,句式为:who+谓语+其他 判断时态情况: 1.主句是一般现在时,从句为各种时态情况 2.主句是一般过去时,从句为各种相应过去时态。注意:从句描绘客观事实,用一般现在时 3.主句是一般将来时,一般从句为一般现在时(“主将从现”) 例题: (1. The teacher told the children that the sun____ round. A. was B. is C. were D. are 选B,因其陈述为无可争议的客观事实 (2. I believe that our team____ the basketball match. A. win B. won C. will win D. wins 选C ,这是讲话人现在对将来情况的主观推测 (3.The soldiers soon reached( )was once an old temple( )the villagers used as a school. A.which;where B.what;which C.where;which D.what;where 答3:选B,动词reach后接宾语从句,从句缺少宾语,where不可,which引导宾语从句时表疑问含义“哪一个…”而此句中并非疑问含义,不知道哪一座庙宇,而是用what从句表陈述含义,意“过去的一座旧庙宇”;te-mple后为对其修饰的定语从句,用关系代词which代替,并在从句中作动词used的宾语,use sth. as…“把…用作… 宾语从句,在复合句中作宾语,位于及物动词后; Tell him which class you are in . Do you know what he likes? (1)主、从句时态一致: 主句谓语过去时,从句相应过去时; He answered that he was listening to me. 主句谓语现在时,从句时态任所需; He says (that) he will leave a message on my desk. They know (that) he is working hard. 具体过去永不变,真理格言现在时; He told me that he was born in 1980. Father told me that practice makes perfect . (2)否定前移,及完成反意问句; 在think/ believe/ suppose/ guess/ imagine/ expect等动词后跟宾语从句否定式时,应转移到主句上去,完成反意疑问句时,应与从句主、谓保持一致。(注: 否定前移的条件是,主句主语是第一人称) I don't think you are right,are you I don't believe they have finished their work yet,have they (3)在表示建议suggest,advise 要求demand 、desire、require、request、propose; 决定 decide; 命令 order、command; 坚决主张 insist; 等动词后跟宾语从句,用(should)+v.(虚拟语气) eg. I suggested that you(should)study hard. He ordered that we should go out at once. (4)如果宾语从句后有宾语补足语,用it作形式宾语,把宾语从句后置 eg.You may think it strange that he would live there. (5)宾语从句that常可省略,但在以下情况下不能省略 A.当主句谓语动词带有两个或两个以上宾语从句时,可以省略第一个that,其他不能省略。 eg.I believe(that)you have done your best and that things will get best? B.当it作形式宾语时 eg.She made it clear that she had nothing to do with him. C.当宾语从句前置时 eg.That our team will win,I believe.分类 A 、作动词的宾语: eg.I heard the news I 主语 heard 谓语动词 the news.名词作宾语 I主语 heard 谓语动词 that he would come here later on.一个句子作宾语---宾语从句 B 、作介词的宾语: eg.He said nothing about this plan。 He主语 said 谓语动词 nothing 代词作动词的宾语 about 介词 the plan. 名词作介词的宾语带有宾语从句的复合句的构成 带有宾语从句的复合句就是用连接词把一个主句和一个宾语从句连接在一起。连接词有:that(可省略),what,who,when,where,why,which,if,whether,how. 注意 A 宾语从句必须用陈述语序。 False: He is wondering when can he finish this difficult job. Right: He is wondering when he can finish this difficult job. B 有时候可以用it 作形式宾语,而把真正的宾语从句放在后面。 Bad: I thought that he could finish this job in just two hours impossible. Good: I thought it impossible that he could finish this job in just two hours. Bad: He left whether we should continue this project to my judgment. Good: He left it to my judgment whether we should continue this project. C 带有宾语从句的复合句的否定形式一般是否定主句。 Bad: I think he doesn’t like the English teacher. Good: I don’t think he likes the English teacher. D False: He wanted to know why he is crying in the corner. Right: He wanted to know why he was crying in the corner. 4.同位语从句(Appositive Clause):与先行词同位或等同的从句叫作同位语从句。其关联词多为that。 5.定语从句(Attributive Clause):用作定语的从句叫定语从句。定语从句一般皆放在被它所修饰的名(代)词之后,这种名(代)词就叫作先行词(Antecedent)。引导定语从句的关联词为关系代词(或称引导词、关系词等)。关系代词在定语从句中可用作主语、宾语、定语等;关系副词在定语从句中用作状语。 ①引导定语从句的关联词有who,whom,whose,that,when,where,why 和 which. 在非限制定语从句中,只可用which,who,whose,where,when.,如果指代前面整个句子,多用which. 例句: The dog that/which was lost has been found. (失踪的狗已经找到了。) Those who are in favor of the proposal are expected to discuss it in detail after the meeting. (有人认为那些对这个提案有兴趣的人最好是在会后再具体讨论它。) There are many organizations whose purpose is to help the homeless. (存在着许多旨在帮助无家可归者的组织。) The days when we had to rely on wool,cotton or silk for our clothes have now passed. (那种必须依赖羊毛,棉花或者蚕丝做衣服的日子已经过去了。) Air moves from places where the pressure was high to places where the pressure is low. (空气从压强高的地方流向压强低的地方。) This is the reason why he refused to help us. (这就是他拒绝帮助我们的原因。) He was born in 1976,when an earthquake struck the country. (他出生于1976年,这一年这个城镇发生了地震。) They turned a blind eye to the suffering of the people,which enraged all of us. (他们对受苦人们的漠视激怒了我们。) ② 当引导定语从句的先行词前有all,any,no,little,much,very first等词,或先行词前为形容词最高级所修饰时,或先行词为all,anything,nothing,something,everything时,从句的引导词只能用that. The only thing that matters to the children is how soon they can have their holiday. (孩子们唯一关心的是他们什么时候放假?) These are the very points that puzzle me. (真正困扰我的是这些观点。) Is there anything that bothers you? (有什么事烦着你吗?) This is the best film that was ever produced by the company. (这部是那个公司有史以来拍摄得最好的电影。) ③as 可做引导词引导定语从句,多和such,the same 连用. As 引导的定语从句也可修饰整个句子,既可放在先行词后,也可放在句子开头. 例句: Such people as you describe are rare nowadays.(你描述的那一类人现在很少了。) The boy was run over by a motor-car,as often happened in pre-liberation Shanghai.(那个男孩被一辆摩托轧过去了,这种事在解放前的上海是不少见的。) As is often the case,the girl forgot to bring her dictionary.(正如往常一样,这个女孩又忘了带上字典。) We are opposed to such ideas as are not based upon objective facts.(我们是反对这种毫无事实根据的想法的。) ④介词+which/whom/whose从句 The driver is the man from whose room she had stolen the gold watch.(她就是从那个司机的房间偷了金表的。) Language is a tool by means of which people communicate ideas with each other.(语言就是人们用来和其他人交流的一种工具。) Jane spent all evening talking about her latest book,of which none of us had ever heard.(Jane一晚上都在谈论着也最近学课本,那些内容我们闻所未闻。) 例题: Water dissolves a part of nearly everything _______ it comes in contact. a. where b. that c with which d as soon as ⑤代/名+介词+which 从句 He is needing a book,the name of which I don't know.(他需要一本书,但是我不知道书名。) In factories and in our daily life,there are many waste materials,all of which can be turned into useful things under certain condition.(在工厂里,在我们的日常生活中都有很多垃圾,其实这些垃圾在某种情况下是可以转变为有用的东西的。) To make an objective test the teacher writes a series of questions,each of which has only one correct answer.(为了能够客观地测试,老师写了一串答案唯一的问题。) ⑥同位语从句和定语从句 The news that he has been admitted by Harvard University is very pleasing.(他被哈佛大学录取的消息非常令人兴奋。) The news that you told me was really exciting.(你告诉我的好个消息真的是很激动人心。) ⑦ 难句: NO.1He is one of the men who were chosen to represent the group.(他是被选为代表该团队的人中一员。) NO.2He is the only one of those boys who is willing to take on another assignment.(他是那些男孩中唯一一个愿意再接受任务的人。) NO.3I shall never forget the day when we first met.(我永远也不会忘记我们第一次见面的那一天。) NO.4I remember the morning when he first came to school.(我记得早上,当他第一次来到学校。) NO.4I shall never forget the days which I spent in the countryside.(我永远不会忘记和你一起度过的日子,我在农村度过的。) NO.5The room where he lived is kept in good repair.(他住的房间是保持良好使用状态。) NO.6Alva found a place in the cellar where he uses as his first laboratory.(馆长在地窖里找到一个地方使用作为他第一次在他的实验室。 NO.7The way in which/that you answered the questions was admirable(以何种方式/这就是你回答了他所提出的问题令人钦佩)时态 1·主句用一般现在时,从句可用任意时态。 2·主句用过去时,从句用过去某个时态。 3·主句用过去时,从句是真理时,只用一般现在时。宾语从句的几类连接词 ①从属连词 连接宾语从句的从属连词主要有that,if,whether. that引导表示陈述句的宾语从句,而if和whether引导表示“是否”的宾语从句. 例句: He told that he would go to the college the next year 他告诉我他下一年上大学. I don’t know if there will be a bus any more. 我不知道是否还会有公交车. Nobody knew whether he could pass the exam. 没人知道他是否会通过考试. ②连接代词 连接代词主要有who,whom,whose,what,whoever,whomever ,whosever,whatever,whichever等. 连接代词一般指疑问,但what,whatever除了指疑问外,也可以指陈述. 例句: Do you know who has won Red Alert game 你知道谁赢了这一局红警游戏吗 I don’t know whom you should depend on. 我不知道你该依靠谁. The book will show you what the best CEOs know. 这本书会告诉你最好的执行总裁该了解些什么. Have you determined whichever you should buy,a Motorola or Nokia cell phone 你决定好是买诺基亚还是摩托罗拉的电话了吗 ③连接副词 连接副词主要有when,where,why,how,whenever,wherever,however等. 例句: He didn’t tell me when we should meet again. 他没有告诉我什么时候我们能再见面. Could you please tell me how you read the new panel 你能展示给我怎么用这个新的操作盘吗 None of us knows where these new parts can be bought. 没有人知道这些的新的零件能在哪里买到.

什么是从句
从句是相对于主句而言的,即它是从属于某一个主句,而不能单独作一个句子,用于复合句中担当某个句子成分的主谓结构。虽说从句自身的句子结构是完整的, 但是它不能视为独立,它离开主语就无法独立完整的表达意思 .在英语中,主要有三大从句,即名词性从句(包括主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句,同位语从句)、形容词性从句(即定语从句)、副词性从句(即状语从句,包括时间、条件、结果、目的、原因、让步、地点、方式等)。
主语从句用作主语,如::
That the earth is round is true. 地球为圆的是真实的。
宾语从句用作宾语。如:
Do you know where he lives?
表语从句用作表语,如:
My opinion is that you should not go alone. 我的意见是你不应单独前往。
同位语从句用于解释说明前面的名词。如:
The fact that the earth is round is true. 地球是圆的的事实是真实的。(that从句用于解释说明the fact)
定语从句相当于一个形容词,用于修饰前面的名词。如:
The student who answered the question was John. 回答问题的学生是John.
状语从句相当于一个副词,如:
When it rains, I usually go to school by bus. 天下雨时,我通常坐公共汽车上学。(时间状语)
If he comes tomorrow, you will see him. 如果他明天来,你就可以看见他。(if 引导的条件状语从句,其结构为:if +状语从句,+主句)。要注意在状语从句中有一个规则是“主将从现”,即主句是将来时,则从句要用一般现在时表示将来。
主句和从句的划分方法是相同的。句子的成分从谓语动词处来划分比较容易。谓语动词前面的部分是主语,后面常接宾语,修饰谓语动词的是状语,修饰主语、宾语的是定语,若谓语是系动词,则系动词后的部分是表语。如:
I am a teacher. 其中,I 是主语,am是谓语,a teacher 是表语。
He likes playing football very mucy. 其中,he是主语,likes是谓语,playing football是宾语,very much是状语。

英语从句讲解视频
英语语法 同位语从句宾语从句主语从句表语从句的具体区别要各带例句的
同位语,宾语,主语和表语从句都使名词性从句以下为区别.
主语从句
主语从句(Subject Clause)
主语从句 定义:在句子中担当主语的是一个从句,这个从句就叫做主语从句.
主语从句是在复合句中充当主语的从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾.
1. It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
It 作形式主语代替主语从句,主要是为了平衡句子结构,主语从句的连接词没有变化.而it引导的强调句则是对句子某一部分进行强调,无论强调的是什么成分,都可用连词that.被强调部分指人是也可用who/whom.例如:
It is a pity that you didn’t go to see the film.
2. 用it 作形式主语的结构
(1) It is +名词+从句
It is a fact that … 事实是…
It is an honor that …非常荣幸
It is common knowledge that …是常识
(2) it is +形容词+从句
It is natural that… 很自然…
It is strange that… 奇怪的是…
(3) it +不及物动词+从句
It seems that… 似乎…
It happened that… 碰巧…
(4) it is+过去分词+从句
It is reported that… 据报道…
It has been proved that… 已证实…
3. 主语从句不可位于句首的五种情况
(1) if 引导的主语从句不可居于复合句句首.
(2) It is said , (reported) …结构中的主语从句不可提前.例如:
It is said that President Jingo will visit our school next week.
(3) It happens…, It occurs… 结构中的主语从句不可提前.例如:
It occurred to him that he failed in the examination.
(4) It doesn’t matter how/whether …结构中的主语从句不可提前.例如:
It doesn’t matter whether he is wrong or not.
(5) 含主语从句的复合句是疑问句时,主语从句不可提前.例如:
Is it likely that it will rain in the evening?
4. What 与that 在引导主语从句时的区别
What 引导主语从句时在从句中充当句子成分,如主语.宾语.表语,而that 则不然.例如:
What you said yesterday is right.
二:宾语从句的几个特征:1、引导词:what\which\whose\when\whether\if\where
2语序:宾语从句必须是用陈述语句.
如:I think that you must work harder.
宾语从句的引导词、连接词的区别、否定转移等现象.
(1)表达时间的几个句型:一般用when或者是what time:
What time will the train leave?
由于时刻都是固定的,也可以用一般现在时代替一般将来时:
What time does the train leave?
(2)时间的表达方式:8:19(nineteen past eight),7:57(three to eight),在时间的中间也可以加上分的单词(minutes)
(3)had better +动词原型.意思是提要求,建议.但是上下级不能用这种方式,因为语气太重:
You had better give up smoking .
(4)sb leave sth +地点
I left my book in my classroom yesterday.
(5)may I have your name(address\age)?一般询问对方的年龄、名字等,不要习惯以前的问法,这样很不礼貌,而是要采访上面的问法.以前的习惯是:how old are you? \what's your name?
(6)修饰名词的代词次序:限-描-大-形---年---颜----籍----物--------类+名词:
this is a bridge.
This is a beautiful bridge
表语从句
表语从句
一 定义:
A 表语从句就是用一个句子作为表语.说明主语是什么或者怎么[1]样,由名词、形容词或相当于名词或形容词的词或短语充当,和连系动词一起构成谓语.
The problem is puzzling.
这问题令人困惑
主语 连系动词 形容词作表语
The problem is when we can get a pay rise.
问题是,当我们可以得到加薪.
主语 连系动词 一个句子作表语---表语从句
B 连接表语从句的连接词有:that, what, who, when, where, which, why,
whether,how.
He has become a teacher.
他已经成为一名教师.
He has become what he wanted to be ten years ago.
他已经成为了他10年前想成为的.
She has remained there for an hour.
她曾在那里停留了一个小时.
She has remained where I stood yesterday for an hour.
她一直在我昨天站的地方站了一个小时.
His suggestion is good.
他的建议是好的.
His suggestion is that we should stay calm.
他的建议是,我们应该保持冷静.
The question is confusing.
这个问题令人困惑.
The question is when he can arrive at the hotel.
问题是,他什么时候可以到达酒店.
who will travel with me to Beijing tomorrow.谁与我明天将前往北京.
why he cried yesterday.
昨天他为什么哭.
how I can persuade her to join us in the party.
我怎么能说服她加入我们的派对.
whether the enemy is marching towards us.
是否敌人正向我们行进.
二 注意:
A 表语从句一定要用陈述语序.
False: The question is when can he arrive at the hotel.
Right: The question is when he can arrive at the hotel.
B 不可以用if,而用whether 连接表语从句(as if 例外).
引导宾语从句时可以互换if/whether 位于介词后要用whether
位于句首时要用whether
引导表语从句,主语从句,同位语从句时要用whether
False: The question is if the enemy is marching towards us.
Right: The question is whether the enemy is marching towards us.
Right: It looked as if he had understood this question.
C 不像宾语从句,在有表语从句的复合句中,主句时态和从句时态可以不一致.
Right: The question is who will travel with me to Beijing tomorrow.
Right: The question is why he cried yesterday.
D that在表语从句中不可以省掉.
表语从句的基本用法
表语从句只能置于主句之后,而主句的动词只能是联系动词.
名词性从句在be等系动词后作表语时被称为表语从句, 例如: The problem is how we can get the things we need.问题是我们怎样能弄到我们需要的东西.(how 在表语从句中充当方式状语)// The scissors are not what I need. 这把剪刀不是我所需要的.(what 在表语从句中充当宾语)// What I told him was that I would find him a good play. 我告诉他的是我会给他找个好剧本.(what在主语从句中作直接宾语, that作为表语从句的引导词在该表语从句中不充当句子成分, 不能省略)// That is what I want to tell you.那就是我想要对你讲的.(what在表语从句中充当直接宾语)// That is why she failed to pass the exam. 那就是她考试不及格的原因.(why 在表语从句中充当原因状语)
注意: “That is why...”是常用句型, 意为“这就是……的原因/因此……”, 其中why引导的名词性从句在句中作表语, 该句型通常用于针对前面已经说明过的原因进行总结, 又如: That is why you see this old woman before you know, Jeanne. 珍妮, 这就是现在这个老太婆出现在你面前的原因.(前文提到Jeanne对老妇人显得苍老憔悴深感诧异, 说话人对她讲述了其中的原因之后,用这一句来进行概括).// That is why I came. 这就是我来的原因.
下面是两个与“That is why...”形式相似的结构, 它们与“That is why...”结构之间的关系要能够辨析清楚:
(1)“That is why...”与“That is the reason why...”同义, 只不过从语法结构上讲, “That is the reason why...”中why引导的是—个定语从句, 将其中的the reason去掉则与“That is why...”结构一样, 例如:
That is (the reason) why I cannot agree. 这就是我不能同意的理由.
(2)“That is because...”句型中从属连词because引导的名词性从句在此作表语, 这也是个常用句型, 意为“这就是为什么……/因为……”.“That is because...”与“That is why...”之间的不同在于“That is because...”指原因或理由, “That is why...”则指由于各种原因所造成的后果, 例如:
He did not see the film last night. That is because he had to help his little sister with her homework.昨天晚上他没有去看电影, 那是因为他得帮助他的妹妹做作业.(第一句话说明结果, 第二句话说明原因)
He had seen the film before. That is why he did not see it last night.他以前曾看过那部电影, 因此他昨天晚上没有去看.(第一句话说明原因, 第二句话说明结果)
同位语从句
一、在复合句中用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句.它一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容.如:
I heard the news that our team had won.我听到了我们队获胜的消息.
I had no idea that you were here.我不知道你在这里.
二、可以跟同位语从句的名词通常有news,idea,fact,promise,question,doubt,thought,hope,message,suggestion,words(消息),possibility等.如:
I’ve come from Mr wang with a message that he won’t be able to see you this afternoon. 我从王先生那里来,他让我告诉你他今天下午不能来看你了.
三、英语中引导同位语从句的词通有连词 that,whether,连接副词 how,when,where等.(注:if,which 不能引导同位语从句.)如:
l have no idea when he will be back.我不知道他什么时候回来.
He must answer the question whether he agrees to it or not.
他必须回答他是否同意这样一个问题.
四、有时同位语从句可以不紧跟在说明的名词后面,而被别的词隔开. 如:
Several years later,word came that Napoleon himself was coming to inspect them.
几年以后,有消息传来说拿破仑要亲自视 察他们.
The thought came to him that maybe the enemy had fled the city.
他突然想起可能敌人已经逃出城了.
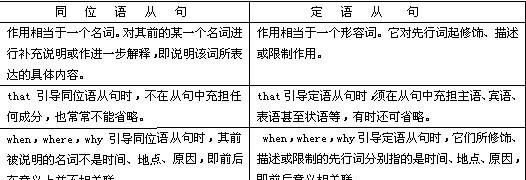
五、同位语从句与定语从句的区别.
1、同位语从句与前面的名词是同位关系,即说明它前面名词的内容;而定语从句与前面的名词是修饰与被修饰关系,即限定它前面的名词范围,或补充一些情况.如:
The news that l have passed the exam is true.我通过了考试这一消息是真的.
(同位语从句,即从句所表达的意思就是前面名词的内容.)
The news that he told me just now is true.他刚才告诉我的消息是真的.
(定语从句,从句对前面名词起修饰限制作用,即“他告诉我的”那个消息,而不是别的消息.)
2、关系词在句中是否做成分 .如:
The idea that computers can recognize human voices surprises many people.
计算机能够识别人的声音的想法使许多人感到惊奇.(that在从句中不充当任何成份.)
The idea that he gave surprises many people.他提出的观点令许多人感到吃惊.
(that在从句中作gave的宾语.)
3、从句是否有疑问的意义.如:
eg.Do you remember the day when i told you that i loved you?(when引导的从句不表示疑问,所以这是一个定语从句.)
eg.I have asked the question why it was true just now.(why引导的从句表示疑问,所以这是一个同位语从句.)
一个名词(或其它形式)对另一个名词或代词进行修饰,限定或说明,这个名词(或其它形
式)就是同位语.同位语与被它限定的词的格要一致,并常常紧挨在一起.
宾语从句
学习宾语从句要抓住三要素:连接词、语序和时态.
1.连接词
连接词一般都是that(指事务或人),which(指事),who(指人)
1.从句为陈述句,常选择连接词that或将that省略,直接与主句相连.
2.从句为一般疑问句,常选择连接词if或whether.在 whether … or not 结构中不能用 if 替换.
3.从句为特殊疑问句,常选择what,when,where,which,who,how等的疑问代、副词作连接词.
注意:当who为主语时,句式为:who+谓语+其他
2.判断时态情况:
1.主句是一般现在时,从句为各种时态情况.
2.主句是一般过去时,从句为各种相应过去时态注意:从句描绘客观事实,用一般现在时.
eg:
1. The teacher told the children that the sun____ round.
A. was B. is C. were D. are
2. I believe that our team____ the basketball match.
A. win B. won C. will win D. wins
3. I don’t know____ to visit the old man.
A. whether B. if C. that D. who
4.The soldiers soon reached( )was once an old temple( )the villagers used as a school.
A.which;where B.what;which C.where;which D.what;where
答:选B,动词reach后接宾语从句,从句缺少宾语,where不可,which引导宾语从句时表疑问含义“哪一个…”而此句中并非疑问含义,不知道哪一座庙宇,而是用what从句表陈述含义,意“过去的一座旧庙宇”;temple后为对其修饰的定语从句,用关系代词which代替,并在从句中作动词used的宾语,use sth. as…“把…用作…
宾语从句用作宾语.如:
Do you know where he lives?
定语从句相当于一个形容词,用于修饰前面的名词.如:
The student who answered the question was John. 回答问题的学生是John.
This is the man whom he is looking for.
Do you know the girl who is in red?
语法~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
宾语从句的用法
1.that引导宾语从句无意义,不充当句子成分常省略.但下列情况除外:
(1)介词宾语从句的that不省略
(2) and连接的几个从句,第二个从句以后的从句的that不省略.
He told me that he had two sons and that they both had gone to college.
(3)在动词+it+宾语补足语+宾语从句结构中,that不省略.
I heard it said that he had gone abroad
We found it impossible that he could finish it in such a short time
2.Whether ,if 引导宾语从句:两词可互换,但是下列情形除外:
(1)whether从句中有or not
(2)whether从句做介词宾语
Everything depends on whether you agree with us
3.许多带复合宾语的句子,宾语从句经常移到句子后部,而用it做形式宾语.结构常是:
主语+动词+it+形容词/名词等宾语补足语+宾语从句
We think it wrong that he told a lie to everyone
4.宾语从句的语序要用陈述句语序
False: He is wondering when can he finish this difficult job.
Right: He is wondering when he can finish this difficult job.
B 有时候可以用it 作形式宾语

以上就是关于同位语从句三要素 ,什么叫从句的全部内容,以及同位语从句三要素 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
