本文目录
宾语从句解析图表
初三系列复习资料(8)宾语从句考点集汇,讲解和训练
5.________ is known to all that WTO stands for World Trade Organization.
A.Which B.What C.As D.It
6.The fact________she works hard is well known to us all.
A.that B.what C.why D.which
7.The mountain is no longer________it used to be.
A.which B.that C.as D.what
8.We know little about the young lady except________you told me.
A.what B.that C.how D.不填
9.I know nothing about her except________she is from Canada.
A.how B.when C.that D.why
10.________ proves that my advice is right.
A.It will happen that B.That has happened
C.What has happened D.When it happened
11.What a pity________is________you didn’t arrive by daylight.
A.there;because B.it;that
C.he;when D.that;for
12.The question he asked was________the electrical equipment should be stored.
A.what B.which C.where D.because
13.________we can’t get seems better than________we have.
A.What;what B.What;that
C.That;that D.That;what
14.________ we’ll go camping tomorrow depends on the weather.
A.If B.Whether C.That D.Where
15.Father made a promise________I passed the examination he would buy me a new dictionary.
A.that B.if C.whether D.that if
16.The reason________she gave for not being present was________the heavy snow prevented her coming.
A./;because B.why;because
C./ ;that D.why;whether
17.________ is the most useful invention?
A.Do you think which of these
B.Which of these do you think
C.Which of these you think
D.You think which of these
18.This is the nicest hotel________I have ever stayed so far.
A.that B.where C.which D./
19.________ there is life on another planet is almost impossible.
A.How B.That C.Why D.Whether
20.It’s not yet clear________of those will be chosen to do the job.
A.that B.whom C.which D.whose
21.It is probable________he told her everything.
A.who B.which C.why D.that
22.________ in the newspaper that the Japanese minister will arrive next Monday.
A.It says B.It is said
C.It has said D.He is said
23.The possibility________the majority of the labor force will work at home is often discussed.
A.which B./ C.that D.what
24.________ you go or stay at home won’t make any differences.
A.If B.When C.That D.Whether
25.It doesn’t matter________I rest or not.
A.if B.whether C.that D.when
26.He doesn’t know________is________he was born.
A.that;where B.that;what
C.where;that D.what;where
27.________ is still a secret when the president will make a public speech.
A.That B.He C.What D.It
28.It worried her a bit________her hair was turning gray.
A.while B.that C.if D.whether
29.________breaks the law should be punished.
A.No matter who B.Whoever
C.All D.Who
30.These photographs will show you ________.
A.what our village looks like
B.what does our village look like
C.how our village looks like
D.how does our village look like
31.________ is to practice using English often.
A.That you should do
B.Which you should do
C.What you should do
D.Whatever should you do
32.—I believe________you’ve done your best and________things will improve.
—Thank you.
A.that;/ B./;/
C.what;that D./;that
33.Please give the book to________wins the first prize.
A.who B.whom
C.whoever D.whomever
34.The fire destroyed________was in the building.
A.all B.what
C.that D.which
35.It looks________he is unhappy today.
A.that B.if
C.as if D.whether
36.After months of research there was little hope________the lost car might be found.
A.that B.which
C.when D.how
37.She dresses well,but the trouble is________the clothes she is wearing don’t go with each other very well.
A.even if B.whether
C.that D.if
38.The suggestion________students should learn some practical knowledge is worth considering.
A.if B.which
C.不填 D.that
39.________ they don’t like us is very clear.
A.What B.That
C.Which D.Where
40.________ you’ve all had a wonderful vacation.
A.It would be good that B.It is good that
C.It was good that D.It will be good that
41.________ the headmaster is not coming to the sports meeting at all.
A.It seems that B.It seem that
C.It seems D.It seemed
42.Has it been announced________the planes are to take off?
A.when B.if
C.which D.what
43.It is not clear________he did it.
A.who B.which
C.whom D.why
44.It has not been decided yet________the meeting will start.
A.when B.why
C.where D.now
45.I don’t doubt________he will come.
A.that B.if
C.what D.whether
46.There’s some doubt________she will be able to repay the money on time.
A.that B.if
C.what D.whether
47.—Little Tom get an “A” in the exam.
—________ he’s been so happy these days.
A.No wonder B.I wonder why
C.It is a wonder D.Because
48.I hope________happy while you are here.
A.you to be B.for your being
C.you will be D.you being
49.You will realize________breaks the law will be punished.
A.that those who B.that those that
C.whoever D.those whoever
50.—I misspelt a word here in the sentence.
—Well,that’s________you were mistaken.
A.when B.what
C.where D.why
51.—It was 3 o’clock________we arrived at the village.
—Oh,it was also at 3 o’clock________we arrived at the village.
A.when;when B.when;that
C.that;that D.that;when
52.________ we have seen is quite from________we have heard.
A.That;that B.What;that
C.That;what D.What;what
53.There are three books on the desk.I don’t know________one he will choose.
A.whose B.which
C.that what D.what
54.The old woman was shocked by________had happened to her daughter.
A.whom B.which
C.what D.that
55.Never take________for granted that I will help you.Better depend on yourself.
A.that B.it
C.which D.this
56.Can you tell me ________?
A.who is that woman B.who the woman is
C.whom is the woman D.that woman is
57.Jack said________to meet the American friends.
A.which he pleased B.he is pleased
C.that he was pleased D.what he was pleased
58.Lei Feng was always thinking of________he could help others.
A.that B.how
C.when D.which
59.—The green typewriter is mine.
—Do you know whose typewriter ________?
A.is this blue one B.this blue one
C.is this blue D.this blue one is
60.It depends on________we have enough time.
A.if B.if or not
C.that D.whether
基础训练15 名词性从句
1~5 AAADD 6~10 ADACC
11~15 BCABD 16~20 CBBBC
21~25 DBCDB 26~30 ADBBA
31~35 CDCBC 36~40 ACDBB
41~45 AADAA 46~50 DACCC
51~55 BDBCB 56~60 BCBDD
1.what引导的表语从句。
2.that引导的同位语从句,其中心词是feeling。
3.what引导的表语从句。
4.That引导主语从句。
5.It用作形式主语。
8.what引导介词宾语从句,what在句中作动词told的宾语。
9.that引导介词宾语从句,that只起引导作用,本身没有什么含义。
14.Whether引导主语从句。注意if不能引导主语从句和表语从句。
15.that引导同位语从句。在同位语从句中又还夹有一个if引导的条件状语从句。
16.第一空所填词引导定语从句修饰先行词reason,由于是作动词gave的宾语,所以可以省略;第二空是that引导的表语从句。
21.前面的it是形式主语,that引导主语从句。
27.前面的it是形式主语,when引导主语从句。
29.全句意为“不管是谁,犯了法就必须受到惩罚”。whoever引导主语从句, No matter who虽然语意相同,但不能引导主语从句。
33.全句意为“把这本书给获得第一名的那个人”。
51.注意两个3 o’clock前一个有介词at,一个没有。第一空引导的是一个时间状语从句,第二空是一个强调句型
英语必修三第四单元思维导图概括
四种非谓语动词:动词不定式、动名词、现在分词、过去分词。
五种简单句:主语+谓语;主语+谓语+宾语;主语+谓语+双宾语;主语+谓语+宾语+宾补;
主语+系动词+表语。
六种复合句:定语从句、状语从句、四种名词性从句(主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句)。
强调句、倒装、省略、虚拟语气、情态动词、冠词、形容词和副词、连词、介词。

思维导图
是一种将思维形象化的方法。我们知道放射性思考是人类大脑的自然思考方式,每一种进入大脑的资料,不论是感觉、记忆或是想法——包括文字、数字、符码、香气、食物、线条、颜色、意象、节奏、音符等,都可以成为一个思考中心,并由此中心向外发散出成千上万的关节点。
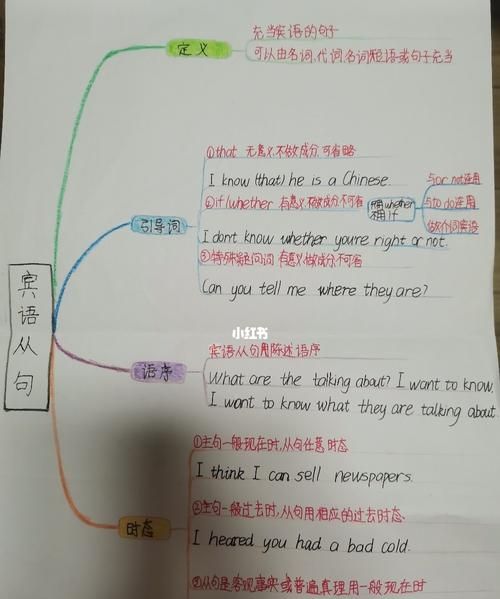
初三英语宾语从句专练
一、定义:宾语是由一个句子来充当,这个句子就称作宾语从句。
I think he is a good student .
二、 可接宾语从句的动词有say 、tell 、think、 know、 see、 hear、 hope、 guess、 find、 feel 等, 或由形容词构成的系表结构,如:afraid、 sure、 glad、 sorry等
I hope that our team will win the match .
I am sure that I can pass the English exam easily .

三、 宾语从句的标点符号。
宾语从句的标点符号取决于主句,如果主句是陈述句,句尾用句号,如果主句是疑问句,句尾用问号。
I don't know what his name is .
Do you know which school he studies in ?

英语八大时态的思维导图简单明了
思维导图 是英国著名心理学家托尼·巴赞在20世纪60年代创立的,是新兴的脑科学,刚开始只是作为一种新的笔记 方法 ,后来逐渐发展成为一种思维工具和 学习方法 。下面我整理了英语八大时态的思维导图,希望大家喜欢!
英语八大时态的思维导图1 英语八大时态的思维导图2 英语八大时态的思维导图3 英语的八大时态1、一般现在时的用法
1) 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
例: every…, sometimes,ofen,always,usually, twice a week, at…, on Sunday等。
I leave home for school at 7 every morning.
He watches Tv once a week .
2) 表示普遍真理,客观存在,科学事实。
The earth moves around the sun.
Shanghai lies in the east ofChina.
3) 格言或警句。
Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round..
4) 表示现在时刻的状态、能力、个性或 爱好 。
I don't want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup.
I am doing my homework now.
第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。再如:Now watch me, I switch on the current and stand back.
第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。
2、一般过去时的用法
1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
时间状语有:yesterday, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982,yesterday morning (afternoon, evening…),last night (week, month, year…), a moment ago , a week ago, three years ago… just now,等。
Where did you go just now?
2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。
When I was a child, I often played football in the street.
Whenever the Browns went during their visit, they were given a warm welcome.
3)句型:
It is time for sb. to do sth "到……时间了" "该……了"
It is time sb. did sth. "时间已迟了" "早该……了"
It is time for you to go to bed. 你该睡觉了。
It is time you went to bed. 你早该睡觉了。
4) wish, wonder, think, hope 等用过去时,作试探性的询问、请求、建议等。
I thought you might have some. 我以为你想要一些。
注意:一般过去时表示的动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在。
Christine was an invalid all her life.
(含义:她已不在人间。)
Mrs. Darby lived in Kentucky for seven years.
(含义:达比太太已不再住在肯塔基州。)
3、现在进行时
1) 表示现在( 指说话人说话时) 正在发生的事情。
We are waiting for you.
2)表示长期的或重复性的动作,说话时动作未必正在进行。
Mr. Green is writing another novel. (说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
She is learning piano under Mr. Smith.
3)瞬时动词的进行时一定表示将来的含义。
瞬时动词:come,go,arrive,leave,finish,end,start,begin等。
We are arriving at London.
持续动词的进行时需要加表示将来的时间状语或有将来的语境时才能表将来。
I am travelling next month.
4)与always, constantly, forever 等词连用,表示反复发生的动作或持续存在的状态,往往带有说话人的主观色彩。
You are always changing your mind.
4、过去进行时
1)过去进行时主要表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作,常和表示过去的状语连用。
例如:(just)then 那时,当时;at this/that time 在这/那时 yesterday afternoon昨天下午;at nine 在九点;last night 昨晚;(at)this time yesterday在昨天这个时候
但在不少情况下,没有表示时间的状语,这时需要通过上下文来表示。
What were you doing at nine last night? 昨晚九点的时候,你在做什么?
I was watching TV at home yesterday afternoon. 我昨天下午正在家里看电视。
They were playing football at this time yesterday.昨天这个时候他们在踢 足球 。
2)过去进行时也可以表示过去某一段时间内正在进行的动作。
常与those days, the whole morning, from 8:00 to 12:00 last night等时间状语连用。
From 1983 to 1998 , he was teaching at Yale . 从1983到1998年,他正在耶鲁大学教书。
They were building a bridge last winter . 去年冬天他们正在造一座桥。
3)过去进行时表示过去将要发生的动作。
现在进行时可以表示将来的动作,同样,过去进行时也可以表示从过去某时看来将要发生的动作,常用在间接引语中。
Lucy arrived in Beijing last Friday. But she was leaving for Hong Kong the next morning.上周五Lucy到达北京,但第二天早晨就要动身去香港了。
She asked him if he was coming back for lunch. 她问他午饭是否准备回来吃。
4)过去进行时与频度副词always forever, continually, constantly等连用时表示过去经常反复的动作,常常带有埋怨、讨厌、赞扬或喜爱等情绪。
My sister was always forgetting things.(表示埋怨)
He was always helping others. (表示赞扬)
5、一般将来时
1)表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或重复发生的动作。
时间状语:tomorrow , soon , next Monday , next year , next weekend , this afternoon , this evening ……
2)will do
表示主观意愿做某事。
I will see a movie this morning.
表示客观的不以人的意志为转移的客观将来。
Fish will die without water.
表示临时决定。
——Mom, where is the newspaper?
——Wait a moment. I will get it for you.
3) be going to +do
表示计划,安排要发生的事。
The play is going to be produced next month。
表示有迹象要发生的事
Look at the dark clouds.There is going to be a storm.
6、过去将来时
立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
He said he would go to Beijing the
I didn't know if she was going to come。
Wang Lei said that she was going to visit her uncle next Saterday。
7、现在完成时
1)表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
标志词:already, yet, just, ever, never, before
I have finished my homework. 我做完家庭作业了。(过去某时开始做,到现在已完成。)
2)表示:过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态,并且有可能继续下去。
标志词:for, since, since…ago
I have studied English for six years. 我已经学了六年英语了。
(六年前开始学英语,一直学到现在, 也可能继续学也可能就此不学了。)
3) have/has gone to 、have/has been to 和have/has been in的区别
have/ has gone to 去了,在去某地的路上或在某地,人还未回来
have/ has been to 曾经去过,人已经回来了
have/ has been in 已经在,常与一段时间连用
如:He has been to Shenyang before. 他以前曾去过沈阳。
He has been in Shenyang for ten years. 他在沈阳10年了。
Has he gone to Shenyang? 他去沈阳了吗?
4)非延续性动词不能用“现在完成时 + 表示一段时间的状语”的句型中。
这类动词有:come, go, start, leave, die, buy, finish, join, borrow, stop等。
但能够用表示持续状态的相应的延续性动词替换句中的非延续性性动词。
arrive, come → be here,
die → be dead
finish, end → be over
go out → be out
join → be in
borrow→keep
finish/end →be over
close →be closed
leave, move → be away
fall asleep → be asleep
8、过去完成时
1)以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.
2)在told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词后的宾语从句。
She said (that) she had never been to Paris.
3)过去完成时的时间状语before, by, until , when, after, once, as soon as。
He said that he had learned some English before.
By the time he was twelve, Edison had began to make a living by himself.
Tom was disappointed that most of the guests had left when he arrived at the party.
以上就是关于初三宾语从句思维导图清晰 ,宾语从句解析图表的全部内容,以及初三宾语从句思维导图清晰 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

