本文目录
定语从句趣味公开课
定语从句公开课教案 篇1
Teaching Aims:(教学目的)
1、初步了解定语从句的概念、结构。
2、初步学习并掌握定语从句的规则,尤其是关系代词『who,which,that以及whose』的用法。
Teaching Points:(教学重点)
1.定语从句三要素及关系词的选用
2.只能that或which的情况;
Teaching Methods:(教学方法)
1、举例讲解,说明定语从句的用法。
2、以讲练结合的方法加深学生印象。
Teaching Steps:(教学步骤)
Step1.导入
一、定语及定语从句的概念:
a beautiful girl a handsome boy a clever child
1、 定语是用来修饰名次或代词的。
This is the boy who is clever.
2、定语从句(Attributive Clauses)定义:在主从复合句中修饰名词或代词的从句 定语从句的特点:
定语从句
的引导词关系代词where (地点状语)关系副词
when (时间状语)
why (原因状语)
Step2:详细讲解定语从句语法知识
1、who和whom指人,在从句中分别做主语和宾语,做宾语时可被省略。
the handsome
the tall
the strong boy The boy is Tom.
the clever
the naughty
The boy is Tom.
2、which指物,在从句中做主语或宾语,做宾语时可被省略。
3、that既可指人也可指物,在从句中做主语或宾语,做宾语时可被省略。
4、whose作定语,用来表示先行词和从句主语之间的所属关系。
Step3 定语从句考查重点:
定语从句在下列情况下只能用that,而不能用which指物。(指人时可以用who/whom)
1. 当先行词被形容词最高级修饰时。如:
2. 当先行词是不定代词everything, anything, nothing (something 除外), all, none, few, little, some等代词时,或当先行词受every, any, all, some, no, little, few, much等代词修饰时。如:
3. 当先行词被序数词修饰时。如:
4. 当先行词被表示“正是”的the very, the only修饰时。如:
5. 当先行词前面有who, which等疑问代词时。如:
6. 当先行词为人与动物或人与物时。如:
Step 4 Summary:(小结) 注意 关系词的实质:
Step 5 Practices(homework):
Part 1.结合课文例句,找出先行词和关系词
1. But the one million people of the city, who thought little of these events, went to bed as usual that nigh.
2. It was heard in Beijing, which is one hundred kilometers away.
3. A huge crack that was eight kilometers long and thirty metres wide cut across houses, roads and canals.
4. The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than 400,000.
5. The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead.
6. Workers built shelters for survivors whose homes had been destroyed.
Part2 名言名句欣赏
1. He laughs best who laughs last.
2. He who makes no mistakes makes nothing.
3. He that gains time gains all things.
4. He who nothing questions, nothing learns.
5. He that cannot ask cannot live.
6. A friend is someone who knows all about you and still loves you.
7. God helps those who help themselves.
8. He who does not reach the Great Wall is not a true man
9. He who does not advance loses ground.
Part3 practice
1. Do you know the girl _____ is talking with your mother?
A. who B. which C. whose D. /
2. This is the kite _______ Billy Fisher gave to Tom
A. who B. which C. / D. Both B and C
3. He was the only one ______ was saved in the earthquake.
A. who B. that C. which D. A and B
4. This is the only present _____ I like.
A. who B. that C. which D. B and C
5. This is the most beautiful place ______ I have ever seen.
A. which B. who C. where D. /
6. All _______ I can do is to give him some money.
A. that B. which C. who D. what
7. Is there anything else _____ you need?
A. which B. that C. who D. what
8. The museum _____ we visited last week isn’t far from here.
A. where B. which C. what D. who
9. Most of the people ____ lost their lives in the earthquake are Sichuan natives.
A. when B. who C. how D. which
10. The boy ____ you saw just now is Tom’s brother.
A. which B. whose C. when D. /
11. The bike and its rider _____ had run over an old woman were helped up by the policeman.
A. which B. that C. it D. whom
12. Is this the factory _____ you worked five years ago?
A. in which B. in where C. in that D. that
二、用适当的关系代词填空
1. Do you like the present _______ I bought you yesterday?
2. The storybook _______ was written by his uncle is quite interesting.
3. The boy _______ computer doesn’t work well needs your help.
4. This is the best movie _______ we have seen this year.
5. The doctor _______ we met in the street is from America.
6. The passengers and the suitcases _____ were in the waiting room had to wait for another plane.
7. Who is the girl _______ you want to make friends with?
8. This is the last lesson _______ Mr. Smith taught us.
9. I, _____ am your friend, will help you out.
10. The building ___________ wall is white is my uncle’s house.
11. The boy _______ John spoke with is my brother.
12. Will you please lend me the very picture _________ you bought yesterday?
13. The students ________ the teacher praised at the class meeting is our monitor.
14. The season _________ comes after spring is summer.
15. This is the first museum __________ we visited last Saturday.
16. The girl ________ leg was broken in the earthquake was taken to the hospital.
17. I found some photos of interesting places _________ were not far away from our city.
18. There is a boy downstairs _________ want to see you.
19. The river ________ banks are covered with trees is very long.
20. I’m going to meet Tom ______ they say is a good boy.
定语从句公开课教案 篇2
一、所需课件: 一课时
学习内容:定语从句中关系代词who, whom ,which ,that ,as的用法。
定语从句是一个很重要的语法项目,为以后的英语学习打下坚定的基础,也是初高考出现频率较高的考点。
二.教学目标分析
知识与目标分析
知识与技能目标:帮助学生掌握关系代词who, whom, which, that, as 的用法,丰富学生的语法知识,形成独立的学习能力,能够运用这些知识去解决定语从句的习题。
过程与方法目标:让学生主动参与感知——积累——理解关系代词的过程,让学生学会关系代词的用法,学会探究解决问题。
情感态度价值观目标:让学生体验到学习定语从句的乐趣。
三.学习者特征分析
初中生刚刚接触与从句,对句子结构认识不够清楚,但是这部分内容很重要,有助于学生完善整个英语语法知识结构。
四.教学策略选择与设计
本课题主要采用启发式教学策略,合作学习,探究学习的策略,在教学中,创设问题情景,以小组为单位进行讨论,合作学习,得出结论。
五.教学资源与工具设计
多媒体教室 计算机 PPT课件
六、教学过程
第一步:复习(检查作业)
第二步:导入
Marry is a beautiful girl.
Marry is a girl who has long hair.
……(讨论句子特征 )
老师总结:什么是定语从句,先行词,引出定语从句由关系代词,关系副词来引导。
第三步:介绍引导定语从句的关系代词。
第四步:详细介绍这些关系代词的用法。
第五步:习题(加深印象)
第六步:课后总结
第七步:布置作业
七、教学评价设计
创建量规,向学生展示他们将被如何评价(来自教师和小组其他成员的评价)。另外,可以创建一个自我评价表,这样学生可以用它对自己的学习进行评价。
八、帮助和总结
教师以启发诱导的方式向学生提供帮助和指导,针对不同的'学习间断的学生采取不同的`帮助和指导,之处不同水平的要求,给予不同的帮助。对于学习能力强的可以以暗示的方式进行指示,对学习能力差的学生可以通过逐步深入的方式进行讨论。
在学习结束后,对学生的学习做出简单的总结,可以布置一些练习题,以强化学习效果。
【拓展内容】
定语从句关系分类
关系从句有限制性关系从句(英语:restrictive relative clause或defining relative clause)和非限制性关系从句(英语:non-restrictive relative clause)之分。限制性关系从句起限定作用,修饰特定的名词或名词短语;而非限制性关系从句只起补充说明某种信息的作用。
例如:The government which promises to cut taxes will be popular.(限制性关系从句,指任何一个减税的政府)
The government, which promises to cut taxes, will be popular. (非限制性关系从句,补充说明(现任的)政府的情况)
There were very few passengers who escaped without serious injury. (限制性关系从句,指逃出来的乘客大多受了伤)
There were very few passengers, who escaped without serious injury. (非限制性关系从句,指游客人数本来就很少,这些游客都逃了出来且没有受伤)
限制性关系从句
从语义上看,限制性关系从句主要起限定作用,修饰特定的人或事物,如果去掉限制性定语从句,整个句子表意会不完整甚至不通顺;从结构上看,限制性关系从句常紧跟先行词,并且同先行词之间一般不加逗号分隔(但不是绝对的)。
限制性关系从句的关系词包括:that, which, who, whom, whose, as, than等。
非限制性关系从句
从语义上看,非限制性关系从句主要起补充说明的作用,有时相当于一个并列分句或状语从句,可以表达原因、目的、结果、条件、让步等意义。
例如:Dr Lee, who had read through the instructions carefully before doing his experiments, did not obtain satisfactory results. (非限制性关系从句表示让步的意义,相当于though Dr Lee had read through the instructions...)
非限制性定语从句的关系词包括:which, who, whom, whose, as等,另外that在非限制性关系从句中并非绝对不可使用。
关系选择
关系词包括关系代词(英语:relative pronoun)、关系副词(英语:relative adverb)和关系限定词(英语:relative determiner)。关系词的选择主要涉及以下因素:
1.先行词是人还是事物;
2.关系词在关系从句中的句法功能;
3.关系从句是限制性的还是非限制性的;
4.是口语还是书面语。
特殊的关系从句
名词性关系从句
名词性关系从句(英语:nominal relative clause)又叫自由关系从句(英语:free relative clause),名词性关系从句在结构上不含有先行词,它的关系词同时扮演了关系词和先行词的角色,因此名词性关系从句的关系词又叫缩合连接代词。例如:
I like what I see.(“what I see”是名词性关系从句,它没有先行词,与此同时缩合连接代词“what”又直接充当了“like”的宾语。)
缩合连接代词“what”可以根据语义解释为“the thing(s) that”或“the person(s) that”。
嵌入式关系从句
嵌入式关系从句(英语:embedded relative clause)是一种较复杂的关系从句,它既是先行词的后置定语,又是另一结构的宾语。
例如:She has an adopted child who she says was an orphan. (关系从句修饰“an adopted child",同时又是“she says”的宾语)
双重关系从句
双重关系从句(英语:double relative clause)是指两个关系从句修饰同一个先行词的语法现象。
例如:You can easily find us;just look for a house whose windows need washing and whose fence needs repairing!
初中英语定语从句讲解
全英定语从句讲解
一、定义
定语从句是指在句中做定语作用,修饰句中的名词或代词的从句,其中被修饰的名词或代词为先行词。当关系代词作定语从句的主语时,其后的谓语动词的人称和数取决于先行词的人称和数。
二、定语从句的结构
定语从句一般位于先行词的后面,定语从句由关系代词who, whom, whose, that, which,that, as和关系副词when, where, why等引导。
(一)关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词所代替的先行词是人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中做主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。
(1)who, whom, that
这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中做主语和宾语。例如:
·Is he the man who/that wants to see you?
他就是你想见的人吗?(who/that在从句中做主语)
·He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday.
他就是我昨天见的那个人。(whom/that在从句中做宾语)
(2)whose 用作关系词表示所属格,也可看作是关系形容词,因为它后面必须接一个名词连用。不能单独使用。例如:
·They rushed over to help the man whose car had broken down.
那人车坏了,大家都跑过去帮忙。
(3)which, that所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可做主语、宾语等。作宾语时常可省略。例如:
·A prosperity which / that had never been seen before appears in the countryside.
农村出现了前所未有的繁荣。(which / that在句中作宾语)
(二)关系副词引导的定语从句
关系副词可代替的先行词是时间、地点或理由的名词,在从句中作状语。
(1)关系副词when, where, why的.含义相当于“介词+ which”结构,因此常常和“介词+ which”结构交替使用。例如:
·There are occasions when(on which)one must yield.
任何人都有不得不屈服的时候。
·Beijing is the place where(in which)I was born.
北京是我的出生地。
·Is this the reason why(for which)he refused our offer?
这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗?
(2)that代替关系副词,可以用于表示时间、地点、方式、理由的名词后取代when, where, why和“介词+ which”引导的定语从句,在口语中that常被省略。例如:
·His father died the year(that / when / in which)he was born.
他父亲在他出生那年逝世了。
·He is unlikely to find the place(that / where / in which)he lived forty years ago.
他不大可能找到他四十年前居住过的地方。
(三)限制性和非限制性定语从句
(1)定语从句有限制性和非限制性两种。
限制性定语从句是先行词不可缺少的部分,去掉它主句意思往往不明确;非限制性定语从句是先行词的附加说明,去掉了也不会影响主句的意思,它与主句之间通常用逗号分开。例如:
·This is the house which we bought last month.
这是我们上个月买的那幢房子。(限制性)
·The house, which we bought last month, is very nice.
这幢房子很漂亮,是我们上个月买的。(非限制性)
(2) 当先行词是专有名词或物主代词和指示代词所修饰时,其后的定语从句通常是非限制性的。例如:
·Charles Smith, who was my former teacher, retired last year.
查理·史密斯去年退休了,他曾经是我的老师。
·My house, which I bought last year, has got a lovely garden.
我去年买的那幢房子带着个漂亮的花园。
·This novel, which I have read three times, is very touching.
这本小说很动人,我已经读了三遍。
(3) 非限制性定语从句还能将整个主句作为先行词, 对其进行修饰, 这时从句谓语动词要用第三人称单数。例如:
·He seems not to have grasped what I meant, which greatly upsets me.
他似乎没抓住我的意思,这使我心烦。
·Liquid water changes to vapor, which is called evaporation.
液态水变为蒸汽,这就叫做蒸发。
说明:关系代词that和关系副词why不能引导非限制性定语从句。
(四)介词+关系词
(1)介词后面的关系词不能省略。
(2)that前不能有介词。
(3)某些在从句中充当时间,地点或原因状语的“介词+关系词”结构可以同关系副词when 和where 互换。例如:
·This is the house in which I lived two years ago.
↓
这是我两年前住过的房子。
↑
·This is the house where I lived two years ago.
·Do you remember the day on which you joined our club?
↓
还记得你加入我们俱乐部的那一天吗?
↑
·Do you remember the day when you joined our club?
(五)as, which 引导的非限定性定语从句
由as, which 引导的非限定性定语从句,as和which可代整个主句,相当于and this或and that。As一般放在句首,which在句中。例如:
·As we know, smoking is harmful to one's health.
如我们所知,吸烟有害健康。
·The sun heats the earth, which is very important to us.
太阳使地球暖起来,这对我们人类很重要。
【特别提示】 as 和which在引导非限制性定语从句时,这两个关系代词都指主句所表达的整个意思,且在定语从句中都可以做主语和宾语。但不同之处主要有两点:
a)as 引导的定语从句可置于句首,而which不可。
b)as 代表前面的整个主句并在从句中做主语时,从句中的谓语必须是系动词;若为行为动词,则从句中的关系代词只能用which.。
三、翻译方法
定语从语从句有以下五种翻译方法:
前置法:这是定语从句的翻译中较常见的一种,即把定语从句的内容翻译成“…………的”,放在被修饰词的前面。这种方法的使用有一个原则即是定语从句内容简短,翻译符合汉语表达习惯。
后置法:与前置法不同,后置法就是把定语从句的翻译放在被修饰词之后,这样做的目的在于使译文符合汉语的表达习惯。在此,定语从句的后置翻译分为三类:由which引导定语从句时一般翻译为“这”;另一些引导词则在翻译时重复先行词,即被修饰词;还有一些引导词在翻译时可以省略不译。
融合法:在限制性定语从句中,由于定语从句与主句关系紧密,所以定语从句往往翻译成句子的谓语部分,主语即是定语从句的先行词。这里讲的融合法即是将定语从句与主句融合为一个简单句的方法。这种用法往往用在“there be”结构带有定语从句的句型中。。
状译法:英语的定语从句中有一类在形式上是主句的定语从句,而其所起的作用却相当于主句的状语,修饰主句的谓语或者全句。这种状语功能常常包括原因、结果、目的、条件、让步等,所以我们在翻译时需要弄清主句和定语从句之间的逻辑关系,从而是译文通顺合理,符合汉语表达习惯。
【真题例句】
Behaviorists suggest that the child who is raised in an environment where there are many stimuli which develop his or her capacity for appropriate responses will experience greater intellectual development.
【解析】
句子可拆分为:Behaviorists suggest //that the child //who is raised in an environment //where there are many stimuli// which develop his or her capacity for appropriate responses// will experience greater intellectual development.
is raised是从属连词who从句的动词;are是where从句的动词;develop是which从句的动词;由于跟在从属连词后的动词不可能是主句的谓语动词,所以前面提到的三个动词全都不是主句的谓语动词。这时,句子里还有两个动词:suggest和will experience;经过分析,will experience前有从属连词that,所以也只是从句的动词。可以得出:本句的谓语动词是suggest。
本句的主干即是Behaviorists suggest that ...;that引导suggest的宾语从句,动词是will experience;who引导修饰child的定语从句,动词为is raised;where引导修饰environment的定语从句,动词为are;which引导修饰stimuli的定语从句,动词为develop。

初中英语宾语从句教案设计范文大全
写好教案设计是保证初中英语宾语从句的教学取得成功,所以初中英语老师在上课之前一定要做好宾语从句的教案设计。下面是我为大家整理的初中英语关于宾语从句的教案设计,希望对你们有帮助。
宾语从句教案设计
教学目标:
1.掌握引导宾语从句的各种连词
2.掌握宾语从句的语序──主句+连接词+主语+谓语
3.掌握宾语从句,主句与从句在时态上的呼应。
教学重点难点
重点:语序和时态呼应
难点:语序和时态呼应;与疑问词+不定式的转化;与状语从句的辨析
宾语从句教学过程
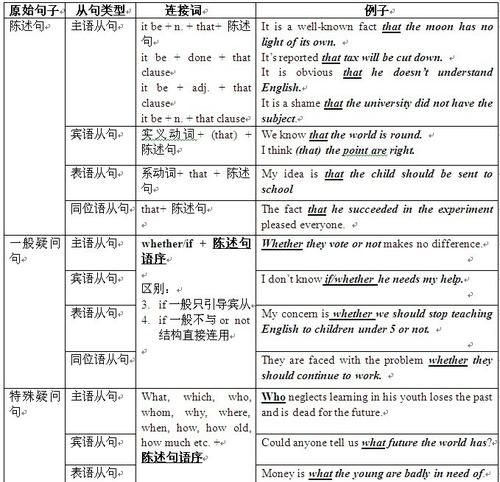
一、宾语从句的连接词
1.连词that,只起连接作用,在从句中不作 句子 成分,也无词汇意义,在口语中常被省略。
eg. He knew (that) he should work hard.
2.连词if 、whether,它们起连接作用,在从句中不作句子成分,作“是否”解,在口语中多用if。
eg. Tom don't know if/whether his grandpa liked the present.
He asked me whether or not I was coming.
一般情况下,if 和whether可以互换,但以下3种情况只能用whether:
①在不定式前:Whether to go there or not hasn't been decided.
②在介词前:It depends on(依靠) whether it is going to rain.
③与or not连用:They are talking about whether to go there or not.
3.连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which,连接副词when, where, why, how, 它们起连接作用,作句子成分,各有自己的意义。
eg. The teacher asked the new students which class he was in.
I wonder where he got so much money.
【注意】
1.由连接代、副词引导的宾语从句可以和“疑问词+不定式”结构转化。
eg. I don't know how I should do with the presents. ==> I don't know how to do with the presents.
2.要注意区分判断由if、when引导的从句类型.
二、宾语从句的语序
宾语从句的语序是陈述语序,即“连接词+主语+谓语+ 其它 成分”。特别强调:它的主语和谓语的语序是陈述语序,而不是疑问句的倒装结构。
Can you tell me who(m) do we have to see?(╳)
Can you tell me who(m) we have to see?( √)
The teacher asked the students what they were doing.(思考: what在从句中的成分)
陈述句变为宾语从句时,要注意人称和时态的变化,语序不变。 eg. She said, “I will leave a message on the desk.” → She said she would leave a message on the desk.
一般疑问句和特殊疑问句变为宾语从句时,也要注意人称和时态的变化,后面接陈述语序。Eg. “Where are the tickets?” I asked him. → I asked him where the tickets are.
三、宾语从句的时态呼应
宾语从句中谓语动词的时态,常常受到主句谓语时态的制约,此为时态呼应。如果主句谓语是一般现在时或将来时,从句谓语的时态不受限制;如果主句谓语的时态是一般过去时,从句一般要随着改为相应的过去时态(一般过去时、过去进行时、过去将来时、过去完成时)。
eg. I thought (that) you are free today. (╳)
I thought (that) you would be free today. ( √)
【注意】当宾语从句叙述的是客观真理时,不管主句谓语的时态如何,从句都用一般现在时。
eg. The teacher told us (that) the earth moves around the sun.
四.其他需要说明的问题
1.标点由主句决定,如主句是陈述句、祈使句,则用句号;是疑问句则用问号。
eg. I heard she had been to the Great Wall. Can you tell me which bus I should take?
2.要注意个别句子中主从句人称的一致。
▲五.宾语从句和状语从句的区分
eg. 1) I will go out tomorrow if it is fine.
2) I don't know if the train has arrived.
句1)中if引导的是状语从句。这个从句表示“条件”,修饰主句。整个句子的意思是如果明天天气好,我就出去。句2)中if引导的是宾语从句,充当谓语动词don't know的宾语。整个句子的意思是我不知道火车是否到达。
判断 方法 :
1.可以从整个句式看。状语从句一般可以放在主句的前面或后面(个别除外),宾语从句只能放在主句谓语动词之后。
2.从引导词看。if充当宾语从句的连接词时,相当于whether, 词义为“是否”,充当状语从句的连接词时,词义为“如果”。when充当宾语从句的连接词时,意为“什么时候”,充当状语从句的连接词时,意为“当……的时候”。
3.从时态看。if和when作连接词时,引导宾语从句要注意:从句的谓语动词的时态应根据主句的时态作相应的变化。if和when充当从属连词时,引导条件和时间状语从句,若主句的谓语动词用一般将来时,则从句的时态应用一般现在时表示将来。
初中英语冲刺技巧
隔天一套题,每天下午三点到五点
山东省特级教师、青岛二中英语教研组组长刘元静告诉记者,最后两个周各学校一般都已经进入了一个“静悟”的阶段,在这个阶段中,既要多思考、 总结 ,同时也不能放下常规的练习。“最好可以保持隔一天做一套题,跟高考保持同样的时间段,下午三点到五点,控制好时间,这样能大体上了解自己的答题节奏,上考场的时候才不会慌。”刘老师介绍说,“如果个人在特定的题型上有所欠缺,也可以重点做一些练习。”
九中的 高三英语 集备组组长匡文超老师也介绍说,考试前两周要掌握学校或老师给总结的重点字、词、句、短文,努力在考试中灵活运用,要平稳心态,按部就班的进行复习。因为考试形式都出入不大,复习时最好放慢速度不要一味地追求突击,难度不要太大,要以梳理语言思维为主。
听力训练最好不要戴耳机
从明年开始,山东高考英语考试中听力将不再出现,今年的考生将会是最后一批考核听力的考生。针对听力的练习,九中的匡文超老师介绍说,因为高考英语是在下午三点到五点之间,所以为了习惯这个时间答题,有条件的情况下最好在这个时间段放听力。
而对于听力的练习,青岛二中的刘元静老师也介绍说,如果有条件的话尽量不要戴着耳机听,以免到时候不适应考场环境。“因为我们高考的时候,听力都是用大喇叭的,在播放的过程中肯定会有一定的失真,音质也没有用耳机好,而且考生座位的不一样听到的声音大小都会有区别。”刘老师介绍说,“考生的心理都会很微妙,如果稍微有些不一样,那么听力的时候就可能会紧张,所以建议大家在家里练习的时候也尽量用喇叭。”
作文 不要背,心态很重要
临近高考,不少考生都以为多背几篇 范文 ,到时候高考的时候没准可以蒙上,对于这种想法,二中的刘老师明确表示没必要。“千万不要让孩子整篇整篇地背诵范文,因为高考考核的是综合运用语言的能力,让你‘押宝’押中了的情况几乎不可能出现。所以大家还是重在积累,把平常遇到的、听力中听到的精彩词句都可以记下来,灵活运用到 高考作文 中去,整篇整篇地背范文反而会限制考生的思维,因此完全没必要。”
“按部就班地放慢步伐复习,不要搞突袭,调整心态,防止考试时状态不好出现问题。”九中的匡老师说道,临考前的心态也很重要。研究近三年高考题,习惯高考题型防止不适应,不要一味要求难度,要梳理培养英语思维,强化二卷答题能力防止非客观因素扣分(粗心等)。强化二卷的答题能力,不要因为粗心或其他情况影响成绩。
小学英语教案模板范文全英
小学英语老师,它们会不会全部用英语来设计课堂上的教案呢?下面是我给大家整理的小学英语教案全英范文,供大家参阅!
小学英语教案全英范文
Teacher: *****
Content: Lesson 14 Unit7 colors (2)
1. Knowledge aim
①The text of lesson 14 is talk about colors.
②Understand and speak out the nine new words: blue, pink, black, white, have, pet, it, rabbit.
③Study the new sentences: “what color is it ” “I have a …” “It’s…” (The answer is color)
2. Teaching aim
①Master the new words.
②Make sentences with the new words.
③Let the students to the color of interrelated inquiries and responses have a clear understanding. ④Develop students’ imaginations.
3. Develop teaching point.
①Speak out the new words and make sentences in right tone. ②Stress the “a” is important to the sentence “I have a….” Many students often miss it.
4. Teaching aids
Cards, tape, some stars (To encourage students)
全英问版小学英语教案设计
Background of English teaching in primary school
It is not a long history that English is as a subject in primary school in our country and the main instructional aims of teaching English in primary school is to cultivate pupils’ basic abilities of their listening and speaking and their good sense of the English language. Our boys and girls are exposed to English for the first time, so it is very important to develop their keen interest in English.
I. Contents:
Today I’m going to talk about Part B of Unit 2, PEP Primary English, Book 3. This lesson includes two parts: Let’s talk and let’s practice. In section 1, it mainly deals with the dialogue about “What’s in the schoolbag ” and the answers. And in section 2, it provides a real situation for the Ss to prastise the pattern: How many +n.(pl.)+ do you have And the answer: I have 23 +n.(pl.)
II. Teaching aims
1. Aims on the knowledge
(1) To enable the Ss to understand and speak: “My schoolbag is heavy. What’s in it Thank you so much.” Make sure that Ss can use these sentences in real situations.
(2) To help Ss to finish the survey.
(3) Let Ss finish the assessment of “Let’s check” in this unit.
2. Aims on the abilities
(1) To develop Ss’ abilities of listening and speaking.
(2) To train the Ss’ ability of working in groups.
(3) To foster Ss’ abilities of communication and their innovation.
( 书村网 *** )
3. Aims on the emotion
(1) To foster Ss’ consciousness of good co-operation and proper competition.
(2) To lead Ss to show their loveliness to the poor.
III. Key-points of this lesson
(1) To help Ss ask and answer the question: What’s in it
(2) To enable Ss to study in groups and co-operate skillfully.
(3) To develop Ss’ interest in English.
全英问版小学英语教案模板
This is a dialogue that happens in the fruit shop .several sentences surround selling and buying the fruit will belearned .During the first and the second part in this unit ,the kids have understood simple instructions and act accordingly ,and they can say simple words ,phrases or sentences by looking at objects and the pictures .eg: lychee, banana, apple,“What’s this It’s an apple.”In Unit seven ,we grasped the numbers from one to ten .
The main language points in this unit is to make sentences using the fruit and numbers freely and communicate with others in English in the fruit shop. And pay close attention to the single and plural forms of the nouns .According to the kids’ English level and the corresponding content in the daily life ,I give them some extra extending .To train their ability of communicate with the others in English ,I prepare the following design .
Teaching aims (教学目标)
1.knowledge and skill aims :(知识技能目标)
Review the names of the ten different kinds of fruit and recognize the numbers from one to ten .
Understand simple instructions about the numbers and act accordingly. Practice English and communicate with others in the situation.
2.Equip them with the emotion ,attitude and value goals :(情感、态度、价值目标)
Cultivate the spirit of co-operations in the group work..

以上就是关于全英讲解英语从句的教案 ,定语从句趣味公开课的全部内容,以及全英讲解英语从句的教案 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

