本文目录
倒装句的英语
在现实的语言实践中,由于语法结构的要求,或是由于修辞的需要,往往要改变句子的自然语序,把一些本应置于主语之后的句子成分提到主语之前。我们称这种语序的变化为“倒装语序”这样的倒装语序可能使句子的内在含义产生细微的、甚至明显的改变。只有注意观察引起倒装的原因,才能更准确地理解句子的含义。为了使句子的某成分突出,我们还会使用强调,而倒装语序大多都用于强调。 主语和谓语是句子的核心,它们之间有两种语序
一是主语在谓语之前称为自然语序(Natural Order);
二是主语在谓语之后则称为倒装语序(Inverted Order)。
而倒装语序中又有完全倒装(Full Inversion)和部分倒装(Partial Inversion)
1.完全倒装(Full Inversion):又称全部倒装,是指将句子中的谓语全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用于一般现在时和一般过去时。
①谓语+主语+……
There be(的各种形式)+主语(+地点或时间状语)
例子:
There was a drop in the temperature.温度下降了
There are birds singing in the tree.鸟儿在树上唱歌。
②副词小品词+谓语动词+名词主语+……
例子:
Out rushed a young lady.
③过去分词或现在分词+be的各种形式+主语+……
例子:
Scattered on the floor were several books and magazines.几本书和杂志散落在地板上
2.部分倒装(Partial Inversion)(又称半倒装句):指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态动词倒装至主语之前,而谓语动词无变化。如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do,does或did,并将其置于主语之前。 英语句子的倒装一是由于语法结构的需要而进行的倒装,二是由于修辞的需要而进行的倒装。
前一种情况,倒装是必须的,否则就会出现语法错误;后一种情况,倒装是选择性的,倒装与否只会产生表达效果上的差异。
1.表示强调
倒装句最突出、最常见的修辞效果就是强调,其表现形式如下:
1.only +状语或状语从句置于句首,被该状语修饰的句子用部分倒装。
例子:
Only in this way can you solve this problem.
只有用这种方法,你才可以解决这个问题。
Only after he had spoken out the word did he realize he had made a big mistake.
只有当他已经说出那个字后才意识到自己犯了个大错误。
2. hardly,in no way,little,scarcely,seldom,never,no more,no longer,not,not only,no sooner,not only … (but also),not until… 等具有否定意义的词或词组位于句首,句子用部分倒装。
例子:
No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
我刚到家就下起了雨。
Seldom do I go to work by bus.
我很少乘公共汽车上班。
Not until twelve o'clock did she go to bed last night .
她昨晚十二点才上床睡觉。
3. so / such...that结构中的so或such位于句首可以构成部分倒装句,表示强调so /such和that之间的部分。
例子:
So unreasonable was his price that everybody startled.
他的要价太离谱,令每个人都瞠目结舌。
To such length did she go in rehearsal that the two actors walked out.
她的彩排进行得那么长,以致于那两个演员都走出去了。
以上各例都用倒装语序突出了句首成分,其语气较自然语序强烈,因而具有极佳的修辞效果。
4.here、there、now、then、thus等副词开头的句子可构成完全倒装。条件是谓语动词是不及物动词,如arise、be、come、exist、go、follow等。需要注意的是,当主语是代词时,不能构成倒装。(方位词在句首,主语是名词,全部倒装)
例子:
Here comes our headmaster。我们的校长来了。
Here it is. 在这里。
Here is your key.这是你的钥匙。
2.承上启下
1.为了避免句子部分内容不必要的重复,常用so+be动词(助动词、情态动词)+主语倒装句式或neither/nor + be动词(助动词、情态动词)+主语的倒装句式。
其中第一个句式表示与前面所述的肯定情况相同,第二个句式表示与前面所述的否定情况相同。
例子:
A:His brother is(not) a college student; B:so is mine.(nor is mine .)
A:他弟弟(不)是大学生,B:我弟弟也是。(我弟弟也不是。)
A:He used to have his further study abroad; B:so did I.(neither did I.)
A:他曾去国外深造过。B:我也去过。(我也没有。)
A:One of my friends can(not) speak three foreign languages; B:so can his wife.(neither can his wife .)
A:我的一个朋友(不)会说三门外国语。B:他的妻子也会。(他的妻子也不会。)
可以概括成:主语相同不倒装,主语不同倒装。
2.倒装可把前一句说到的人或物,或与前一句有联系的人或物在下一句紧接着先说出来,从而使前后两句在意思上的关系更加清楚,衔接更加紧密,起到承上启下的作用。
例子:
They broke into her uncle's bedroom and found the man lying on the floor,dead. Around his head was a brown snake.
他们破门进入她叔叔的卧室,发现他躺在地板上死了。一条棕褐色的蛇缠在他头上。
We really should not resent being called paupers. Paupers we are,and paupers we shall remain.
我们确实不应因为被称作穷光蛋而愤愤不平。我们的确是穷光蛋,而且还会继续是穷光蛋。
3.制造悬念渲染气氛
在新闻或文学创作中,有时为了内容的需要,或是为了强调,作者常常运用倒装来制造悬念,渲染气氛。
如朗费罗(Longfellow)《雪花》中的一节:
Out of the bosom of the Air,
Out of the cloud-folds of her garments shaken,
Over the woodlands brown and bare,
Over the harvest-fields forsaken,
Silent,and soft,and slow,
Descends the snow.
它来自天上。
叠叠乌云抖衣裳,
落在光秃秃的棕色树林,
和收割过的孤寂田野上。
静悄悄,不慌张,
绵绵雪花降;
在这一节诗里,诗人就富有创意地运用了倒装。在前五行中,诗人堆砌了七个状语,状语连续出现而主语和谓语却迟迟未露,造成一种悬念效应。全节读罢,读者才对诗歌的主题恍然大悟,因而收到了不同凡响的艺术效果。
4.平衡结构
英语修辞的一个重要原则是尾重原则,即把句子最复杂的成分放在句尾以保持句子平衡。在语言使用中为了避免产生头重脚轻、结构不平衡的句子,我们常采用倒装语序。
1. 以作状语的介词短语开头:当主语较长或主语所带修饰语较长时,为了使句子平衡,常将状语置于句首,句子用完全倒装语序。
例子:
1.A. To the coal mine came a com-pany of PLA soldiers with orders from the headquarters to rescue the trapped miners.
B. A company of PLA soldiers came to the coal mine with orders from the headquarters to rescue the trapped miners.
一个连队的解放军战士来到了那座煤矿,奉司令部之命解救受困的矿工。
2.A. On the ground lay some air conditioners,which are to be shipped to some other cities.
B. Some air conditioners lay on the ground,which are to be shipped to some other cities.
地上放着一些空调,等着用船运到其他城市去。
例句(2)包含一个非限制性定语从句,B句未倒装,则从句的先行词与引导词which中间被状语分隔开,不易于理解,而A句倒装使得先行词air conditioner与引导词which的关系一目了然。
从例句中可看出,采用倒装语序的A句结构平衡稳妥,读起来自然流畅,而采用自然语序的B句结构零乱,读起来也别扭。因而,在主语较长时就应采用倒装语序以取得理想的表达效果。
2. 以表语开头的句子:有时为了把较长的主语放在后面,须将表语和谓语都提到主语前。
例子:
Such would be our home in the future.
我们家就将是这个样子。
3. 以副词here,there开头的句子,也采用完全倒装来保持句子平衡。
例子:
Here is the letter you have been looking forward to.
你盼望已久的信在这儿。
5.使描写生动
有时为了使叙述或描绘更加生动形象,增加语言效果,可将表示方向的副词(如:down,up,out,in,off,on,away等)或拟声词(bang,crack等)置于句首,句子采用全部倒装的语序(主语为人称代词的句子除外)。
例子:
Up went the rocket into the air.
嗖地一声火箭就飞上天了。
Down jumped the criminal from the third floor when the policeman pointed his pistol at him.
当警察把手枪瞄准那个罪犯时,嘭地一下他就从三楼跳了下去。
Boom went the cannon!
轰隆一声大炮开火了!
Bang came another shot!
砰!又是一声枪响!
以上句子简洁明快,生动逼真地描述了有关动作,令我们一览此类倒装的风采。但这种倒装句的修辞功能在语段中可以体现得更为清楚。
“Stop thief! Stop thief!” There is a magic cry in the sound. The tradesman leaves his counter,... Away they run,pell—mell,helter—skelter,yelling—screaming,...
“Stop thief ! Stop thief !” The cry is taking by a hundred voices,... Away they fly,splashing through the mud,up go the window,out run the people. ( Dickens )
作者在第一段和第二段中分别用副词away,up和out位于句首引出四个倒装句Away they run,Away they fly,up go the window,out run the people。从而制造出一种紧张、急促的气氛,生动地刻画了一个紧张、混乱的捉贼场面。
倒装是英语中一个重要的修辞手段。倒装句的使用丰富了我们的语言表达,了解并掌握倒装句各种句式的用法,不仅会提高我们对英语语言的欣赏能力,对英语表达能力的提高也将大有裨益。因此,写作中适当用一些倒装句式定会使文章表达更生动、有力。

英语的倒装句有哪几种形式呢
用于部分倒装的情况:1 表示否定意义或半否定意义的词置于句首时。常见的有
seldom,never,hardly,no not,little 等。
2 由 only,not until 引导的状语置于句首时。
3 no sooner…than, hardly…when等结构中,no sooner 和hardly 置于句首时
主语用部分倒装。
4 在so/such…that 引导的结果状语从句中,so/such引导的部分置于句首时主
句用倒装。
5 “so/neither/nor+be/助动词/情态动词+主语”so与前面的肯定句呼应,nor
neither 与后面的否定句呼应。其中的动词形式取决于前一句的动词。表示前
者的情况也适用于后者或一者具备两种情况。
6 省略if的虚拟条件句以had/were/should 开头引起的倒装。
全倒装的情况:较常见的是here/there 等表示方向的词放句首或介词短语放句首

英语倒装句怎么写
一、倒装句的意义
1. 适应一定的语法结构的需要,主要是指疑问句句型结构的需要。
e.g. May I come in?
Was the People's Liberation Army founded in 1927?
2. 为了强调某一部分,而把这部分放到句首,构成倒装。
e.g. Never have I been late for school this term.
So early did he come to school that no other students came.
二、倒装的用法
1. 在“there be”结构里,there是引导词,主语在be后。
在“there + be”结构中的谓语动词有时不用be , 而用表示类似“存在”观念的其他不及物动词。如:live, stand, come, lie, flow, enter, rise 和appear等。
e.g. There is a box on the table.
There came shouts for help from the river.
There lies a large wheat field in front of the house.
Many years ago there lived an old man in the wooden house.
2. 在疑问句中。
e.g. Is she singing in the classroom?
What does your mother do?
3. 在here, there等副词开头的某些句子里(要用一般现在时态)。如果主语是人称代词,主语和主要动词的词序不变。(完全倒装)
e.g. There goes the bell.
Here is an apple for you.
There she comes.
Ex:There ________. And here ________.
A. goes the phone; she comes B. is the phone going; is she C. does the phone go; does she come D. the phone goes; come she
4. 重复倒装句型,用在以so, nor, neither开头,表示谓语所述的情况也适用于另一个人或一事物的肯定或否定句中。so用于肯定句,表示“也一样”“也这样”;nor, neither用于否定句,表示“同样也不,也不这样”。
e.g. I am watching TV. So is she.
My parents didn't watch TV last night. Neither (Nor) did I.
She is busy doing her homework. So is her brother.
You passed the exam. So did I.
He doesn’t like shopping. Neither do i.
He can’t speak any foreign language. Nor can his father.
表示两人的同样一个情况时,只能表示一件事,即上、下句所使用的动词、时态要一致。
否则要用so it is with…
His uncle is a worker and has been working in the factory for more than ten years. So it is with his aunt.
Ex:1)I don't know how to swim, ____.
A. and my sister doesn't neither B. nor my sister can C. nor does my sister D. and my sister does either
2)She's passed the test. ____. A. So am I B. So have I C. So I have D. Also I have
5. 直接引语的全部或一部分放在句首时,主句中的主谓也常直接倒装。(完全倒装)
e.g. "Very well," said the French student.
"Bring me two eggs and a cup of tea, please." said he.
6. 在以hardly(scarcely), never, not, not only, little, few,seldom, no sooner…(than), not until, no where等否定或半否定意义的副词、连词放在句首时要用倒装句,采用部分倒装。如不放在句首就不要倒装。
e.g. Little did he say at the meeting.
Never shall I forget the day when I joined the Army.
Hardly(Scarcely) had he reached the station when the train started.
Not once did we visit the city of our own.
Seldom in all my life have I met such a determined person.
Not only was there no electricity, but also no water.
Not until he shouted at the top of his voice did she turn her head.
比较:I shall never forget the day when I joined the Army.
Ex:1) Hardly ________ the airport when the plane took off. A. I had arrived at B. had I arrived C. had I reached D. I had got to
2) —Have you ever seen anything like that before? —No, ________ anything like that before.
A. I never have seen B. never I have seen C. never have I seen D. I have seen
7. 用于以only所修饰的副词、介词短语或状语从句的句子中。
e.g. Only when the war was over in 1918 was he able to get happily back to wrk.
Only in this way can we learn English well.
注意:如果only后的词组不是状语,不需倒装。
e.g. Only Wang Lili knows this. only
Only a few young men went to the theatre. (修饰主语时则不用倒装)
Ex:1)Only in this way ___ make progress in your English. A. you B. can you C. you be able to D. will you able to
2) Only when the meeting was over___ go back to meet his friend. A. he could B. he was able to C. was he able to D. was able to he
3)Only after liberation___ to be treated as human beings.
A.did they begin B. they had begun C.they did begin D. had they begun
8. 为了表达生动,有时把表地点、方位的副词,如 up, down, out, away, in等放在句首,同时把谓语动词放在主语之前。若主语为人称代词,主语和谓语动词的位置不变,只将副词放在句首。(完全倒装)
e.g. Away hurried the boy.
Out rushed the girl.
Away she went with tears in her eyes.
Ex:Out ____, with a stick in his hand. A. did he rush B. rushed he C. he rushed D. he did rush
表示地点的介词短语 (如on the wall, under the tree, in front of the house, in the middle of the room等)放在句首时,要全部倒装。如:
On the top of the hill stands a pine tree.
In front of the classroom is a playground.
Ex:Under a big tree ________, half asleep.
A. did sat a fat manB. a fat man sat C. did a fat man satD. sat a fat man
9. 在虚拟结构中,条件从句的谓语含有were, had 和should这三个词是,可省去if,将这些词移至主语之前。
e.g. Had I time (= If I had time), I would go and help you.
Were I you (= If I were you), I would go abroad.
Should he come (=If he should come), tell him to ring me up.
10. as引导让步状语从句时要倒装(形容词/ 副词/ 名词/ 动词 + as + 主语 + 谓语)。
e.g. Proud as they are, they are afraid to see me.
Child as he is, he seems to know everything.(child前不加冠词)
Hard as he worded, he made little progress.
Ex:________, he's honest. A. As he is poor B. Poor is he C. Poor as he is D. Poor as is he
_____, he knows a lot of things. A. A child as he is B. Child as he is C. A child as is he D. Child as is he
11. 用于某些表示祝愿的句子里。
e.g. May you succeed!
Long live the People's Republic of China!
12. So + 形容词、副词及such 置于句首时要倒装。
So happy did he feel.
Such was me.
13.固定搭配 hardly…when; scarcely…when…; no sooner…than… 可以用正常语序 had hardly done when… did 或用倒装句式Hardly had + 主语+ done when… did 句式。hardly所在的句子用过去完成时。
The bell hardly had rung when the class began.= Hardly had the bell rung when the class began.
No sooner had he arrived in Beijing than he began to work.
Ex:Hardly ____down ___he stepped in.
A.had I sat …than B. I had sat …when C.had I sat …then D. had I sat…when
14. 在以often, well, many a time, now and again 等方式或频度副词(短语)开头的句子中,要用部分倒装结构。如:
Many a time has John given me good advice.
Often have we made that test.
Ex:Many a time ________ swimming alone. A. the boy went B. went the boy C. did the boy go D. did go the boy
15. so+ 形容词/副词that 的结构状语从句可以用正常语序表示,也可以把so+形容词/副词放于句首构成倒装。句型如下: so +形容词/副词+be/助动词/情态动词that +从句。
Light travels so fast that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed.
= So fast does light travel that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed.
So easy was the work that they finished it in a few days.
16. "分词(代词) + be + 主语"结构。如:
Walking at the head of the line was our teacher.
Such was the story he told me.
done做形容词在句中做表语时,常把表语放在句首,要用倒装句式。
Gone forever are the days when the Chinese people had to use foreign oil.
17.为了保持句子的平蘅或为了强调表语和状语,或使上下文紧密衔接,把它们放在句首用倒装句。该结构不需加助动词。
East of the town lies a beautiful lake.
In a lecture hall of a university in England sits a professor.
Outside the doctor’s clinic were twenty patients.
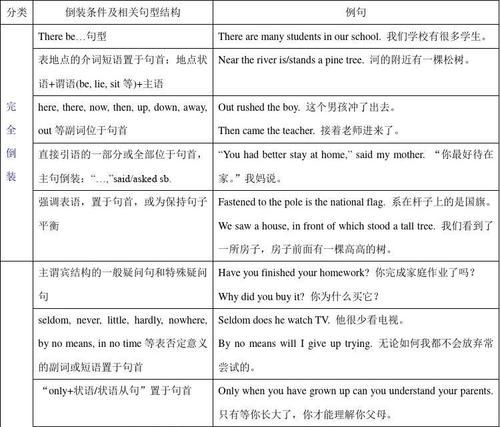
英语倒装句
英语倒装句有:
1、Only when you have got good preparation can the opportunities come to you naturally.
只有当你有充分的准备,机会才会自然地来到你身边。
2、We really should not resent being called paupers. Paupers we are, and paupers we shall remain.
我们真的不应该因为被称为穷光蛋而生气。我们是穷光蛋,以后也会是穷光蛋。

3、So hard did he work that he finally won the fame.
他工作如此努力,终于赢得了名声。
4、Nearby were two canoes in which they had come to the island.
附近有两只独木舟,是他们来岛上时乘坐的。
5、Not only was every tree cut down in the forest, but also all the animals disappear permanently.
不仅森林里的每棵树都被砍倒了,所有的动物也永远消失了。
以上就是关于倒装句用英语怎么表达 ,倒装句的英语的全部内容,以及倒装句用英语怎么表达 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

