本文目录
七年级英语一般过去时的句子
英语时态的常用时间状语
*可用刮号里的代替。
1.一般现在时:
always,usually,often,sometimes,seldom,rarely,never,
every day(morning,Monday,week,...etc.)
every other day,every there years,
once a week(day,month,...etc.),...
2.一般过去时:
last week(night,Monday,month,year,...etc.)
four years ago(days,month,...etc.)
before1980(three,liberation,从句,...etc.)
the day before yesterday,the day before last,
the year before last,just now,a monent ago,
yesterday,yesterday morning,this morning,
at first,at last,in the end,finally,then,...
3.一般将来时:
next week(Monday,month,year,...etc.)
in three days(an hour,...etc.)
tomorrow,tomorrow morning,the day after tomorrow,the day after next,the year after next,tonight,in 2010(2016...etc.)
this evening,this Saturday,after Wednesday,soon,sometime next week,one day in futuer,sooner or later,...
4..现在进行时:
now,these days(weeks,months,...etc.)
this month(week,...etc.)
Look!,Listen!,...
5.过去进行时:
this time yesterday,this time last Friday,in those days,at nine last night,from one to three yesterday afternoon,...
6.现在完成时:
since then(1949,last Monday,two o'clock,从句...,etc.),ever since then,
for three days(a long time,two hours,...etc.)
just,alreadly,yet,never,ever,now,before,this week,today,these days,once,twice,three times,...
7.过去完成时:
by then(1977,yesterday,eight last night,the time we got there,...etc.)
by the end of last term(week,year,month,...etc.)
有些时间状语可用在不同的时态中,各有其意:
now:1)I am speaking English now.
2)We have finished our homework now.
3)He's in the classroom now.
this afternoon:1)We had a class meeting this afternoon.
2)We're going to see a film this afternoon.
today:1)I've got two letters today.
2)We will learn a new lesson today.
3)She's cleaning her room today.
after seven:1)Mary will wash her clothes after seven.
2)Mary washed her clothes after seven.
for a week:1)John stayed in Wuxi for a week.
2)John has stayed in Wuxi for a week.
3)John will stay in Wuxi for a week.
除之外,过去将来时主要用于宾语从句(主句为过去时);故事;小说中等表过去的打算。

初一下册英语语法知识点总结归纳
初一下册英语语法知识点总结 篇1
初一下册英语语法知识
一、时间的表达法
(1)直读式,即直接读出时间数字
7: 05 sevenfive 8:16 eight sixteen
(2) 过、差式,即几点差几分,几点过几分。(以30分为分界线)
1:25 twenty-five pastone 2:30 halfpast two
3:43 seventeen to four 4:38 twenty-two to five
(3)12小时制
6:00 a.m. 上午6点 8:20 p.m. 下午8点20分
(4)24小时制
13:00 13点钟 22:15 22点15分
(5)15分可用quarter
4:15 a quarter pastfour 5:45 a quarter to six
(6)时间前通常用介词at
at 5 o’clock at 7:30 p.m.
二、关于时间的问法
(1)以when提问,“什么时候”可以是较长的时间段,也可以是较短的时间点,如:
①When is your birthday? 你的生日是什么时候?
②My birthday is Dec. 29th. 我的生日是12月29日。
这里就是指一天的时间段
①When do you go home? 你几点回家?
②I go home at 4:30 p.m. 我下午4:30回家.
这里when问的是具体的时间。
(2)具体几点我们通常用what time提问,如:
①What time is it now?/What’s the time now? 现在几点了?
It’s 9:26. 现在九点二十六。
②What time is it by your watch? 你手表几点了?
It’s 8:36. Oh, It’s50 minutes late. 8:36,哦,它慢了50分钟。
③What time do you get up? 你几点起床?
I get up at 6:00 a.m. 我早上6点起床。
初一英语基础知识
短语归纳
1. post office 邮局
2. police station 警察局
3. pay phone 付费电话
4. Bridge Street 桥街
5. Center Street 中心大街
6. Long Street 长街
7. near here 附近
8. across from 在……对面
9. next to 挨着,靠近
10. between…and… 在……和……之间
11. in front of 在……前面
12. excuse me 劳驾
13. far from 离……远
14. go along… 沿着……走
15. turn right/left 向右/左转
16. on the(或one’s) right/left 在(某人的)右边/左边
17. in my neighborhood 在我的街区
18. look like 看起来像
19. in life 一生中
20. be free 免费的/有空的
用法集萃
1. Turn right / left at the +序数词+ crossing. 在第几个路口向右 / 左转。
2. spend + 时间 /金钱 + on sth. 花费时间/金钱在......
spend + 时间 / +金钱 (in) doing sth. 花费时间/金钱做某事
3. watch sb. doing 观看某人正在做某事
4. enjoy doing sth. 喜欢做某事
典句必背
1. —Is there a hospital near here? 这附近有医院吗?
—Yes, there is. It’s on Bridge Street. 是的,有。它在桥街上。
2. —Oh… where’s Center Street? 噢……中心大街在哪里?
—It’s not too far from here. 它离这儿不太远。
3. Go along Long Street and it’s on the right. 沿着长街走,它在右边。
4. Turn right at the first crossing. 在第一个十字路口向右转。
初一英语知识重点
一、in the tree/ on the tree
in the tree 与 on the tree.译成中文均为"在树上"但英语中有区别。in the tree表示某人、某事(不属于树本身生长出的别的东西)落在树上,表示树的枝、叶、花、果等长在树上时,要使用on the tree.如:
There are some apples on the tree. 那棵树上有些苹果。
There is a bird in the tree. 那棵树上有只鸟。
二、 some/ any
(1)some和 any既可修饰可数名词,也可修饰不可数名词。但有以下两点需要
注意。
some常用于肯定句中,any常用于否定句和疑问句中。如:
There is some water in the glass.
Is there any water in the glass?
There isn't any water in the glass.
(2)在说话者希望得到肯定答复的一般疑问句中,或在表示请求,邀请的疑问句中,我们依然用some。如:
Would you like some tea?
三、tall/ high
(1)说人,动物,树木等有生命的东西,主要用tall,不用high,例如
a tall woman 一个高个子妇女
a tall horse 一个高大的马
(2)说一个不与地面接触的人和物的高时,要用high,而不用tall,比如人站在桌子上时,飞机飞上天时,例如:
He is high up in the tree. 他高高地爬在树上。
The plane is so high in the sky. 飞机在空中这么高。
(3)指建筑物、山时要tall或high都可以,不过high的程度比tall高。
(4)high可作副词,tall不能。
(5)tall的反义词为short, high的反义词为low.
初一下册英语语法知识点总结 篇2
初一英语语法——一般现在时
一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或表示现在的特征或状态。
其动词形式是:动词原形(只有第三人称单数作主语时除外,要加-s)其疑问句和否定句需要用助动词do或does
1)肯定句用行为动词原形表示
Theygetupveryearlyeverymorning.他们每天早晨起来很早。
Ivisitmygrandparentsfourtimesamonth.我一个月去看望祖父母四次。
2)否定句用don’t+动词原形来表示
Idon’tthinkyoulikethiscolour.我想你不喜欢这个颜色。
3)一般疑问句则是把助动词do提前至句首,后面动词用原形。回答时,肯定用“Yes,主语+do”;否定句用“No,主语+don’t”。
–Dotheygotoschoolatseveno’clock?他们七点去上学吗?
--Yes,theydo.
--Doyoulikethisskirt?你喜欢这条裙子吗?
--No,Idon’t.不,我不喜欢。
一般现在时用来表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与以下的时间状语连用:often经常,always总是,sometimes有时,usually通常,everyday/week每天/周等。
Heusuallygoestoschoolbybike.通常他骑车上学。
Ivisitmygrandparentseveryweek.我每个星期都去看祖父母。
Sheisalwayslateforclass.她总是上课迟到。
MyparentsandIsometimesgoouttoeat.我和父母有时出去吃饭。
Itoftenrainshere.这儿常常下雨。
初一下册英语语法知识点总结 篇3
初一 主要掌握几种时态
1,一般现在时
2,一般过去时
3,一般将来时
4,现在进行时
还有几种词
1,名词
2,代词
3,形容词
4,动词
5,冠词
初一英语语法
一、词法
1、名词
A)、名词的数
我们知道名词可以分为可数名词和不可数名词,而不可数名词它没有复数形式,但可数名词却有单数和复数之分,复数的构成如下:
一)在后面加s。如:fathers, books, Americans, Germans, apples, bananas
二)x, sh, ch, s, tch后加es。如:boxes, glasses, dresses, watches, wishes, faxes
三)1)以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加es 如:baby-babies, family-families, duty-duties, comedy-comedies, documentary-documentaries, story-stories
2)以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。如:day-days, boy-boys, toy-toys, key-keys, ways
四)以o结尾加s(外来词)。如:radios, photos, 但如是辅音加o的加es:如: tomatoes西红柿, potatoes马铃薯
五)以f或fe结尾的变f为v再加es(s)。如:knife-knives, wife-wives, half-halves, shelf-shelves, leaf-leaves, yourself-yourselves
六)单复数相同(不变的)有:fish, sheep, deer鹿子, Chinese, Japanese
七)一般只有复数,没有单数的有:people, pants, shorts, shoes, glasses, gloves, clothes, socks
八)单词形式不变,既可以是单数也可以是复数的有:police警察局,警察, class班,同学, family家,家庭成员
九)合成的复数一般只加主要名词,多数为后一个单词。如:action movie-action movies, pen pal-pen pals; 但如果是由man或woman所组成的合成词的复数则同时为复数。如:man doctor-men doctors, woman teacher-women teachers
十)有的单复数意思不同。如:fish鱼 fishes鱼的种类, paper纸 papers报纸,卷子,论文, work工作 works作品,工厂, glass玻璃 glasses玻璃杯,眼镜, orange桔子水 oranges橙子, light光线 lights灯, people人 peoples民族, time时间 times时代, 次数, chicken 鸡肉 chickens 小鸡
十一) 单个字母的复数可以有两种形式直接加s或’s。如:Is (I’s), Ks (K’s)。但如是缩略词则只加s。如:IDs, VCDs, SARs
十二) 特殊形式的有:child-children, man-men, woman-women, fooot-feet, mouse-mice, policeman-policemen, Englishman-Englishmen
B)名词的格
当我们要表示某人的什么东西或人时,我们就要使用所有格形式。构成如下:
一)单数在后面加’s。如:brother’s, Mike’s, teacher’s
二)复数以s结尾的直接在s后加’,如果不是以s结尾的与单数一样处理。如:Teachers’ Day教师节, classmates’; Children’s Day六一节, Women’s Day三八节
三)由and并列的名词所有时,如果是共同所有同一人或物时,只加最后一个’s,但分别拥有时却分别按单数形式处理。如:Mike and Ben’s room迈克和本的房间(共住一间),Mike’s and Ben’s rooms迈克和本的房间(各自的房间)
2、代词
项目 人称代词 物主代词 指示代词 反身代词
人称 主格 宾格 形容词 名词性
第一人称 单数 I me my mine myself
复数 we us our ours ourselves
第二人称 单数 you you your yours yourself
复数 you you your yours yourselves
第三人称 单数 she her her hers herself
he him his his himself
it it its its this that itself
复数 they them their theirs these those themselves
3、动词
A) 第三人称单数
当动词是第三人称单数时,动词应该像名词的单数变动词那样加s,如下:
一)一般在词后加s。如:comes, spells, waits, talks, sees, dances, trains
二)在x, sh, ch, s, tch后加es。如:watches, washes, wishes, finishes
三)1)以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加es。如:study-studies, hurry-hurries, try-tries
2)以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。如:plays, says, stays, enjoys, buys
四)以o结尾加es。如:does, goes
五)特殊的有:are-is, have-has
B) 现在分词
当我们说某人正在做什么事时,动词要使用分词形式,不能用原形,构成如下:
一)一般在后加ing。如:spell-spelling, sing-singing, see-seeing, train-training, play-playing, hurry-hurrying, watch-watching, go-going, do-doing
二)以不发音e的结尾的去掉e再加ing。如:dance-dancing, wake-waking, take-taking, practice-practicing, write-writing, have-having
三)以重读闭音节结尾且一个元音字母+一个辅音字母(注意除开字母组合如show –showing, draw-drawing)要双写最后的.辅音字母再加ing。如:put-putting, run-running, get-getting, let-letting, begin-beginning
四)以ie结尾的变ie为y再加ing。如:tie-tying系 die-dying死 lie-lying 位于
4、形容词的级
我们在对两个或以上的人或物进行对比时,则要使用比较或最高级形式。构成如下:
一) 一般在词后加er或est(如果是以e结尾则直接加r或st)。如:greater-greatest, shorter –shortest, taller –tallest, longer –longest, nicer- nicest, larger -largest
二)以重读闭音节结尾且1个元音字母+1个辅音字母(字母组合除外,如few-fewer fewest)结尾的双写结尾的辅音再加er /est。如:big-bigger biggest, red-redder reddest, hot-hotter hottest
三) 以辅音字母+y结尾的变y为i加er/est。如:happy-happier happiest, sorry-sorrier sorriest, friendly-friendlier friendliest(more friendly most friendly), busy-busier busiest, easy-easier easiest
四)特殊情况:(两好多坏,一少老远)
good/well - better best many/much - more most bad/ill – worse worst
little- less least old- older/elder oldest/eldest far- farther/further farthest/furthest
5、数词 (基变序,有规则;一、二、三,自己背;五、八、九、十二;其它后接th;y结尾,变为i, eth跟上去。) first, second, third; fifth, eighth, ninth, twelfth; seventh, tenth, thirteenth, hundredth; twenty-twentieth, forty-fortieth, ninety-ninetieth
二、句式
1.陈述句
肯定陈述句
a) This is a book. (be动词)
b) He looks very young. (连系动词)
c) I want a sweat like this. (实义动词)
d) I can bring some things to school. (情态动词)
e) There’s a computer on my desk. (There be结构)
否定陈述句
a) These aren’t their books
. b) They don’t look nice.
c) Kate doesn’t go to No. 4 Middle School.
d) Kate can’t find her doll.
e) There isn’t a cat here. (=There’s no cat here.)
2. 祈使句
肯定祈使句
a) Please go and ask the man.
b) Let’s learn English!
c) Come in, please.
否定祈使句
a) Don’t be late.
b) Don’t hurry.
3. 疑问句
1) 一般疑问句
a) Is Jim a student?
b) Can I help you?
c) Does she like salad?
d) Do they watch TV?
e) Is she reading?
肯定回答:
a) Yes, he is.
b) Yes, you can.
c) Yes, she does.
d) Yes, they do.
e) Yes, she is.
否定回答:
a) No, he isn’t
b) No, you can’t.
c) No, she doesn’t.
d) No, they don’t.
e) No, she isn’t.
2) 选择疑问句 Is the table big or small?
回答 It’s big./ It’s small.
3) 特殊疑问句
① 问年龄 How old is Lucy? She is twelve.
② 问种类 What kind of movies do you like? I like action movies and comedies.
③ 问身体状况 How is your uncle? He is well/fine.
④ 问方式 How do/can you spell it? L-double O-K.
How do we contact you? My e-mail address is cindyjones@163.com.
⑤ 问原因 Why do you want to join the club?
⑥ 问时间 What’sthe time? (=What time is it?) It’s a quarter to ten a.m..
What time do you usually get up, Rick? At five o’clock.
When do you want to go? Let’s go at 7:00.
⑦ 问地方 Where’s my backpack? It’s under the table.
⑧ 问颜色 What color are they? They are light blue.
What’s your favourite color? It’s black.
⑨ 问人物 Who’s that? It’s my sister.
Who is the boy in blue? My brother.
Who isn’t at school? Peter and Emma.
Who are Lisa and Tim talking to?
⑩ 问东西 What’s this/that (in English)? It’s a pencil case.
What else can you see in the picture? I can see some broccoli, strawberries and hamburgers.
11问姓名 What’s your aunt’s name? Her name is Helen./She’s Helen.
What’s your first name? My first name’s Ben.
What’s your family name? My family name’s Smith.
12 问哪一个 Which do you like? I like one in the box.
13 问字母 What letter is it? It’s big D/small f.
14 问价格 How much are these pants? They’re 15 dollars.
15 问电话号码 What’s your phone number? It’s 576-8349.
16 问谓语(动作) What’s he doing? He’s watching TV.
17 问职业(身份) What do you do? I’m a teacher.
What’s your father? He’s a doctor.
三、时态
1、一般现在时 表示普遍、经常性的或长期性的动作时使用一般现在时,它有:
Be 动词:She’s a worker. Is she a worker? She isn’t a worker.
情态动词:I can play the piano. Can you play the piano? I can’t play the piano.
行为动词:They want to eat some tomatoes. Do they want to eat any tomatoes? They don’t want to eat any tomatoes.
Gina has a nice watch. Does Gina have a nice watch? Gina doesn’t have a watch.
2、现在进行时 表示动词在此时正在发生或进行就使用进行时态,结构为sb be v-ing sth + 其它.
I’m playing baseball. Are you playing baseball? I’m not playing baseball.
Nancy is writing a letter. Is Nancy writing a letter? Nancy isn’t writing a letter.
They’re listening to the pop music. Are they listening the pop music? They aren’t listening to the pop music.
初一下册英语语法知识点总结 篇4
1)在代词what, which, who, none, some, any, more, most,all等词的单复数由其指代的词的单复数决定。
All is right. (一切顺利。)
All are present. (所有人都到齐了。)
2)集体名词作主语时,谓语的数要根据主语的意思来决定。如family, audience, crew, crowd, class, company,committee等词后用复数形式时,意为这个集体中的各个成员,用单数时表示该个集体。
His family isn't very large.他家不是一个大家庭。
His family are music lovers.他的家人都是音乐爱好者。
但集合名词people, police, cattle, poultry等在任何情况下都用复数形式。
Are there any police around?
3)有些名词,如variety, number, population, proportion, majority等有时看作单数,有时看作复数。
A number of +名词复数+复数动词。
The number of +名词复数+单数动词。
A number of books have lent out.
The majority of the students like English.
初一下册英语语法知识点总结 篇5
at the end of
at the end of +时间点或地点,“在…的尽头,在…的末尾”
They will have a sports meeting at the end of March. (时间)
He put some books at the end of the bed. (地点)
动词的种类
动词是表示动作或状态的词,按其词义和在句子中的作用可分为行为动词,连系动词,助动词和情态动词。
1.行为动词
行为动词可分为及物动词 (vt)和不及物动词(vi),及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,后跟宾语;不及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,但后面不能直接跟宾语,如要带宾语则与介词或副词构成短语。
如:
More and more people study English.(vt)
The students are listening to the teacher carefully.(vi)
2.连系动词
连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。常用的连系动词有 be, get, turn, become, look, feel, grow, seem, sound, taste, smell等。
如:
Our country is becoming stronger and stronger.
It feels damp.
3.助动词
助动词本身无词义,不能单独作谓语,只能和主要动词一起构成谓语动词,表示否定,疑问及动词的时态、语态、人称和数等语法特征,助动词有 be,do,have,shall,will等。
如:
How do you usually come to school?
The children are playing yo-yo now.
4.情态动词
情态动词本身有一定的意义,但不能独立作谓语,只能和主要动词原形一起构成谓语,表示说话人的语气和情态。情态动词没有人称和数的变化。情态动词有 can (could),may(might),must, need, ought to, dare等。
如:
Can I help you?
- Must we go now? -No, you needn't .
a. can与be able to的用法有所区别。can只用于一般现在时和过去时,指本身有能力的"能";be able to用于各种时态均可,指须经过努力而"能"。
b. must与have/has to的用法。must表示说话人主观认为"必须",只用于一般现在时和一般将来时;have/has to表示客观需要,意为"不得不",它可用于各种时态。
c.need和dare既可作情态动词也可作行为动词。
以上对动词的种类知识的内容讲解学习,相信同学们已经能很好的掌握了吧,希望同学们在考试中取得很好的成绩。

初一下册的英语语法知识点总结手抄报
语法是英语考试中的重中之重,所占分值也多。提高英语能力的方法是多读多练多积累。我在这里整理了初一下册的英语语法供大家阅读,希望能帮助到您。
初一下册英语语法
一. 情态动词can的用法
can+动词原形,它不随主语的人称和数而变化。
1. 含有can的肯定句:主语+can+谓语动词的原形+其他。
2. 含有can的否定句:主语+can't+动词的原形+其他。
3. 变一般疑问句时,把can提前:Can+主语+动词原形+其他? 肯定回答:Yes,主语+can。否定回答:No,主语+can't.
4. 含有can的特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+can+主语+动词原形+其他?
I can speak English.→I can't speak English.→Can you speak English? →What can you speak?
二.、what time和when引导的特殊疑问句
1. 询问钟点时用what time,询问日期、月份、年份时用when。
2. What's the time?=What time is it?现在几点了?
3. 时刻表达法:顺读法和逆读法。
顺读法:“钟点+分钟”直接读数字。
如:7: 05 seven five;8:16 eight sixteen
逆读法:借助介词past或to表示,要先说分再说钟点。
a. 当分钟不超过30分钟时(包括30分钟),即<或=30,用past表示。其结构为:“分钟+past+整点” 意为“几点过几分”。
如:1:25 twenty-five past one
b. 当超过30分钟时,即>30,用to表示。其结构为:“所差分钟(即60—所 过分钟数)+to+下一个整点”,to译成“差”,差几分钟到几点。
如:4:38 twenty-two to five
c. 当分钟为30分钟用half表示,当分钟为15分钟用a quarter。
三、 how引导的特殊疑问句
1. how 引导的特殊疑问句提问交通方式,其答语分三种情况:
a. take a/an/the+交通工具(单数)
b. by+交通工具(单数)
c. on/in+限定词+交通工具
---How do you go to school every day?
---I take a bus to go to school every day./I go to school by bus every day./I go to school on the bus every day.
2. how far 用来提问距离,多远,其答语分为两种:
(1)用长度单位表示:It is five kilometers.
(2)用时间表示:It’s twenty minutes’walk.
3. how long 用来提问时间,意为多久回答常用“for+段时”。
----How long have you learnt English?
----For 3 years.
4. how soon 用来提问做完某事还需要多长时间, 用于将来时态, 常用“in+时间段”来回答。
----How soon will you arrive in Beijing? ----In 3 hours.
四. 祈使句
祈使句一般表示请求、命令、劝说、号召、警告等。一般以动词原形开头,句末可以用感叹号或句号。
1. 肯定的祈使句:
(1) 实义动词原形+其他 :Please look at that boy.
(2) be动词原形+形容词+其他:Be quiet, please.
2. 否定的祈使句:
(1) Don’t+实义动词+原形 Don't stand there.
(2) Don’t be+形容词+其他 Don't be so noisy.
(4) No+n./V-ing
No photos. 不许照相。
No talking. 不许谈话。
五. 现在进行时
现在进行时指当前时间正在发生的动作。常与now,at this moment,listen,look等词连用。
1. 现在进行时的基本结构
肯定式:am/is/are+doing(现在分词),否定式:am/is/are not +doing(现在分词),一般疑问式:Am/Is/Are + 主语 +doing(现在分词)+ 其他,特殊疑问式:特殊疑问词+一般疑问式
They’re having a meeting now. 他们现在正在开会。
They aren't having a meeting now. 他们现在没有在开会。
Are they having a meeting now? 他们现在正在开会吗?
What are they doing now? 他们现在正在做什么?
2. 现在进行时的基本用法
(1)表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。常与now,at the moment,look,listen等词连用。
The little boy is watching TV now. 这个小男孩现在正在看电视。
Listen!She is playing the guitar in the next room. 听!她正在隔壁房间弹吉他。
(2)表示现阶段一直在进行着或是重复发生着的动作,不强调此时此刻正在做。常与表示时间段的时间状语连用。
I am studying computer this term. 这个学期我一直在学习计算机。
(3)表示说话人褒义或贬义的情感色彩,如赞许、批评、喜欢、厌恶等。此时常与alway、often等频度副词连用。
He is always thinking of others , not of himself. 他总是为他人着想,而不为自己。(表示赞许)
One of my roommates is often leaving things about. 我的一个室友经常乱扔东西。(表示不满)
(4)表示在近期按计划或安排要发生的动作。(现在进行时表示一般将来的含义。)
① 瞬时动词的进行时在任何情况下都表示将来含义。这些动词包括go , come , leave,arrive , return等。
I am leaving. 我将要离开了。
I am leaving tomorrow. 我将会明天离开。
② 持续动词的进行时,只有在有将来时间状语或将来语境的情况下才可以表示将来含义。An American professor is giving a lecture this afternoon. 今天下午一位美国教授将要作报告。(将来含义)
An American professor is giving a lecture. 一个美国教授正在作报告。(进行含义)
3. 现在分词(doing)的变化规则
(1)一般在情况下,在动词词尾加-ing。
go——going
play——playing
know——knowing
(2)以不发音的字母e结尾动词,先去e再加-ing。
make——making
arrive——arriving
come——coming
(3)以重读闭音节结尾,且动词词尾只有一个辅音字母时,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing。
run——running
stop——stopping
swim——swimming
run——running
put——putting
sit——sitting
begin——beginning
plan——planning
cut——cutting
get——getting
shop——shopping
chat——chatting
regret——regretting
dig——digging
(4)以-ie结尾,先将-ie改成y,再加-ing。
tie——tying
die——dying
lie——lying
六. There be结构
1. There be句型主要用以表达“某处有某人(某物),强调存在”其基本结构为“There be+某物(某人)+某地”,有时为了强调地点,也可把地点状语放在句首。
There is a book on the desk.
On the desk there is a book.
(1)肯定句:“There be+主语(某人/某物)+介词短语”
There are three people in my family. 我家有三口人。
There is a pen and two books on the desk. 书桌上有一支钢笔和两本书。
(2)否定式:“There be +not+主语+介词短语”
There isn’t a boy in the room.房间里没有一个男孩。
There aren’t any books on the desk.书桌上没有书。
注意:“There be句型”的否定式的构成和含有be动词的其他句型一样,在be后加not或no即可。
注意not和no的不同:not是副词,no为形容词,所以not a/an/any+n,相当于no+n。
There aren’t any pictures on the wall.=There are no pictures on the wall.
There isn’t a bike behind the tree.=There is no bike behind the tree.
(3)疑问式:Be there+主语+介词短语?”
肯定回答是:“Yes, there be.”否定回答是:“No, there+be与not的缩写形式”。
—Is there a lamp in your bedroom?在你的卧室里有台灯吗?
—Yes, there is.是的,有。
—Are there any clock in the living room?客厅里有钟吗?
—No, there aren’t.不,没有。
(4)特殊疑问句:一般有两种句型结构
How many+复数名词+are/were there+介词短语?
There’re many children in the park.
How many children are there in the park?
How much+不可数名词+is/was there+介词短语?
There was little rain around the year.
How much rain was there around the year?
2. have表示“某人拥有某人或某物,强调拥有和所属关系”。
The man has two cars.
3. There be句型中的就近原则,即be和距其最近的主语保持一致。
There are some pens and a book on the floor. =There is a book and some pears on the floor.
七. 选择疑问句
选择疑问句是指说话人提出两种或以上的情况,让对方选择是哪一种,两个选择部分用or连接。选择疑问句不用yes或no来回答,直接在两个选择里选一个回答。
---Is she tall or short? ---She is tall.
---Can you play the piano or play the guitar? ---I can play the piano
八. 既是可数名词又是不可数名词的单词
chicken当“鸡肉”讲时是不可数,当“小鸡”讲时可数;
room当“空间”讲时不可数,当“房间”讲时可数;
fish当食物用“鱼、鱼肉”讲时不可数,当“鱼的种类”讲时可数;
hair泛指“毛发”时不可数,当“一根或几根毛发”讲时可数;
sound意思是“一般性的声音”时,不可数,指“一次发出的声音”时可数;
paper当“纸”讲时不可数,当“试卷”、“论文”、“证件”讲时可数;
time当“时间”讲时不可数,当“时代、倍数、次数”讲时可数;
exercise泛指“锻炼”时不可数,当“练习、做操”讲时可数
九. 一般过去时
一般过去时表示在过去某个时间所发生的动作或所处的状态(与现在无关) 。常与yesterday, last week, in 1989, just now, a moment ago, the other day等过去具体时间状语连用。
He was here just now.
他刚才还在这里。
What did you do yesterday?
你昨天做了什么事?
一般过去时基本结构
1. 肯定句形式:主语+动词过去式+其他
I was an English teacher one year ago.
一年前我是一名英语老师。
I bought a yellow dress yesterday afternoon.
昨天下午我买了一条黄裙子。
2. 否定句形式:①was/were+not; ②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词
I wasn't an English teacher one year ago. 一年前我不是一名英语老师。
I didn't buy a yellow dress yesterday afternoon. 昨天下午我没买一条黄裙子。
3. 一般疑问句:①was/were提到句首; ②Did+主语+动词原形+其他?
Were you an English teacher one year ago? 一年前你是一名英语老师吗?
Did you buy a yellow dress yesterday afternoon? 昨天下午你买了一条黄裙子吗?
4. 特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
What were you one year ago? 一年前你是做什么的?
学好初中英语的建议
一、明确学习动机
同学们要知道,我们学习英语最直接的目的是什么?就是为了能考上好大学。学习成绩好的同学,大部分都是有意无意的遵循了学习规律,有了自己的一套学习方法,养成了良好的学习习惯。
然而成绩不是很好的同学则看不到上大学的希望,因而失去了学习的原动力,也就是学习动机,怎么办呢?
这个时候就我们需要告诉自己,凡事积极乐观,有自信,有恒心,有坚韧不拔的毅力,成功是早晚的事,成绩不好只是暂时。
就拿学习英语来说,要看到学好英语,说好英语的作用,我们都知道,成功从来都是偏向有准备的人,多一项本领,将来就会多一项选择。
二、爱上英语
想学好哪一学科,首先要爱上这一学科,这也就是我们所说的学习兴趣。兴趣不是与生俱来的,可以是老师的培养,可以是家庭环境影响。
如果这两个条件你都没有,那么我们就自己来想办法吧。有两个好办法:
一个是从我们感兴趣的英文电影开始吧。具体看什么电影,现在网络方便,同学们都能查找到的。电影的选择一定是原声的,最好是中英文双字幕,反复多次看几遍。
另一种方法就是朗读背诵课文,在教学中我一直强调阅读,因为我认为阅读是其他项目的基础,它是输入,是吸收,而各方面的运用则属于输出。
没有输入哪来输出?不读文章怎么会写文章呢?这个方法在百家号人生底色看语文的上一篇文章中有详细介绍,同学们可以搜索查看。
坚持这两种方法,你会慢慢爱上英语的,你会发现越看越喜欢,越读越有自信,这么做还有一个最大的好处是可以培养英语语感。
三、坚强意志
坚强的意志能使人在各种环境中奋发向上,自强不息。
同学们的思维活跃,兴趣广泛,求知欲强,但缺乏持久的恒心和毅力,所以我们要做的是善于发现自己的进步与不足。
树立信心、决心和恒心,战胜学习上的困难,走向成功
本次整理就到这里啦,祝大家在考试中能金榜题名!
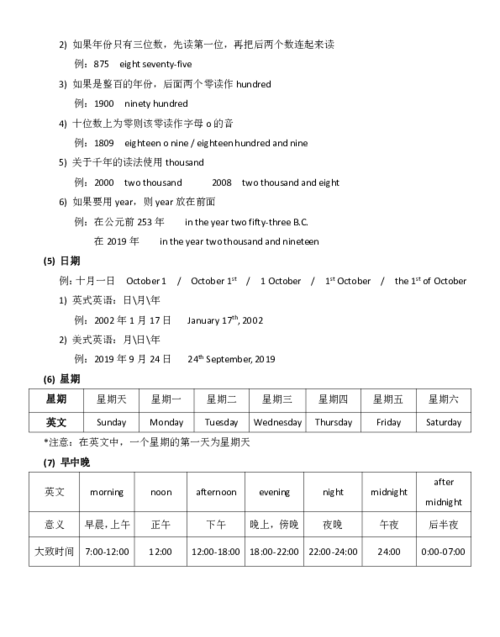
用英语表示时间的三种用法
1:20 one twenty、twenty past one
2:30 two thirty 、thirt past two
3:45 three forty-five 、fifteen to four
5:10 five ten、ten past five
6:58 six fifty-eight、two to seven
7:05 seven five、five past seven
4:44four forty-four、sixteen to five

以上就是关于七年级下册英语时间表示法 ,七年级英语一般过去时的句子的全部内容,以及七年级下册英语时间表示法 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

