本文目录
英语语法时态讲解视频
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。以下是我整理的英语语法16种时态讲解,希望对大家 英语学习 有所帮助。
英语语法时态讲解:一般现在时
英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。
用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。
B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。)
D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持 主句、从句时态一致。
E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动 、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词 )可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用 。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.
(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。)
How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)
F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事 情。
例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份 报告 的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。)
英语语法时态讲解:现在进行时(be doing)
用法:现在正在进行的动作。
英语语法时态讲解:现在完成时(have done)
用法:A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have twohouses.
A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell
答案是C) haven't sold。
B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。
例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified bythe work of scientists of our time.
A) are to challenge C) have been challenged
B) may be challenged D) are challenging
全句的意思是:“虽然牛顿是个伟大的人物,但他的许多见解直到今天还在受到挑战,并且被现代科学家的工作所修正。”challenge是及物动词,在本句中应当是被动语态;其动作延续到今天,所以要用现在完成时态。可见答案是C) have been challenged。A) are to challenge和D) arechallenging都是主动语态,不可能是答案。B) may be challenged虽然是被动语态,但意思与全句内容不合,所以不对。
C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose等。
例:John has broken his left leg.(约翰摔断了左腿。)
注意事项:A) 现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带。现在完成时和过去时的区别在于:现在完成时强调动作的动态,或受动态的影响,是动态的结果,对现在有影响;过去时只表示过去的某个具体时间里发生的动作,与现在没有联系。
例:He worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他曾经在那家医院工作了8年。这只是讲述一个过去的事实,他现在已经不在那家医院了。)
He has worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他已经在那家医院里工作了8年。表示他从过去开始工作,一直工作到现在,现在仍在那家医院工作。)
B) 因为含有for加一段时间或since加一个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以不能使用终端动词或瞬间动词。
例:My sister has been married for 5 years.(过去分词做表语表示状态,可以延续)
My sister has married. Don't disturb her.(终端动词)
C) 在"this is the first/ second/ third…… time that……"句型里要求用完成时。
例:This is the second time that the products of our company have been shown in theInternational Exhibition.(这是我公司产品第二次参加国际展览会。)
D) 句型"It is/ has been……since"所使用的两种时态都正确。
例:It is/ has been 10 years since I last saw him.(从我上次见到他以来已经10年了。)
E) 在"no sooner than"、"hardly/ scarcely ……when"、"before"、"prior to"等句型中,主句要求完成时。
例:I haven't met that professor prior to today.(以前我从未见过那位教授。)
英语语法时态讲解:现在完成进行时(have been doing)
用法:表示某一动作开始于过去某一时间,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。
例:We have been working on this project for over a month now.(到目前为止,我们一直在处理那个项目,已经花了一个多月时间了。)
注意事项:与现在完成时相比,现在完成进行时更强调:在从过去到现在的时间里,动作或状态一直持续或一直反复出现。
例:It seems oil ___________ from this pipe for some time. We'll have to take the machine apartto put it right.
A) had leaked B) is leaking
C) leaked D) has been leaking
从本题上下文看,这两个 句子 的意思是:“看来,这个管道漏油已有一段时间了,我们将不得不拆卸机器排除故障。”第二句表示将要采取的 措施 。第一句动作发生在第二句之前,并且延续到现在为止仍在继续。因此,空格中需用现在完成时或现在完成进行时。D) has been leaking是现在完成进行时,因此是本题的答案。有11%的考生误选了B) is leaking。由于本句有时间状语for sometime,表示谓语动作延续,谓语不能用现在进行时,必须用和完成时有关的时态。有些考生误选了C) leaked或A) had leaked。是因为他们没有注意到本题第二句是一般将来时,所以第一句的谓语不能用过去时或过去完成时。
英语语法时态讲解:一般过去时
用法:A) 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。
B) 表示过去习惯性动作。特别是由would/ used to do表达的句型,本身表示的 就是过去时。
例:The old man would sit on a bench in the quiet park and look at others for hours without doinganything or talking to anybody.(老人过去常常坐在宁静的公园里的一条长椅上,看着其他的人,一坐就是数个小时,什么也不干,也不和任何人交谈。)
He used to visit his mother once a week.(他以前总是每周看望一次他的母亲。)
C) 有时可代替一般现在时,表达一种婉转、客气、礼貌、商量的语气。
例:I wanted to ask you if I could borrow your car?(我想向您借车用一用,可以吗?)
Would you mind my sitting here?(您介意我坐在这里吗?)
注意事项:A) 注意时间状语的搭配。一般过去时的时间状语应该是表示过去某个时间的词或词组,如:yesterday, last month, in 1999, two days ago等,绝对不可与recently, in the past 10 years, this month等连用,因为这样的时间状语都与现在有关系,应该用现在完成时或一般现在时。
B) used to do的否定形式和疑问形式很特别:你怎么写都正确。以否定形式为例:used not to do, didn't used to do, didn't use to do都对。
Used to do经常与 be used to doing sth/ sth结构进行对比。前者表示"过去常常或
过去曾经",要求加动词原形;后者表示"习惯于",要求加名词或动名词。
英语语法时态讲解:过去完成时(had done)
用法:表示在过去的某个时间或动作以前已经发生的动作或已经存在的状态。就是我们常说的:表示"过去的过去的动作或状态"。
Until then, his family _________ from him for six months.
A) didn't hear C) hasn't heard B) hasn't been hearing D) hadn't heard
全句的意思是:“到那时为止,他家里已经有六个月没得到他的消息了。”由此可以看出,谓语动词的动作延续到过去的某一时刻才完成,因此谓语要用过去完成时。答案是D)。 其它 选项中:A) didn't hear,因为一般过去时只表示过去发生的事情或存在的状态,所以不能与时间状语for sixmonths连用。B) hasn't been hearing,现在完成进行时表示过去某时刻继续到现在或现在还在进行的动作,与题意不符。C) hasn't heard,现在完成时表示从过去某一时刻到现在为止发生的动作。而题中的then只表示过去的某一时刻,不能表示现在时间。
注意事项:“过去的过去”这种逻辑关系常通过上下文体现出来,而不一定受某个时间状语的限制。
例:There had been some one in our room just now, because I noticed a burning cigarette end onthe floor when we opened the front door.(刚才有人在我们的房间里,因为我们打开前门进来时,我注意到地板上有一支仍在燃烧的香烟。)
分析:虽然时间状语是just now,似乎应该使用一般过去时,但是“在房间里”这个状态是在"开门"和"注意"这两个过去的动作之前就存在的,所以应该用过去完成时。
英语语法时态讲解:过去将来时(would/ should do)
用法:表示从过去的某个时间看将要发生的事。
例:I said on Thursday I should see my friend the next day.(我星期四说我将于第二天 拜访 我的朋友。)
注意事项:由于过去将来时是由过去时和将来时组合而成的,所以其注意事项可以参考过去时和将来时的相关注意事项。
英语语法时态讲解:过去进行时(was/ were doing)
用法:A) 表示在过去一个比较具体的时间正在发生的动作。
例:Mary was listening to light music 10 minutes ago.(10分钟前,玛丽正在听轻音乐。)
B) 如果when, while这样的时间状语引导词所引导的主从句之一是一般过去时,则另一个句子常用过去进行时。
例:I was washing my hair when you knocked at the front door.(你敲前门时我正在洗头发。)。
注意事项:其它与将来时有关的事项请参见下面所讲的一般将来时
英语语法时态讲解:一般将来时
用法:A) 基本结构是will / shall do。
例:We shall send her a glass hand-made craft as her birthday gift.(我们将送给她一个玻璃的手工制品,作为给她的生日礼物。)
B) 有些动词,如:arrive, be close, come, do, done, go, have, leave, open, play, return, sleep, start, stay等,用于一般进行时,并且通常与一个表示将来时间的时间状语连用,可以表示将来时。
例:My mother is coming to visit me next week and is staying here until May.(我妈妈下周将来看我,并会呆到5月。)
C) 表示“打算去……,要……”时,可用be going to do。
例:This is just what I am going to say.(这正是我想说的。)
D) 表示“即将、正要”时,可用be about to do。强调近期内或马上要做的事。
例:Don't worry, I am about to make a close examination on you.(别担心,我马上就给你做一次仔细的检查。)
E) "be to do"的5种用法:
a) 表示“按计划、安排即将发生某事或打算做某事”。
例:She is to be seen in the lab on Monday.(星期一你准会在实验室见到她。)
b) 该做或不该做的事情(语气上接近于should, must, ought to, have to),表示一种命令、规劝性语气。
例:You are to go to bed and keep quiet, kids. Our guests are arriving in less than 5 minutes.(孩子们,你们必须 上床睡觉,不准吵闹。我们的客人5分钟之内就要到了。)
c) 能或不能发生的事情(接近can, may)
例:How am I to pay such a debt?(我怎么可能还得起这么大的一笔债呢?)
d) 不可避免将要发生的事情,后来将要发生的事情。
例:I assure you that the matter _______ as quickly as possible. Have a little patience.
A. will be attended B. will be attended to
C. is attended D. is attended to
will be attended to关键的一点是:attend表示“处理,解决”时是不及物动词,必须与to连用。另外,从上下文看,事情显然尚未解决,所以应该用将来时的被动语态。答案是B。
e) 用于条件从句“如果……想,设想”(接近if ……want to,或if ……should)
例:Greater efforts to increase agricultural production must be made if food shortage ____________ avoided.
A) is to be B) can be C) will be D) has been
答案是A) is to be。全句的意思是:“如果要避免食品短缺,就必须作出更大努力来增加农业产量。”
F) 同样可以表示“正要、将要”的意思的句型是be on the point of doing。
例:The coach is on the point of giving up the game because our team has been scored 7 points.(教练想要放弃这场比赛了,因为对方已经射进了7个球。)
例:I was _______ the point of telephoning him when his letter arrived.
A) in B) to C) at D) on
答案是D)。on the point of doing 是固定词组,意思是“正要、打算”。全句的意思是:“当他的信到的时候我正要打电话给他。”
注意事项:
在以if, when, as long as, as soon as, after, before, in case, until, unless等连词以及具有连词作用的副词(immediately, the moment, directly)等引导的状语从句,一般用现在时代替将来时。强调延续性或动态时,可用完成时。
例:I hope his health will have improved by the time you come back next year.(我希望到明年你回来的时候,他的身体已经好多了。)
英语语法时态讲解:将来进行时(will be doing)
用法:强调在将来的某个具体时间正在发生的动作或事情。
例:Don't worry, you won't miss her. She will be wearing a red T-shirt and a white skirt at thattime.(别担心,你不会认不出她的。她到时会穿一件红色的T恤衫和一条白色的短裙。)
注意事项:由于本时态是由将来时和进行时融合在一起的,所以关于本时态的注意事项,可参考"一般将来时"和"现在进行时"的有关注意事项。
英语语法时态讲解: 将来完成时(will have done)
用法:表示从将来的某一时间开始、延续到另一个将来时间的动作或状态,或是发生在某个将来时间,但对其后的另一个将来时间有影响的动作或状态。就好象把现在完成时平移到时间轴的将来时时段一样。其用法从和过去及现在有关,变成了和将来及将来的将来有关。
例: The conference __________ a full week by the time it ends.
A) must have lasted B) will have lasted
C) would last D) has lasted
本题考核谓语动词的时态。全句的意思是:“会议从开始到结束将持续整整一个星期。”句中by thetime it ends表示动作要延续到将来某一时刻,因此要用将来完成时。答案是B) will have lasted。如果选A),因为情态动词must后面接动词不定式的完成时形式表示对已经发生的事情的一种肯定推测,而本句的时间状语是by the time it ends而非by the time it ended,所以犯了时态不呼应的错误。Would虽可以表示推测或可能性,但would last不能表示延续到将来某一时刻的动作,所以C) would last错误。因为D) has lasted是现在完成时,表示到现在为止已经完成的动作,不能表示延续到将来某一时刻的动作,所以也不正确。
注意事项:由于本时态是由将来时和完成时融合在一起的,所以关于本时态的注意事项,可以参考“一般将来时”和“现在完成时”的有关注意事项。
英语语法时态讲解: 将来完成进行时
shall have been doing ,will have been doing
例:By the end of next month, the project will have been being worked for 3 years. (到下个月底为止,这项工程就已经不停地进行了3年了。)(被动语态)
英语语法时态讲解: 过去完成进行时
had been doing
例:The old clock had been being taken apart of and fixed up again for several times by my 10-year old son before I came back home.(我回到家之前,我10岁大的儿子已经把这个旧钟表拆卸并重新组装了好几回了。)(此处强调“拆卸”和“组装”这两个过去的过去的动作一直在反复进行。)(被动语态)
英语语法时态讲解: 过去将来进行时
should be doing , would be doing
例:The government promised that a new highway would be being built next July.(政府承诺说第二年7月将有一条新的高速公路正在修建。)(此句的时间状语是具体的将来时间,所以最好用将来进行时。)(此句为被动语态)
英语语法时态讲解: 过去将来完成时
should have done , would have done
例:I believed by the end of that year an advanced version of that software would have beendeveloped, but I was wrong.(我坚信到那年年底为止,那个软件的新版本将被开发出来。但是我错了。)(此句为被动语态)
英语语法时态讲解:过去将来完成进行时
should have been doing , would have been doing
例:They said that by the end of the following month, the project would have been being workedfor 3 years. (他们说到第二个月底为止,这项工程就已经不停地进行了3年了。)
猜你喜欢:
1. 英语几种时态的知识点
2. 六级英语语法
3. 英语语法讲座英语语法详解
4. 16种英语时态总结归纳
5. 16种时态的用法口诀
英语的八大时态的具体概念是什么
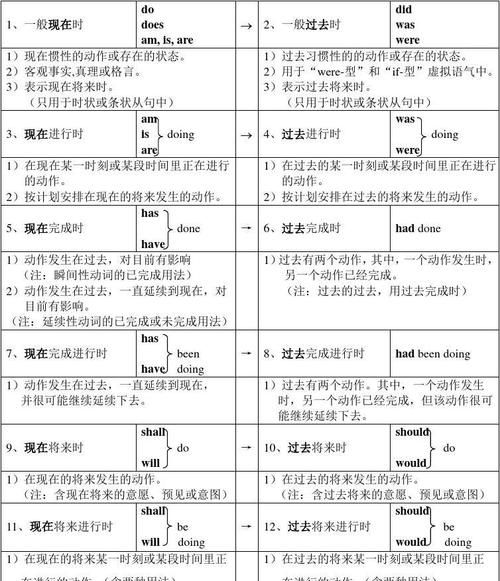
一、 一般现在时:
1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2.时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays,
3.基本结构:动词 原形 (如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加(e)S)
4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
6.例句:. It seldom snows here.
He is always ready to help others.
Action speaks louder than words.
二、 一般过去时:
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词
4.否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
6.例句:She often came to help us in those days.
I didn't know you were so busy.
三、 现在进行时:
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.
3.基本结构:am/is/are+doing
4.否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing.
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6.例句: How are you feeling today?
He is doing well in his lessons.
四、 过去进行时:
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3.基本结构:was/were+doing
4.否定形式:was/were + not + doing.
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit.
When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
五、 现在完成时:
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,in the past few years, etc.
3.基本结构:have/has + done
4.否定形式:have/has + not +d one.
5.一般疑问句:have或has。
6.例句:I've written an article.
It has been raining these days.
六、 过去完成时:
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc.
3.基本结构:had + done.
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.
By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books
七、 一般将来时:
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
3.基本结构:am/is/are/going to + do;will/shall + do.
4.否定形式:was/were + not; 在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies.
It is going to rain.
八、 过去将来时:
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:was/were/going to + do;would/should + do.
4.否定形式:was/were/not + going to + do;would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6.例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day.
I asked who was going there .
英语语法时态结构
英语时态
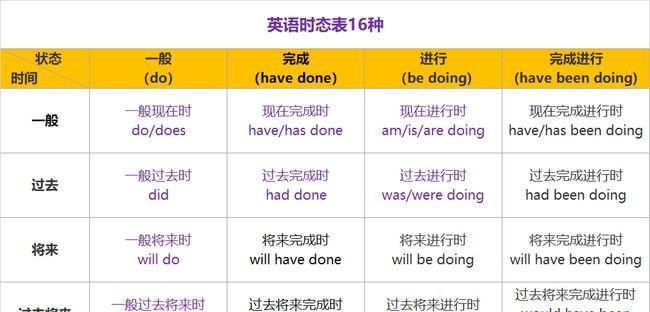
一般现在时表示现在、经常或习惯的动作或状态和普遍现象、常识或客观真理;一般过去时用于过去某一时间内发生的或过去习惯性的动作或状态;一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态,将来打算做的事情;现在完成时表示过去发生的动作造成目前的结果和对现在造成的影响或表示从过去延续至今的动作、状态和习惯等;将来完成时表示将来某时之前业已完成或发生的事情;过去完成时表示过去某时间之前已经发生的动作或状况,即过去的过去.注意每一种时态与其他时态的交叉使用情况.英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例):
一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 study
studies am studying
is studying
are studying have studied
has studied have been studying
has been studying
过去 studied was studying
were studying had studied had been studying
将来 shall study
will study shall be studying
will be studying shall have studied
will have studied shall have been studying
will have been studying
过去将来 should study
would study should be studying
would be studying should have studied
would have studied should have been studying
would have been studying
但考试中出现的一般有以下几种.
第一节 一般现在时
一、表示一般性或经常发生的动作或状态
1) In general 〔A〕 , newspapers emphasize current news, whereas 〔B〕 magazines dealt 〔C〕 more with 〔D〕 background materials.
2) The adult mosquito usually lives for about 〔A〕 thirty days, although 〔B〕 the life span varied 〔C〕 widely with temperature, humidity, and other 〔D〕 factors of the environment.
3) Industrial buyers 〔A〕 are responsible 〔B〕 for supplying 〔C〕 the goods and services that an organization required 〔D〕 for its operations.
二、表示习惯性动作和状态或普遍的现象或常识
4) It is an accepted 〔A〕 custom in west countries that 〔B〕 men removed 〔C〕 their hats when a woman enters 〔D〕 the room.
5) Certain layers of the atmosphere have special names .
〔A〕which indicated their character properties 〔B〕whose characteristic properties were indicating
〔C〕what characterize their indicated properties 〔D〕that indicate their characteristic properties
三、表示客观事实、客观规律和客观真理.在宾语从句中,即使主句的谓语动词用了过去时,只要从句表示的是客观真理,从句的谓语动词也要用一般现在时
6) The teacher told them since 〔A〕 light travels faster than 〔B〕 sound, lightning appeared 〔C〕 to go before 〔D〕 thunder.
7) As 〔A〕 a child, I was told that 〔B〕 the planet earth, which has 〔C〕 its own satellite, the moon, moved 〔D〕 round the sun.
四、祈使句必须用动词原形,其否定结构用“don`t+动词原形”,如:Go and fetch some water. / Don`t do that.
五、在反义疑问句中,如果主句用肯定句,那么,反问句用否定形式;如果主句用否定形式,那么,反问句就用肯定形式.而且前后在时态上要一致.但祈使疑问句用won`t you?进行反问.如:See a film tonight, won`t you?
[WT6BZ]注:① 祈使句后边可用附加疑问句,以加强语气.如果祈使句用肯定形式,附加疑问句用否定形式;如果祈使句用否定形式,附加句用肯定形式;如: Come here next Sunday, won`t you? / Don`t tell it to anyone, will you? ② 但如果祈使句的前一句有了表示强烈[ZZ(]肯定[ZZ)]的语言环境,即使祈使句用了肯定形式,其附加成分也可以用“will you”(表示肯定,如果是在口语中用降调).如:Give me the book, will you?
六、例题解析
1) C错.“in general”表示“一般”,所以主句用一般现在时,并列从句的谓语也是表示一般性,所以C处也应用一般现在时,故将其改为deal,而不是过去时dealt.
2) C错.本句的主从句中的“usually”表示“经常”,用一般现在时;而让步状语从句的谓语也是表示同一情况,所以也应当用一般现在时.故把C处的 varied改为varies.
3) D错.本句表述的是一般状况,前面的主句用的是现在时,后面的定语从句也应用现在时,应将required改为 requires.
4) C错.这里“it”是形式主语,代表主语从句“that…”,既然主句表示习惯(“an accepted custom”),那么谓语就应当用一般现在时,而不能用过去时.所以将C处的removed改为remove.
5) D为正确答案.本句表述的也是自然现象,主句和从句都应用一般现在时,故A和B都不对;C不合语法,以“what”引导的从句不能作定语,只有D正确,这里“that”引导定语从句,修饰前边的名词“names”.
6) C错.本句宾语从句所表述的是客观事实,即“…light travels faster than sound,”虽然主句谓语动词用的是过去式“told”,从句也要用一般现在时,所以把C处的appeared改为appears.
7) D错.虽然主句的主语用了过去时“was told”,其宾语从句表示的是“地球绕着太阳转”这一客观规律,所以将D处的moved改为moves.注意:不能将C处的has改为had,因为这也是表示客观事实,也得用一般现在时.
第二节 一般过去时
一、一般过去时主要表示过去某一时刻发生的动作或情况,句中通常有表示过去某一时刻的状语 a day ago, last week, in 1996, during the night, in anceint times等,表示“过多少时间之后”用after, 但在现在完成时中用in, 如in the past few years等
1) How many people remember 〔A〕 listening 〔B〕 to Orson Welles` 1938 radio broadcast 〔C〕 , “ The War of the Worlds”, which convince 〔D〕 thousands that space aliens(外星人) had invaded the Earth?
2) The instructor had gone over 〔A〕 the problems many times 〔B〕 before 〔C〕 the students will take 〔D〕 the final examination.
3) Anthropologists agree 〔A〕 that our primitive ancestors 〔B〕 who inhabit 〔C〕 the tropics probably have natural protection against 〔D〕 the Sun.
二、例题解析
1) D错,改用过去时 convinced,因此处表述的是过去(1938年)所发生的情况,而现在则不是这样.“which”引导的从句修饰“…1938 radio breadcast”.
2) D错.由于主句使用的是过去完成时,表示在 过去 的某一动作发生之前,本句中的“before…”从句引导一个表示过去的时间状语.所以状语从句的谓语应用过去时态,应把将来时“will take”改为一般过去时took,以便和主句的过去完成时呼应.
3) C错,改为inhabited,既然是“我们的祖先 居住 的热带地区”,“居住”这一动作发生在过去,所以要用过去时.这里也要提醒大家:做语法题不仅要看特定的提示词如时间状语等,关键还在于读懂句子的意思.如,虽然本句的主语还是同一表示过去的名词主语“primitive ancestors”,其谓语动词就用现在时“have”.“我们的祖先有……”,这里的“有”,是现在我们看来的一种事实,所以用一般现在时.
第三节 一般将来时
一、一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或状况
1) But the weather experts 〔A〕 are now paying more attention to West Antarctic, which may be affected 〔B〕 by only a few degrees of warming: in other words, by a warming on the scale that would 〔C〕 possibly take place in the next fifty years from the burning 〔D〕 of fuels.(92年阅读理解题)
2) If traffic problems are not solved soon 〔A〕 , driving 〔B〕 in 〔C〕 cities becomes 〔D〕 impossible.
二、在表示时间和条件的状语从句中,一般现在时代替一般将来时.这些时间副词有when, as soon as等,表示条件的连词有if,as long as等(参见“第十四章第二节”).
3 ) A desert area that has been 〔A〕 without water 〔B〕 for six years will still 〔C〕 bloom when rain will come 〔D〕 .
4) Come and see me whenever .(84年考题)
〔A〕 you are convenient 〔B〕 you will be convenient
〔C〕 it is convenient to you〔D〕 it will be convenient to you
5) The task is extremely difficult. If no one able to do it, we will have to find somebody else.
〔A〕 were
〔B〕 was
〔C〕 is
〔D〕 would
注意:如果这些副词或连词引导的是名词从句作宾语而不是状语从句时,这些名词从句的谓语动词则用该用的时态:I don`t know when he will come.而且表示将来的助动词will还可以用以条件从句中,译为“愿意、肯”等.
三、一些表示方向及变化的瞬间动词可用进行时或现在时表示将要发生的动作
We leave (are leaving) for California the day after tomorrow.我们(计划)后天动身去加利福尼亚州.
May I have your attention please. The plane for Wuhan is about to take off.请注意,飞往武汉的飞机就要起飞了.
四、另外,“be +to +动词原形”也可表示打算做的事,还可表示责任、意向和可能性
You are to follow the doctor’s advice.你应遵从医嘱.
No shelter was to be seen.找不到避难处.
五、例题解析
1) C错,改为will.本题有表示将来的时间状语“in the next fifty years…”,所以谓语用一般将来时.
2) D错.由于从句中有表示时间的状语“soon”(不久,不远的将来),主句的谓语也是在这一时间发生,所以要用将来时,那么D改为will become.
3) D错.本句主语是A desert area…will still bloom,状语从句是由when引导,表示“雨季到来时”,从句的谓语应用一般现在时表示将来,所以将C处的will come改为comes.
4) 正确答案为C.本题除了时态上的问题(即不用一般将来时)之外还涉及到主语和它的表语的逻辑问题.根据上述语法特点,首先排除B和D;题中“convenient”是“方便的”之意.虽然汉语“在你方便的时候”,似乎“方便”的主语是“你”,但在英语中就不是那么回事儿,“convenient”的英文的解释是“(sth) suited to personal ease or comfort or to easy performance of some act or function”(某事或物对某人来说感到舒适或容易作),其主语应是“物”而不是“人”.本题应选C.所以学英语时,不仅要懂英语单词的汉语译文,更重要的是掌握英语单词的内涵与用法.建议身边备一个“英英”字典,如Longman Dictionary of Comtempory English.
5) C为正确答案.理由同上.
第四节 现在完成时
一、现在完成时的构成式是have(has)+动词的?ED分词
1) Research 〔A〕 in molecular(分子的) biology has demonstrate 〔B〕 phenomenal similarities 〔C〕 between 〔D〕 humans and apes(类人猿).
2) Gore Vidal has steadily pursue 〔A〕 a literary career 〔B〕 remarkable 〔C〕 for its productivity, versatility(多样性) and unpredictability 〔D〕 (多变性).
3) For centuries large communities of people have living 〔A〕 on houseboats in parts 〔B〕 of the world where 〔C〕 the climate is warm and the waters are calm 〔D〕 .
二、现在完成时表示到现在为止的一段时间内发生的情况或动作,强调的是对现在的影响,可能是已完成的动作,也可表示多次动作的总和,或习惯性的行为和持续的动作
4) Ninety?eight percent of all animal species 〔A〕 in 〔B〕 history had 〔C〕 died out 〔D〕 .
5) The domestic 〔A〕 dog, considered to be the first tamed animal, is coexisting 〔B〕 with human beings since 〔C〕 the days of the cave dwellers 〔D〕 (居住者).
三、如果句中有表示到现在为止这段时间的状语时,用现在完成时,这些时间状语有 now, today, this week, this month, this year,现在完成时不和表示具体的时间状语连用,如yesterday, last year等,但可以和always, before, just, in/during the past(few weeks, years, fifty years)连用,这时in表示“过去多少时间”,不能用after
6) Industrial 〔A〕 management is the aspect 〔B〕 of business 〔C〕 management that was 〔D〕 most prominent in the United States in the past eight years.
7) Learning a foreign language is especially 〔A〕 difficult for those 〔B〕 who had 〔C〕 never learned one before 〔D〕 .
四、在有already, as yet, yet, ever, just, never 这类副词作状语的情况下,用现在完成时
8) In just 〔A〕 the last 〔B〕 few years, football is become 〔C〕 more popular than baseball in that country 〔D〕 .
9) Coupled with the growing quantity of information is the development of technologies which enable the storage and delivery of more information with greater speed to more locations than has been possible before.
〔A〕 ever
〔B〕 everest
〔C〕 more
〔D〕 most
10) President Andrew Jackson was a controversial 〔A〕 figure in his own 〔B〕 day and is one 〔C〕 ever since 〔D〕 .
五、有“since+时间点,for+一段时间”引导的状语时,主句谓语用现在完成时态
11) Jekyll Island has been one 〔A〕 of Georgia’s state 〔B〕 parks 〔C〕 in 〔D〕 1954.
12) He is 〔A〕 in this country now 〔B〕 for five years, but he makes 〔C〕 no attempt to speak 〔D〕 our language.
13) The Browns 〔A〕 are living a hard 〔B〕 life because Mr. Brown has been unemployed 〔C〕 since 〔D〕 half a year.
六、现在完成时用于将来的情况,即主语为一般将来时,时间和条件从句中的谓语用现在完成时(而不能用将来完成时)表示将来某时完成的动作
14) Smith is to study medicine as soon as he military service.
〔A〕 will finish
〔B〕 has finished
〔C〕 finish
〔D〕 would finish
15) Once you that brand of whisky, you will never want to drink any other.
〔A〕 drunk
〔B〕 have drunk
〔C〕 will drink
〔D〕 drank
七、例题解析
1) B错,改为has demonstrated.
2) A错,改为pursued.
3) A错,改为have lived.
4) C错.本句的汉语意思是“历史上90%的动物种类已经灭绝”,表示到现在为止“已经”发生的事,而且还在延继下去.所以时态应该用现在完成时.表示在过去的某一时间之前已经完成的动作才用过去完成时,所以本题应把C处的had改为have.
5) B错.应改为现在完成时has coexisted,因为本句表示到现在为止这段时间内发生的情况(持续性的),最关键的是抓住句中的状语“since…dwellers”(自从…到现在).
6) D错,改为has been.
7) C错,改为have.
8) C错,改为has become.
9) A为正确答案.
10) C错.since在本句中是副词,意思是“从那时到现在”, ever亦为副词修饰 since,起强调作用,因此本句应用现在完成时,将“is one”改为“ has been one”.
11) D错.in 1954表示的是确定的某个时刻(过去),但由于句中的谓语动词所使用的是现在完成时,所以应将介词in改为 “since”.“ since 1954”表示“从1954年以来”,本句的谓语动词用现在完成时.
12) A错,改为has been.
13) D错,改为for.
14) 正确答案是B.主句用的是将来时“…be about to”,时间状语从句由as soon as引导,四个选项中,用现在完成时表示将来要完成的动作最合适.所以B为正确答案.
15) 正确答案是B.由于主句用的是一般将来时,“Once…”引导的时间状语从句中应该用现在完成时,所以B为正确答案.
第五节 将来完成时和过去完成时
一、将来完成时表示将来某时业已发生的动作和情况,或已经存在的状态
1) By the end of this month, the generating set for a whole year.
〔A〕 will run
〔B〕 has run
〔C〕 runs
〔D〕 will have run
二、过去完成时表示在过去某一时刻之前业已发生了的动作或现象,句中通常会出现有表示过去某一时刻的时间状语
2) Although she law for only a little over eight years, Florence Allen became in 1922 the first woman to sit on a state supreme court.
〔A〕 will practice 〔B〕 practices 〔C〕 had practiced 〔D〕 has been practicing
3) Before 1970 many 〔A〕 technological advances have been made 〔B〕 in the field of computer science, which 〔C〕 resulted in more efficient 〔D〕 computers.
三、例题解析
1) 正确答案 是D.“By the end of this month”表示将来的某一时间,到那时业已完成的动作应用将来完成时,所以选D为正确答案.
2) C为正确答案.本句的主句有表示过去某刻的时间状语in 1922,用的是过去时,而空白处应填入在1922年前已发生的动作(从事律师业8年多),故应使用过去完成时.
3) B错,改为had been made,因为本句明显表示过去某刻之前( before 1970)业已发生的情况.
第六节 进 行 时 态
一、现在进行时表示现在或现阶段进行的动作,但也和always, constantly, forever等频度副词连用表示一个经常进行的动作或现在存在的状态
1) Because of 〔A〕 the effects of tidal friction(摩擦力), the earth’s rotation, which forms 〔B〕 the basis for time units, is 〔C〕 gradually slow down 〔D〕 .
2) All things 〔A〕 consist of 〔B〕 atoms or molecules,which be 〔C〕 constantly moving 〔D〕 .
二、瞬间动词和一些表示状态及感觉的动词一般不用进行时,而用一般现在时或一般过去时代替.这些动词包括:appear(显然), arrive, be, come, desire, go, find, hate, hope, join, know, leave, like, love, join, possess, start, sail, see, suggest, taste, think(认为), understand等,类似的动词还有belong to, consist of,seem(似乎)等
3) He was seeing 〔A〕 somebody creeping 〔B〕 into the house through 〔C〕 the open 〔D〕 window last night.
4) Among 〔A〕 the most important 〔B〕 jazz innovators 〔C〕 in the twentieth century are being 〔D〕 Louis Armstrong, Fletcher Henderson, Duke Ellington, and Dizzy Gillespie.
三、过去完成进行时
过去完成进行时表示到过去的某一时间点或某一时间段里一直在进行的动作或行为
5) They received the parcel that they for a long time.
〔A〕 expected 〔B〕 have expected 〔C〕 had been expecting 〔D〕 had expected
There is a well?known incident in one of Moliere′s plays, where the author makes the hero express unbounded delight on being told that he had been talking prose during the whole of his life.(93年翻译)
四、例题解析
1) D错.slow只有作为不及物动词用时才与up或down连用,表示“慢慢向上”或“慢慢向下”.所以我们说,这里的slow是动词而不是形容词,应将动词slow后边加上“ing”,改为(is) slowing down,构成现在进行时.
2) C错,改为are.
3) A错,改为saw.
4) D错,改为are.
5) C为正确答案.
英语的时态和语法有什么区别
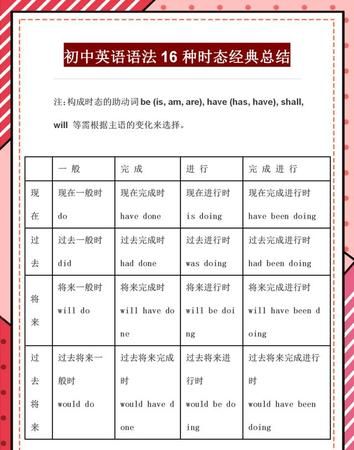
一、一般将来时:
概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
时间状语:tomorrow,next day(week,month,year…),soon,in a few minutes,by…,the day after tomorrow,etc.
基本结构:主语+am/is/are+going to + do;will/shall + do.
二、一般现在时:
概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为某种状况。
时间状语:always,usually,often,sometimes,every week (day,year,month…),once a week,on Sundays,
基本结构:动词 原形 (如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式)
三、一般过去时
概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
基本结构:be动词;行为动词的过去式
四、现在进行时
概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
时间状语:now,at this time,days,etc. look . listen
五、过去进行时
概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
时间状语:at this time yesterday,at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
基本结构 s+was/were+doing
六、现在完成时
完成时的这种用法通常与由since或for引导的时间状语连用。如:
The old man has lived here for more than twenty years。
扩展资料:
英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
一般过去时与现在完成时的转换
在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能。
但是,可用别的表达方式:
瞬间动词用于“一段时间
+ ago”的一般过去时的句型中;
瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用;
瞬间动词用于“It is + 一段时间 +
since + 一般过去时”的句型,请看:
一般现在时与现在进行时的转换
在一般现在时中,at加上名词表示“处于某种状态”,如at work(在工作),at school(上学、上课)等。此短语可与进行时态转换。
现在进行时与一般将来时的转换
在现在进行时态中go,come,leave,start,arrive等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作。
be going to+动词原形”与“will(shall)+动词原形”结构的转换
be going to+动词原形”、表示打算、计划要做的事;将来时“will(shall)+动词原形”结构在书面语中,当主语为第一人称时,常用助动词shall。
在口语中,所有人称都可以用will。
参考资料来源:百度百科——时态
以上就是关于英语时态的逻辑 ,英语语法时态讲解视频的全部内容,以及英语时态的逻辑 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
