本文目录
高中英语基础差该从哪里开始入门
高中英语基础语法入门
英语口语的锻炼是一个循序渐进的过程,现实学习中可以借助英语口语入门培训、一对一电话英语等各种资源平台, 将自己的英语口语得到完善。以下是我整理的关于高中英语基础语法入门,希望大家认真阅读!

专题一:英语句子的考点集汇,讲解和训练
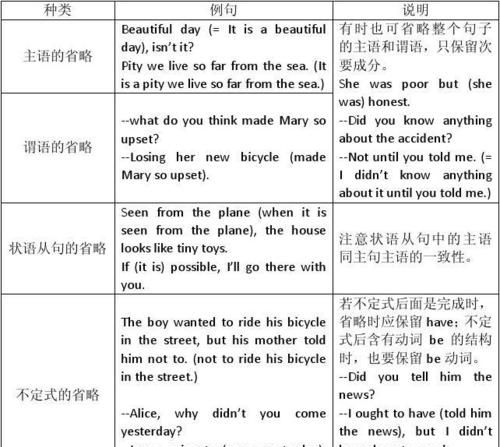
一.陈述句的构成形式及基本用法
1.陈述句:
陈述句是用来陈述一个事实或表达说话人看法(包括肯定和否定)的句子。通常用降调,句末用句号“.”。
Tomhasanewcar.
Theflowerisn’tbeautiful.
二.祈使句的构成形式及基本用法
祈使句是用来表示命令、请求、建议、号召等的句子,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号“!”或句号“.”。朗读时一般用降调。
1.肯定的祈使句:
(1)祈使句主语是you时,you常省略,但如果要特别强调对方或表达某种强烈的情绪时可以有主语或称呼语。
Bequiet.
Youbequiet!
(2)“Do+祈使句”表示一种强烈的感情或请求,do起强调作用。
Docomebackatonce!
Dobecareful.
2.否定祈使句通常以Don’t或Never开头。其结构通常是:“Don’t(Never)+动词原形+其他成分”例如:
Don’tdothatagain!
Neverleavetoday’sworkfortomorrow!
Don’tbelatenexttime!
三.一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句、反意疑问句的构成形式及基本用法
1.一般疑问句:
(1)一般疑问句的肯定形式
一般疑问句一般是指以助动词、情态动词、be动词或have(有)开始,通常要求以yes,或no来回答的疑问句,一般疑问句读时通常用升调。
DoyouknowMr.Smith?
Canyouswim?
2.特殊疑问句
特殊疑问句由“疑问代词或疑问副词+一般疑问句”构成,句子一般用倒装语序,但如果主语是疑问代词或由疑问代词修饰时,用陈述句的语序。特殊疑问句不能用yes或no回答,读时用降调。例如:
Whoisondutytoday?
HowlonghaveyoubeeninBeijing?
Whattimedoyougetupeverymorning?
WhatmustIdonow?
3.选择疑问句:
选择疑问句是说话者提出两种或两种以上的不同情况,让对方选择回答的疑问句。其结构是“疑问句+选择部分”。选择部分由or连接,or前面的部分读升调,or后面的部分读降调。
选择疑问句不能用yes或no回答,而必须具体的选择答复。
Isyourbagyelloworblack? It’sblack.
Wouldyoulikesometeaorcoffee? Eitherwilldo.
Whichdoyoulikebetter,singingordancing? Ilikedancingbetter.
4.反意疑问句:
反意疑问句是指在陈述句之后附加一个意思与之相反的简短问句,问对方是否赞同的疑问句。附加问句的.否定式必须缩写。
(1)肯定的陈述句后跟否定的附加问句,否定的陈述句后跟肯定的附加问句。
Iamyourteacher,aren’tI?
Hedidn’tstudyhard,didhe?
(2)如果陈述句中含有否定副词never(从不,决不),hardly(几乎不)或其他表示否定代词或形容词,如nothing,nonenoone,nobody,neither,few,little等,则附加问句只能用肯定式。如:
Theyhardlywritetoeachother,dothey?
Hehasfoundnothing,hashe?
Fewpeopleknewthesecret,didthey?
---Youwon’tbeawayforlong,willyou?你不会离开太久,是吗?
---Yes,Iwill.不,我会离开很久。
---No,Iwon’t.是的,我不会离开很久。
-
四.由what,how引导的感叹句的构成形式、用法及区别
感叹句是表示喜、怒、哀、乐以及惊异等感情的句子。句末用感叹号“!”,读时用降调,感叹句往往由what或how引导,what修饰名词,how修饰形容词,副词或动词。
1.what引导的感叹句:
(1)what+a/an+形容词+单数可数名词+陈述句(主语+谓语)
Whatabeautifulcityitis!
Whataninterestingstoryshetold!
(2)what+形容词+复数可数名词/不可数名词+陈述句(主语+谓语)
Whatexpensivewatchestheyare!
Whatterribleweatheritis!
2.How引导的感叹句:
(1)How+形容词/副词+陈述句(主语+谓语)
Howcolditis!
Howhardheworks!
(2)How+陈述句(主语+谓语)
Howheloveshisson!
HowImissyou!
(3)How+形容词+a/an+单数可数名词+陈述句(主语+谓语)
Howtallatreeitis!
(4)上述两种感叹句可以互相转换。例如:
Whatacleverboyheis!→Howclevertheboyis!
Whatacolddayitis!→Howcolditis!
简单句
简单句根据语法形式,即句子的结构,英语的句子可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
简单句的基本形式是由一个主语加一个谓语构成。其它各种句子形式都是由此句型发展而来,如五大基本句型:
1.基本句型一:SV主+谓)
主语+谓语,这种句型简称为主谓结构,其谓语一般都是不及物动词,例:
Thingschange.事物是变化的。
Nobodywent.没有人去。
--Didyougobysea?你们走的是海路吗?
--NO,weflew.不,我们是飞去。
2.基本句型二:SVP(主+系+表)
这种句型称为主系表结构,其实连系动词在形式上也是一种谓语动词,但实质上表语成了谓语,例:
Mr.Turnerisanartist.特纳先生是位画家。
Themilkturnedsour.牛奶变酸了。
Shebecamealawyer.她当了律师。
常见的系动词有be(am,are,is),turn,go,become,grow,turn,fall,get,go,come,run,keep,rest,remain,stay,lie,stand,feel,smell,sound,taste等.
3.基本句型三:SVO(主+谓+宾)
这种句型可称为主谓宾结构,它的谓语一般多是及物动词,例:
Weneverbeatchildren.我们从来不打孩子。
Mysisterwillfixeverything.我姐姐会料理一切。
4.基本句型四:SVoO(主+谓+间宾+直宾)
这种句型可称为主谓双宾结构,其谓语应是可有双宾语的及物动词,两个宾语一个是间接宾语,一个是直接宾语,例:
Hegavethebooktohissister.他把这本书给了他的妹妹。
I'llwriteyoualongletter.我将写给你一封长信。
5.基本句型五:SVOC(主+谓+宾+宾补)
这种句型可简称为主谓宾补结构,其补语是宾语补语,与宾语一起即构成复合宾语,例:
Ifoundthebookeasy.我发现这本书不难。
Hefoundhisnewjobboring.
Thisplacedhiminaverydifficultposition.
I'lllethimgo.我将让他去。(不定式go用作补语)
Didyounoticehimcomein?
注意:有时两个或更多的并列主语拥有一个共同的谓语,甚至并列有两个主语和两个谓语,这样的句子仍然是简单句,例:
ChinaandothercountriesintheeastAsiaaredevelopingrapidly.中国和东亚其它国家正在迅速地发展。(Chinaandothercountries并列主语)
Mr.WangandIoftenworktogetherandhelpeachother.王先生和我常在一起工作互相帮助。
专题二:宾语从句考点集汇,讲解和训练
一.宾语从句的种类
宾语从句是一种名词性从句,在句中作宾语,根据引导宾语从句的不同连词,宾语从句可分为三类。
1.由that引导的宾语从句。That只有语法作用,没有实在的意义,在口语
和非正式文体中可以省略。例如:
Hesaid(that)hewantedtostayathome.
Shedoesn’tknow(that)sheisseriouslyill.
Iamsure(that)hewillsucceed.
2.由连接代词who,whom,whose,what,which和连接副词when,where,why,how引导的宾语从句。这些连接代词和连接副词在宾语从句中充当某个成分。例如:
Doyouknowwho(whom)theyarewaitingfor?
Heaskedwhosehandwritingwasthebest.
CanyoutellmewheretheNo.3busstopis?
Idon’tknowwhythetrainislate.
3.由if或whether引导的宾语从句。If和whether在句中的意思是“是否”。例如:
Iwanttoknowif(whether)helivesthere.
Heaskedmewhether(if)Icouldhelphim.
二.宾语从句的语序
宾语从句的语序应为陈述句的语序。例如:
Ihear(that)physicsisn’teasy.
Ithink(that)youwilllikethisschoolsoon.
CanyoutellmehowIcangettozoo?
Pleasetellmewhenwe’llhavethemeeting.
三.宾语从句的时态
1.如果主句的时态是一般现在时,宾语从句该用什麽时态就用什麽时态。例如:
Idon’tthink(that)youareright.
Pleasetelluswhereheis.
CanyoutellmehowIcangettotherailwaystation?
2.如果主句的时态是一般过去时,宾语从句只能用相应的过去时态(一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时,过去完成时)。例如:
Heaskedwhattimeitwas.
Hetoldmethathewaspreparingforthesportsmeet.
HeaskedifyouhadwrittentoPeter.
HesaidthathewouldgobacktotheU.S.soon.
3.如果宾语从句所陈述的是客观真理,其时态常用一般现在时。例如:
OurteachersaidthatJanuaryisthefirstmonthoftheyear.
Scientistshaveprovedthattheearthturnsaroundthesun.
专题三:状语从句的考点集汇,讲解和训练
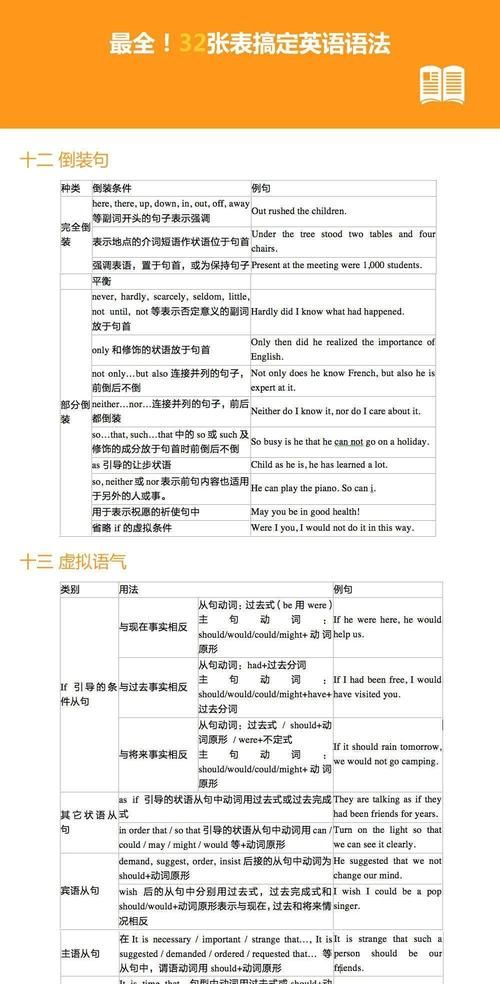
用来修饰主句中的动词,副词和形容词的从句叫状语从句。根据其含义状语从句可分为时间状语从句,地点状语从句,条件状语从句,原因状语从句,结果状语从句,比较状语从句,目的状语从句,让步状语从句。
1.时间状语从句
(1)时间状语从句常用when,as,while,before,after,since,till,until,assoonas等连词来引导。例如:
ItwasraininghardwhenIgottoschoolyesterday.
Whilehewasdoinghishomework,thetelephonerang.
Ashewalkedalongthelake,hesanghappily.
HehadlearnedalittleChinesebeforehecametoChina.
Afterhefinishedmiddleschool,hewenttoworkinafactory.
(2)在时间状语从句里,通常不用将来时态,用现在时态表示将来的动作或状态。例如:
I’llringyouupassoonasIgettoNewYork.
Iwilltellhimeverythingwhenhecomesback.
Hewon’tbelieveituntilheseesitwithhisowneyes.
2.条件状语从句
(1)条件状语从句通常由if,unless引导。例如:
Whatshallwedoifitsnowstomorrow?
Don’tleavethebuildingunlessItellyouto.
(2)在条件状语从句里,谓语动词通常用现在时态表示将来的动作或状态。例如:
I’llhelpyouwithyourEnglishifIamfreetomorrow.
Hewon’tbelateunlessheisill.
(3)“祈使句+and(or)+陈述句”在意思上相当于一个带有条件状语从句的复合句。例如:
Hurryup,oryou’llbelate.
=Ifyoudon’thurryup,you’llbelate.
Studyhardandyouwillpasstheexam.
=Ifyoustudyhard,youwillpasstheexam.
3.原因状语从句
原因状语从句通常由because,since,as引导。例如:
Hedidn’tcometoschoolbecausehewasill.
Asitisraining,weshallnotgothezoo.
Sinceyoucan’tanswerthequestion,I’llasksomeoneelse.
4.结果状语从句
(1)结果状语从句由so…that,such…that,sothat引导。例如:
Heissopoorthathecan’tbuyabikeforhisson.
Sheissuchagoodteacherthateverybodylikesher.
Mypencilfellunderthedesk,sothatIcouldn’tseeit.
(2)so…that语such...that可以互换。例如:
在由so...that引导的结果状语从句中,so是副词,与形容词连用。其结构是:“...so+形容词(副词)+that+从句”。例如:
Hewassogladthathecouldn’tsayaword.
Thehallissobigthatitcanhold2,000people.
Motherlivessofarawaythatwehardlyeverseeher.
有时上述两种结构是可以互换的。例如:
Itwassuchawonderfulfilmthatallofuswantedtoseeitagain.
=Thefilmwassowonderfulthatallofuswantedtoseeitagain.
Itissuchanimportantmatchthatnobodywantstomissit.
=Thematchissoimportantthatnobodywantstomissit.
5.比较状语从句
比较状语从句通常由as…as,比较级+than…等连词引导。例如:
TomrunsfasterthanJohndoes.
Thisclassroomisasbigasthatone.
6.目的状语从句
(1)目的状语从句通常由sothat,inorderthat引导。例如:
Westartedearlysothatwecouldcatchthefirsttrain.
Hestudieshardsothathecouldworkbetterinthefuture.
Weusedthecomputerinorderthatwemightsavetime.
(2)sothat既可引导目的状语从句,又可引导结果状语从句。区别这两种从句的办法有两个:1)目的状语从句里往往带有情态动词can,could,may,might等。2)从意思上看,目的状语从句往往表示的目的很明确。例如:
Speakclearlysothattheymayunderstandyou.(目的状语从句)
Jackisbadlyillsothathehastorest.(结果状语从句)
7.让步状语从句
(1)让步状语从句通常由although,though等连词引导。例如:
Thoughheisyoung,heknowsalot.
AlthoughIamtired,Imustgoonworking.
(2)although(though)不能用在同一个句子中。例如:
我们不能说:Thoughitwasraininghard,buthestillwentout.
应该说:Thoughitwasraininghard,hestillwentout.或Itwasraininghard,buthestillwentout.
8.地点状语从句
地点状语从句常常由where来引导。例如:
Gowhereyoulike.
Wherethereisawill,thereisaway.
专题四:定语从句的考点集汇,讲解和训练
一.定语从句的功用和结构
在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫做定语从句。被定语从句修饰的词叫做先行词。定语从句必须放在先行词之后。引导定语从句的关联词有关系代词和关系副词。例如:
Thisisthepresentthathegavemeformybirthday.
Doyouknoweverybodywhocametotheparty?
IstillrememberthenightwhenIfirstcametothevillage?
ThisistheplacewhereChairmanMaooncelived.
二.关系代词和关系副词的功用
关系代词和关系副词用来引导定于从句,在先行词和定语从句之间起纽带作用,使二者联系起来。关系代词和关系副词又在定语从句中充当一个成分。关系待客做主语,宾语,定语,关系副词可作状语。
1.作主语:关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词的人称和数须和先行词一致。例如:
Idon’tlikepeoplewhotalkmuchbutdolittle.
ThecarswhichareproducedinHubeiProvincesellverywell.
2.作宾语:
SheisthepersonthatImetattheschoolgateyesterday.
Thebookthatmygrandmothergavemeiscalled“TheGreatEscape”.
3.作定语
关系代词whose在定语从句中作定语用。例如:
What’sthenameoftheyoungmanwhosesisterisadoctor?
Thegirlwhosefatherisateacherstudiesveryhard.
4.作状语
I’llneverforgetthedaywhenIfirstcametoBeijing.
ThisisthehousewhereIwasborn.
三.各个关系代词和关系副词的具体用法
1.who指人,在定语从句中作主语。例如:
Thepersonwhobrokethewindowmustpayforit.
Theboywhoiswearingtheblackjacketisveryclever.
2.whom指人,在定语从句中作宾语。例如:
Doyouknowtheyoungman(whom)wemetatthegate?
MrLee(whom)youwanttoseehascome.
3.whose指人,在定语从句中作定语。例如:
Thegirlwhosemotherisillisstayingathometoday.
Iknowtheboywhosefatherisaprofessor.
4.which指物,在定语从中作主语或宾语。例如:
Adictionaryisabookwhichgivesthemeaningofwords.
Hereisthebook(which)theteachermentionedyesterday.
5.that多指物,有时也指人,在定语从句中作主语或宾语。例如:
I’vereadthenewspaperthat(which)carriestheimportantnews.
Whoisthepersonthatisreadingthenewspaperoverthere?
6.when指时间,在定语从句中作状语。例如:
I’llneverforgetthetimewhenweworkedonthefarm.
HearrivedinBeijingonthedaywhenIleft.
7.where指地点,在定语从句中作状语。例如:
Thisisthehousewherewelivedlastyear.
Thefactorywherehisfatherworksisintheeastofthecity.
四.关系代词whom,which在定语从句中作介词宾语时,可以和介词一起放于先行词与定语从句之间,有时为了关系紧凑也可以将whom与which与先行词紧挨着书写,而将介词置于定语从句的后面,如:Thatwastheroominwhichwehadlivedfortenyears.=Thatwastheroom
whichwehadlivedinfortenyears.
五.具体使用时还要注意下列问题:
1.只能使用that,不用which的情况:
(1)先行词是all,few,little,nothing,everything,anything等不定代词时。
例如:
Allthathesaidistrue.
(2)先行词被only,no,any,all,等词修饰时。例如:
Heistheonlyforeignerthathasbeentothatplace.
(3)先行词是序数词或被序数词修饰的词。例如:
Hewasthesecond(person)thattoldmethesecret.
(4)先行词是形容词最高级或被形容词最高级修饰的词。
Thisisthebestbook(that)Ihavereadthisyear.
(5)先行词既包括人又包括物时。例如:
Hetalkedaboutthepeopleandthethingsheremembered.
2.只能用which,不用that的情况:
(1)在非限制性定语从中。例如:
Themeetingwasputoff,whichwasexactlywhatwewanted.
(2)定语从句由介词+关系代词引导,先行词是物时。例如:
Thethingaboutwhichheistalkingisofgreatimportance.
;高中英语五种基本句型详解
英语的语法是写好作文,练好口语的基石,我们能说好中文是因为我们习惯了中文的语序,但是英语缺截然不同。只有搞清句子成分,明白主谓关系才能将口语说得灵活且自然。
下面就跟着小编一起来看看英语学习中最常用的5种句型吧!

句子的组成成分叫句子成分。在句子中,词与词之间有一定的组合关系,按照不同的关系,可以把句子分为不同的组成成分。句子成分由词或词组充当。
现代汉语里一般的句子成分有六种,即主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语和补语。英语的基本成分有六种:主语(subject)、谓语(predicate)、表语(predicative)、宾语(object)、定语(attribute)和状语(adverbial)。
英语五种基本句型:
基本句型 一
此句型的句子有一个共同特点,即句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等。
S+V (不及物动词) 主+谓
1. The sun │was shining.
2. The moon │rose.
3. We all │breathe, eat, and drink.
4. Lucy and Mary │get up early every morning.
5. What he said │does not matter.

基本句型 二
此句型的句子有一个共同的特点:句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做连系动词。系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类,表示情况;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化。be 本身没有什么意义,只起连系主语和表语的作用。其它系动词仍保持其部分词义。
S
高中英语五种基本句型详解
英语五种基本句型结构
上了高中,英语成绩直线下降?觉得知识学得很散?面对高考这场硬仗,还不知道从哪头抓起?如果你中了其中一条,建议读完本文,先来恶补一下英语五种基本句型结构吧!
英语里,通过词/短语地“有机”组合,形成了句子,大家知道的“主谓宾表定状补”这七个句子成分能够神奇的创造出五种基本句型结构及其扩大、组合、省略或倒装。掌握这五种基本句型,是掌握各种英语句子结构的基础。小编将逐一土话道出。
Number1:“主系表”结构
The dinner smells good.这顿饭闻起来很香!
这是典型的“主系表”结构。
首先,谓语“smell”(闻)表达的意思不是相对完整,需要在其后添个“good”(好),来将意思表达的更清晰、完整,其实这个“good”是系动词;这个“good”是表语,且是这个句子的“复合谓语”。
知识拓展一:复合谓语,通常根据谓语在句子中的复杂程度,分为简单谓语和复合谓语。复合谓语的两种情况:第一种情态动词、助动词+不带to的动词不定式构成的复合谓语。例如:What does this word mean?I won’t do it again.I’ll go and move away the bag of rice with Lin Tao.You’d better catch a bus.第二种就是本篇文章中第一个句子结构——“主系表”结构中包含的“复合谓语”,即,由系动词+表语构成。
知识拓展二:常考系动词有这些,背下来,通常所在的简单句,都是“主系表”结构:
be(是)
become(成为)
get(变成)
remain(还是)
seem(似乎是)
look(看上去)
feel(感觉)
appear(出现、显现)
sound(听起来)
feel(摸起来)
taste(尝起来)
smell(闻起来)
grow(渐渐变得)
turn(变成)
Number2:主谓结构(“谓语”是不及物动词)
例:The man cooks.男人做饭。这类句子结构的共同点:谓语动词能够表达完整的意思,不需要再添加额外的宾语。这类动词被称为不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等等。
知识拓展一:“不及物动词”
不及物动词,本身意义是完整的,其后不必接宾语。
如果需要在不及物动词后面添加宾语,必须先在其后添加上某个介词,如“to、of、at”,再在其后添加宾语。但是!这个不及物动词后面添加哪个介词,需要大家提前储备些动词短语了。最常见的不及物动词有这些:
work
sing
swim
fish
jump
arrive
come
die
disappear
cry
happen
知识拓展二:如何巧妙判断这个动词是不是“不及物动词”
词典里词后标有vi(全称 intransitive verb)的就是不及物动词;词典里词后标有vt(全称 transitive verb)的就是及物动词。
知识拓展三:不及物动词,没有被动语态
Number3:主谓宾结构(谓语是“及物动词”)
He likes watching TV. 他喜欢看电视。
这类句子结构的共同点:谓语动词有实际的意义,是主语发出的动作,但是并不能表达出完整的意思,后面必须接一个宾语,也就是主语发出动作的承受者,才能让整个句子的语义表达清楚、完整。(这个谓语,就是咱说的“及物动词”。)
Number4:主谓宾宾(谓语是“及物动词”、第一个宾语是“间接宾语”、第二个宾语是“直接宾语”)
She brought you a picture.她给你带来了一张照片。这类句子结构的共同点:谓语动词后面一定要配备两个宾语才能将句意表达的相对完整。
知识拓展一:这个动词谓之“双宾语动词”表达出相对完整的意思,并且这个谓语动词后的第一个宾语“you”是动作的直接承受者;第二个宾语“a picture”是动作的间接承受者,一般指人的宾语是间接宾语,指物的宾语是直接宾语。
Number5:主谓宾宾补(谓语是“及物动词”)
They called her Iris.他们叫他Iris。这类句子结构的共同点:谓语动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语“her”还不能将意思表达的完整,必须在句子后面加上一个补充成分“Iris”来补足宾语,才能让别人明白你在说啥。
知识拓展一:宾语补足语的作用是说明宾语的动作或者状态,宾语和它的补足语共同构成复合宾语。宾语补足语可以由名词、动词不定式、形容词、副词和介词短语充当。
知识拓展二:英语里的“使役动词”,就是表示“使、令、让、帮、叫”等意义的词,常考的有这些
有leave(离开)
get(得到)
keep(保持)
make(使,令)
let(让)
help(帮助)
have(有;让;从事;允许;拿)
知识拓展三:在使役动词make、let、have等引起的复合宾语中,若宾语补足语是动词不定式,则需要省去不定式的符号to。

高一英语语法大全汇总
高一英语语法是学习整个高中英语语法的开始,也关系到整个高中英语语法的基础好坏,那么高一英语语法有哪些内容呢?下面由我为大家整理的高一英语语法大全,希望对大家有所帮助!
高一英语语法大全
虚拟语气在各种从句的应用
主语从句的虚拟
1. It is + adj. + that sb. (should) do
常见的形容词有:necessary, important, strange, natural
It's important that he take my advice.
2. It is + n. + that sb. (should) do
常见的名词有:a pity, a shame, no wonder, one's wish
It's a pity that he be so silly.
3. It is + done + that sb. (should) do
常见的过去分词有:suggested, advised, demanded, requested, required, asked, ordered,
proposed, decided, desired, insisted等。
It's requested that she go home as soon as possible.
宾语从句的虚拟
1. 表命令,表建议,表要求的动词,后接宾语从句虚拟。虚拟的构成为(should) do。
I advise that he stay at home.
2. wish后接从句,虚拟的构成是往过去推一个时态。
I wish I had watched the football match last night.
注意以下几组词或短语用于虚拟语气中。
1. as if, as though
He speaks English as if he were a native speaker.
2. otherwise, but, even though
He was ill. Otherwise he would have been there.
3. with, without, but for
Without your help, I would have died two years ago.
But for your help, I would have died two years ago.
4. would rather I'd rather you told me yourself.
5. It's time that
It's time that you went to bed.
It's time that you should go to bed.
表语从句中的虚拟
在表语从句中,表示间接的命令,要求、请求、建议、决定等,主句中的主语通常是suggestion, proposal, request, orders, idea等。从句谓语形式是"(should)+动词原形"。如:
His suggestion is that we (should) leave at once.
名词从句部分
1. that不可省略的情况
2. that引导同位语从句和that引导定语从句的区别:同位语从句中的that是连词,不做成分,只连接主从句,不能省略;定语从句中的that要代替先行词在从句中做主语、宾语或者表语,并且做宾语时可以省略。从语义上看,同位语从句是对前面名词的解释、说明或内容;而定语从句时对前面名词的限定。
We should consider the students’request that the school library provide more books on
popular science. (that引导同位语从句)
The only hope that he expressed was that they would do what they could to help the people
in disaster areas. (that引导定语从句)
3. 要根据句子结构尤其是谓语动词判断从句的类型:
What is known to us all is that the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.
本句含有一个主语从句和一个表语从句,主句的动词为is。
It is known to us all that the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.
本句含有一个主语从句,主句的动词为is known to。
As is known to us all, the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.
本句含有一个定语从句,主句的动词为took place,as引导非限制性定语从句。
4. 名词性从句的语序和语态。
名词性从句均应用陈述语序,不能用疑问语序,其时态应该和主句时态保持一致。
5. 名词性从句中连词的省略。
介词后的连词以及引导主语从句和同位语从句的连词不可省略。that引导名词从句(除了引导第一个宾语从句可省略外)都不可省略,但是引导定语从句并在从句中做宾语时可以省略。
that不能省略的情况:
1)介词后面的that不能省略:
Peter is a good student except that he is sometimes careless.
2)当that引导的宾语从句位于句首时:
That he ever did such a thing I don’t believe.
3)主句谓语动词和that从句之间有插入语,that不省略:
She said that, if she failed, she would try again.
4)当宾语从句有其他从属连词时,that不省略:
He told me that if it was necessary they would work extra time.
6.名词性从句中it的使用:
为了保持句子平衡,多数情况下,it作形式主语或形式宾语,将真正的主语或宾语从句后置。
定语从句
关系代词有who, whom, whose, which, that, as,和关系副词when, where, why。
(1)that指物时一般可与which互换,但在下列情况下,要用that而不用which。
a. 先行词有all, everything等不定代词时,如,
Everything (that) he did is wrong.
b. 先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much等修饰时,如,
I'll read all the books (that) you lend me.
c. 先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时,
This is the first letter (that) the boy has written.
d. 先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时,如
He is the very man (that) I'm looking for.
e. 只用which的情况
在介词后或在非限定性定语从句中
This is the book about which we have talked a lot.
The book, which he gave me yesterday, is very interesting.
f. where和when作关系副词
This is the room where I worked.
This is the room which I stayed in.
I remembered the day when we lived there.
I remembered the day that I spent there.
g. as和which
as 可以放于句首,而which 不可以
As you know, he is good at English.
three of them 和three of which
I have a lot of books, three of which are in Russian.
I have a lot of books and three of them are in Russian.
(2. )“介词+关系代词”的情况:
在固定短语中介词不能提前;判断介词的口诀:瞻前顾后看意义
瞻前——看先行词;顾后——找从句动词;看意义——看全句表达含义
(3. )先行词在从句中充当地点状语时,关系词用where 或者介词加which;先行词在从句中充当时间状语时,关系词用when或者介词加which;先行词在从句中充当原因状语时,关系词用why或者for which。
(4. )注意as和which在非限制性定语从句中代表主句所表达的内容的区别:
位置不同:as从句放在主句前或后均可;而which从句只能放在主句后
作用不同:as从句动词常常是see know等,因而相当于插入语;which从句则在陈述一件事实。
状语从句部分
1.while 是高考中的高频词,它既可引导时间状语从句,又可引导并列句,还可引导让步状语从句,表示“尽管”。
2. no matter wh- 与wh-ever 的联系及区别:no matter wh- 只引导让步状语从句,此时与wh-ever通用。wh-ever又可引导名词性从句,No matter wh-不能。
No matter when / Whenever he comes back, he should be invited to the party.
3. 在条件,时间和让步从句中,用一般现在时表示一般将来时,用现在完成时表将来完成时,
用一般过去时表过去将来时。在since 引导的时间状语从句中,动词一般都用一般过去时,而主句常用现在完成时。
4. 状语从句的倒装一般有下面几种情况:①否定词开头;②so 加adj. 开头;③as /
though引导的让步状语从句。
5. 连词before小结:
We had sailed four days before we saw land. (……才)
We hadn’t run a mile before he felt tired. (不到……就)
Please write it down before you forget it. (趁……)
Before I could get in a word, he had measured me. (还没来得及)
It will be/was…before…要过多久才……
6. because, since, as 引导原因从句的区别:because表达直接原因,语气最强,回答why;
since通常放句首,译为“既然”;as引导不谈自明的原因,语气最弱;
7. as可以引导多种从句,要注意其中的区别。
8. till, until和not…until的区别;if和unless的区别。
非谓语动词部分
动词不定式几点注意。
1.下列动词或动词短语后接不定式:agree, seem, appear, offer, happen, wish, hope, pay,
expect, long, plan, intend, promise, pretend, decide, afford, manage, choose, be said to,
would like to等。
2. 不定式常用的句型:too…to do (太……而不能), …enough to do…(够……就能
……), so as to do/in order to do(为了……),so…as to do/such…as to do(如
此……结果……)。
3. 不定式的三个结构:即否定结构、复合结构和疑问结构。
否定结构为“not (never) to do”;疑问结构是特殊疑问词“how (what, which, who, whether…) to do”;复合结构是“for/ of +名词(或代词宾格)+ to do ”。
4. let/ make/ have/ see/ hear/ notice/ observe/ listen to/ look at/ watch/feel
这些动词带不定式作宾补时,省掉to, 若这些动词以被动形式出现时,应加上to。
5. 当前面是the first, the second, the last, need, plan, time, chance, right,determination,
ability, opportunity(机会),way时,一般用不定式作定语。
6. but/ except + to do/ do 结构,要根据谓语动词来确定其后面的形式。当谓语动词是do,
does, did时,but后用动词原形;谓语动词是其他动词时,but后用“to + 动词原形”的形式。
7. 形容词后一般用不定式(除busy, worth 两个外)。
You are sure to succeed. 你一定能成功。
He is busy preparing his lessons at present. 他现在正忙于预习功课。
8. 不定式作定语和表语时,有时需要在后面放上一个适当的介词。
This is a bench to sit on.(这是用来坐的凳子。)
This room is comfortable to live in. (这个房间住起来很舒适。)
9. 在“主语+系动词+adj.+不定式”这个句型中,当主语是不定式的逻辑宾语时,不定式不用被动,不能在动词后再放宾语。
The question is easy to answer. (question是answer的宾语,不能说:The question is easy to be answered. 也不能说:The question is easy to answer it .)
包含高中英语全部语法的13个句型
1. as 句型
(1) as引导方式状语从句句型:“按照……;正如……”
例:As(it is)in your country, we grow wheat in the north and rice in the south.
正如(像) 你们国家一样,我们北方种植小麦,南方种植水稻。
(2) as+形容词/副词原级+(a /an)+名词+as ; 否定式:not as/so --- as
例:He is as good a player as his sister.
他和他姐姐一样是位优秀的运动员。
(3) such + n. + as to do 如此……以致于……
例:She is such a fool as to believe what he said.
她是一个如此的一个笨蛋以致相信了他所说的话。
(4) so + adj./adv. + as to do sth 如此……以致于……
例:He was so strong as to carry the heavy box.
他是如此的强壮以致于能提起那重箱子。
(5) such...as... 象……之类的…… (接名词或定语从句)
例:He wished to be such a man as Lei Feng was.
他希望成为一个像雷锋这样的人。
(6) the same +名词+as 和……一样的…… (接名词或定语从句)
例:He is not the same man as he used to be.
他不是从前的那样子了。
(7) as 引导非限制性定语从句
例:As is known to us, knowledge is power.
众所周知,知识就是力量。
(8)引导时间状语从句,与while意义相近
例:We get wiser as we get older.
随着我们长大,我们也变得越来越聪明。
(9) 引导原因状语从句,与 because的用法相近
例:As it was getting very late, we soon turned back.
因为越来越迟了,所以我们不久就回来了。
(10) 引导让步状语从句
例:Child as he is, he knows much about science.
尽管他是一个小孩,但他对科学了解得很多。
2. prefer 句型
(1) prefer to do sth
例:I prefer to stay at home.
我宁愿呆在家里。
(2) prefer doing sth
例:I prefer playing in defence.
我喜欢打防守。
(3) prefer sb to do sth
例:Would you prefer me to stay?
你愿意我留下来吗?
(4) prefer to do sth rather than do sth… 宁愿…...而不愿...
例句:I prefer to stay at home rather than go out.
我宁愿呆在家里而不愿出去.
(5) prefer doing sth to doing sth
例:I prefer watching football to playing it.
我喜欢看篮球,不喜欢打篮球。
(6) prefer sth to sth
例:I prefer tea to coffee.
我要茶不要咖啡。
3. when 句型
(1) was/were doing sth...when...
例:He was still smiling when the door opened and his wife came in.
他正笑着的时候门突然开了,他妻子走了进来。
(2) was/were about to do sth ... when ...
例:We were about to start when it began to rain.
我们刚要出发,天就开始下雨了。
(3) had just done ... when ...
例:I had just gone to bed after a very hard day when the phone rang.
在劳累了一天之后我刚刚就寝,电话铃就响了。
4. seem 句型
(1) It +seems + that从句
例:It seemed that everyone was satisfied.
看来好像每个人都很满意。
(2) It seems to sb that ...
例:It seems to me that she is right.
我看她是对的,
(3) There seems to be ...
例:There seems to be a heavy rain.
看上去要有一场大雨。
(4) It seems as if ...
例:It seemed that she couldn't come to class.
看样子她不能来上课了。
5. 表示“相差……; 增加了……; 增加到……”的句型
(1) She is taller than I by three inches.
她比我高三英寸
(2) There is one year between us.
我们之间相差一岁。
(3) She is three years old than I.
她比我大三岁。
(4) They have increased the price by 50%.
他们把价格上涨了50%
(5) His salary has rised to 10,000 yuan per month.
他的工资已经涨到了每月10,000元。
6. what 引导的名词性从句
(1) what 引导主语从句
例:What surprised me is that everybody seemed to be very indifferent to her.
让我吃惊的是每个人似乎对她都很冷淡。
[ indifferent adj.不关心的;冷漠的]
(2) what 引导宾语从句
例:We can learn what we do not know.
我们能学会我们不懂的东西。
(3) what 引导表语从句
例:That is what I want.
那正是我所要的。
(4) what 引导同位语从句
例:I have no idea what they are talking about.
我不知道他们正在谈论什么。
7. too句型
(1) too ... to do ...
例:Politics is too important to be left to the politicians.(=Politics is so important that it can't be left to the politicians.)
政治太重要了,不能由政治家来决定。
(2) only too ... to do ...
例:I shall be only too pleased to get home.
我要回到家里就非常高兴。
(3) too + adj + for sth
例:These shoes are much too small for me.
我穿这双鞋太小了。
(4) too + adj + a + n.
例:This is too difficult a text for me.
这篇课文对我来说太难了。
(5) can't … too +形容词 无论……也不为过
例:We cannot emphasize the importance of protecting our eyes too much.
我们再怎么强调保护眼睛的重要性也不为过。
8. where 句型
(1) where 引导的定语从句
例:This is the house where he lived last year.
这就是他去年住过的房子。
(2) where 引导的状语从句
例:Where there is a will,there is a way.
有志者事竟成。
He left his key where he could find.
他将钥匙放在易找到的地方。
I will go where I want to go.
我要去我想去的地方。
(3) where 引导的表语从句
例:This is where you are wrong.
这正是你错的地方。
9. wish 句型
(1) wish that sb did sth 希望某人现在做某事
例:I wish I were as strong as you.
我希望和你一样强壮。
(2) wish that sb had done sth 希望某人过去做某事
例: I wish you had told me earlier
要是你早点告诉我就好了。
(3) wish that sb would/could do sth 希望某人将来做某事
例:I wish you would succeed this time.
我希望你这次会成功。
10. would rather 句型
(1) would rather do sth than do sth 宁愿做……而不愿做……
例:She would rather die than turn against his motherland.
她宁可死也不去背叛祖国。
(2) would rather have done sth 宁愿过去做过某事
例:I would rather have taken his advice.
我宁愿过去接受他的意见。
(3) would rather sb had done sth 宁愿某人过去做过某事
例:I would rather I had passed the examination last week.
我真希望通过上星期的考试。
(4) would rather sb did sth 宁愿某人现在或将来做某事
例: Who would you rather went with you?
你宁愿谁和你一起去?
11. before 句型
(1) before sb can/ could … 某人还没来得及……
例:Before I could get in a word ,he had measured me.
我还没来得及插话,他就给我量好了尺寸。
(2) It will be +时间+ before + 还有多长时间……
例:It will be 4 years before he graduates.
他还有四年时间变毕业了。
(3) had done some time before (才……)
例:We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land.
我们航行了四天四夜才见到陆地。
(4) had not done ... before ... 不到……就……
例:We hadn’t run a mile before he felt tired.
我们还没走到一英里路就觉得累了。
(5) It was not +一段时间+ before 不多久就……
例:It wasn’t two years before he left the country.
还没到两年他们离开了那国家。
12. 强调句型
(1) It is /was +被强调部分+that(who)...
例:It was I who wrote to my uncle yesterday.
是我昨天给我叔叔写信的。
(2) Is/was it + 被强调部分 + that (who) ...
例:Was it your brother that you met in the street?
在街上你遇见的是你兄弟吗?
(3) Where/who/what/how等特殊疑问词 + is/was it that ...
例:How is it that you will go to visit her tomorrow?
明天你究竟怎样去看望她?
(4) do/does/did +谓语动词 (强调谓语)
例:They do know the place well.
他们的确很熟悉那个地方。
13. 用于表示过去未实现的希望和计划的句型
(1)would like to/ would love to have done sth.
例:I would like to have written to you.
我本想给你写信的。
(2) was / were going to do sth.(用过去将来时态表示原打算做什么)
例:Lucy was going to watch a basketball match.
Lucy 原打算看一场篮球比赛。
以上就是关于高中英语语法句型大全 ,高中英语基础差该从哪里开始入门的全部内容,以及高中英语语法句型大全 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
